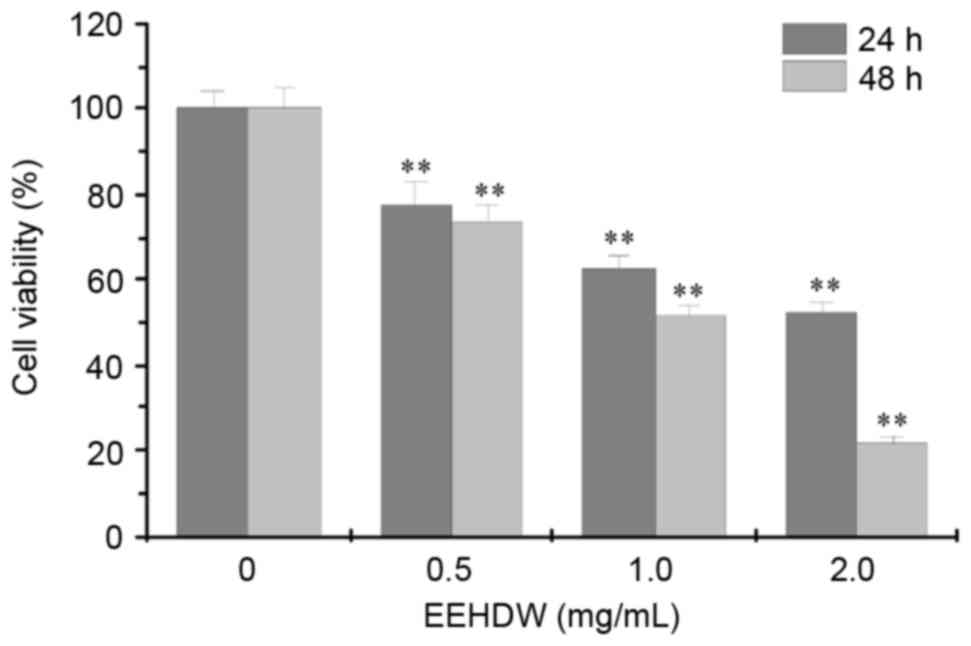
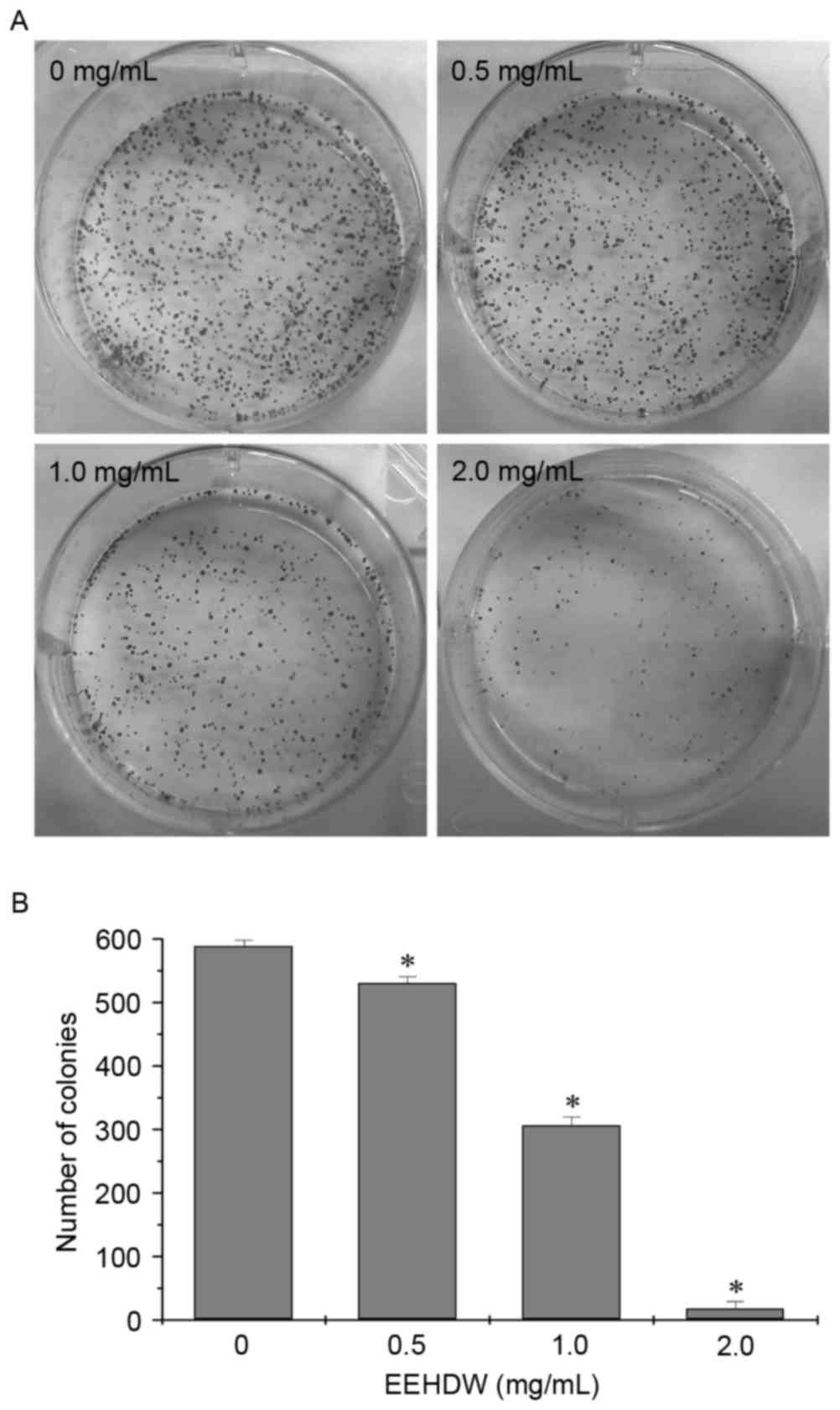
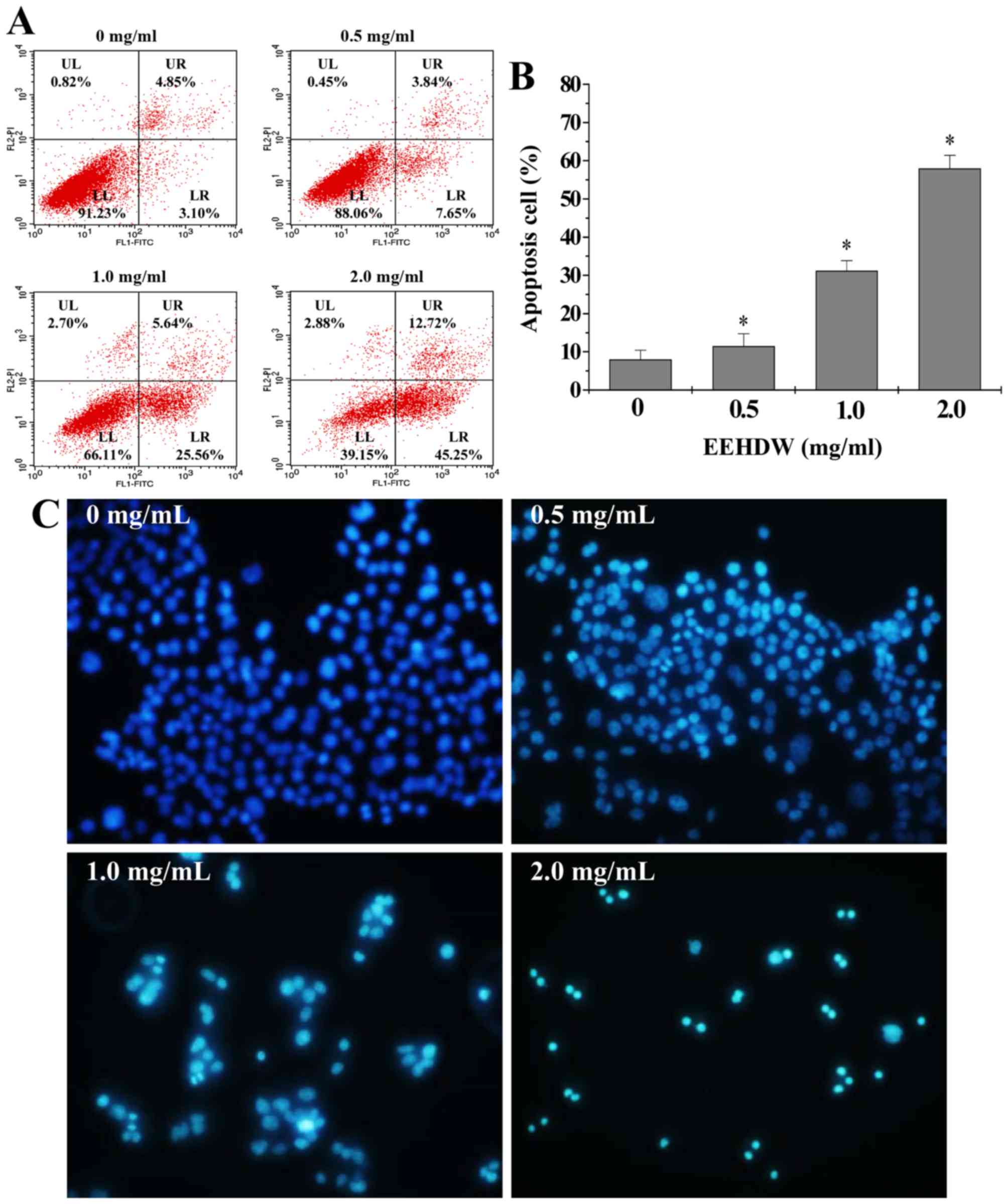
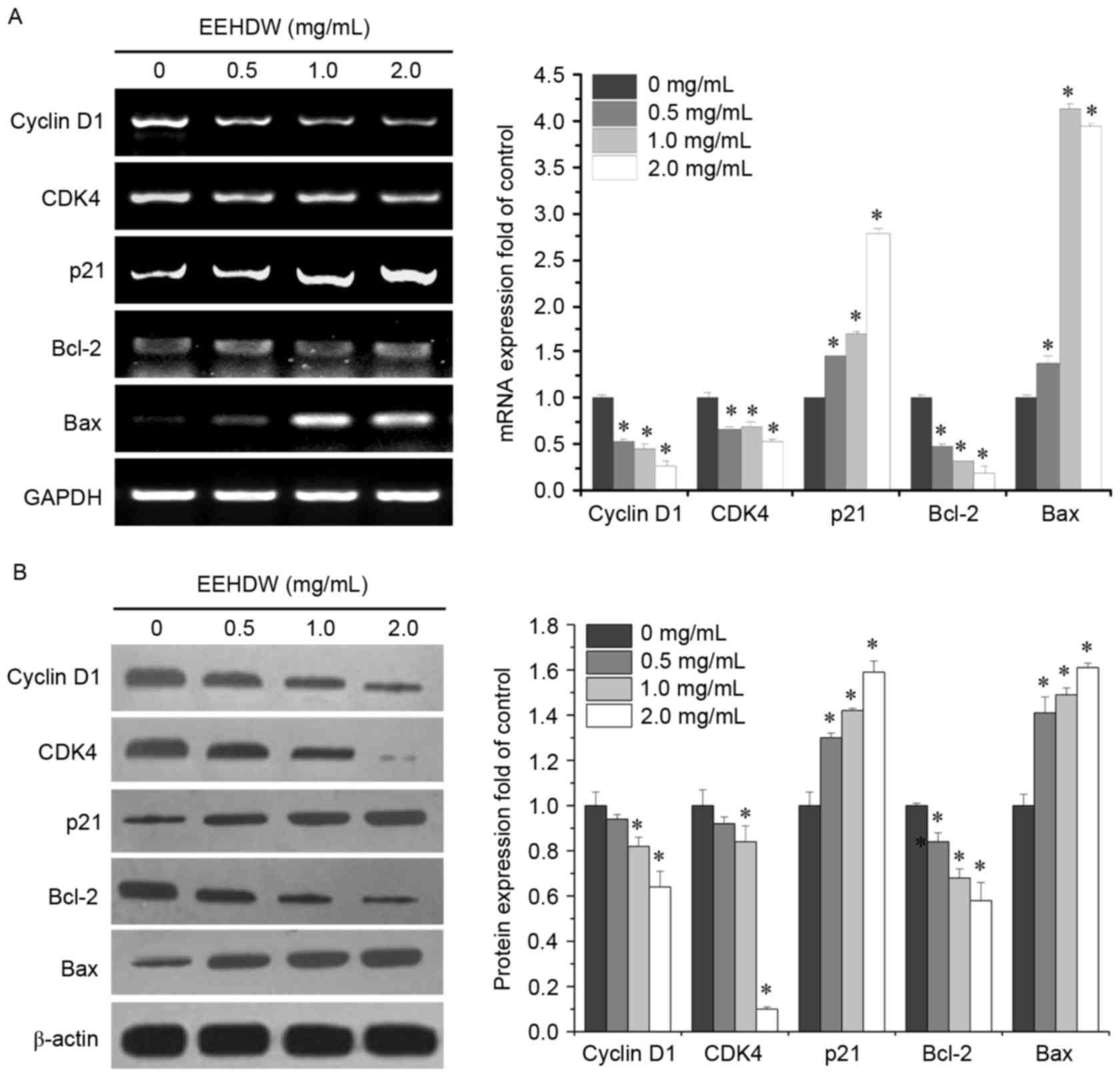
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Van Cutsem E, Nordlinger B and Cervantes
A: ESMO Guidelines Working Group: Advanced colorectal cancer: ESMO
clinical practice guidelines for treatment. Ann Oncol. 21 Suppl
5:v93–v97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li W, Zhang H, Assaraf YG, Zhao K, Xu X,
Xie J, Yang DH and Chen ZS: Overcoming ABC transporter-mediated
multidrug resistance: Molecular mechanisms and novel therapeutic
drug strategies. Drug Resist Updat. 27:14–29. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mittal B, Tulsyan S, Kumar S, Mittal RD
and Agarwal G: Cytochrome P450 in cancer susceptibility and
treatment. Adv Clin Chem. 71:77–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan ST, Li ZL, He ZX, Qiu JX and Zhou SF:
Molecular mechanisms for tumour resistance to chemotherapy. Clin
Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 43:723–737. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartholomeusz C and Gonzalez-Angulo AM:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 16:121–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song L, Xiong H, Li J, Liao W, Wang L, Wu
J and Li M: Sphingosine kinase-1 enhances resistance to apoptosis
through activation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway in human non-small
cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 17:1839–1849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Housman G, Byler S, Heerboth S, Lapinska
K, Longacre M, Snyder N and Sarkar S: Drug resistance in cancer: An
overview. Cancers (Basel). 6:1769–1792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Danielsen SA, Eide PW, Nesbakken A, Guren
T, Leithe E and Lothe RA: Portrait of the PI3K/AKT pathway in
colorectal cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1855:104–121.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brotelle T and Bay JO: PI3K-AKT-mTOR
pathway: Description, therapeutic development, resistance,
predictive/prognostic biomarkers and therapeutic applications for
cancer. Bull Cancer. 103:18–29. 2016.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu D, Lu Q and Hu X: Down-regulation of
P-glycoprotein expression in MDR breast cancer cell MCF-7/ADR by
honokiol. Cancer Lett. 243:274–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Xia Y, Wang H and Hou Z: Chinese
herbs of Shenghe Powder reverse multidrug resistance of gastric
carcinoma SGC-7901. Integr Cancer Ther. 6:400–404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Angelini A, Di Ilio C, Castellani ML,
Conti P and Cuccurullo F: Modulation of multidrug resistance
p-glycoprotein activity by flavonoids and honokiol in human
doxorubicin- resistant sarcoma cells (MES-SA/DX-5): Implications
for natural sedatives as chemosensitizing agents in cancer therapy.
J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 24:197–205. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Zhang J, Qi B, Jiang G, Liu J,
Zhang P, Ma Y and Li W: The anti-tumor effect and bioactive
phytochemicals of Hedyotis diffusa willd on ovarian cancer
cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 192:132–139. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li YL, Zhang J, Min D, Hongyan Z, Lin N
and Li QS: Anticancer effects of
1,3-dihydroxy-2-methylanthraquinone and the ethyl acetate fraction
of Hedyotis diffusa willd against HepG2 carcinoma cells
mediated via apoptosis. PLoS One. 11:e01515022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang P, Zhang B, Gu J, Hao L, Hu F and
Han C: The study of the effect of Hedyotis diffusa on the
proliferation and the apoptosis of the cervical tumor in nude mouse
model. Cell Biochem Biophys. 72:783–789. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kuo YJ, Yang JS, Lu CC, Chiang SY, Lin JG
and Chung JG: Ethanol extract of Hedyotis diffusa willd
upregulates G0/G1 phase arrest and induces apoptosis in human
leukemia cells by modulating caspase cascade signaling and altering
associated genes expression was assayed by cDNA microarray. Environ
Toxicol. 30:1162–1177. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin J, Chen Y, Wei L, Chen X, Xu W, Hong
Z, Sferra TJ and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd extract
induces apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrion-dependent
pathway in human colon carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 37:1331–1338.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin JM, Wei LH, Xu W, Hong Z, Liu X and
Peng J: Effect of Hedyotis diffusa willd extract on tumor
angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 4:1283–1288. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan
Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa
willd inhibits colorectal cancer growth in vivo via inhibition of
STAT3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6117–6128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin J, Wei L, Shen A, Cai Q, Xu W, Li H,
Zhan Y, Hong Z and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa willd extract
suppresses sonic hedgehog signaling leading to the inhibition of
colorectal cancer angiogenesis. Int J Oncol. 42:651–656. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin J, Li Q, Chen H, Lin H, Lai Z and Peng
J: Hedyotis diffusa willd. Extract suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis via IL-6-inducible STAT3 pathway inactivation
in human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 9:1962–1970.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Q, Wang X, Shen A, Zhang Y, Chen Y,
Sferra TJ, Lin J and Peng J: Hedyotis diffusa Willd
overcomes 5-fluorouracil resistance in human colorectal cancer
HCT-8/5-FU cells by downregulating the expression of P-glycoprotein
and ATP-binding casette subfamily G member 2. Exp Ther Med.
10:1845–1850. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Elledge SJ: Cell cycle checkpoints:
Preventing an identity crisis. Science. 274:1664–1672. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Taulés M, Rius E, Talaya D, López-Girona
A, Bachs O and Agell N: Calmodulin is essential for
cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) activity and nuclear accumulation
of cyclin D1-Cdk4 during G1. J Biol Chem. 273:33279–33386. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen XZ, Cao ZY, Chen TS, Zhang YQ, Liu
ZZ, Su YT, Liao LM and Du J: Water extract of Hedyotis
diffusa willd suppresses proliferation of human HepG2 cells and
potentiates the anticancer efficacy of low-dose 5-fluorouracil by
inhibiting the CDK2-E2F1 pathway. Oncol Rep. 28:742–748. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu JJ, Lin M, Yu JY, Liu B and Bao JK:
Targeting apoptotic and autophagic pathways for cancer
therapeutics. Cancer Lett. 300:105–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Denicourt C and Dowdy SF: Medicine.
Targeting apoptotic pathways in cancer cells. Science.
305:1411–1413. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
Targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tsuchiya T, Tsuno NH, Asakage M, Yamada J,
Yoneyama S, Okaji Y, Sasaki S, Kitayama J, Osada T, Takahashi K and
Nagawa H: Apoptosis induction by p38 MAPK inhibitor in human colon
cancer cells. Hepatogastroenterology. 55:930–935. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wu H, Hait WN and Yang JM: Small
interfering RNA-induced suppression of MDR1 (P-glycoprotein)
restores sensitivity to multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 63:1515–1519. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiao M and Nan KJ: Activation of PI3
kinase/Akt/HIF-1α pathway contributes to hypoxia-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 40:461–468. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang HY, Zhang PN and Sun H: Aberration
of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in epithelial ovarian cancer and its
implication in cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 146:81–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lima RT, Martins LM, Guimarães JE, Sambade
C and Vasconcelos MH: Specific downregulation of Bcl-2 and xIAP by
RNAi enhances the effects of chemotherapeutic agents in MCF-7 human
breast cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 11:309–316. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wong KK, Engelman JA and Cantley LC:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet
Dev. 20:87–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|