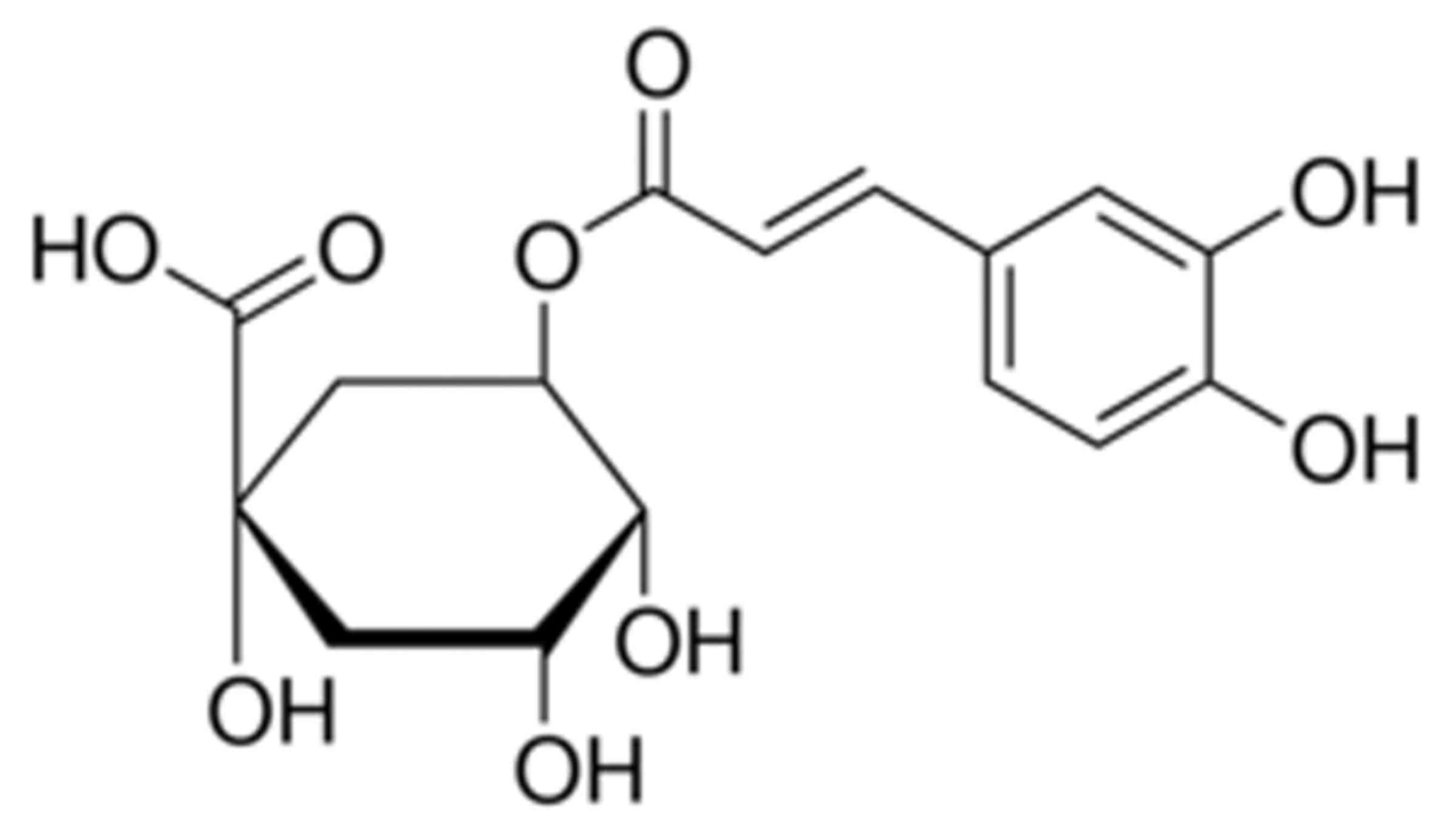
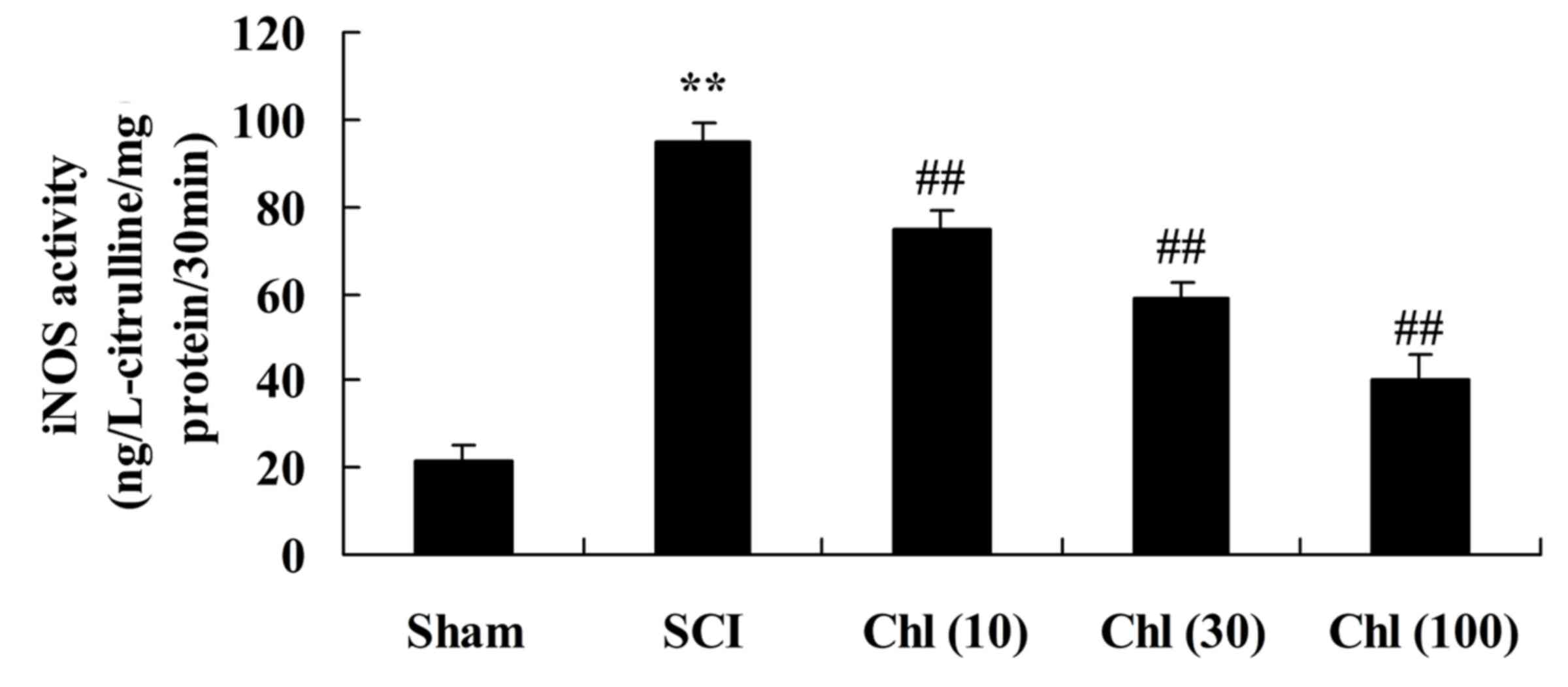
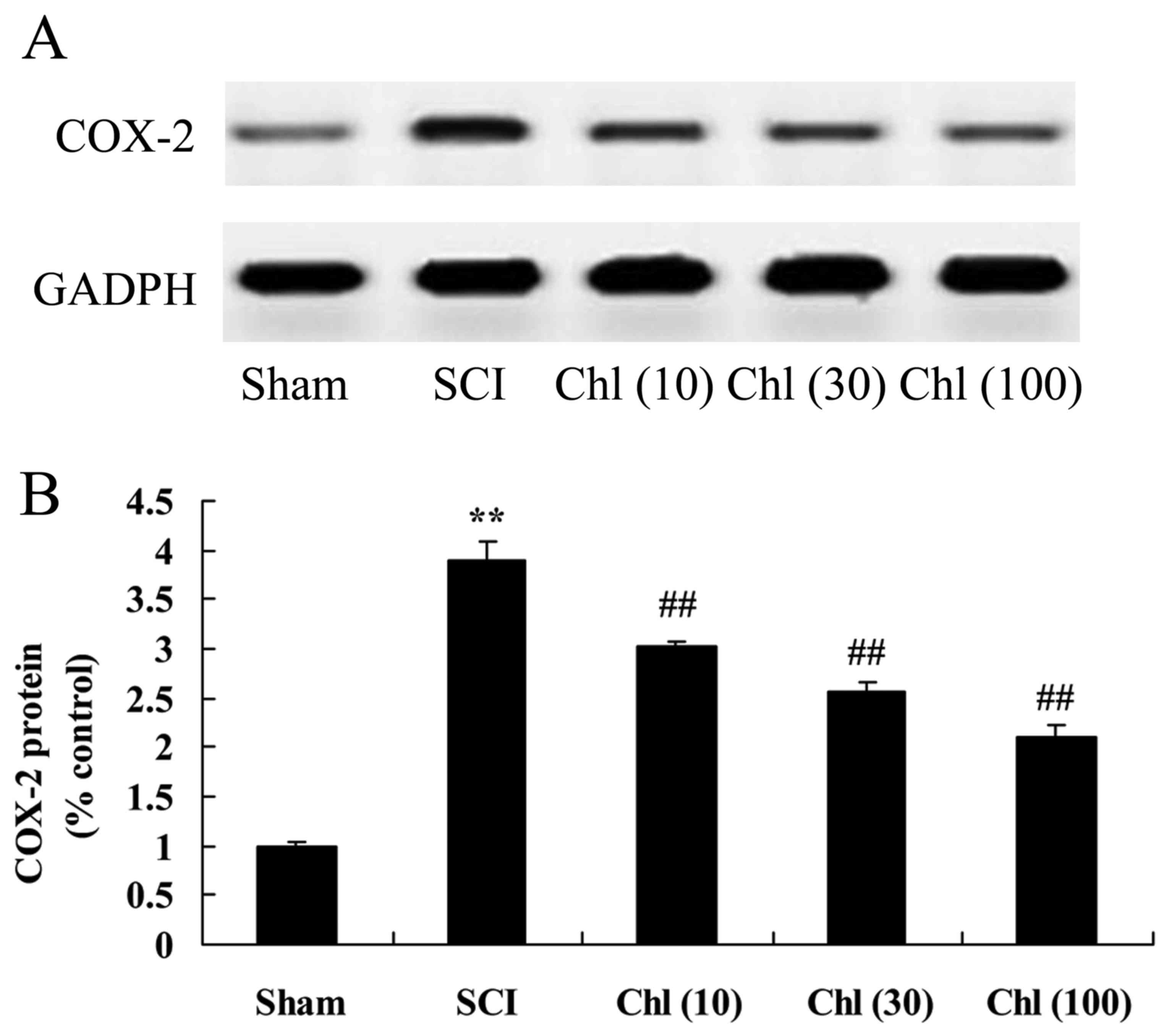
|
1
|
Casha S, Zygun D, McGowan MD, Bains I,
Yong VW and Hurlbert RJ: Results of a phase II placebo-controlled
randomized trial of minocycline in acute spinal cord injury. Brain.
135:1224–1236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ren Y and Young W: Managing inflammation
after spinal cord injury through manipulation of macrophage
function. Neural Plast. 2013:9450342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thrasher TA, Ward JS and Fisher S:
Strength and endurance adaptations to functional electrical
stimulation leg cycle ergometry in spinal cord injury. Neuro
Rehabilitation. 33:133–138. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
van Leeuwen CM, van der Woude LH and Post
MW: Validity of the mental health subscale of the SF-36 in persons
with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 50:707–710. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zangrillo A, Buratti L, Carozzo A,
Casiraghi G, Landoni G, Lembo R, Pasin L, Marone EM, Melissano G
and Chiesa R: Intrathecal lactate as a predictor of early-but not
late-onset spinal cord injury in thoracoabdominal aneurysmectomy. J
Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 28:473–478. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goldshmit Y, Frisca F, Kaslin J, Pinto AR,
Tang JK, Pébay A, Pinkas-Kramarski R and Currie PD: Decreased
anti-regenerative effects after spinal cord injury in spry4−/−
mice. Neuroscience. 287:104–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Margraf S, Lögters T, Reipen J, Altrichter
J, Scholz M and Windolf J: Neutrophil-derived circulating free DNA
(cf-DNA/NETs): A potential prognostic marker for posttraumatic
development of inflammatory second hit and sepsis. Shock.
30:352–358. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meves JM and Zheng B: Extrinsic inhibitors
in axon sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord injury.
Neural Regen Res. 9:460–461. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mortazavi MM, Verma K, Harmon OA,
Griessenauer CJ, Adeeb N, Theodore N and Tubbs RS: The microanatomy
of spinal cord injury: A review. Clin Anat. 28:27–36. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kigerl KA, de Rivero Vaccari JP, Dietrich
WD, Popovich PG and Keane RW: Pattern recognition receptors and
central nervous system repair. Exp Neurol. 258:5–16. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Adibhatla RM and Hatcher JF: Phospholipase
A(2), reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation in CNS
pathologies. BMB Rep. 41:560–567. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng S, Cao J, Feng Q, Peng J and Hu Y:
Roles of chlorogenic Acid on regulating glucose and lipids
metabolism: A review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:8014572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen WP and Wu LD: Chlorogenic acid
suppresses interleukin-1β-induced inflammatory mediators in human
chondrocytes. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:8797–8801. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Del Rio D, Stalmach A, Calani L and
Crozier A: Bioavailability of coffee chlorogenic acids and green
tea flavan-3-ols. Nutrients. 2:820–833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ruifeng G, Yunhe F, Zhengkai W, Ershun Z,
Yimeng L, Minjun Y, Xiaojing S, Zhengtao Y and Naisheng Z:
Chlorogenic acid attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced mice
mastitis by suppressing TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur
J Pharmacol. 729:54–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ravikumar R, Fugaccia I, Scheff SW, Geddes
JW, Srinivasan C and Toborek M: Nicotine attenuates morphological
deficits in a contusion model of spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma.
22:240–251. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chio CC, Lin JW, Chang MW, Wang CC, Kuo
JR, Yang CZ and Chang CP: Therapeutic evaluation of etanercept in a
model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurochem. 115:921–929. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gwak YS, Kang J, Unabia GC and Hulsebosch
CE: Spatial and temporal activation of spinal glial cells: Role of
gliopathy in central neuropathic pain following spinal cord injury
in rats. Exp Neurol. 234:362–372. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu PG, Feng H, Yuan SJ, Zhang RW, Li M, Hu
R, Liu ZS and Yin J: Effect of preconditioning with hyperbaric
oxygen on neural cell apoptosis after spinal cord injury in rats. J
Neurosurg Sci. 57:253–258. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fan T, Wang CC, Wang FM, Cheng F, Qiao H,
Liu SL, Guo W and Xiang FY: Experimental study of the protection of
ischemic preconditioning to spinal cord ischemia. Surg Neurol.
52:299–305. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo J, Zhu Y, Yang Y, Wang X, Chen B,
Zhang W, Xie B, Zhu Z, Yue Y and Cheng J: Electroacupuncture at
Zusanli (ST36) ameliorates colonic neuronal nitric oxide synthase
upregulation in rats with neurogenic bowel dysfunction following
spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 54:1139–1144. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao W and Li J: Targeted siRNA delivery
reduces nitric oxide mediated cell death after spinal cord injury.
J Nanobiotechnology. 15:382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brown R, Celermajer D, Macefield V and
Sander M: The effect of nitric oxide inhibition in spinal cord
injured humans with and without preserved sympathetic control of
the vasculature. Front Neurosci. 10:952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yue K, Wang X, Wu Y, Zhou X, He Q and Duan
Y: microRNA-7 regulates cell growth, migration and invasion via
direct targeting of PAK1 in thyroid cancer. Mol Med Rep.
14:2127–2134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang WG, Xiu RJ, Xu ZW, Yin YX, Feng Y,
Cao XC and Wang PS: Protective effects of Vitamin C against spinal
cord injury-induced renal damage through suppression of NF-κB and
proinflammatory cytokines. Neurol Sci. 36:521–526. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nelissen S, Vangansewinkel T, Geurts N,
Geboes L, Lemmens E, Vidal PM, Lemmens S, Willems L, Boato F,
Dooley D, et al: Mast cells protect from post-traumatic spinal cord
damage in mice by degrading inflammation-associated cytokines via
mouse mast cell protease 4. Neurobiol Dis. 62:260–272. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Genovese T, Esposito E, Mazzon E, Di Paola
R, Caminiti R, Bramanti P, Cappelani A and Cuzzocrea S: Absence of
endogenous interleukin-10 enhances secondary inflammatory process
after spinal cord compression injury in mice. J Neurochem.
108:1360–1372. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shi H, Dong L, Jiang J, Zhao J, Zhao G,
Dang X, Lu X and Jia M: Chlorogenic acid reduces liver inflammation
and fibrosis through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 signaling
pathway. Toxicology. 303:107–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Silverman N and Maniatis T: NF-kappaB
signaling pathways in mammalian and insect innate immunity. Genes
Dev. 15:2321–2342. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park SY, Jin ML, Kim YH, Kim Y and Lee SJ:
Anti-inflammatory effects of aromatic-turmerone through blocking of
NF-κB, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in amyloid
beta-stimulated microglia. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:13–20. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun SC, Harhaj EW, Xiao G and Good L:
Activation of I-kappaB kinase by the HTLV type 1 Tax protein:
Mechanistic insights into the adaptor function of IKKgamma. AIDS
Res Hum Retroviruses. 16:1591–1596. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meunier A, Latrémolière A, Dominguez E,
Mauborgne A, Philippe S, Hamon M, Mallet J, Benoliel JJ and Pohl M:
Lentiviral-mediated targeted NF-κB blockade in dorsal spinal cord
glia attenuates sciatic nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain in
the rat. Mol Ther. 15:687–697. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|