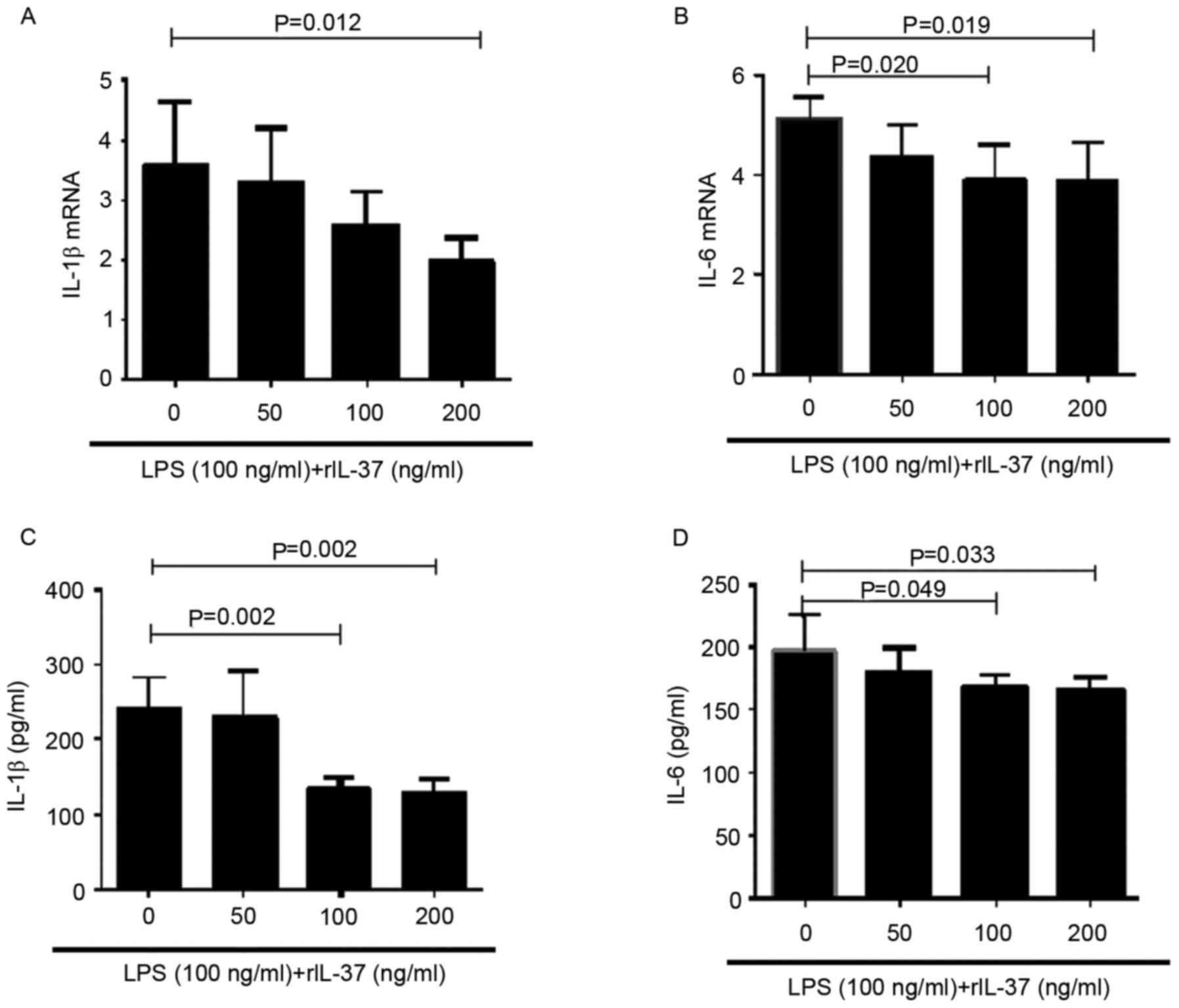
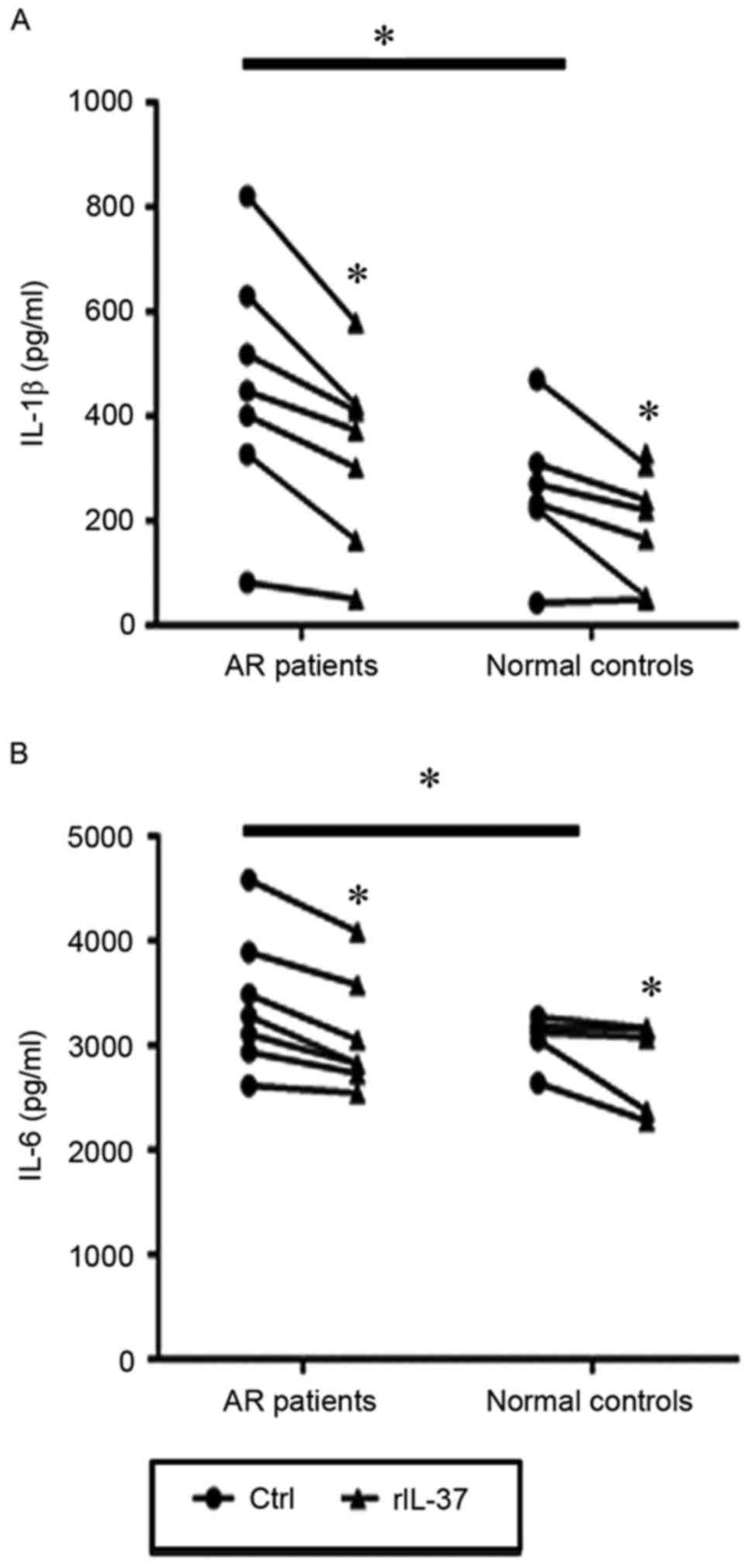
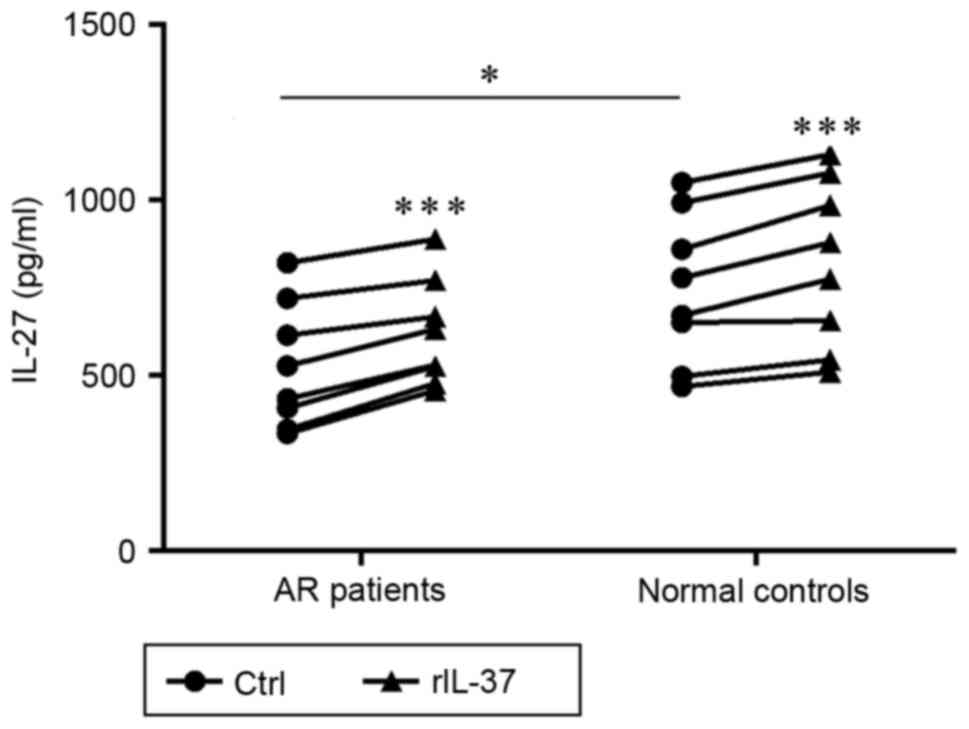
|
1
|
Togias A: Rhinitis and asthma: Evidence
for respiratory system integration. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
111:1171–1184. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shen J, Ke X, Hong S, Zeng Q, Liang C, Li
T and Tang A: Epidemiological features of allergic rhinitis in four
major cities in Western China. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med
Sci. 31:433–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Young MC: Rhinitis, sinusitis, and
polyposis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 19:211–218. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leynaert B, Neukirch F, Demoly P and
Bousquet J: Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and rhinitis
comorbidity. J Allergy ClinImmunol. 106 Suppl 5:S201–S205. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nold MF, Nold-Petry CA, Zepp JA, Palmer
BE, Bufler P and Dinarello CA: IL-37 is a fundamental inhibitor of
innate immunity. Nat Immunol. 11:1014–1022. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garlanda C, Dinarello CA and Mantovani A:
The interleukin-1 family: Back to the future. Immunity.
39:1003–1018. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boraschi D, Lucchesi D, Hainzl S, Leitner
M, Maier E, Mangelberger D, Oostingh GJ, Pfaller T, Pixner C,
Posselt G, et al: IL-37: A new anti-inflammatory cytokine of the
IL-1 family. Eur Cytokine Netw. 22:127–147. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Luo Y, Cai X, Liu S, Wang S, Nold-Petry
CA, Nold MF, Bufler P, Norris D, Dinarello CA and Fujita M:
Suppression of antigen-specific adaptive immunity by IL-37 via
induction of tolerogenic dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:15178–15183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ye Z, Wang C, Tang J, Zhou Y, Bai L, Liu
Y, Kijlstra A and Yang P: Decreased interleukin-37 expression in
Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease and upregulation following
immunosuppressive treatment. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 35:265–272.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ye Z, Wang C, Kijlstra A, Zhou X and Yang
P: A possible role for interleukin 37 in the pathogenesis of
Behcet's disease. Curr Mol Med. 14:535–542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bouali E, Kaabachi W, Hamzaoui A and
Hamzaoui K: Interleukin-37 expression is decreased in Behçet's
disease and is associated with inflammation. Immunol Lett.
167:87–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda J
and Yamamoto-Furusho JK: Interleukin 35 (IL-35) and IL-37:
Intestinal and peripheral expression by T and B regulatory cells in
patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine. 75:389–402.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ye L, Ji L, Wen Z, Zhou Y, Hu D, Li Y, Yu
T, Chen B, Zhang J, Ding L, et al: IL-37 inhibits the production of
inflammatory cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Its correlation with
disease activity. J Transl Med. 12:692014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Wang Z, Yu T, Chen B, Zhang J, Huang
K and Huang Z: Increased expression of IL-37 in patients with
Graves' disease and its contribution to suppression of
proinflammatory cytokines production in peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. PLoS One. 9:e1071832014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen B, Huang K, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang J,
Zhang J, Fan X, Liu X, Li L, Sun J, et al: Interleukin-37 is
increased in ankylosing spondylitis patients and associated with
disease activity. J Transl Med. 13:362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao PW, Jiang WG, Wang L, Jiang ZY, Shan
YX and Jiang YF: Plasma levels of IL-37 and correlation with TNF-α,
IL-17A, and disease activity during DMARD treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis. PLoS One. 9:e953462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xia T, Zheng XF, Qian BH, Fang H, Wang JJ,
Zhang LL, Pang YF, Zhang J, Wei XQ, Xia ZF and Zhao DB: Plasma
interleukin-37 is elevated in patients with plasma interleukin-37
is elevated in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Its correlation
with disease activity and Th1/Th2/Th17-related cytokines. Dis
Markers. 2015:7950432015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lunding L, Webering S, Vock C, Schröder A,
Raedler D, Schaub B, Fehrenbach H and Wegmann M: IL-37 requires
IL-18Rα and SIGIRR/IL-1R8 to diminish allergic airway inflammation
in mice. Allergy. 70:366–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Berraïes A, Hamdi B, Ammar J, Hamzaoui K
and Hamzaoui A: Increased expression of thymic stromal
lymphopoietin in induced sputum from asthmatic children. Immunol
Lett. 178:85–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Charrad R, Berraïes A, Hamdi B, Ammar J,
Hamzaoui K and Hamzaoui A: Anti-inflammatory activity of IL-37 in
asthmatic children: Correlation with inflammatory cytokines TNF-α,
IL-β, IL-6 and IL-17A. Immunobiology. 221:182–187. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg
J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, Zuberbier T, Baena-Cagnani CE, Canonica
GW, van Weel C, et al: Allergic rhinitis and its impact on asthma
(ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health
Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen). Allergy. 63 Suppl 86:S8–S160.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
No authors listed: Position paper:
Allergen standardization and skin tests. The European Academy of
Allergology and Clinical Immunology. Allergy. 48 Suppl 14:S48–S82.
1993.
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Raedler D, Ballenberger N, Klucker E, Böck
A, Otto R, da Costa Prazeres O, Holst O, Illig T, Buch T, von
Mutius E and Schaub B: Identification of novel immune phenotypes
for allergic and nonallergic childhood asthma. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 135:81–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu W, Deng L, Chen Y, Sun C, Wang J, Zhou
L, Li H and Luo R: Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-37b in children
with allergic rhinitis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:7468462014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wojno ED and Hunter CA: New directions in
the basic and translational biology of interleukin-27. Trends
Immunol. 33:91–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen Y, Yuan XD, Hu D, Ke X, Wang XQ, Hu
GH, Hong SL and Kang HY: Association between interleukin-27 gene
polymorphisms and susceptibility to allergic rhinitis. Hum Immunol.
75:991–995. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen Y, Tang XY, Yang YC, Ke X, Kou W, Pan
CK and Hong SL: Impaired balance of Th17/Treg in patients with
nasal polyposis. Scand J Immunol. 74:176–185. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|