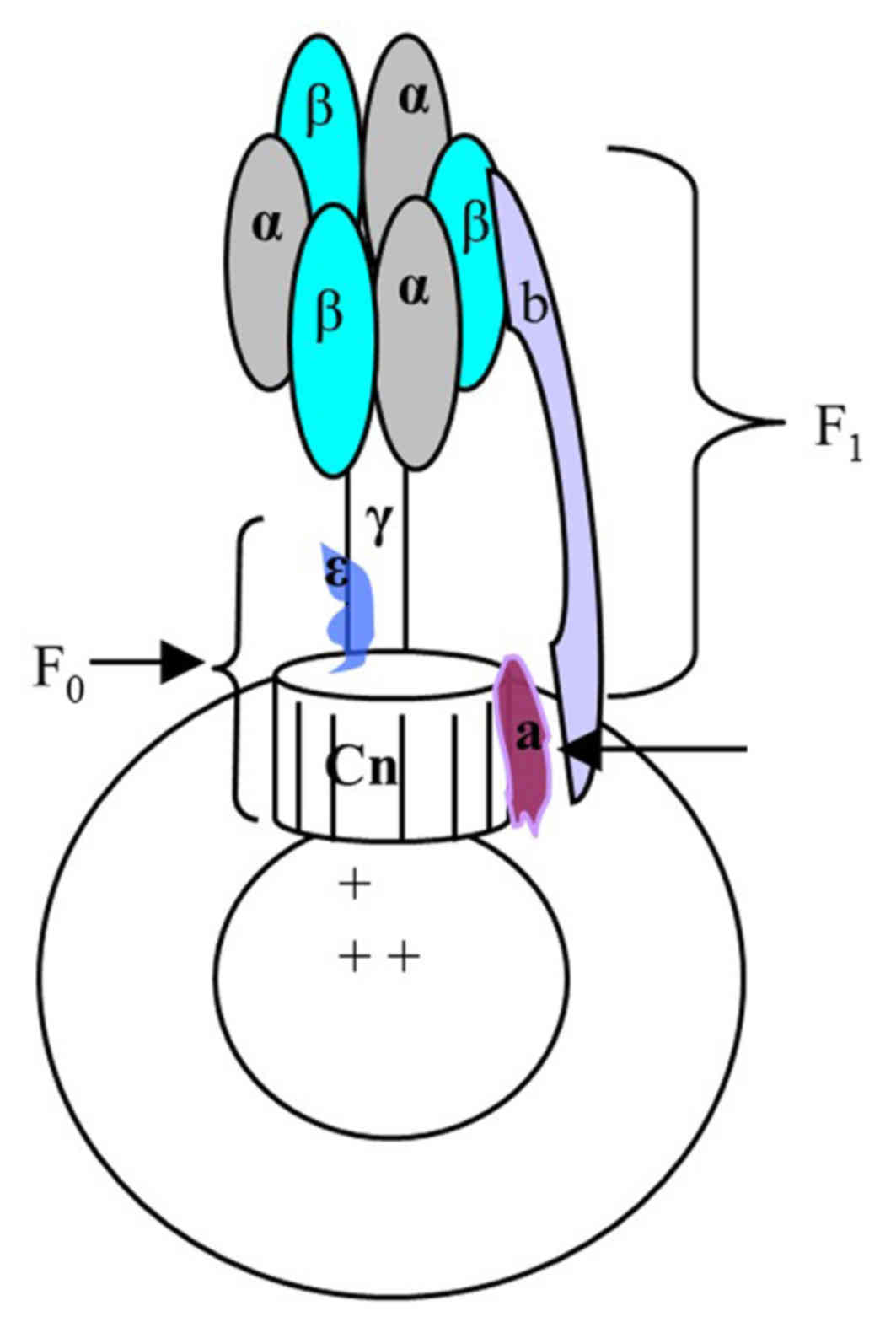
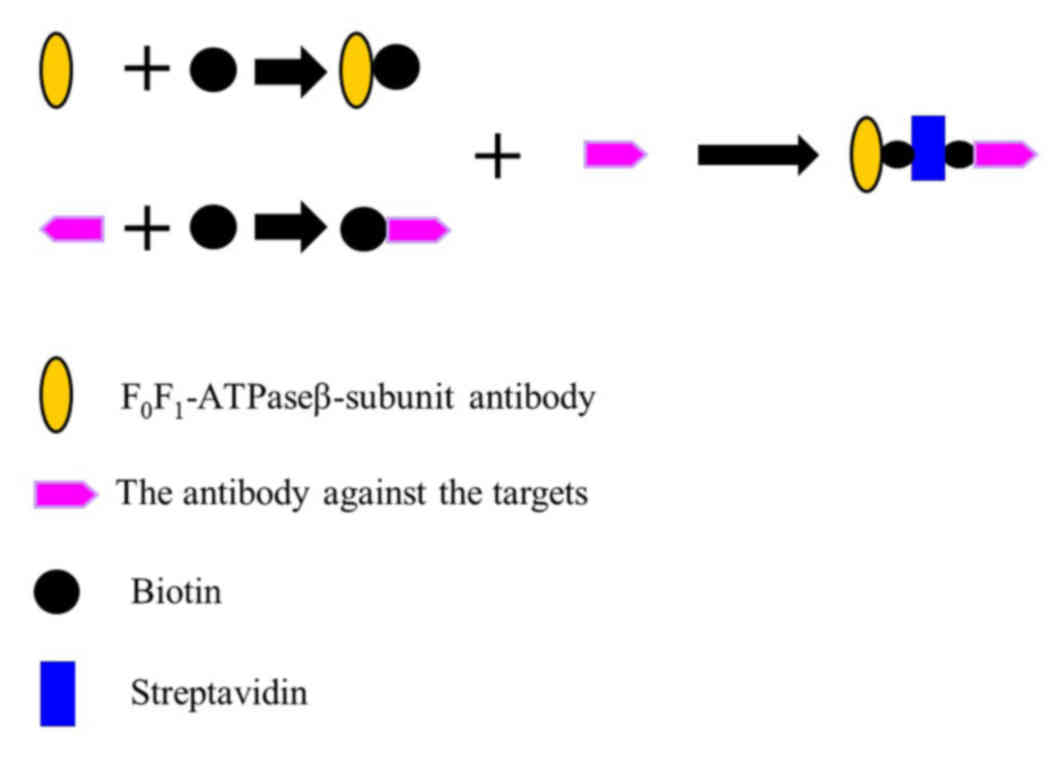
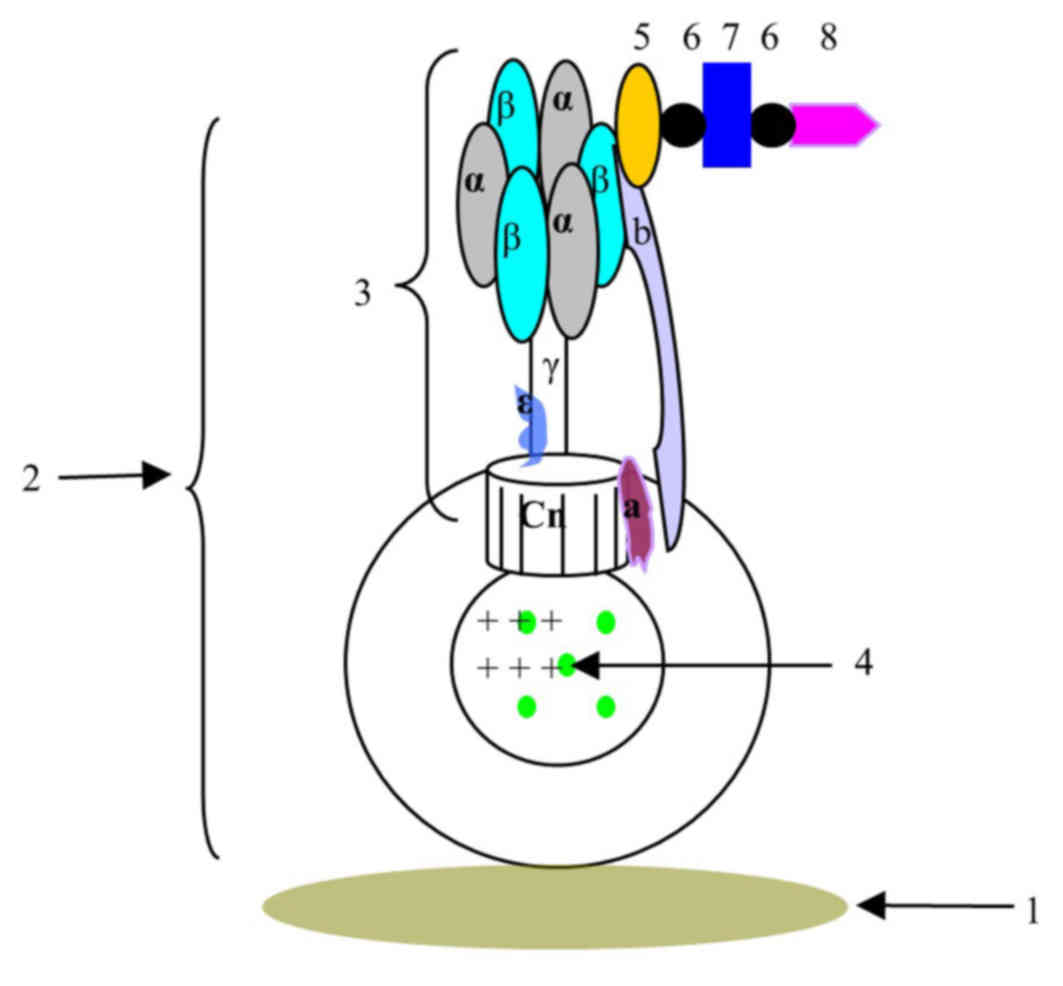
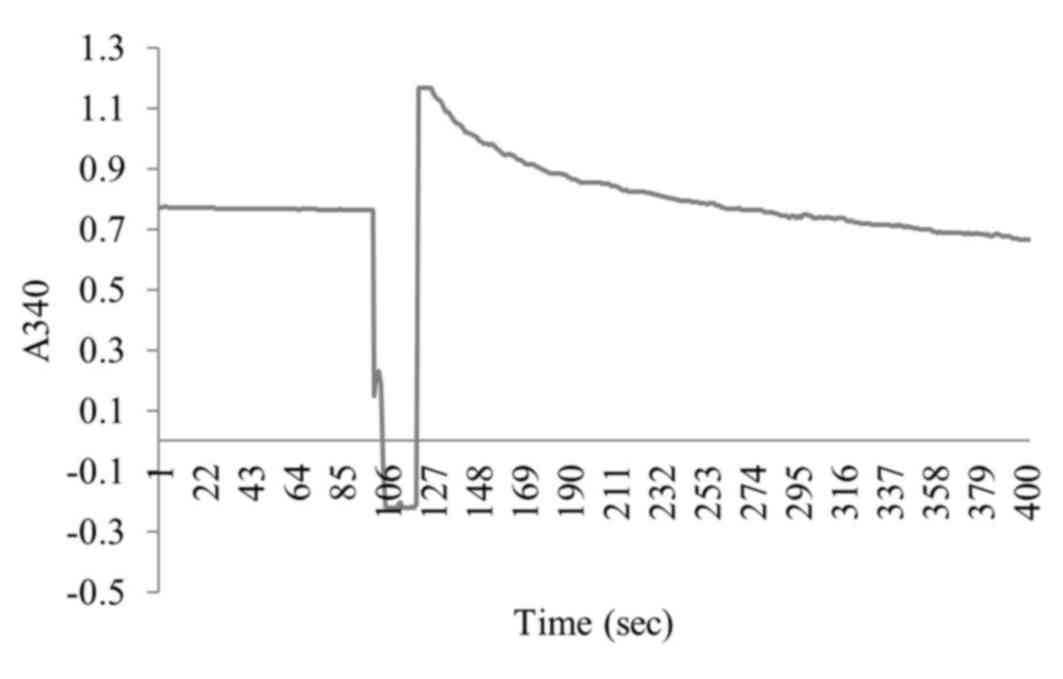
|
1
|
Naugle AL, Holt KG, Levine P and Eckel R:
Food safety and inspection service regulatory testing program for
Escherichia coli O157:H7 in raw ground beef. J Food Prot.
68:462–468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang HH and Wu RM: Survey on contamination
status of food-borne pathogens in chilled broilers. Shiyong Yufang
Yixue. 17:1314–1315. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Yue J, Jiang P and Zhang
Z: F0F1-ATPase as biosensor to detect single virus. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 342:1319–1322. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu HJWL and Liu QJ: Application of nano
biosensortechnology in chloramphenicol detection. Food Sci.
31:167–170. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Wu HJ, Wei L, Lun YZ, Kang ZJ and Zhao L:
The preliminary study of a rapid detecting technology for
Listeria monocytogenes based on immunobiosensor. Zhongguo
Weishengtai Xue Zazhi. 22:743–745. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Deng Z, Zhang Y, Yue J, Tang F and Wei Q:
Green and orange CdTe quantum dots as effective pH-sensitive
fluorescent probes for dual simultaneous and independent detection
of viruses. J Phys Chem B. 111:12024–12031. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yun Z, Zhengtao D, Jiachang Y, Fangqiong T
and Qun W: Using cadmium telluride quantum dots as a proton flux
sensor and applying to detect H9 avian influenza virus. Anal
Biochem. 364:122–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu XL, Zhang XA, Cui YB, Yue JC, Luo ZY
and Jiang PD: Mechanically driven proton conduction in single
delta-free F0F1-ATPase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 347:752–757.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhao Y, Wang P, Wang F, Zhou H, Li W, Yue
J and Ha Y: A novel biosensor regulated by the rotator of
F0F1-ATPase to detect deoxynivalenolrapidly.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:195–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu HT, Zhang Y, Yue JC, et al: Application
of immuno-rotary biosensor based on FoF1-ATPase in Chromatophores
for detecting clenbuterol. Food Science. 28:446–450. 2007.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Capaldi RA and Aggeler R: Mechanism of the
F(1)F(0)-type ATP syn-thase, a biological rotary motor. Trends
Biochem Sci. 27:154–160. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karplus M and Gao YQ: Biomolecular motors:
The F1-ATPase para-digm. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 14:250–259. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Clark LC Jr and Lyons C: Electrode systems
for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 102:29–45. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei L, Wu HJ, Li BM, et al: The pollution
and detection research progress of four pathogenic bacterias. Food
Sci. 32:302–306. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Wei L, Wu HJ, Lun YZ, Li BM, Gao LJ, Zhang
XL and Kang ZJ: An immunobiosensor for rapid detection of
Staphylococcus aureusenes. Zhongguo Shipin Weisheng Zazhi.
22:498–501. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Mousavi SL, Rasooli I, Nazarian S and
Amani J: Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7,
toxigenic Vibrio cholerae and Salmonella typhimurium
by multiplex PCR. Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious Diseases.
4:97–103. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Zordan MD, Grafton MM, Acharya G, Reece
LM, Cooper CL, Aronson AI, Park K and Leary JF: Detection of
pathogenic E. coli O157:H7 by a hybrid microfluidic SPR and
molecular imaging cytometry device. Cytometry A. 75:155–162. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bahşi ZB, Buyukaksoy A, Aslan MH and Oral
AY: DNA biosensors for E. coli O157:H7 detection in drinking water
resources using sol-gel derived waveguides. South Biomed Eng Conf.
24:203–206. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Oda M, Morita M, Unno H and Tanji Y: Rapid
detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 by using green
fluorescent protein-labeled PP01 bacteriophage. Appl Environ
Microbiol. 70:527–534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li F, Zhao C, Zhang W, Cui S, Meng J, Wu J
and Zhang DY: Use of ramification amplification assay for detection
of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other E. J Clin Microbiol.
43:6086–6090. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang Z, Kotov NA and Giersig M:
Spontaneous organization of single CdTe nanoparticles into
luminescent nanowires. Science. 297:237–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nanduri V, Bhunia AK, Tu SI, Paoli GC and
Brewster JD: SPR biosensor for the detection of L.
monocytogenes using phage-displayed antibody. Biosens
Bioelectron. 23:248–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao P, Xu G, Shi X, Yuan K and Tian J:
Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus by a combination of
monoclonal antibody-coated latex and capillary electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis. 27:1784–1789. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu X, Liu H, Liu J, Haley KN, Treadway JA,
Larson JP, Ge N, Peale F and Bruchez MP: Immunofluorescent labeling
of cancer marker Her2 and other cellular targets with semiconductor
quantum dots. Nat Biotechnol. 21:41–46. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chan WC and Nie S: Quantum dot
bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science.
281:2016–2018. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nou X, Arthur TM, Bosilevac JM,
Brichta-Harhay DM, Guerini MN, Kalchayanand N and Koohmaraie M:
Improvement of immunomagnetic separation for Escherichia
coli O157:H7 detection by the PickPen magnetic particle
separation device. J Food Prot. 69:2870–2874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fu Z, Rogelj S and Kieft TL: Rapid
detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 by immunomagnetic
separation and real-time PCR. Int J Food Microbiol. 99:47–57. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chapman PA, Malo AT, Siddons CA and Harkin
M: Use of commercial enzyme immunoassays and immunomagnetic
separation systems for detecting Escherichia coli O157 in
bovine fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 63:2549–2553.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|