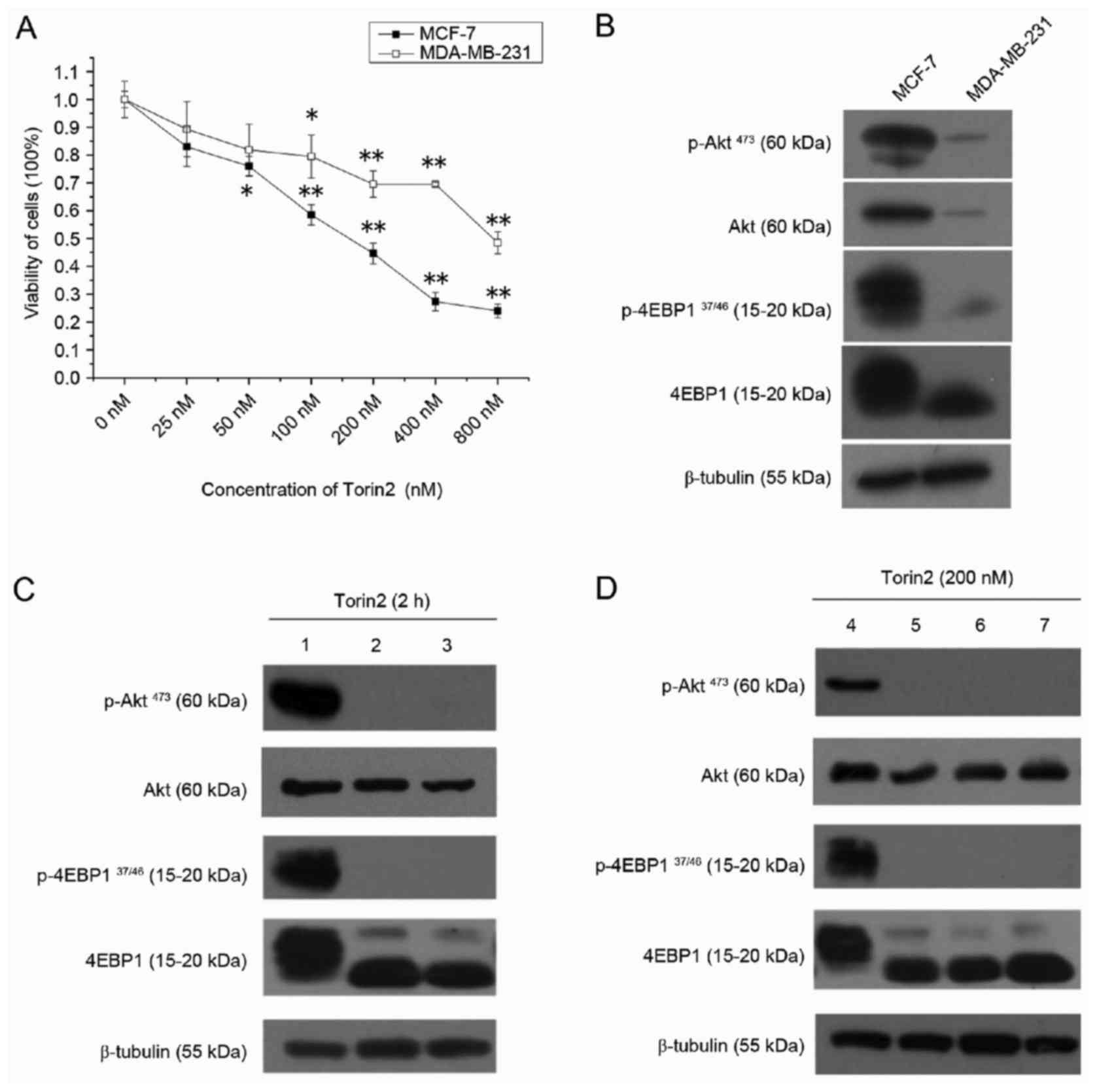
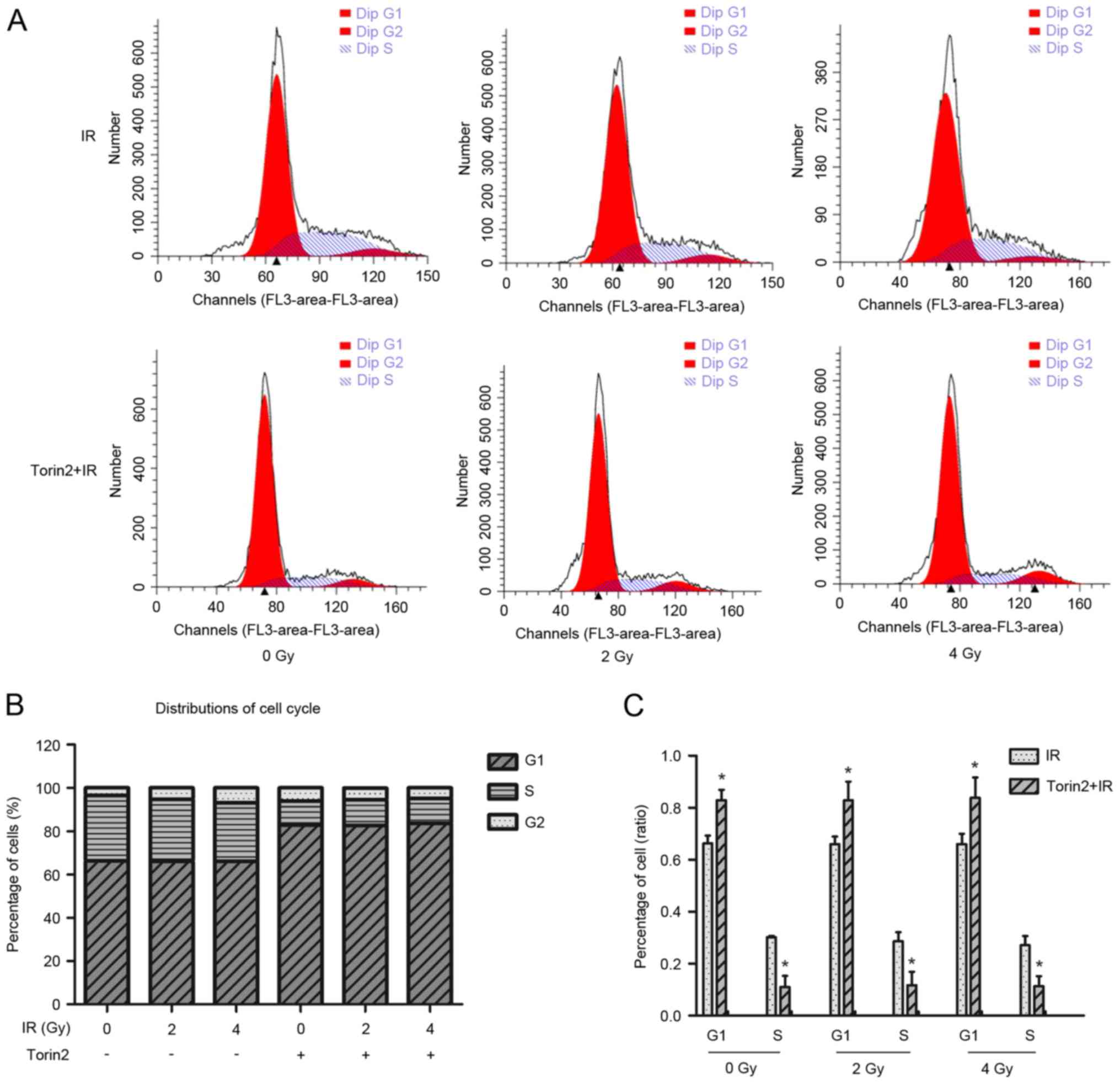
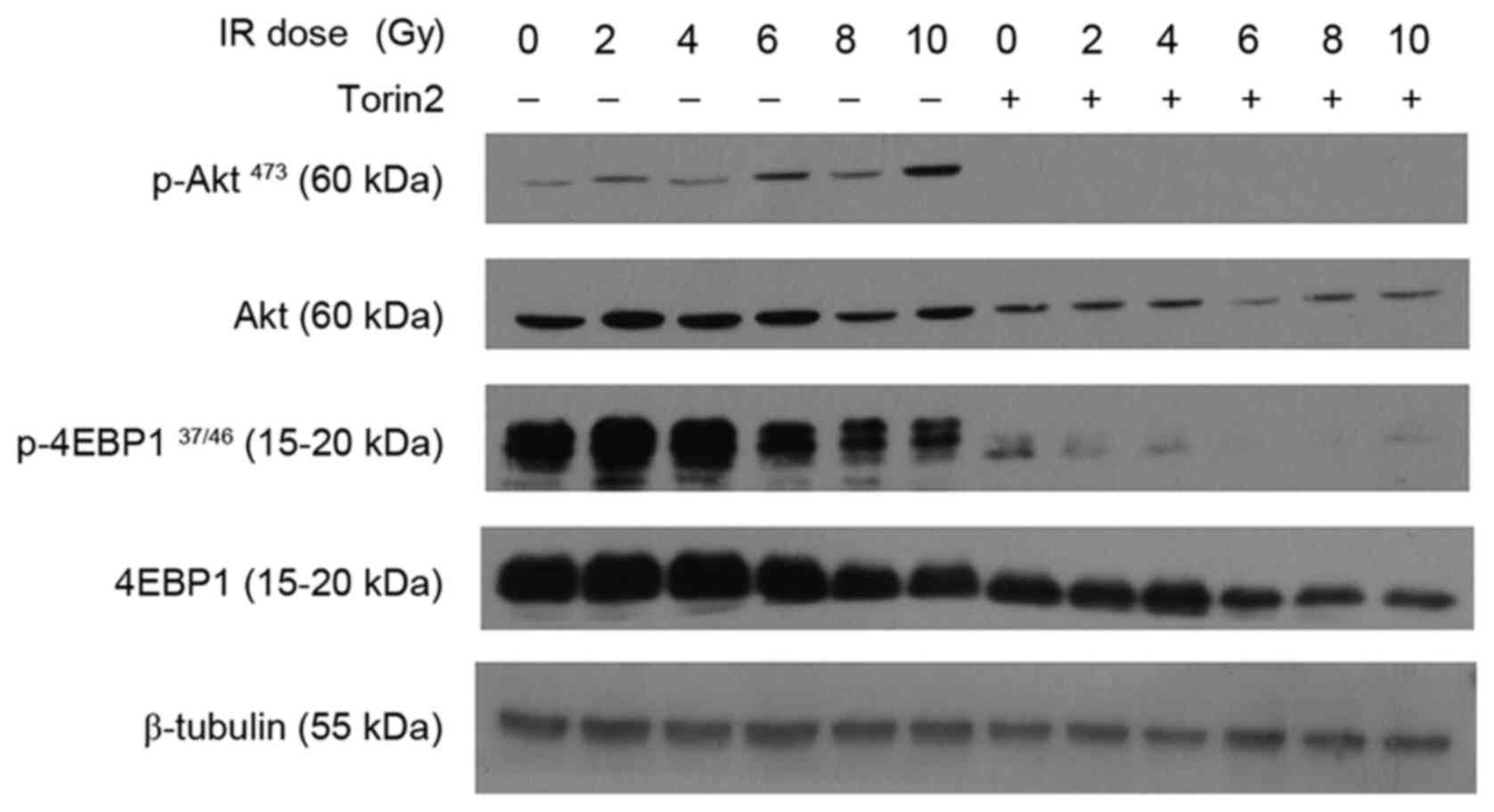
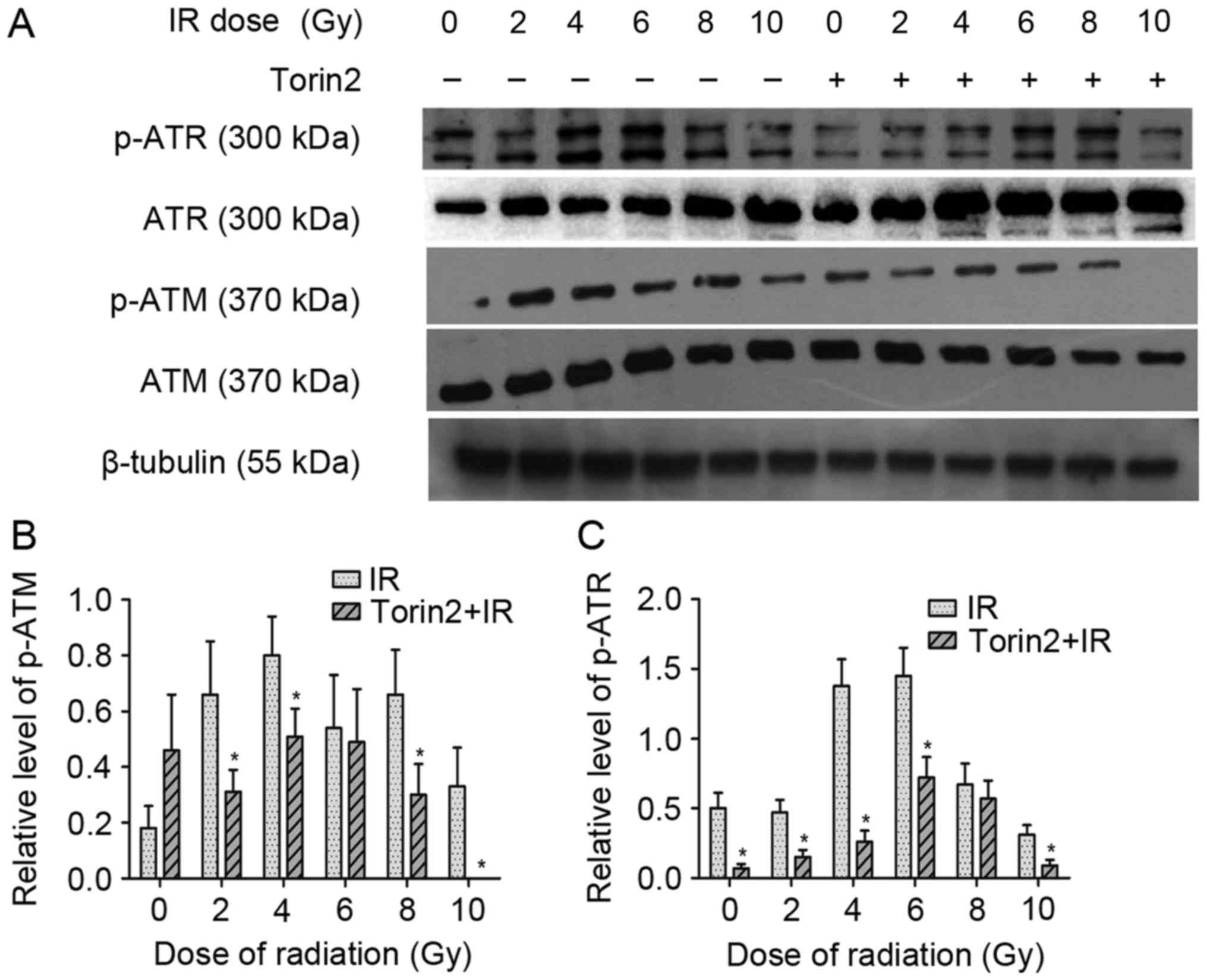
|
1
|
Langlands FE, Horgan K, Dodwell DD and
Smith L: Breast cancer subtypes: Response to radiotherapy and
potential radiosensitisation. Br J Radiol. 86:201206012013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S4, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fisher CM and Rabinovitch R: Frontiers in
radiotherapy for early-stage invasive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
32:2894–2901. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee HC, Kim SH, Suh YJ, Chung MJ, Kang DG,
Choi HJ and Lee JH: A prospective cohort study on postoperative
radiotherapy with TomoDirect using simultaneous integrated boost
technique in early breast cancer. Radiat Oncol. 9:2442014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Cosimo S, Bianchi GV, Bregni G and de
Braud F: Prognosis of women with early breast cancer and PIK3CA
mutations. Breast. 24:283–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guerrero-Zotano A, Mayer IA and Arteaga
CL: PI3K/AKT/mTOR: Role in breast cancer progression, drug
resistance and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 35:515–524. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mamaeva V, Niemi R, Beck M, Özliseli E,
Desai D, Landor S, Gronroos T, Kronqvist P, Pettersen IK, McCormack
E, et al: Inhibiting notch activity in breast cancer stem cells by
glucose functionalized nanoparticles carrying gamma-secretase
Inhibitors. Mol Ther. 24:926–936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang L, Graham PH, Ni J, Hao J, Bucci J,
Cozzi PJ and Li Y: Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the
treatment of prostate cancer radioresistance. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 96:507–517. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
García-Carracedo D, Villaronga MÁ,
Álvarez-Teijeiro S, Hermida-Prado F, Santamaría I, Allonca E,
Suárez-Fernández L, Gonzalez MV, Balbín M, Astudillo A, et al:
Impact of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation on the prognosis of
patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncotarget.
7:29780–29793. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loi S, Michiels S, Baselga J, Bartlett JM,
Singhal SK, Sabine VS, Sims AH, Sahmoud T, Dixon JM, Piccart MJ and
Sotiriou C: PIK3CA genotype and a PIK3CA mutation-related gene
signature and response to everolimus and letrozole in estrogen
receptor positive breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e532922013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Hu H, Pan Y, Wang R, Li Y, Shen L,
Yu Y, Li H, Cai D, Sun Y and Chen H: PIK3CA mutations frequently
coexist with EGFR/KRAS mutations in non-small cell lung cancer and
suggest poor prognosis in EGFR/KRAS wildtype subgroup. PLoS One.
9:e882912014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moulder SL, Rivera E, Ensor J,
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Cristofanilli M, Murray JL, Booser D, Giordano
SH, Brewster A, Moore J, et al: Phase I trial of escalating doses
of weekly everolimus (RAD001) in combination with docetaxel for the
treatment of metastatic breast cancer (MBC). J Clin Oncol.
118:2378–2384. 2012.
|
|
13
|
Liu Q, Xu C, Kirubakaran S, Zhang X, Hur
W, Liu Y, Kwiatkowski NP, Wang J, Westover KD, Gao P, et al:
Characterization of Torin2, an ATP-competitive inhibitor of mTOR,
ATM, and ATR. Cancer Res. 73:2574–2586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hussain AR, Al-Romaizan M, Ahmed M,
Thangavel S, Al-Dayel F, Beg S, Uddin S, Siraj AK and Al-Kuraya KS:
Dual targeting of mTOR activity with Torin2 potentiates anticancer
effects of cisplatin in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Med.
21:466–478. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sadowski SM, Boufraqech M, Zhang L, Mehta
A, Kapur P, Zhang Y, Li Z, Shen M and Kebebew E: Torin2 targets
dysregulated pathways in anaplastic thyroid cancer and inhibits
tumor growth and metastasis. Oncotarget. 6:18038–18049. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang C, Wang X, Su Z, Fei H, Liu X and Pan
Q: The novel mTOR inhibitor Torin-2 induces autophagy and
downregulates the expression of UHRF1 to suppress hepatocarcinoma
cell growth. Oncol Rep. 34:1708–1716. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman
J and van Bree C: Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc.
1:2315–2319. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mukherjee B, Tomimatsu N, Amancherla K,
Camacho CV, Pichamoorthy N and Burma S: The Dual PI3K/mTOR
inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 is a potent inhibitor of ATM- and
DNA-PKCs-mediated DNA damage responses. Neoplasia. 14:34–43. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cejalvo JM, Perez-Fidalgo JA, Ribas G,
Burgués O, Mongort C, Alonso E, Ibarrola-Villava M, Bermejo B,
Martínez MT, Cervantes A and Lluch A: Clinical implications of
routine genomic mutation sequencing in PIK3CA/AKT1 and
KRAS/NRAS/BRAF in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 160:69–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Basho RK, Gagliato DM, Ueno NT, Wathoo C,
Chen H, Shariati M, Wei C, Alvarez RH, Moulder SL, Sahin AA, et al:
Clinical outcomes based on multigene profiling in metastatic breast
cancer patients. Oncotarget. 7:76362–76373. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tabesh Azizi G, Izadi P, Fereidooni F,
Razavi Emami AN and Bazzaz Tavakkoly J: The high frequency of
PIK3CA mutations in Iranian breast cancer patients. Cancer Invest.
35:36–42. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu ZG, Tang J, Chen Z and Zhang H, Wang
H, Yang J and Zhang H: The novel mTORC1/2 dual inhibitor INK128
enhances radiosensitivity of breast cancer cell line MCF-7. Int J
Oncol. 49:1039–1045. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kao J, Salari K, Bocanegra M, Choi YL,
Girard L, Gandhi J, Kwei KA, Hernandez-Boussard T, Wang P, Gazdar
AF, et al: Molecular profiling of breast cancer cell lines defines
relevant tumor models and provides a resource for cancer gene
discovery. PLoS One. 4:e61462009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yahyanejad S, Theys J and Vooijs M:
Targeting Notch to overcome radiation resistance. Oncotarget.
7:7610–7628. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim BM and Hong Y, Lee S, Liu P, Lim JH,
Lee YH, Lee TH, Chang KT and Hong Y: Therapeutic implications for
overcoming radiation resistance in cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26880–26913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heavey S, O'Byrne KJ and Gately K:
Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:445–456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shimura T: Acquired radioresistance of
cancer and the AKT/GSK3β/cyclin D1 overexpression cycle. J Radiat
Res. 52:539–544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimura T, Kakuda S, Ochiai Y, Nakagawa H,
Kuwahara Y, Takai Y, Kobayashi J, Komatsu K and Fukumoto M:
Acquired radioresistance of human tumor cells by
DNA-PK/AKT/GSK3beta-mediated cyclin D1 overexpression. Oncogene.
29:4826–4837. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimura T: Targeting the AKT/cyclin D1
pathway to overcome intrinsic and acquired radioresistance of
tumors of effective radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol. 93:381–385.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Javvadi P, Makino H, Das AK, Lin YF, Chen
DJ, Chen BP and Nirodi CS: Threonine 2609 phosphorylation of the
DNA-dependent protein kinase is a critical prerequisite for
epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated radiation resistance. Mol
Cancer Res. 10:1359–1368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bunimovich YL, Nair-Gill E, Riedinger M,
McCracken MN, Cheng D, McLaughlin J, Radu CG and Witte ON:
Deoxycytidine kinase augments ATM-Mediated DNA repair and
contributes to radiation resistance. PLoS One. 9:e1041252014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guy JB, Rancoule C, Méry B, Espenel S,
Wozny AS, Simonet S, Vallard A, Alphonse G, Ardail D,
Rodriguez-Lafrasse C and Magné N: Radiosensitivity and/or
radioresistance of head and neck cancers: Biological angle. Bull
Cancer. 103:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|