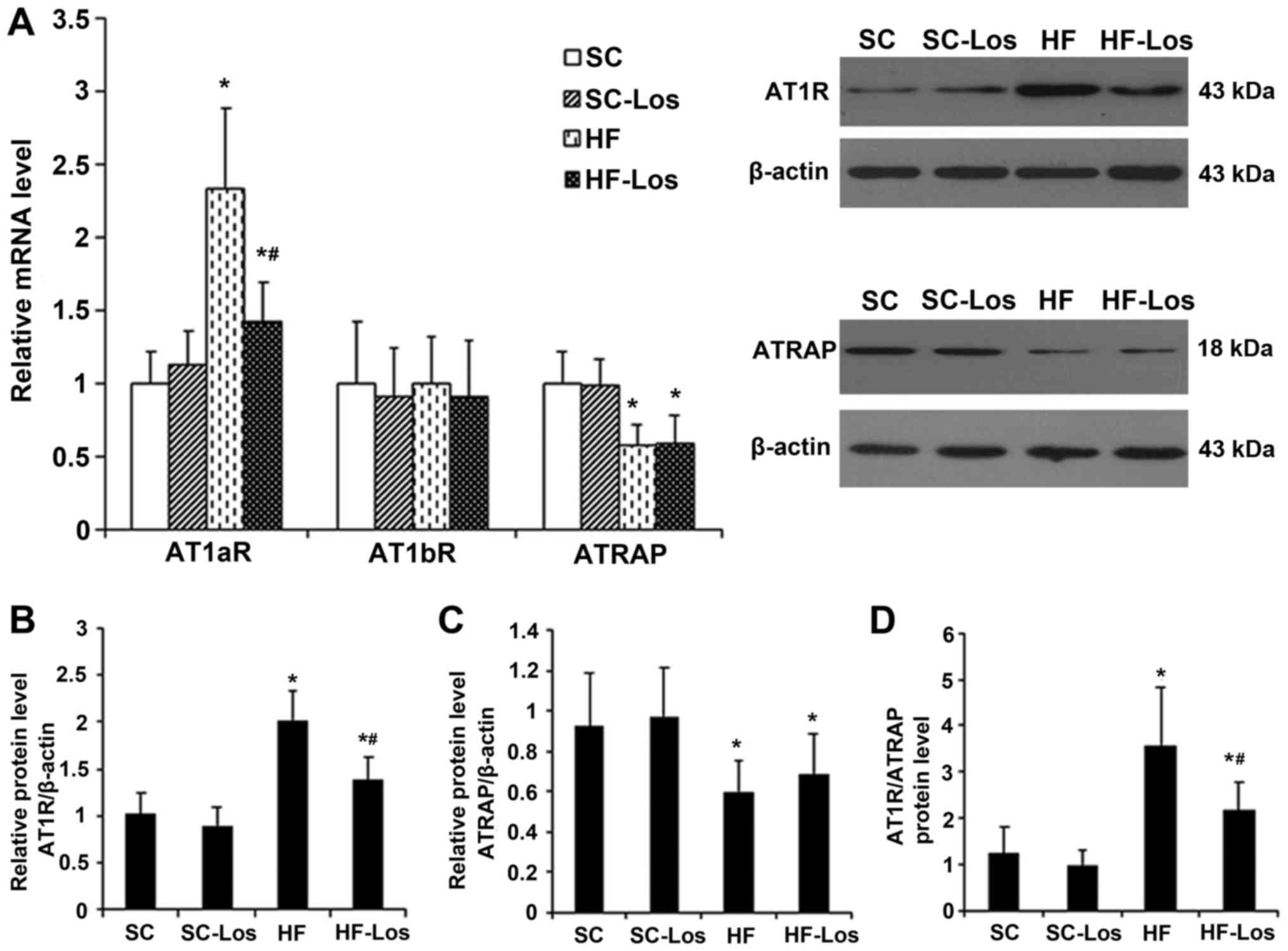
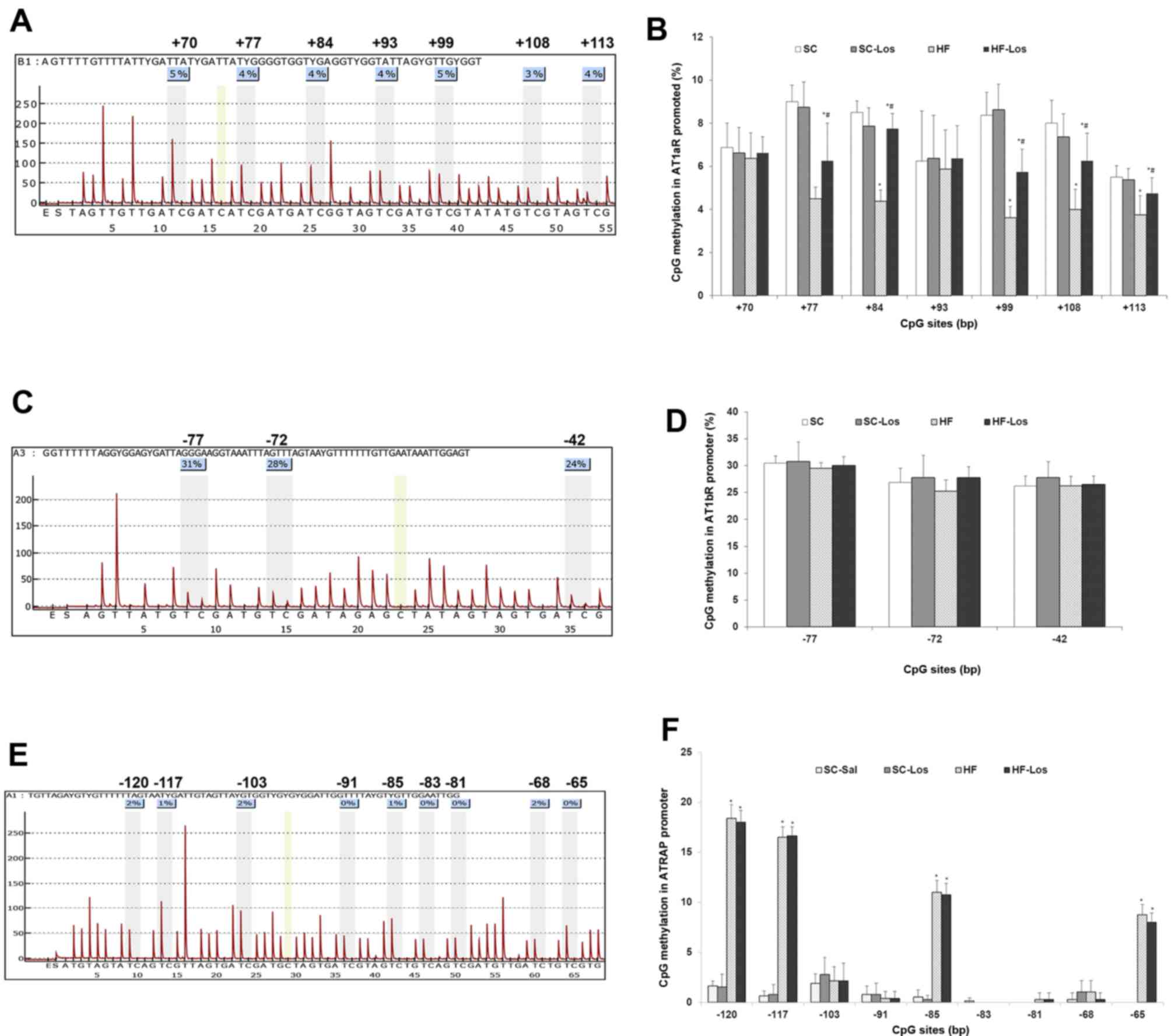
|
1
|
Galassi A, Reynolds K and He J: Metabolic
syndrome and risk of cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis. Am J
Med. 119:812–819. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Peng F, Lin J, Lin L and Tang H: Transient
prehypertensive treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats: A
comparison of losartan and amlodipine regarding long-term blood
pressure, cardiac and renal protection. Int J Mol Med.
30:1376–1386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Maury E and Brichard SM: Adipokine
dysregulation, adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic syndrome.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 314:1–16. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jing F, Mogi M and Horiuchi M: Role of
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in adipose tissue dysfunction.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 378:23–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lastra G and Sowers JR: Obesity and
cardiovascular disease: Role of adipose tissue, inflammation, and
the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Horm Mol Biol Clin
Investig. 15:49–57. 2013.
|
|
6
|
Bogdarina I, Welham S, King PJ, Burns SP
and Clark AJ: Epigenetic modification of the renin-angiotensin
system in the fetal programming of hypertension. Circ Res.
100:520–526. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Xiao D, Dasgupta C, Li Y, Huang X and
Zhang L: Perinatal nicotine exposure increases angiotensin II
receptor-mediated vascular contractility in adult offspring. PLoS
One. 9:e1081612014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Mao C, Liu R, Bo L, Chen N, Li S, Xia S,
Chen J, Li D, Zhang L and Xu Z: High-salt diets during pregnancy
affected fetal and offspring renal renin-angiotensin system. J
Endocrinol. 218:61–73. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Schübeler D: Function and information
content of DNA methylation. Nature. 517:321–326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jones PA: Functions of DNA methylation:
Islands, start sites, gene bodies and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
13:484–492. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Deaton AM and Bird A: CpG islands and the
regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25:1010–1022. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and
microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: Results of
the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Heart Outcomes Prevention
Evaluation Study Investigators. Lancet. 355:253–259. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Maeda A, Tamura K, Wakui H, Ohsawa M,
Azushima K, Uneda K, Kobayashi R, Tsurumi-Ikeya Y, Kanaoka T,
Dejima T, et al: Effects of Ang II receptor blocker irbesartan on
adipose tissue function in mice with metabolic disorders. Int J Med
Sci. 11:646–651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Fernandez-Twinn DS and Ozanne SE: Early
life nutrition and metabolic programming. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1212:78–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lindl T, Gross U, Ruhdel I, von Aulock S
and Völkel M: Guidance on determining indispensability and
balancing potential benefits of animal experiments with costs to
the animals with specific consideration of EU directive 2010/63/EU.
Altex. 29:219–228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ray MA, Johnston NA, Verhulst S, Trammell
RA and Toth LA: Identification of markers for imminent death in
mice used in longevity and aging research. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci.
49:282–288. 2010.
|
|
17
|
Widdop RE and Li XC: A simple versatile
method for measuring tail cuff systolic blood pressure in conscious
rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 93:191–194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xie LD, Chen DG, Zhang S, Wang HJ and Chen
HJ: Sympatholytic effect of captopril in regression of
cardiovascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive rats.
Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 15:123–128. 1994.
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xie LD, Lin PS, Xie H and Xu CS: Effects
of atorvastatin and losartan on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary
artery remodeling in rats. Clin Exp Hypertens. 32:547–554. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen HF, Xie LD and Xu CS: The signal
transduction pathways of heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation in
vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 333:49–56. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang TJ, Lin X, Lian GL, Zhong HB and Xie
LD: The effect of early losartan treatment on methylation of
angiotensin II type 1 receptor subtype b and angiotensin II type 1
receptor associated protein genes in the myocardium of
spontaneously hypertensive rats. Chin J Hypertens. 24:141–146.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee AM, Gurka MJ and DeBoer MD: Trends in
metabolic syndrome severity and lifestyle factors among
adolescents. Pediatrics. 137:e201531772016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Knight SF, Quigley JE, Yuan J, Roy SS,
Elmarakby A and Imig JD: Endothelial dysfunction and the
development of renal injury in spontaneously hypertensive rats fed
a high-fat diet. Hypertension. 51:352–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cao J, Inoue K, Sodhi K, Puri N, Peterson
SJ, Rezzani R and Abraham NG: High-fat diet exacerbates renal
dysfunction in SHR: Reversal by induction of HO-1-adiponectin axis.
Obesity (Silver Spring). 20:945–953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tontonoz P and Spiegelman BM: Fat and
beyond: The diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem.
77:289–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Singh KD and Karnik SS: Angiotensin
receptors: Structure, function, signaling and clinical
applications. J Cell Signal. 1:pii: 111. 2016.
|
|
28
|
Tamura K, Wakui H, Maeda A, Dejima T,
Ohsawa M, Azushima K, Kanaoka T, Haku S, Uneda K, Masuda S, et al:
The physiology and pathophysiology of a novel angiotensin
receptor-binding protein ATRAP/Agtrap. Curr Pharm Des.
19:3043–3048. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shigenaga A, Tamura K, Wakui H, Masuda S,
Azuma K, Tsurumi-Ikeya Y, Ozawa M, Mogi M, Matsuda M, Uchino K, et
al: Effect of olmesartan on tissue expression balance between
angiotensin II receptor and its inhibitory binding molecule.
Hypertension. 52:672–678. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Spalding KL, Arner E, Westermark PO,
Bernard S, Buchholz BA, Bergmann O, Blomqvist L, Hoffstedt J,
Naslund E, Britton T, et al: Dynamics of fat cell turnover in
humans. Nature. 453:783–787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Xiao D, Yang S and Zhang L: Promoter
methylation represses AT2R gene and increases brain
hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats. Neurobiol Dis. 60:32–38.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
McKinsey TA: Therapeutic potential for
HDAC inhibitors in the heart. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
52:303–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xiao D, Dasgupta C, Chen M, Zhang K,
Buchholz J, Xu Z and Zhang L: Inhibition of DNA methylation
reverses norepinephrine-induced cardiac hypertrophy in rats.
Cardiovasc Res. 101:373–382. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cho HM, Lee HA, Kim HY, Han HS and Kim IK:
Expression of Na+−K+ −2Cl−
cotransporter 1 is epigenetically regulated during postnatal
development of hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 24:1286–1293. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu Z, Siuda D, Xia N, Reifenberg G, Daiber
A, Münzel T, Förstermann U and Li H: Maternal treatment of
spontaneously hypertensive rats with pentaerythritol tetranitrate
reduces blood pressure in female offspring. Hypertension.
65:232–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|