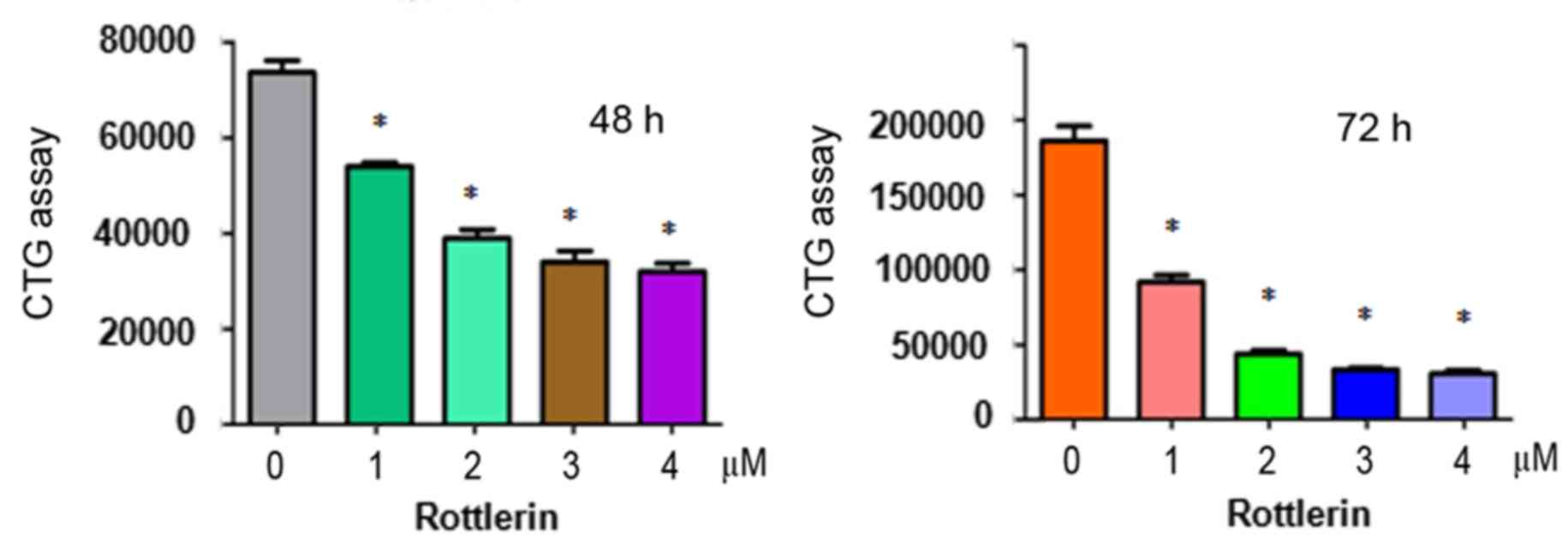
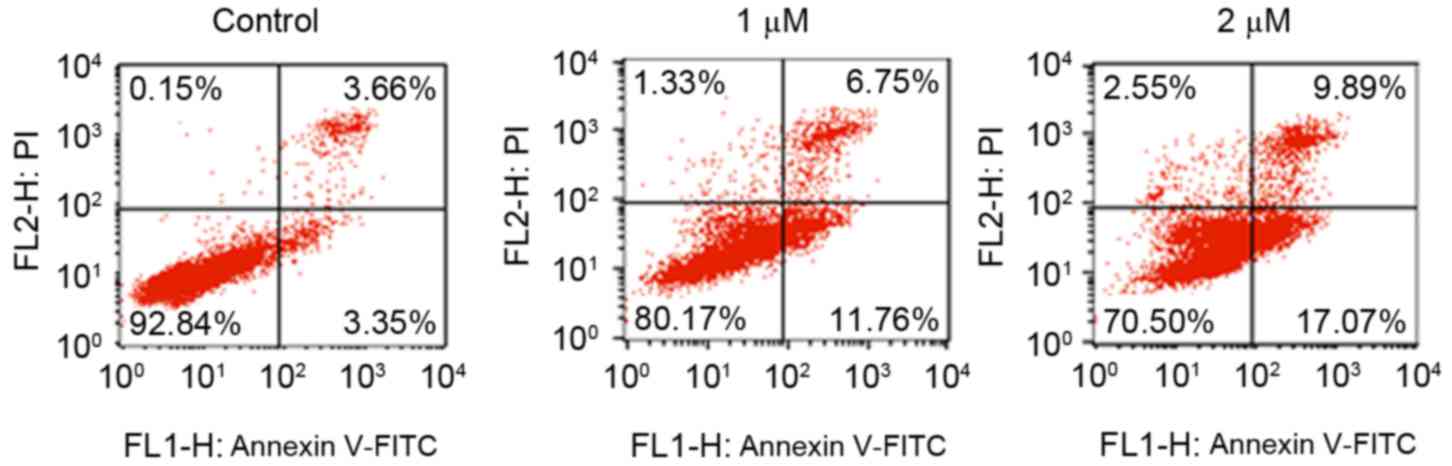
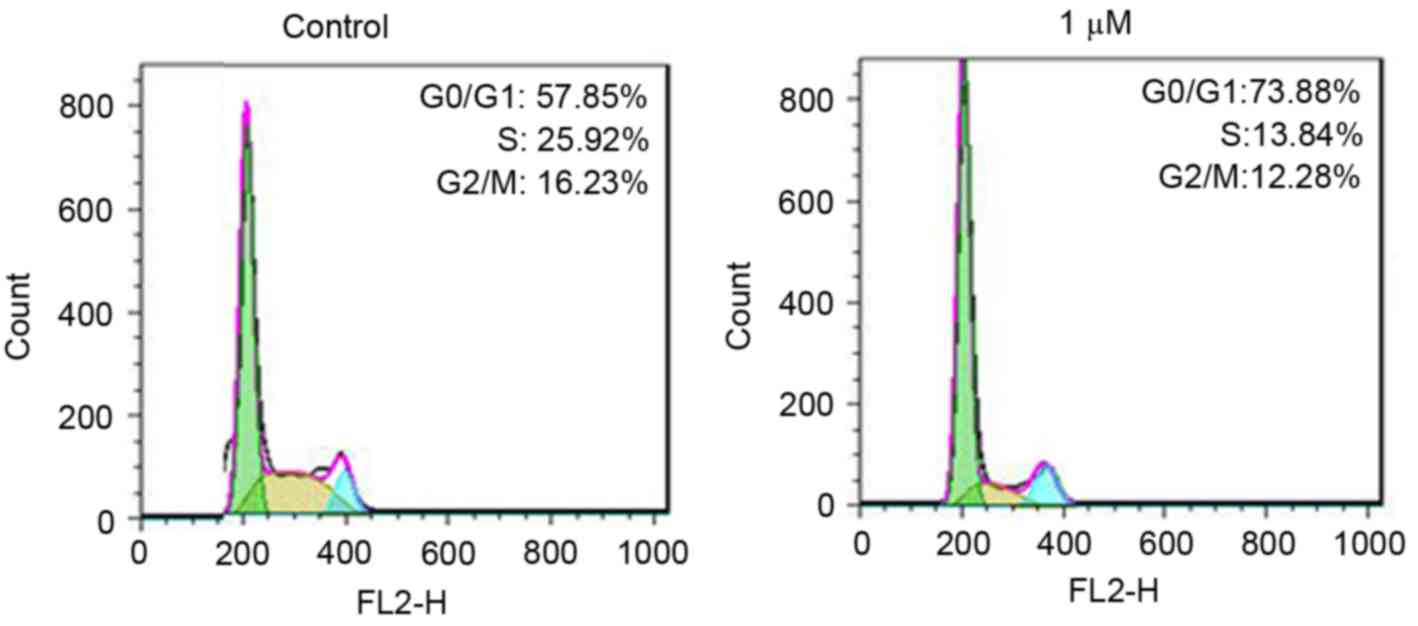
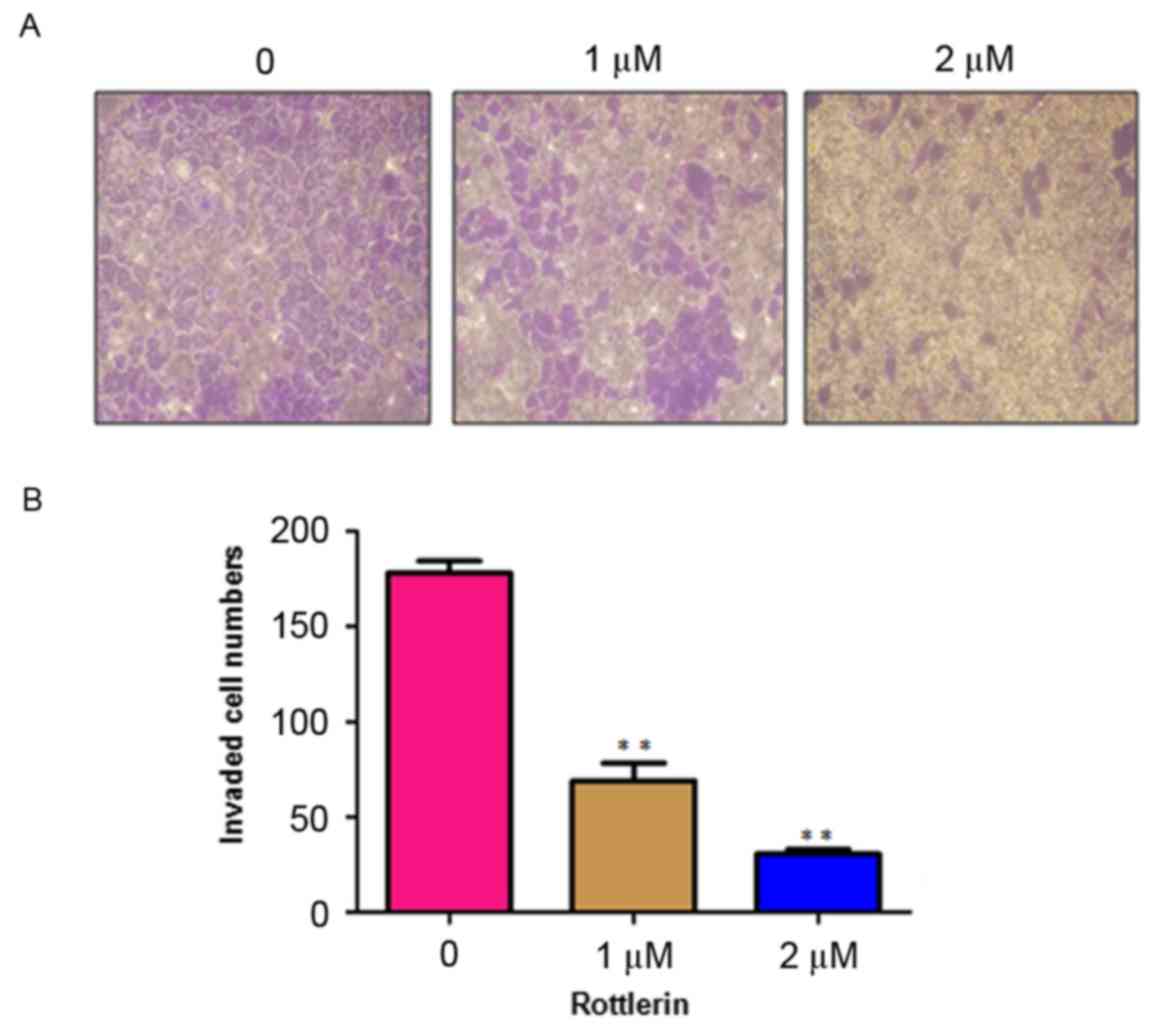
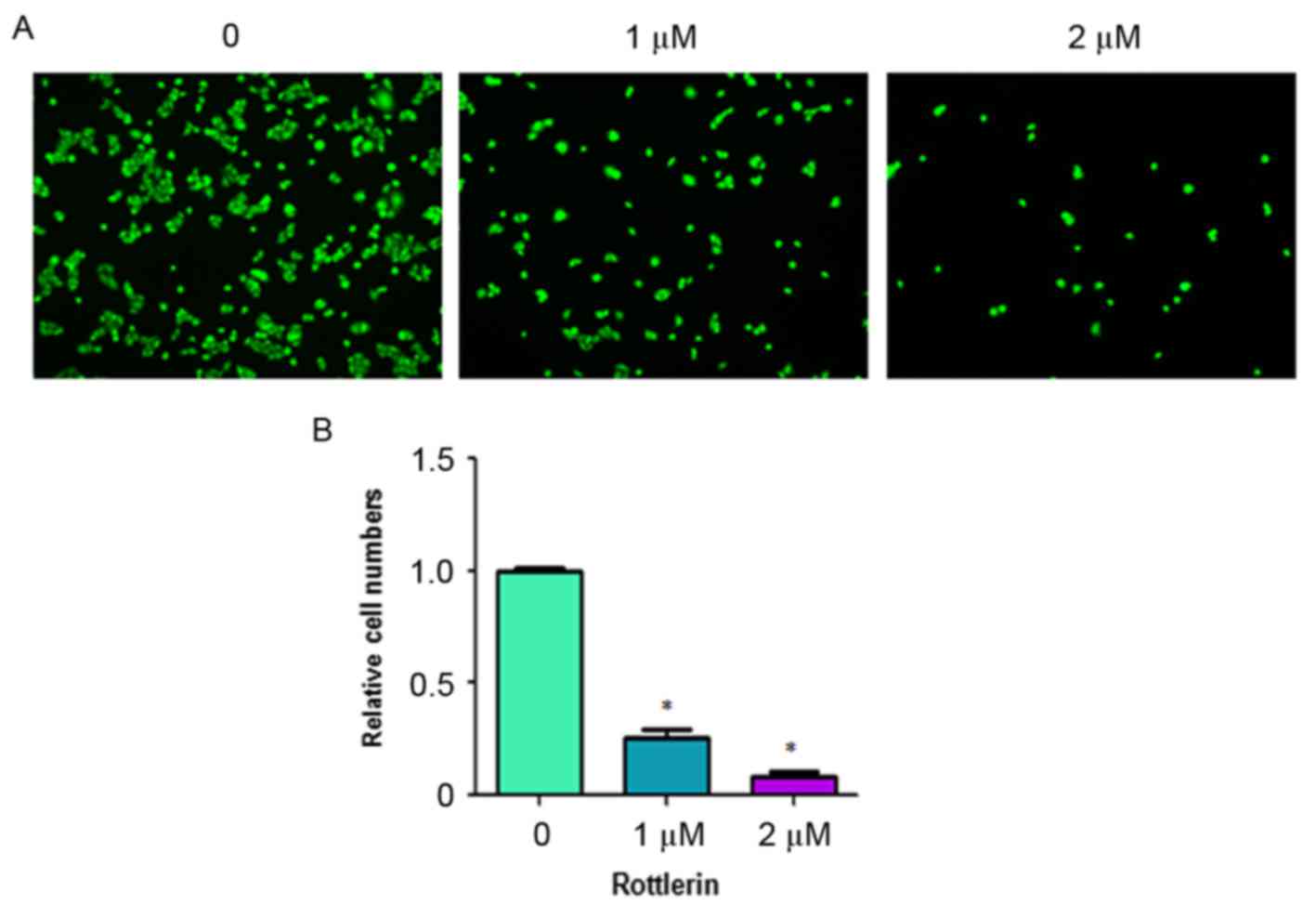
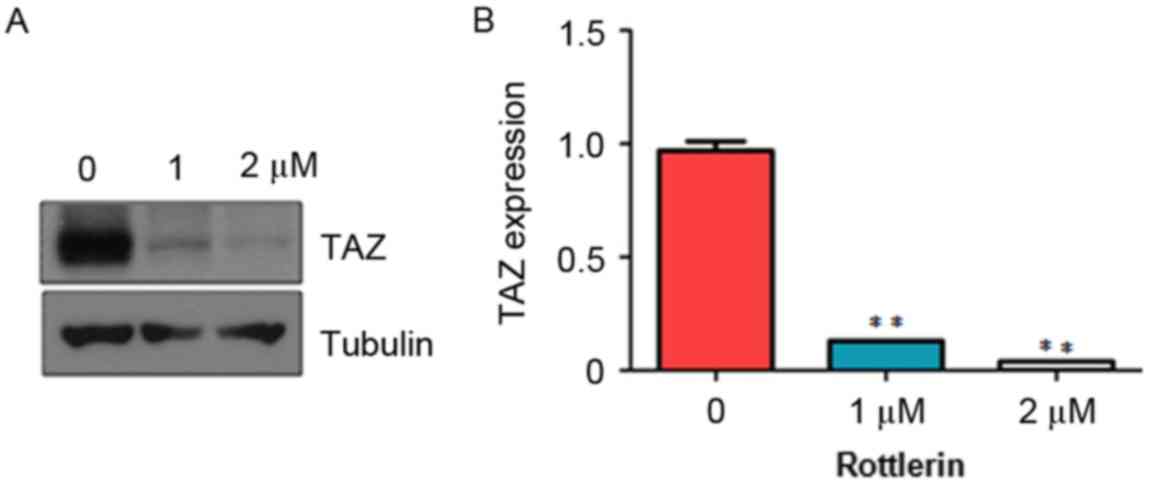
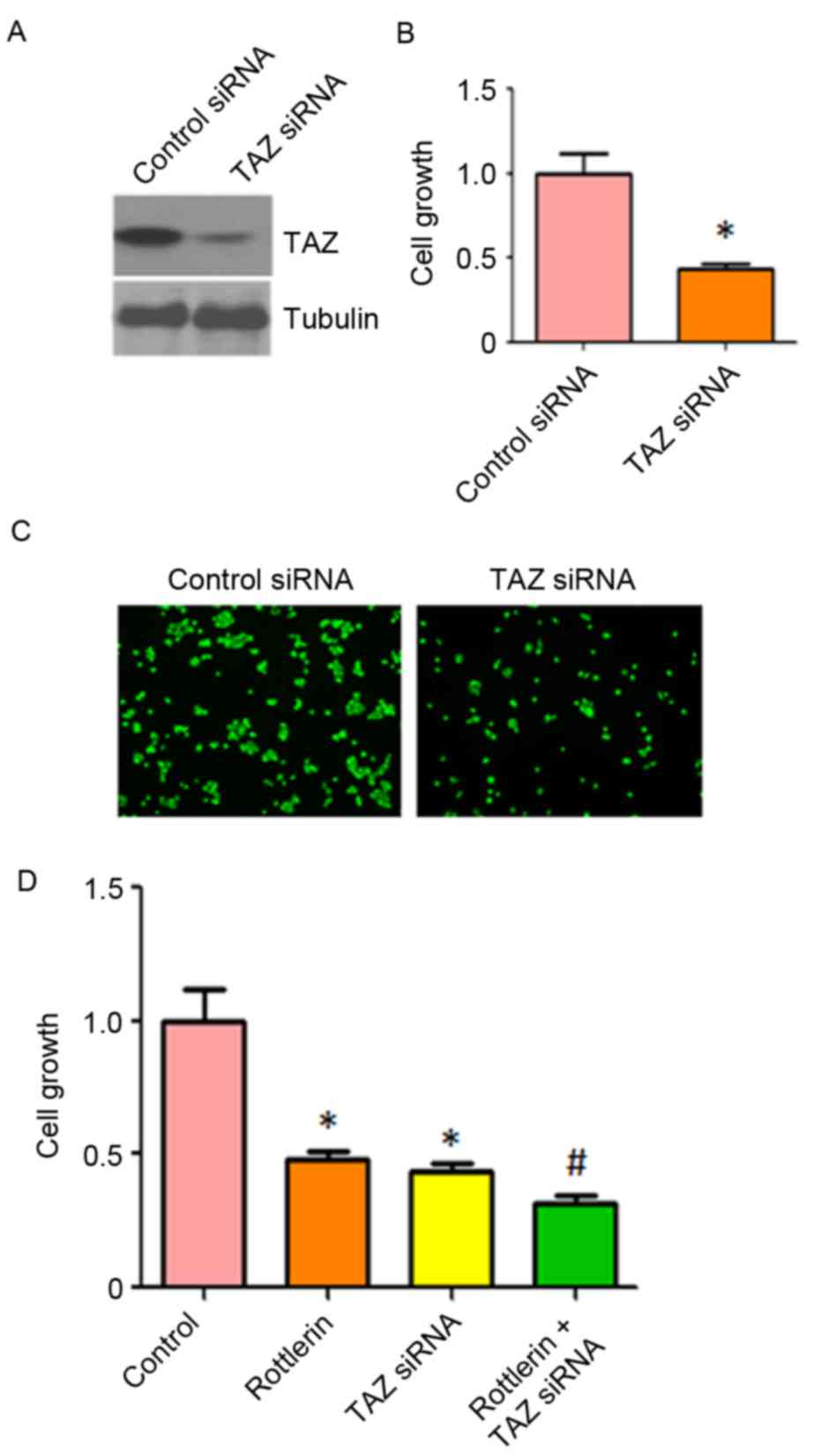
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kudo M, Trevisani F, Abou-Alfa GK and
Rimassa L: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Therapeutic guidelines and
medical treatment. Liver Cancer. 6:16–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maioli E, Torricelli C and Valacchi G:
Rottlerin and cancer: Novel evidence and mechanisms. Scientific
World Journal. 2012:3508262012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gschwendt M, Müller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang
R, Kittstein W, Rincke G and Marks F: Rottlerin, a novel protein
kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:93–98. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parmer TG, Ward MD and Hait WN: Effects of
rottlerin, an inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III,
on cellular proliferation, viability, and cell cycle distribution
in malignant glioma cells. Cell Growth Differ. 8:327–334.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ni H, Ergin M, Tibudan SS, Denning MF,
Izban KF and Alkan S: Protein kinase C-delta is commonly expressed
in multiple myeloma cells and its downregulation by rottlerin
causes apoptosis. Br J Haematol. 121:849–856. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tillman DM, Izeradjene K, Szucs KS,
Douglas L and Houghton JA: Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma
cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria
independent of protein kinase C. Cancer Res. 63:5118–5125.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim EH, Kim SU and Choi KS: Rottlerin
sensitizes glioma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by inhibition of
Cdc2 and the subsequent downregulation of survivin and XIAP.
Oncogene. 24:838–849. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Torricelli C, Fortino V, Capurro E,
Valacchi G, Pacini A, Muscettola M, Soucek K and Maioli E:
Rottlerin inhibits the nuclear factor kappaB/cyclin-D1 cascade in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Life Sci. 82:638–643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Basu A, Adkins B and Basu C:
Down-regulation of caspase-2 by rottlerin via protein kinase
C-delta-independent pathway. Cancer Res. 68:2795–2802. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song KS, Kim JS, Yun EJ, Kim YR, Seo KS,
Park JH, Jung YJ, Park JI, Kweon GR, Yoon WH, et al: Rottlerin
induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a
PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells:
The protective role of autophagy in apoptosis. Autophagy.
4:650–658. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barron DA and Kagey JD: The role of the
Hippo pathway in human disease and tumorigenesis. Clin Transl Med.
3:252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng J, Ren P, Gou J and Li Z: Prognostic
significance of TAZ expression in various cancers: A meta-analysis.
Onco Targets Ther. 9:5235–5244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Xue C, Cui H and Huang Z: High
expression of TAZ indicates a poor prognosis in retinoblastoma.
Diagn Pathol. 10:1872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zanconato F, Battilana G, Cordenonsi M and
Piccolo S: YAP/TAZ as therapeutic targets in cancer. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 29:26–33. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su J, Wang L, Yin X, Zhao Z, Hou Y, Ye X,
Zhou X and Wang Z: Rottlerin exhibits anti-cancer effect through
inactivation of S phase kinase-associated protein 2 in pancreatic
cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2178–2191. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin X, Zhang Y, Su J, Hou Y, Wang L, Ye X,
Zhao Z, Zhou X, Li Y and Wang Z: Rottlerin exerts its anti-tumor
activity through inhibition of Skp2 in breast cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:66512–66524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zanconato F, Cordenonsi M and Piccolo S:
YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell. 29:783–803. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lu W, Lin C and Li Y: Rottlerin induces
Wnt co-receptor LRP6 degradation and suppresses both Wnt/β-catenin
and mTORC1 signaling in prostate and breast cancer cells. Cell
Signal. 26:1303–1309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar D, Shankar S and Srivastava RK:
Rottlerin induces autophagy and apoptosis in prostate cancer stem
cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Lett.
343:179–189. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S and
Srivastava RK: Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic
cell death through inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human
pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:1154–1163.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lim JH, Woo SM, Min KJ, Park EJ, Jang JH,
Seo BR, Iqbal T, Lee TJ, Kim SH, Choi YH and Kwon TK: Rottlerin
induces apoptosis of HT29 colon carcinoma cells through NAG-1
upregulation via an ERK and p38 MAPK-dependent and PKC
δ-independent mechanism. Chem Biol Interact. 197:1–7. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Ye X, Cai X, Su J, Ma R, Yin X,
Zhou X, Li H and Wang Z: Curcumin suppresses cell growth and
invasion and induces apoptosis by down-regulation of Skp2 pathway
in glioma cells. Oncotarget. 6:18027–18037. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang S, Ma K, Chen L, Zhu H, Liang S, Liu
M and Xu N: TAZ promotes cell growth and inhibits Celastrol-induced
cell apoptosis. Biosci Rep. 36:pii: e00386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen G, Xie J, Huang P and Yang Z:
Overexpression of TAZ promotes cell proliferation, migration and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett.
12:1821–1825. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie D, Cui J, Xia T, Jia Z, Wang L, Wei W,
Zhu A, Gao Y, Xie K and Quan M: Hippo transducer TAZ promotes
epithelial mesenchymal transition and supports pancreatic cancer
progression. Oncotarget. 6:35949–35963. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo L, Zheng J, Zhang J, Wang H, Shao G
and Teng L: Knockdown of TAZ modifies triple-negative breast cancer
cell sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors by regulating YAP expression.
Oncol Rep. 36:729–736. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gruber R, Panayiotou R, Nye E,
Spencer-Dene B, Stamp G and Behrens A: YAP1 and TAZ control
pancreatic cancer initiation in mice by direct up-regulation of
JAK-STAT3 signaling. Gastroenterology. 151:526–539. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Higashi T, Hayashi H, Kitano Y, Yamamura
K, Kaida T, Arima K, Taki K, Nakagawa S, Okabe H, Nitta H, et al:
Statin attenuates cell proliferative ability via TAZ (WWTR1) in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 33:1232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou X, Su J, Feng S, Wang L, Yin X, Yan J
and Wang Z: Antitumor activity of curcumin is involved in
down-regulation of YAP/TAZ expression in pancreatic cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 7:79076–79088. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gao Y, Shi Q, Xu S, Du C, Liang L, Wu K,
Wang K, Wang X, Chang LS, He D and Guo P: Curcumin promotes KLF5
proteasome degradation through downregulating YAP/TAZ in bladder
cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 15:15173–15187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oku Y, Nishiya N, Shito T, Yamamoto R,
Yamamoto Y, Oyama C and Uehara Y: Small molecules inhibiting the
nuclear localization of YAP/TAZ for chemotherapeutics and
chemosensitizers against breast cancers. FEBS Open Bio. 5:542–549.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|