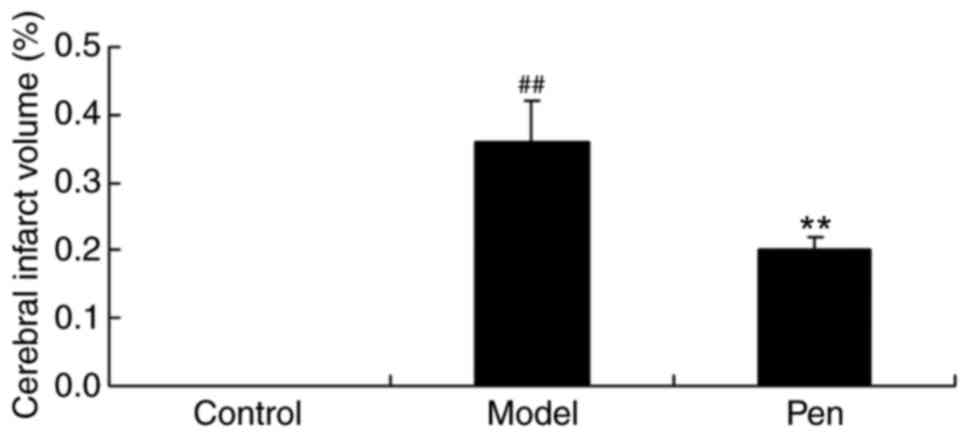
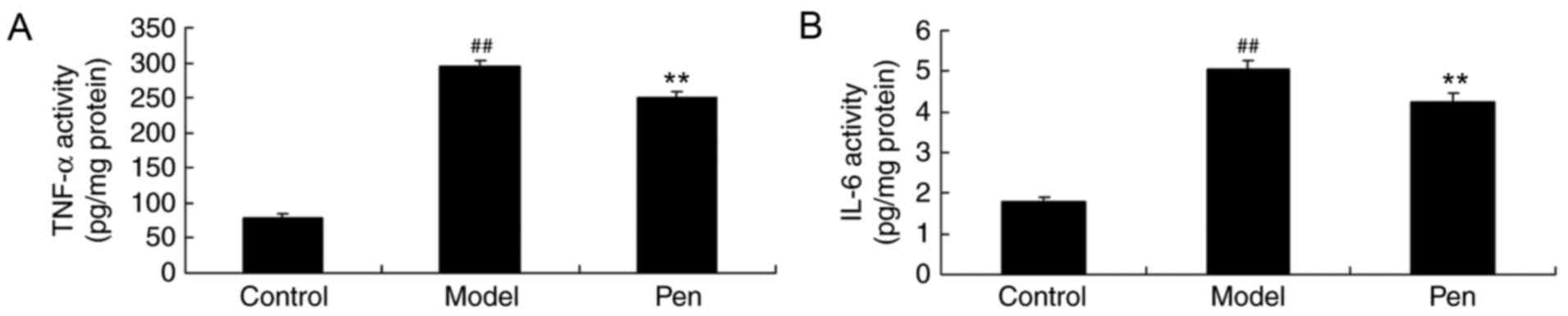
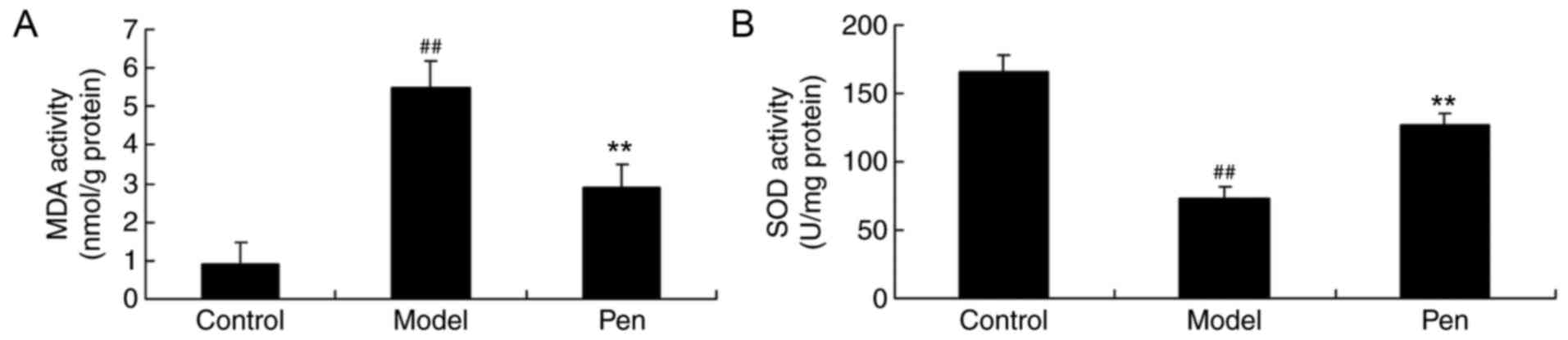
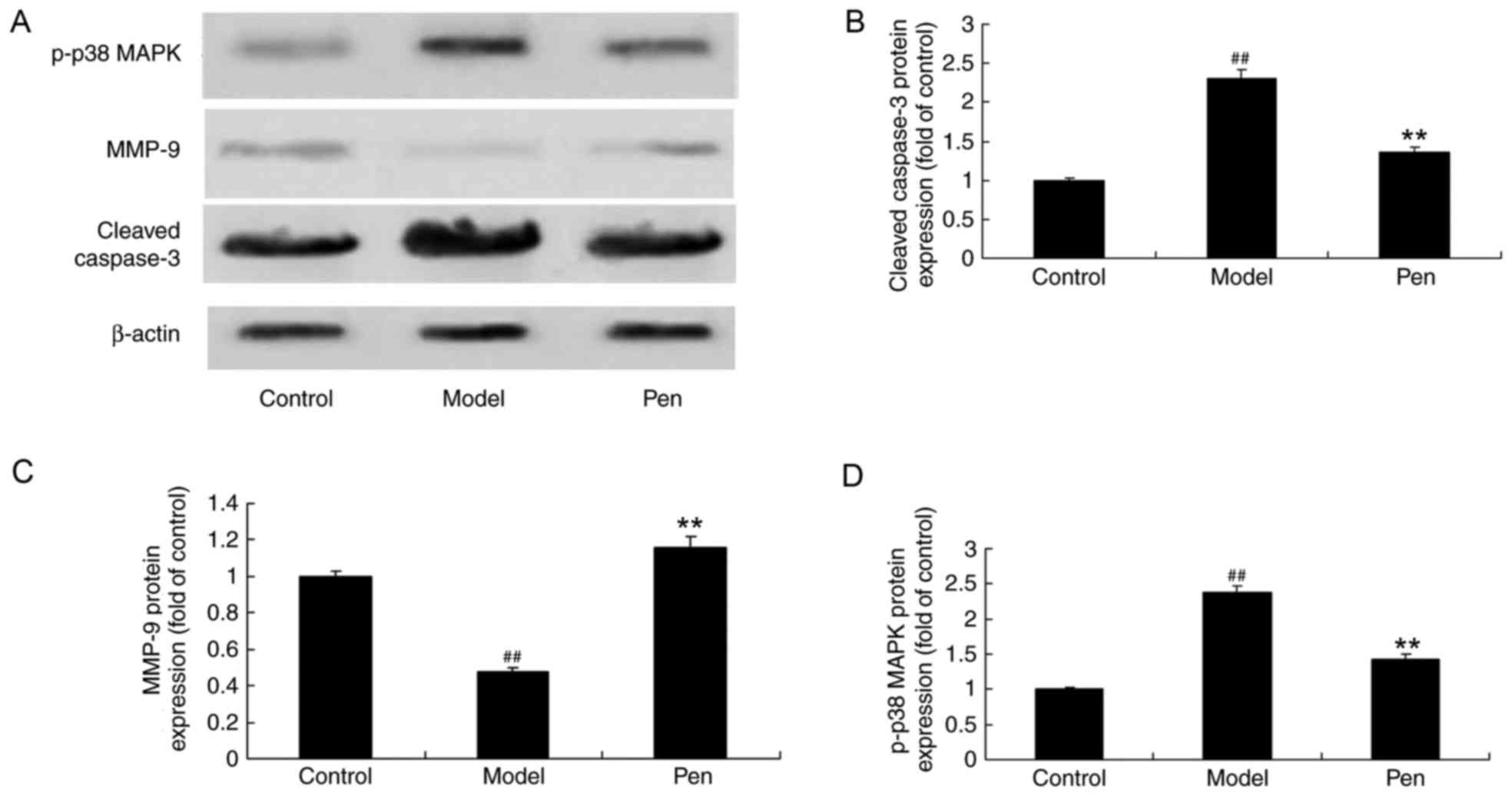
|
1
|
Martins VL, Caley MP, Moore K, Szentpetery
Z, Marsh ST, Murrell DF, Kim MH, Avari M, McGrath JA, Cerio R, et
al: Suppression of TGFβ and angiogenesis by type VII collagen in
cutaneous SCC. J Natl Cancer Inst. 108:pii: djv293. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao Y, Wang D, Xu T, Liu P, Cao Y, Wang
Y, Yang X, Xu X, Wang X and Niu H: Bladder cancer cells re-educate
TAMs through lactate shuttling in the microfluidic cancer
microenvironment. Oncotarget. 6:39196–39210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rodriguez DA, de Lima RF, Campos MS, Costa
JR, Biancardi MF, Marques MR, Taboga SR and Santos FCA:
Intrauterine exposure to bisphenol A promotes different effects in
both neonatal and adult prostate of male and female gerbils
(Meriones unguiculatus). Environ Toxicol. 31:1740–1750.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khoo NK, Cantu-Medellin N, St Croix C and
Kelley EE: In vivo immuno-spin trapping: Imaging the footprints of
oxidative stress. Curr Protoc Cytom. 74(12): 42.1–11. 2015.
|
|
5
|
Yue K, Trujillo-de Santiago G, Alvarez MM,
Tamayol A, Annabi N and Khademhosseini A: Synthesis, properties,
and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA)
hydrogels. Biomaterials. 73:254–271. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yan Y, Martin LM, Bosco DB, Bundy JL,
Nowakowski RS, Sang QX and Li Y: Differential effects of acellular
embryonic matrices on pluripotent stem cell expansion and neural
differentiation. Biomaterials. 73:231–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koyano-Nakagawa N, Shi X, Rasmussen TL,
Das S, Walter CA and Garry DJ: Feedback mechanisms regulate Ets
variant 2 (Etv2) gene expression and hematoendothelial lineages. J
Biol Chem. 290:28107–28119. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Warsinske HC, Ashley SL, Linderman JJ,
Moore BB and Kirschner DE: Identifying mechanisms of homeostatic
signaling in fibroblast differentiation. Bull Math Biol.
77:1556–1582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyamoto DT, Zheng Y, Wittner BS, Lee RJ,
Zhu H, Broderick KT, Desai R, Fox DB, Brannigan BW, Trautwein J, et
al: RNA-Seq of single prostate CTCs implicates noncanonical Wnt
signaling in antiandrogen resistance. Science. 349:1351–1356. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gill SE, Rohan M and Mehta S: Role of
pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis in murine
sepsis-induced lung injury in vivo. Respir Res. 16:1092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang YR, Kim DH, Seo YK, Park D, Jang HJ,
Choi SY, Lee YH, Lee GH, Nakajima K, Taniguchi N, et al: Elevated
O-GlcNAcylation promotes colonic inflammation and tumorigenesis by
modulating NF-κB signaling. Oncotarget. 6:12529–12542. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thurber AE, Omenetto FG and Kaplan DL: In
vivo bioresponses to silk proteins. Biomaterials. 71:145–157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, Mao J, Gao L, Liu J
and Wu T: Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2:787–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deng H, Zuo X, Zhang J, Liu X, Liu L, Xu
Q, Wu Z and Ji A: Α-lipoic acid protects against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Mol Med Rep.
11:3659–3665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saiardi A, Guillermier C, Loss O, Poczatek
JC and Lechene C: Quantitative imaging of inositol distribution in
yeast using multi-isotope imaging mass spectrometry (MIMS). Surf
Interface Anal. 46 Suppl 1:S169–S172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hosseini Y, Agah M and Verbridge SS:
Endothelial cell sensing, restructuring, and invasion in collagen
hydrogel structures. Integr Biol (Camb). 7:1432–1441. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Siddiqui A, Bhaumik D, Chinta SJ, Rane A,
Rajagopalan S, Lieu CA, Lithgow GJ and Andersen JK: Mitochondrial
quality control via the PGC1α-TFEB signaling pathway is compromised
by parkin Q311X mutation but independently restored by rapamycin. J
Neurosci. 35:12833–12844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhattacharya P, Pandey AK, Paul S, Patnaik
R and Yavagal DR: Aquaporin-4 inhibition mediates piroxicam-induced
neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
in rodents. PLoS One. 8:e734812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bassuk JA, Wu D, Lozano H, Arias J,
Kurlansky P, Lamas GA and Adams JA: Non-selective cyclooxygenase
inhibition before periodic acceleration (pGz) cardiopulmonary
resuscitation (CPR) in a porcine model of ventricular fibrillation.
Resuscitation. 77:250–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang T, Zhai L, Zhang H, Zhao L and Guo Y:
Picroside II Inhibits the MEK-ERK1/2-COX2 signal pathway to prevent
cerebral ischemic injury in rats. J Mol Neurosci. 57:335–351. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Brzozowski T, Konturek PC, Konturek SJ,
Pajdo R, Kwiecien S, Pawlik M, Drozdowicz D, Sliwowski Z and Pawlik
WW: Ischemic preconditioning of remote organs attenuates gastric
ischemia-reperfusion injury through involvement of prostaglandins
and sensory nerves. Eur J Pharmacol. 499:201–213. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salinas G, Rangasetty UC, Uretsky BF and
Birnbaum Y: The cycloxygenase 2 (COX-2) story: It's time to
explain, not inflame. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 12:98–111. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marques GM, Rasslan R, Belon AR, Carvalho
JG, Neto Felice R, Rasslan S, Utiyama EM and Montero EF:
Pentoxifylline associated to hypertonic saline solution attenuates
inflammatory process and apoptosis after intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 29:735–741. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mayyas F, Alzoubi KH and Al-Taleb Z: An
evaluation of the effect of pentoxifylline on blood pressure and
myocardial oxidative status following intake of western diet. Clin
Exp Hypertens. 37:666–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xin L, Hou Q, Xiong QI and Ding X:
Association between matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 polymorphisms and endometriosis: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Biomed Rep. 3:559–565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun J, Zhu Y, Zhang L and Ma Y: Effects of
xuelian injection on cerebral TNF-α, IL-1β and MMP-9 in rats
experienced focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 7:2632–2638. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zheng M, Wei J, Tang Y, Yang C, Wei Y, Yin
X and Liu Q: ApoE-deficient promotes blood-brain barrier disruption
in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via alteration of
MMP-9. J Mol Neurosci. 54:282–290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim SJ and Lee SR: Protective effect of
melatonin against transient global cerebral ischemia-induced
neuronal cell damage via inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9.
Life Sci. 94:8–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xin H, Liang W, Mang J, Lin L, Guo N,
Zhang F and Xu Z: Relationship of gelatinases-tight junction
proteins and blood-brain barrier permeability in the early stage of
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Neural Regen Res. 7:2405–2412.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garcia FA, Pinto SF, Cavalcante AF,
Lucetti LT, Menezes SM, Felipe CF, Alves AP, Brito GA, Cerqueira GS
and Viana GS: Pentoxifylline decreases glycemia levels and
TNF-alpha, iNOS and COX-2 expressions in diabetic rat pancreas.
Springerplus. 3:2832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
de Campos T, Deree J, Martins JO, Loomis
WH, Shenvi E, Putnam JG and Coimbra R: Pentoxifylline attenuates
pulmonary inflammation and neutrophil activation in experimental
acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 37:42–49. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu XW, Ji EF, He P, Xing RX, Tian BX and
Li XD: Protective effects of the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 on
NMDA-induced injury in primary cerebral cortical neurons. Mol Med
Rep. 10:1942–1948. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu MH, Chio CC, Tsai KJ, Chang CP, Lin NK,
Huang CC and Lin MT: Obesity exacerbates rat cerebral ischemic
injury through enhancing ischemic adiponectin-containing neuronal
apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol. 53:3702–3713. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Nakajima Y,
Omura S and Maruyama M: MicroRNA signature in diabetic wound
healing: Promotive role of miR-21 in fibroblast migration. Int
Wound J. 9:355–361. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Costantini TW, Deree J, Martins JO, Loomis
WH, Bansal V and Coimbra R: Pentoxifylline attenuates leukoreduced
stored blood-induced neutrophil activation through inhibition of
mitogen-activated protein kinases. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
32:74–81. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|