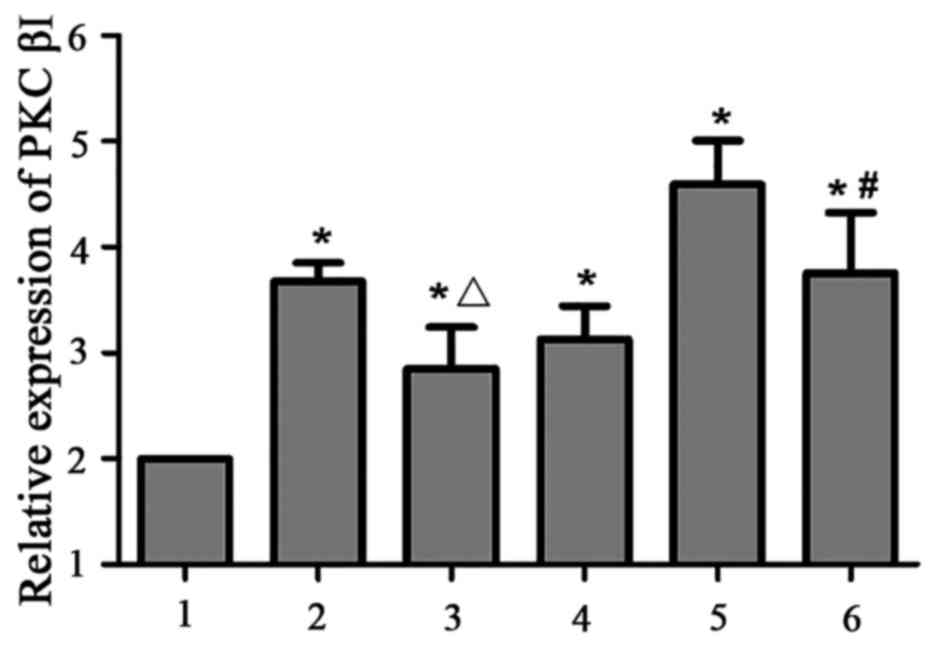
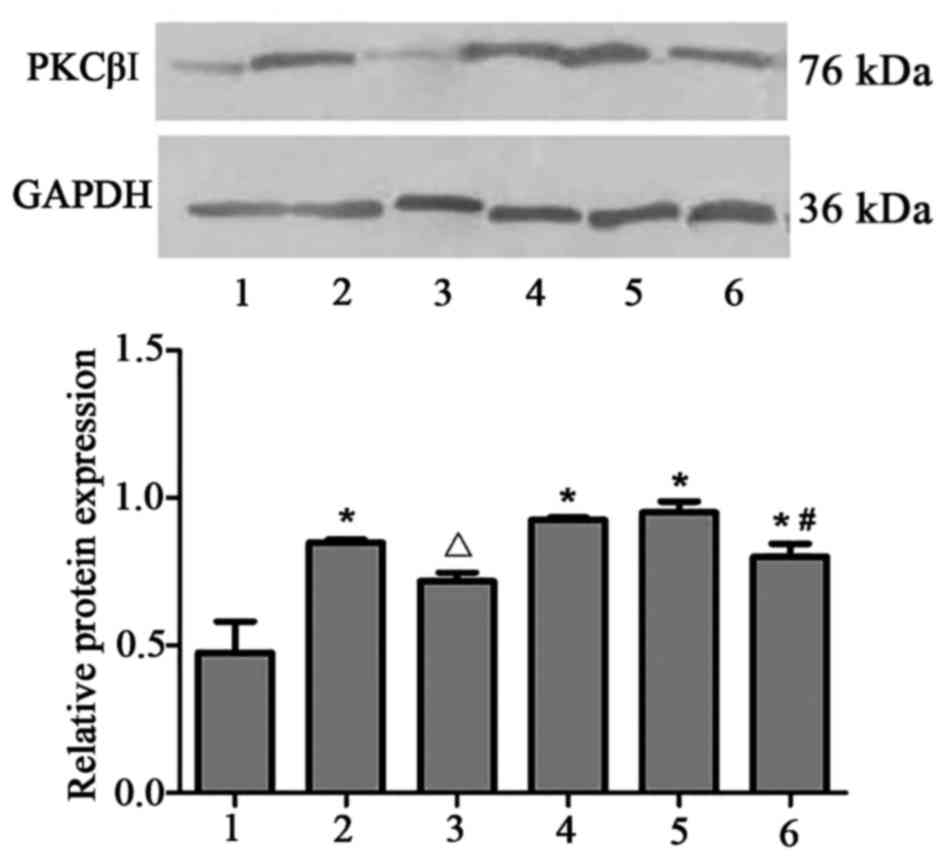
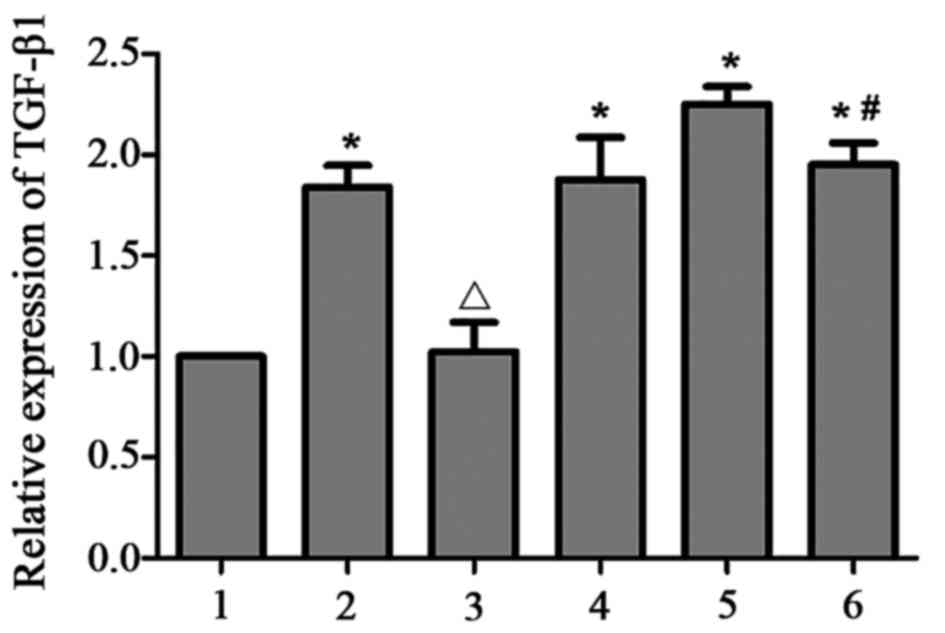
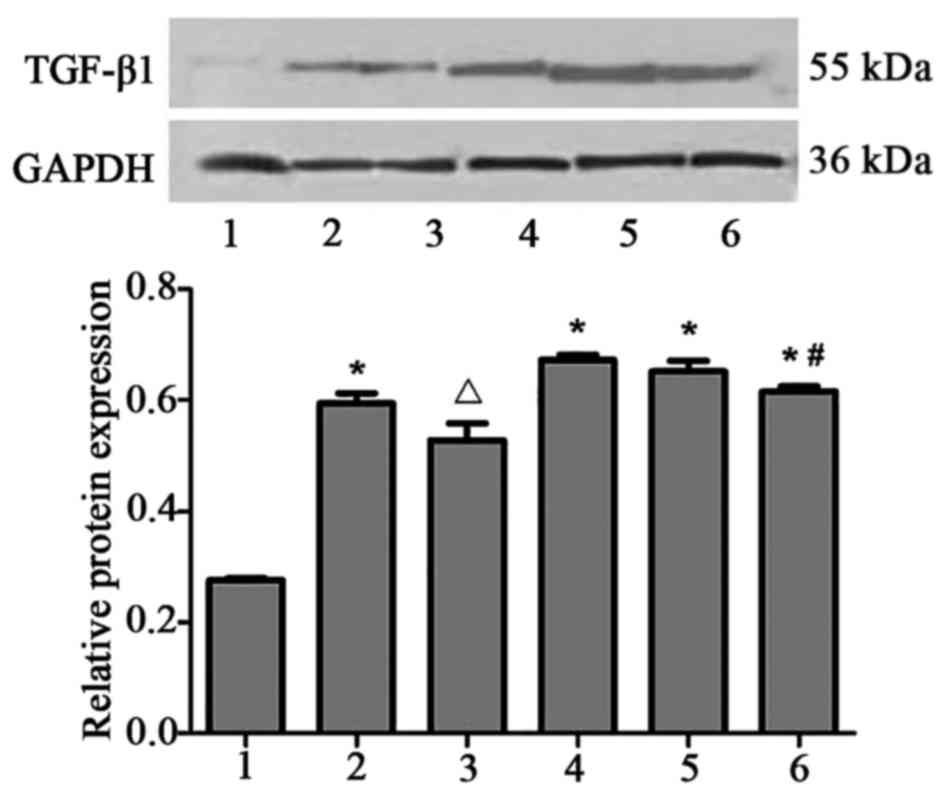
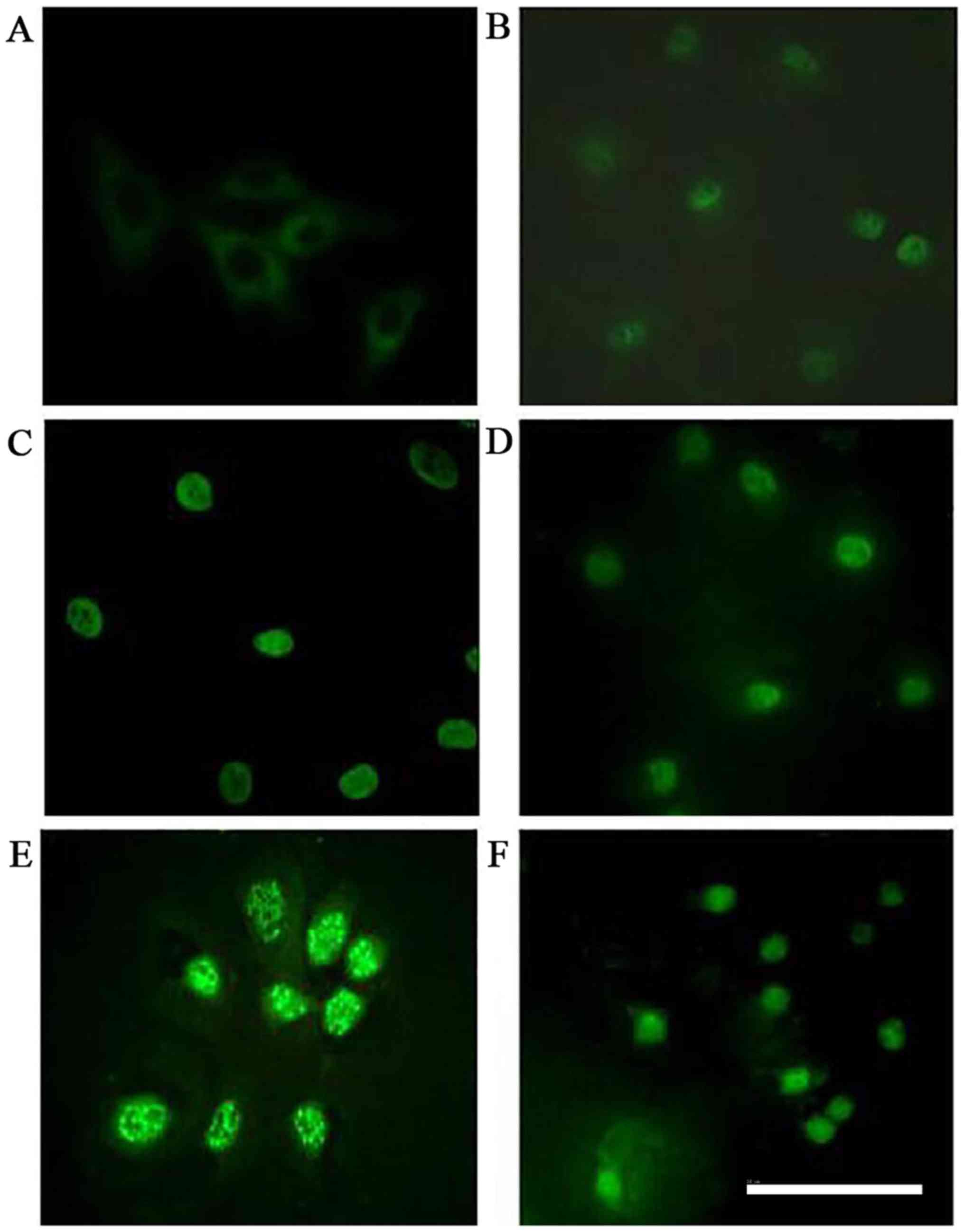
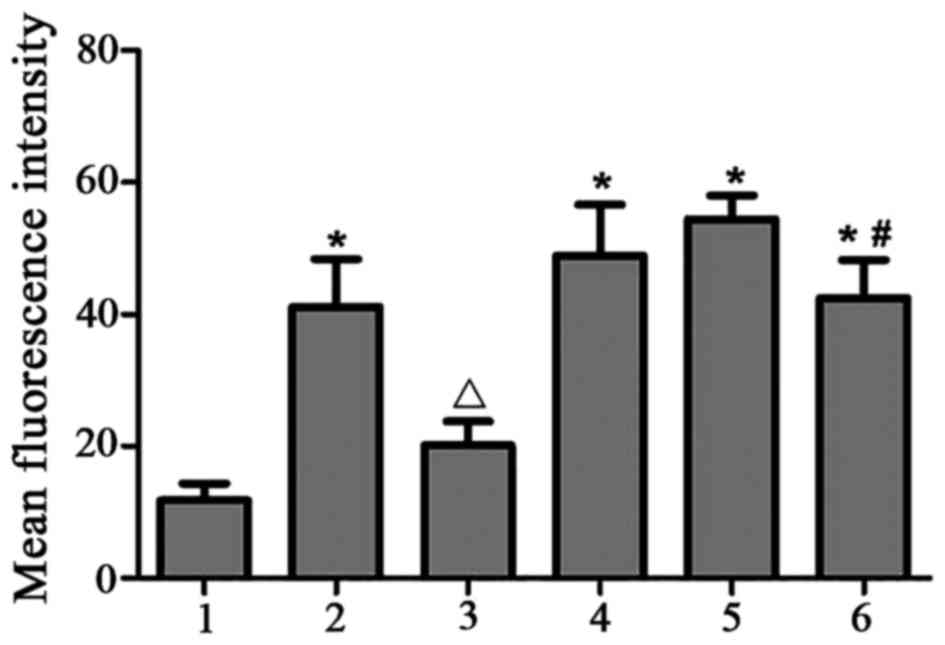
|
1
|
Schernthaner G, Mogensen CE and
Schernthaner GH: The effects of GLP-1 analogues, DPP-4 inhibitors
and SGLT2 inhibitors on the renal system. Diab Vasc Dis Res.
11:306–323. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang MH, Feng L, Zhu MM, Gu JF, Jiang J,
Cheng XD, Ding SM, Wu C and Jia XB: The anti-inflammation effect of
Moutan Cortex on advanced glycation end products-induced rat
mesangial cells dysfunction and High-glucose-fat diet and
streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
151:591–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xie S, Lu K, Zhang Y, Song X, Tan M and
Wang C: Effects of Jiangya Xiaoke prescription on TGF-beta1 in
diabetic nephropathy rats with hypertension and its mechanisms. Int
J Clin Exp Med. 8:5129–5136. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou SX, Lei MX and Zhao JJ: The study of
the effects of platelet activating factor (PAF) on the relation
between the endothelial cell and mesangial cells exposed to high
glucose and high lysophosphatidylcholine. Chin J Diabetes.
18:591–593. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Al-Khodor S and Abu KY: Triggering Ras
signalling by intracellular Francisella tularensis through
recruitment of PKCalpha and betaI to the SOS2/GrB2 complex is
essential for bacterial proliferation in the cytosol. Cell
Microbiol. 12:1604–1621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Noh H and King GL: The role of protein
kinase C activation in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl.
S49–S53. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bryant DM, Roignot J, Datta A, Overeem AW,
Kim M, Yu W, Peng X, Eastburn DJ, Ewal AJ, Werb Z and Mostov KE: A
molecular switch for the orientation of epithelial cell
polarization. Dev Cell. 31:171–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meier M, Park JK, Overheu D, Kirsch T,
Lindschau C, Gueler F, Leitges M, Menne J and Haller H: Deletion of
protein kinase C-beta isoform in vivo reduces renal hypertrophy but
not albuminuria in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse model.
Diabetes. 56:346–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Idris I and Donnelly R: Protein kinase C
beta inhibition: A novel therapeutic strategy for diabetic
microangiopathy. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 3:172–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Muñoz-Felix JM, Oujo B and Lopez-Novoa JM:
The role of endoglin in kidney fibrosis. Expert Rev Mol Med.
16:e182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang T, Chen SS, Chen R, Yu DM and Yu P:
Reduced beta 2 glycoprotein I improves diabetic nephropathy via
inhibiting TGF-β1-p38 MAPK pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:2321–2333. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hathaway CK, Gasim AM, Grant R, Chang AS,
Kim HS, Madden VJ, Bagnell CR Jr, Jennette JC, Smithies O and
Kakoki M: Low TGFβ1 expression prevents and high expression
exacerbates diabetic nephropathy in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:pp. 5815–5820. 2015; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gao P, Li L, Ji L, Wei Y, Li H, Shang G,
Zhao Z, Chen Q, Jiang T and Zhang N: Nrf2 ameliorates diabetic
nephropathy progression by transcriptional repression of TGFβ1
through interactions with c-Jun and SP1. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1839:1110–1120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duan JG, Chen XY, Wang L, Lau A, Wong A,
Thomas GN, Tomlinson B, Liu R, Chan JC, Leung TW, et al: Sex
differences in epidemiology and risk factors of acute coronary
syndrome in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A long-term
prospective cohort study. PLoS One. 10:e1220312015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bakris GL, Pitt B, Weir MR, Freeman MW,
Mayo MR, Garza D, Stasiv Y, Zawadzki R, Berman L and Bushinsky DA:
AMETHYST-DN Investigators: Effect of patiromer on serum potassium
level in patients with hyperkalemia and diabetic kidney disease:
The AMETHYST-DN randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 314:151–161. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Panduru NM, Saraheimo M, Forsblom C, Thorn
LM, Gordin D, Wadén J, Tolonen N, Bierhaus A, Humpert PM and Groop
PH; FinnDiane Study Group, : Urinary adiponectin is an independent
predictor of progression to end-stage renal disease in patients
with type 1 diabetes and diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Care.
38:883–890. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Nicola L, Provenzano M, Chiodini P,
Borrelli S, Garofalo C, Pacilio M, Liberti ME, Sagliocca A, Conte G
and Minutolo R: Independent role of underlying kidney disease on
renal prognosis of patients with chronic kidney disease under
nephrology care. PLoS One. 10:e1270712015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu X, Yang G, Fan Q and Wang L: Proteomic
profile in glomeruli of type-2 diabetic KKAy mice using
2-dimensional differential gel electrophoresis. Med Sci Monit.
20:2705–2713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abe H: Recent progress in understanding
the molecular pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Rinsho Byori.
59:179–186. 2011.(In Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rossert J, Terraz-Durasnel C and Brideau
G: Growth factors, cytokines, and renal fibrosis duringthe course
of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Metab. 26 Suppl 4:S16–S24.
2000.
|
|
22
|
Zhou L: Research progress in impact of
high glucose and hyperlipidemia on glomerular cells. New Med.
286–289. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Li L, Yin Q, Tang X, Bai L, Zhang J, Gou
S, Zhu H, Cheng J, Fu P and Liu F: C3a receptor antagonist
ameliorates inflammatory and fibrotic signals in type 2 diabetic
nephropathy by suppressing the activation of TGF-β/smad3 and IKBα
pathway. PLoS One. 9:e1136392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li HG, Cai YJ and Zou JH: The effects of
high-gucrose and high-fat diet on tubulointerstitial fibrosis in
New Zanland white rabbits. Chinese J Zoology. 145–150. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Yoshikawa M, Matsumoto K, Iida M, Akasawa
A, Moriyama H and Saito H: Effect of extracellular matrix proteins
on platelet-activating factor-induced eosinophil chemotaxis. Int
Arch Allergy Immunol. 128 Suppl 1:S3–S11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yao LJ, Wang JQ, Zhao H, Liu JS and Deng
AG: Effect of telmisartan on expression of protein kinase C-alpha
in kidneys of diabetic mice. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:829–838. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wogensen L, Krag S, Chai Q and Ledet T:
The use of transgenic animals in the study of diabetic kidney
disease. Horm Metab Res. 37 Suppl 1:S17–S25. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mishra S and Vinayak M: Ellagic acid
checks lymphoma promotion via regulation of PKC signaling pathway.
Mol Biol Rep. 40:1417–1428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
do Carmo A, Balça-Silva J, Matias D and
Lopes MC: PKC signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
14:287–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Manabe E, Handa O, Naito Y, Mizushima K,
Akagiri S, Adachi S, Takagi T, Kokura S, Maoka T and Yoshikawa T:
Astaxanthin protects mesangial cells from hyperglycemia-induced
oxidative signaling. J Cell Biochem. 103:1925–1937. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ochi S, Harigai M, Mizoguchi F, Iwai H,
Hagiyama H, Oka T and Miyasaka N: Leflunomide-related acute
interstitial pneumonia in two patients with rheumatoid arthritis:
Autopsy findings with a mosaic pattern of acute and organizing
diffuse alveolar damage. Mod Rheumatol. 16:316–320. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schwartz SG, Flynn HW Jr and Aiello LP:
Ruboxistaurin mesilate hydrate for diabetic retinopathy. Drugs
Today (Barc). 45:269–274. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang F, Huang D, Zhu W, Li S, Yan M, Wei M
and Li J: Selective inhibition of PKCbeta2 preserves cardiac
function after myocardial infarction and is associated with
improved angiogenesis of ischemic myocardium in diabetic rats. Int
J Mol Med. 32:1037–1046. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kelly DJ, Zhang Y, Hepper C, Gow RM,
Jaworski K, Kemp BE, Wilkinson-Berka JL and Gilbert RE: Protein
kinase C beta inhibition attenuates the progression of experimental
diabetic nephropathy in the presence of continued hypertension.
Diabetes. 52:512–518. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koya D, Haneda M, Nakagawa H, Isshiki K,
Sato H, Maeda S, Sugimoto T, Yasuda H, Kashiwagi A, Ways DK, et al:
Amelioration of accelerated diabetic mesangial expansion by
treatment with a PKC beta inhibitor in diabetic db/db mice, a
rodent model for type 2 diabetes. FASEB J. 14:439–447.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hinz B: The extracellular matrix and
transforming growth factor-β1: Tale of a strained relationship.
Matrix Biol. 47:54–65. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kajdaniuk D, Marek B, Borgiel-Marek H and
Kos-Kudła B: Transforming growth factor β1 (TGFβ1) in physiology
and pathology. Endokrynol Pol. 64:384–396. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang W, Xu C, Kahng KW, Noble NA, Border
WA and Huang Y: Aldosterone and TGF-beta1 synergistically increase
PAI-1 and decrease matrix degradation in rat renal mesangial and
fibroblast cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 294:F1287–F1295.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sam R, Wanna L, Gudehithlu KP, Garber SL,
Dunea G, Arruda JA and Singh AK: Glomerular epithelial cells
transform to myofibroblasts: Early but not late removal of
TGF-beta1 reverses transformation. Transl Res. 148:142–148. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Alvarez ML and DiStefano JK: Functional
characterization of the plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 gene
(PVT1) in diabetic nephropathy. PLoS One. 6:e186712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Koga K, Yokoi H, Mori K, Kasahara M,
Kuwabara T, Imamaki H, Ishii A, Mori KP, Kato Y, Ohno S, et al:
MicroRNA-26a inhibits TGF-β-induced extracellular matrix protein
expression in podocytes by targeting CTGF and is downregulated in
diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 58:2169–2180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Alvarez ML, Khosroheidari M, Eddy E and
Kiefer J: Role of microRNA 1207-5P and its host gene, the long
non-coding RNA Pvt1, as mediators of extracellular matrix
accumulation in the kidney: Implications for diabetic nephropathy.
PLoS One. 8:e774682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hwang M, Kim HJ, Noh HJ, Chang YC, Chae
YM, Kim KH, Jeon JP, Lee TS, Oh HK, Lee YS and Park KK: TGF-beta1
siRNA suppresses the tubulointerstitial fibrosis in the kidney of
ureteral obstruction. Exp Mol Pathol. 81:48–54. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|