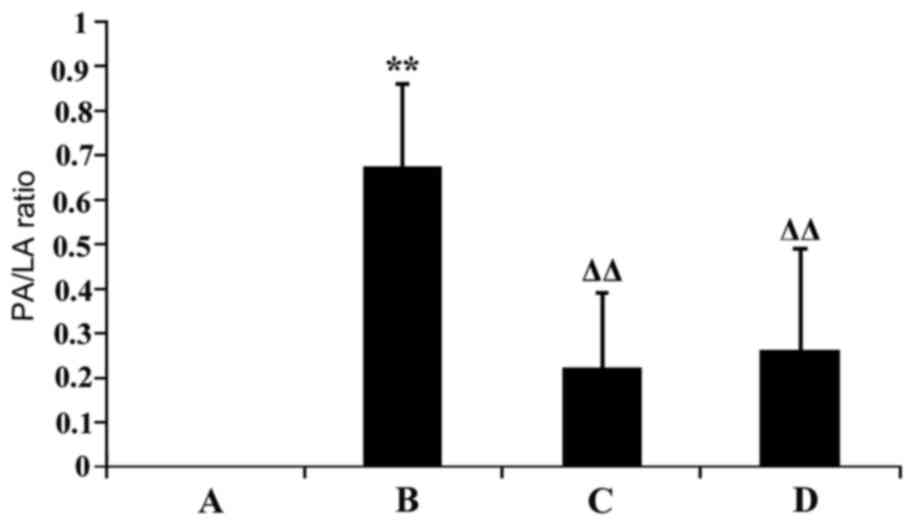
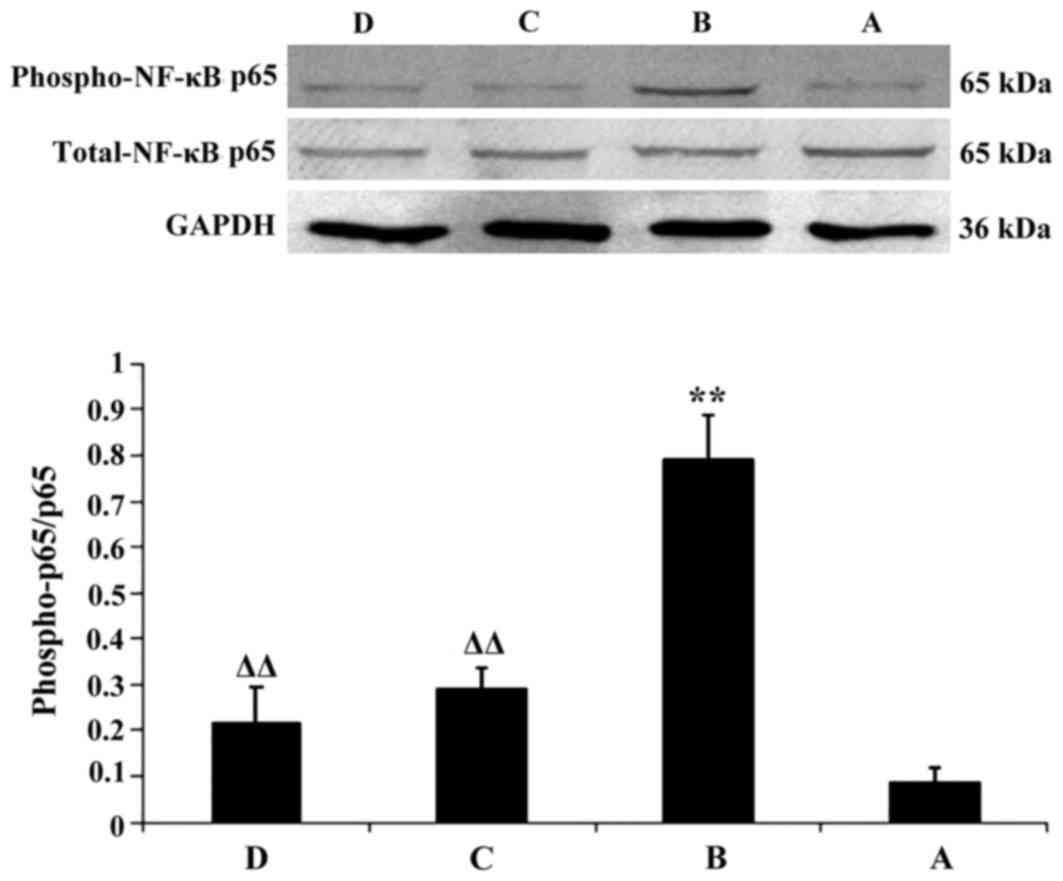
|
1
|
Lehrke M and Lebherz C: AAV-mediated gene
therapy for atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 16:4342014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sidney S, Rosamond WD, Howard VJ and
Luepker RV: National Forum for Heart Disease and Stroke Prevention:
The ‘heart disease and stroke statistics-2013 update’ and the need
for a national cardiovascular surveillance system. Circulation.
127:21–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen WW, Gao RL and Liu LS: The Chinese
cardiovascular disease report 2014 Profile. Chin Circulat J.
617–622. 2015.
|
|
4
|
Anogeianaki A, Angelucci D, Cianchetti E,
D'Alessandro M, Maccauro G, Saggini A, Salini V, Caraffa A, Tete S,
Conti F, et al: Atherosclerosis: A classic inflammatory disease.
Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 24:817–825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Charakida M, O'Neil F, Masi S,
Papageorgiou N and Tousoulis D: Inflammatory disorders and
atherosclerosis: New therapeutic approaches. Curr Pharm Des.
17:4111–4120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ross R: Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory
disease. Am Heart J. 138:S419–S420. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
An D, Hu J, Zhao M and Zheng J: Effect of
Tianxiangdan on serum vascular endothelial growth factor and
correlative factors in coronary heart disease. Chin J Integrat Med
Cardio/Cerebrovas Dis. 5:662–664. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
An D, Zhou M, Zhang X and Ling C: Effect
of Tianxiangdan on thrombosis and myocardial ultramicrostructure in
rat model with myocadial ischemia. J Xinjiang Med Uni. 30:434–437.
2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Yin J, Zhu J, Liu Q and An Q: The effect
of Tianxiangdan granule on T-SOD, GSH-Px, MDA, LD in serum of
angina of coronary heart disease patients. Chin J Inform Trad Chin
Med. 10:13–15. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Wang XY, Jiao YJ and An DQ: Effects of
different concentrations of Tianxiangdan on blood lipid and VEGF
levels in ApoE (−/-) gene knockout mice with atherosclerosis. J
Emer Trad Chin Med. 23(400–403): 415S42014.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
An DQ: A medicine for treating coronary
heart disease and its preparation method. CN200910210063.9. Filed
Nov 4, 2009; issued May 11. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Gao Z, Ablimiti A and Wufuer H: Thinking
about the establishment of animal model of cold dryness syndrome in
Northwest China. Chin J Inf Tradit Chin Med. 17:6–7. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Niyazi G, An DQ and Li M: Study on
Establishing Animal Model of Huizhuo Tanzu Type Atherosclerosis.
Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form. 19:265–269. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Xu SY, Bian RL and Chen X: The
Experimental Method of Pharmacology. Third edition. Beijing:
People's Med Publishing House; 2013, (In Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lucas AR, Korol R and Pepine CJ:
Inflammation in atherosclerosis: Some thoughts about acute coronary
syndromes. Circulation. 113:e728–e732. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li YJ, Yang Q and Zhu XX: TCM
anti-inflammation: An effective approach for treating
atherosclerosis. Mod Tradit Chin Med Mater Med-World Sci Technol.
9:22–28. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Daviglus ML, Talavera GA, Avilés-Santa ML,
Allison M, Cai J, Criqui MH, Gellman M, Giachello AL, Gouskova N,
Kaplan RC, et al: Prevalence of major cardiovascular risk factors
and cardiovascular diseases among hispanic/latino individuals of
diverse backgrounds in the United States. JAMA. 308:1775–1784.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Sen R and Baltimore D: Multiple unclear
factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell.
46:705–716. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gordon JW, Shaw JA and Kirshenbaum LA:
Multiple facets of NF-κB in the heart: To be or not to NF-κB. Circ
Res. 108:1122–1132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ghosh S, May MJ and Kopp EB: NF-kappa B
and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune
responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 16:225–260. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Misra A, Haudek SB, Knuefermann P, Vallejo
JG, Chen ZJ, Michael LH, Sivasubramanian N, Olson EN, Entman ML and
Mann DL: Nuclear factor-kappaB protects the adult cardiac myocyte
against ischemia-induced apoptosis in a murine model of acute
myocardial infarction. Circulation. 108:3075–3078. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Morita M, Yano S, Yamaguchi T and Sugimoto
T: Advanced glycation end products-induced reactive oxygen species
generation is partly through NF-kappa B activation in human aortic
endothelial cells. J Diabetes Complications. 27:11–15. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lawrence T, Gilroy DW, Nash Colwille PR
and Willoughby DA: Possible new role for NF-kappa B in the
resolution of inflammation. Nat Med. 7:1291–1297. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Freund C, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Baurand A,
Dunger S, Schneider W, Loser P, El-Jamali A, Dietz R, Scheidereit C
and Bergmann MW: Requirement of nuclear factor-kappaB in
angiotensin II- and isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy in
vivo. Circulation. 111:2319–2325. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zelarayan L, Renger A, Noack C, Zafiriou
MP, Gehrke C, van der Nagel R, Dietz R, de Windt L and Bergmann MW:
NF-kappaB activation is required for adaptive cardiac hypertrophy.
Cardiovasc Res. 84:416–424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liuzzo G, Santamaria M, Biasucci LM,
Narducci M, Colafrancesco V, Porto A, Brugaletta S, Pinnelli M,
Rizzello V, Maseri A and Crea F: Persistent activation of nuclear
factor kappa-B signaling pathway in patients with unstable angina
and elevated levels of C-reactive protein evidence for a direct
proinflammatory effect of azide and lipopolysaccharide-free
C-reactive protein on human monocytes via nuclear factor kappa-B
activation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:185–194. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu XL, Zheng B, Jin LS, Zhang RN, He M,
Yang Z and Wen JK: Chinese medicine Tongxinluo reduces
atherosclerotic lesion by attenuating oxidative stress and
inflammation in microvascular endothelial cells. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6323–6333. 2015.
|
|
29
|
Kang Q, Liu W, Liu H and Zhou M: Effect of
compound chuanxiong capsule on inflammatory reaction and
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway in atherosclerosis. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2015:5845962015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Latkovslds G, Licis N and Kalnms U:
C-reactive protein levels and common polymorphisms of the
interleukin-1 gene cluster and interleukin-6 gene in patients with
coronary heart disease. Eur J Immunogenet. 31:207–213. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhu T, Zhang L, Ling S, Duan J, Qian F, Li
Y and Xu JW: Scropolioside B inhibits IL-1β and cytokines
expression through NF-κB and inflammasome NLRP3 pathways. Mediators
Inflamm. 2014:8190532014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Popa C, Netea MG, van-Riel PL, van der
Meer JW and Stalenhoef AF: The role of TNF-alpha in chronic
inflammatory conditions, intermediary metabolism, and
cardiovascular risk. J Lipid Res. 48:751–762. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang H, Park Y, Wu J, Chen Xp, Lee S,
Yang J, Dellsperger KC and Zhang C: Role of TNF-alpha in vascular
dysfunction. Clin Sci (Lond). 116:219–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Novitskiy G, Ravi R, Potter JJ,
Rennie-Tankersley L, Wang L and Mezey E: Effects of acetaldehyde
and TNF alpha on the inhibitory kappa B-alpha protein and nuclear
factor kappa B activation in hepatic stellate cells. Alcohol
Alcohol. 40:96–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Morello S, Ito K, Yamamura S, Lee KY,
Jazrawi E, Desouza P, Barnes P, Cicala C and Adcock IM: IL-1beta
and TNF-alpha regulation of the adenosine receptor (A2A)
expression: Differential requirement for NF-kappa B binding to the
proximal promoter. J Immunol. 177:7173–7183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schramek H: MAP kinases: From
intracellular signals to physiology and disease. News Physiol Sci.
17:62–67. 2002.
|
|
37
|
Garrington TP and Johnson GL: Organization
and regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 11:211–218. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dunn KL, Espino PS, Drobic B, He S and
Davie JR: The Ras-MAPK signal transduction pathway, cancer and
chromatin remodeling. Biochem Cell Biol. 83:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ju H, Behm DJ, Nerurkar S, Eybye ME,
Haimbach RE, Olzinski AR, Douglas SA and Willette RN: p38 MAPK
inhibitors ameliorate target organ damage in hypertension: Part1.
p38 MAPK-dependent endothelial dysfunction and hypertension. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 307:932–938. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Goldstein DM and Gabriel T: Pathway to the
clinic: Inhibition of P38 MAP kinase. A review of ten chemotypes
selected for development. Curr Top Med Chem. 5:1017–1029. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
He X, Shu J, Xu L, Lu C and Lu A:
Inhibitory effect of astragalus polysaccharides on
lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-a and IL-1β production in THP-1
cells. Molecules. 17:3155–3164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang K, Qiu BY, Yan J, Yang YX, Zhang T,
Chen X, Zou YP, Gan HT and Huang XL: Blockade of p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway ameliorates delayed
gastric emptying in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int
Immunopharmacol. 23:696–700. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
El Bekay R, Alvarez M, Monteseirín J, Alba
G, Chacón P, Vega A, Martin-Nieto J, Jiménez J, Pintado E, Bedoya
FJ and Sobrino F: Oxidative stress is a critical mediator of the
angiotensin II signal in human neutrophils: Involvement of
mitogen-activated protein kinase, calcineurin, and the
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Blood. 102:662–671. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lindroos PM, Rice AB, Wang YZ and Boner
JC: Role of nuclear factor-kappaB and mitogen-activated protein
kinase signaling pathways in IL-1beta-mediated induction of
alpha-PDGF receptor expression in rat pulmonary myofibroblasts.
Immunol. 161:3464–8. 1998.
|
|
45
|
Zhang X, Wu M, Jiang H, Hao J, Zhang Q,
Zhu Q, Saren G, Zhang Y, Meng X and Yue X: Angiotensin II
upregulates endothelial lipase expression via the NF-kappa B and
MAPK signaling pathways. PLoS One. 9:e1076342014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
An DQ, Zhao MF, Zheng J, et al: Xinjiang
obstruction of dirty phlegm syndrome retraces. Xinjiang J Tradit
Chin Med. 25:1–2. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
47
|
Xiao Y, Wang YC, Li LL, Jin YC, Sironi L
and Wang Y and Wang Y: Lactones from Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort.
reduces atherosclerotic lesions in apoE-deficient mice via
inhibiting over expression of NF-kB-dependent adhesion molecules.
Fitoterapia. 95:240–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liang CJ, Lee CW, Sung HC, Chen YH, Wang
SH, Wu PJ, Chiang YC, Tsai JS, Wu CC, Li CY and Chen YL: Magnolol
reduced TNF-α-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression
in endothelial cells via JNK/p38 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Am J
Chin Med. 42:619–636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chen Z, Cai Y, Zhang W, Liu X and Liu S:
Astragaloside IV inhibits platelet-derived growth
factor-BB-stimulated proliferation and migration of vascular smooth
muscle cells via the inhibition of p38 MAPK signaling. Exp Ther
Med. 8:1253–1258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
50
|
Shen DZ, Xin SL, Chen C and Liu T: Effect
of atorvastatin on expression of TLR4 and NF-κB p65 in
atherosclerotic rabbits. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 6:493–496. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bao MH, Zhang YW and Zhou HH: Paeonol
suppresses oxidized low-density lipoprotein induced endothelial
cell apoptosis via activation of LOX-1/p38MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 146:543–551. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Liang CJ, Lee CW, Sung HC, Chen YH, Wang
SH, Wu PJ, Chiang YC, Tsai JS, Wu CC, Li CY and Chen YL: Magnolol
reduced TNF-α-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression
in endothelial cells via JNK/p38 and NF-κB signaling pathways. Am J
Chin Med. 42:619–637. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Park Haeng S, Sung YY, Nho Jin K and Kim
Kyoung H: Anti-atherosclerotic effects of Polygonum aviculare L.
ethanol extract in ApoE knock-out mice fed a Western diet mediated
via the MAPK pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 151:1109–1115. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chang YL, Chen CL, Kuo CL, Chen BC and You
JS: Glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits ICAM-1 expression via blocking JNK
and NF-kappaB pathways in TNF-alpha-activated endothelial cells.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:546–553. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|