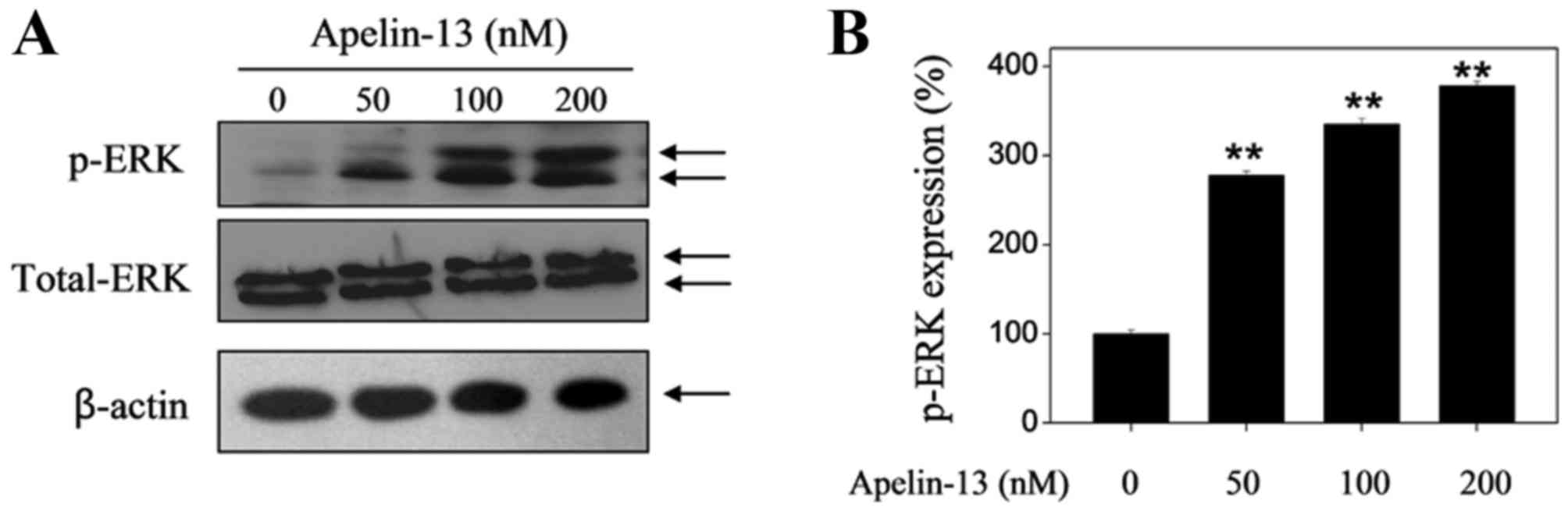
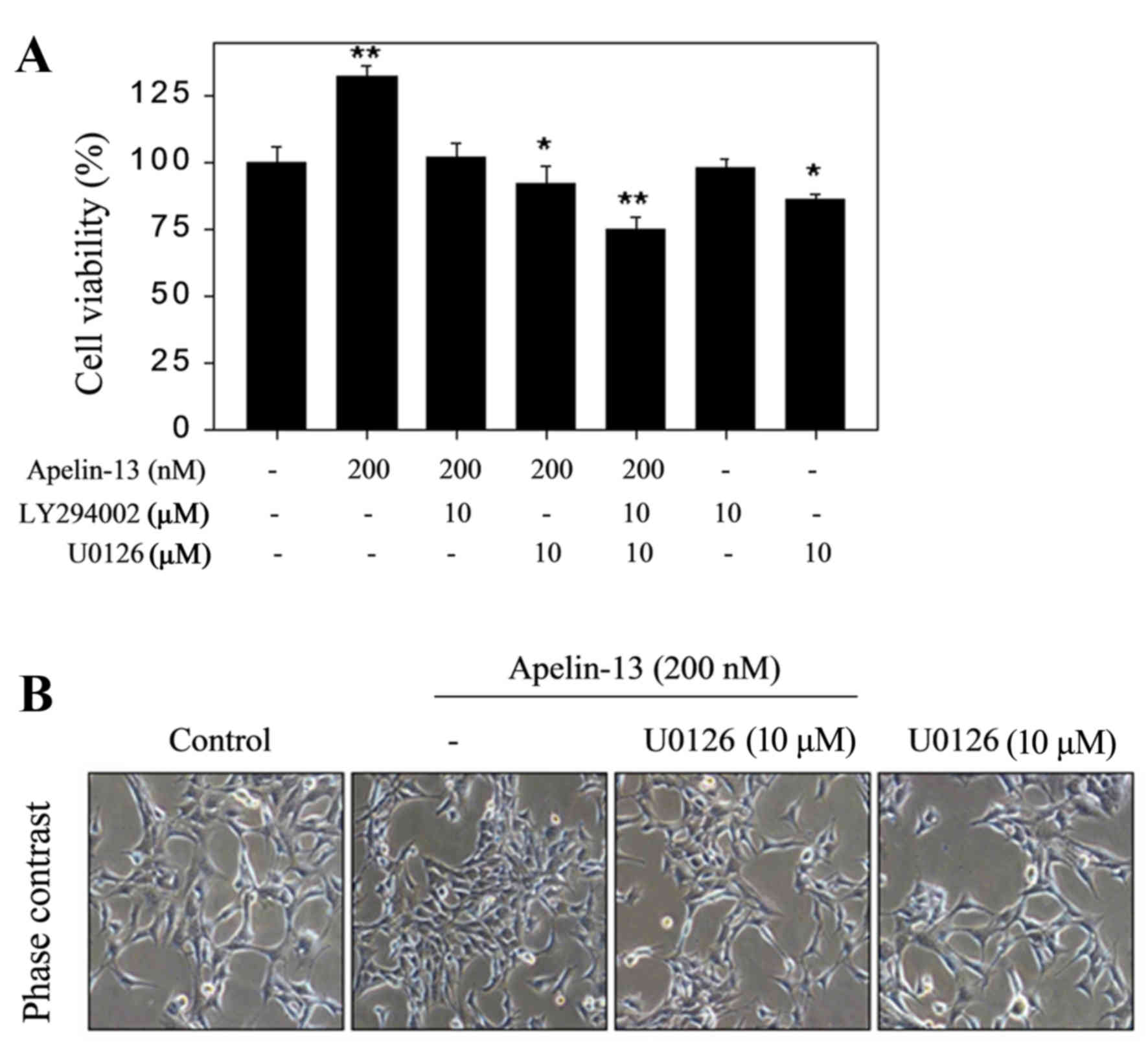
|
1
|
Tatemoto K, Hosoya M, Habata Y, Fujii R,
Kakegawa T, Zou MX, Kawamata Y, Fukusumi S, Hinuma S, Kitada C, et
al: Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide
ligand for the human APJ receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
251:471–476. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lesur O: Myocardial impact and
cardioprotective effects of apelin-13 and a c-terminal-modified
analog during lps and clp experimental sepsis. Intensive Care Med
Exp. 3:A4362015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Paine SK, Basu A, Mondal LK, Sen A,
Choudhuri S, Chowdhury IH, Saha A, Bhadhuri G, Mukherjee A and
Bhattacharya B: Association of vascular endothelial growth factor,
transforming growth factor beta, and interferon gamma gene
polymorphisms with proliferative diabetic retinopathy in patients
with type 2 diabetes. Mol Vis. 18:2749–2757. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu Q, Jiang YR, Qian J and Tao Y:
Apelin-13 regulates proliferation, migration and survival of
retinal Müller cells under hypoxia. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
99:158–167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bai B, Cai X, Jiang Y, Karteris E and Chen
J: Heterodimerization of apelin receptor and neurotensin receptor 1
induces phosphorylation of ERK(1/2) and cell proliferation via
Galphaq-mediated mechanism. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2071–2081. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu QF, Yu HW, Sun LL, You L, Tao GZ and
Qu BZ: Apelin-13 upregulates Egr-1 expression in rat vascular
smooth muscle cells through the PI3K/Akt and PKC signaling
pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 468:617–621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qin D, Zheng XX and Jiang YR: Apelin-13
induces proliferation, migration, and collagen I mRNA expression in
human RPE cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk signaling pathways. Mol
Vis. 19:2227–2236. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tao J, Zhu W, Li Y, Xin P, Li J, Liu M,
Redington AN and Wei M: Apelin-13 protects the heart against
ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibition of ER-dependent
apoptotic pathways in a time-dependent fashion. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 301:H1471–H1486. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang S, Li H, Tang L, Ge G, Ma J, Qiao Z,
Liu H and Fang W: Apelin-13 protects the heart against
ischemia-reperfusion injury through the RISK-GSK-3β-mPTP
pathway. Arch Med Sci. 11:1065–1073. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liou SF, Hsu JH, Chen YT, Chen IJ and Yeh
JL: KMUP-1 attenuates endothelin-1-induced cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy through activation of heme oxygenase-1 and suppression
of the Akt/GSK-3β, calcineurin/NFATc4 and RhoA/ROCK
pathways. Molecules. 20:10435–10449. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dong WQ, Chao M, Lu QH, Chai WL, Zhang W,
Chen XY, Liang ES, Wang LB, Tian HL, Chen YG and Zhang MX:
Prohibitin overexpression improves myocardial function in diabetic
cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget. 7:66–80. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zou Y, Wang B, Fu W, Zhou S, Nie Y and
Tian S: Apelin-13 protects PC12 cells from corticosterone-induced
apoptosis through PI3K and ERKs activation. Neurochem Res.
41:1635–1644. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li YG, Han BB, Li F, Yu JW, Dong ZF, Niu
GM, Qing YW, Li JB, Wei M and Zhu W: High glucose induces
down-regulated GRIM-19 expression to activate STAT3 signaling and
promote cell proliferation in cell culture. PLoS One.
11:e01536592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yin J, Hu H, Li X, Xue M, Cheng W, Wang Y,
Xuan Y, Yang N, Shi Y and Yan S: Inhibition of Notch signaling
pathway attenuates sympathetic hyperinnervation together with the
augmentation of M2 macrophages in rats post-myocardial infarction.
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 310:C41–C53. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khan M, Maryam A, Qazi JI and Ma T:
Targeting apoptosis and multiple signaling pathways with icariside
II in cancer cells. Int J Biol Sci. 11:1100–1102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bircan B, Cakir M, Kırbağ S and Gül HF:
Effect of apelin hormone on renal ischemia/reperfusion induced
oxidative damage in rats. Ren Fail. 38:1122–1128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dalzell JR, Rocchiccioli JP, Weir RA,
Jackson CE, Padmanabhan N, Gardner RS, Petrie MC and McMurray JJ:
The emerging potential of the apelin-APJ system in heart failure. J
Card Fail. 21:489–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boal F, Timotin A, Roumegoux J, Alfarano
C, Calise D, Anesia R, Parini A, Valet P, Tronchere H and Kunduzova
O: Apelin-13 administration protects against
ischaemia/reperfusion-mediated apoptosis through the FoxO1 pathway
in high-fat diet-induced obesity. Br J Pharmacol. 173:1850–1863.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang W, McKinnie SM, Patel VB, Haddad G,
Wang Z, Zhabyeyev P, Das SK, Basu R, McLean B, Kandalam V, et al:
Loss of Apelin exacerbates myocardial infarction adverse remodeling
and ischemia-reperfusion injury: Therapeutic potential of synthetic
Apelin analogues. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0002492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tycinska AM, Sobkowicz B, Mroczko B,
Sawicki R, Musial WJ, Dobrzycki S, Waszkiewicz E, Knapp MA and
Szmitkowski M: The value of apelin-36 and brain natriuretic peptide
measurements in patients with first ST-elevation myocardial
infarction. Clin Chim Acta. 411:2014–2018. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kleinz MJ and Baxter GF: Apelin reduces
myocardial reperfusion injury independently of PI3K/Akt and P70S6
kinase. Regul Pept. 146:271–277. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Helske S, Kovanen PT, Lommi J, Turto H and
Kupari M: Transcardiac gradients of circulating apelin: Extraction
by normal hearts vs. release by hearts failing due to pressure
overload. J Appl Physiol (1985). 109:1744–1748. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang Y, Zhang XJ, Li LT, Cui HY, Zhang C,
Zhu CH and Miao JY: Apelin-13 protects against apoptosis by
activating AMP-activated protein kinase pathway in ischemia stroke.
Peptides. 75:96–100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|