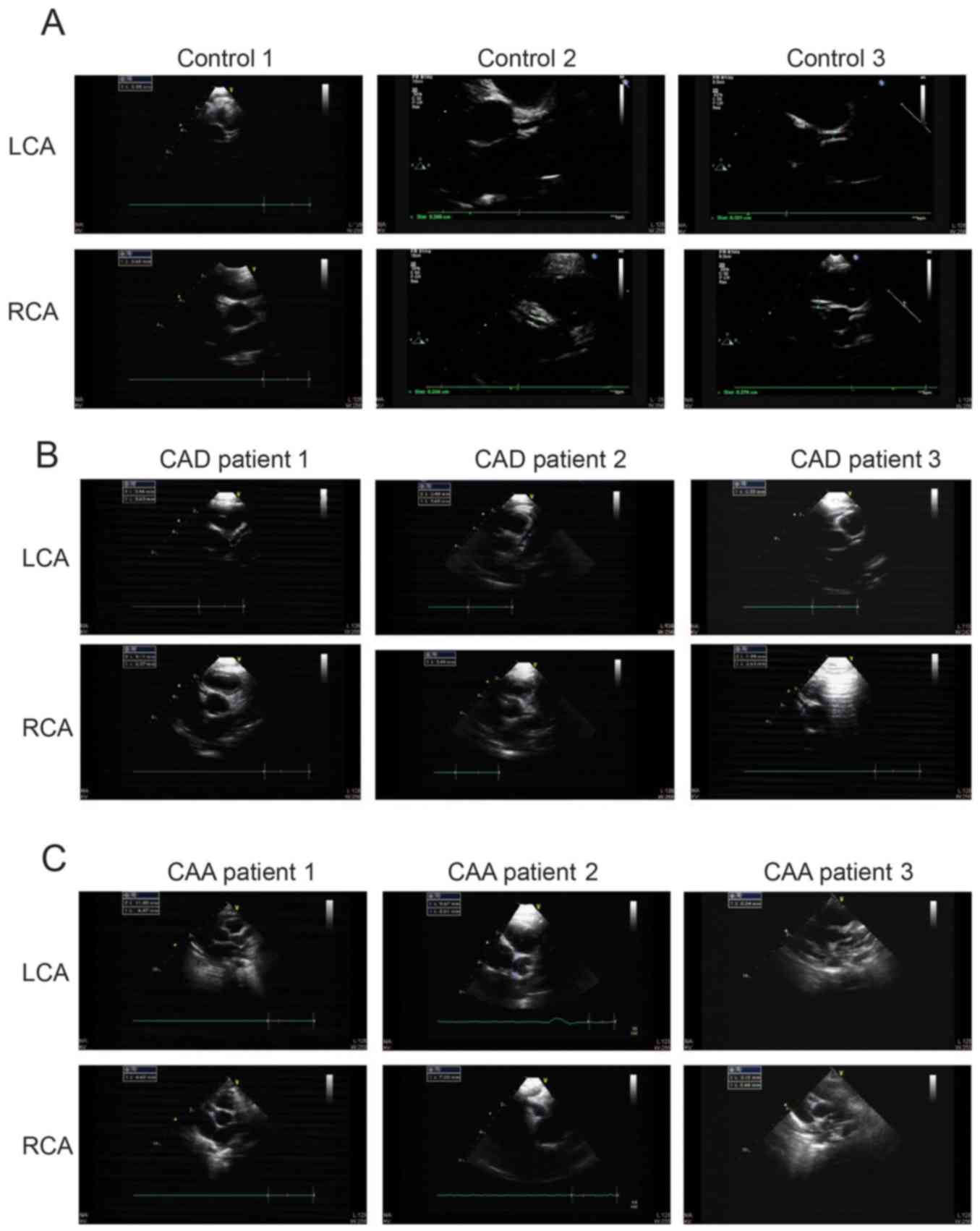
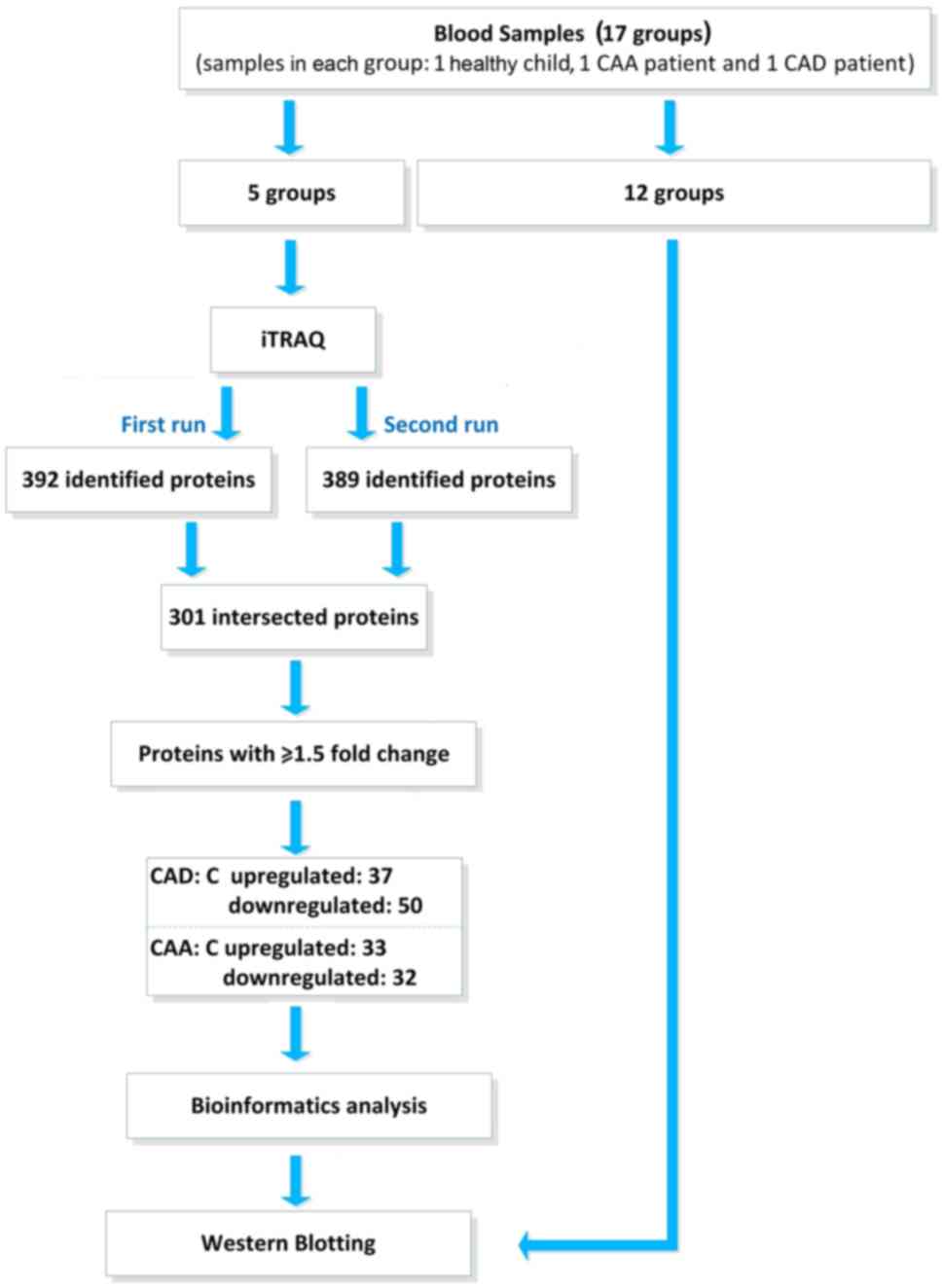
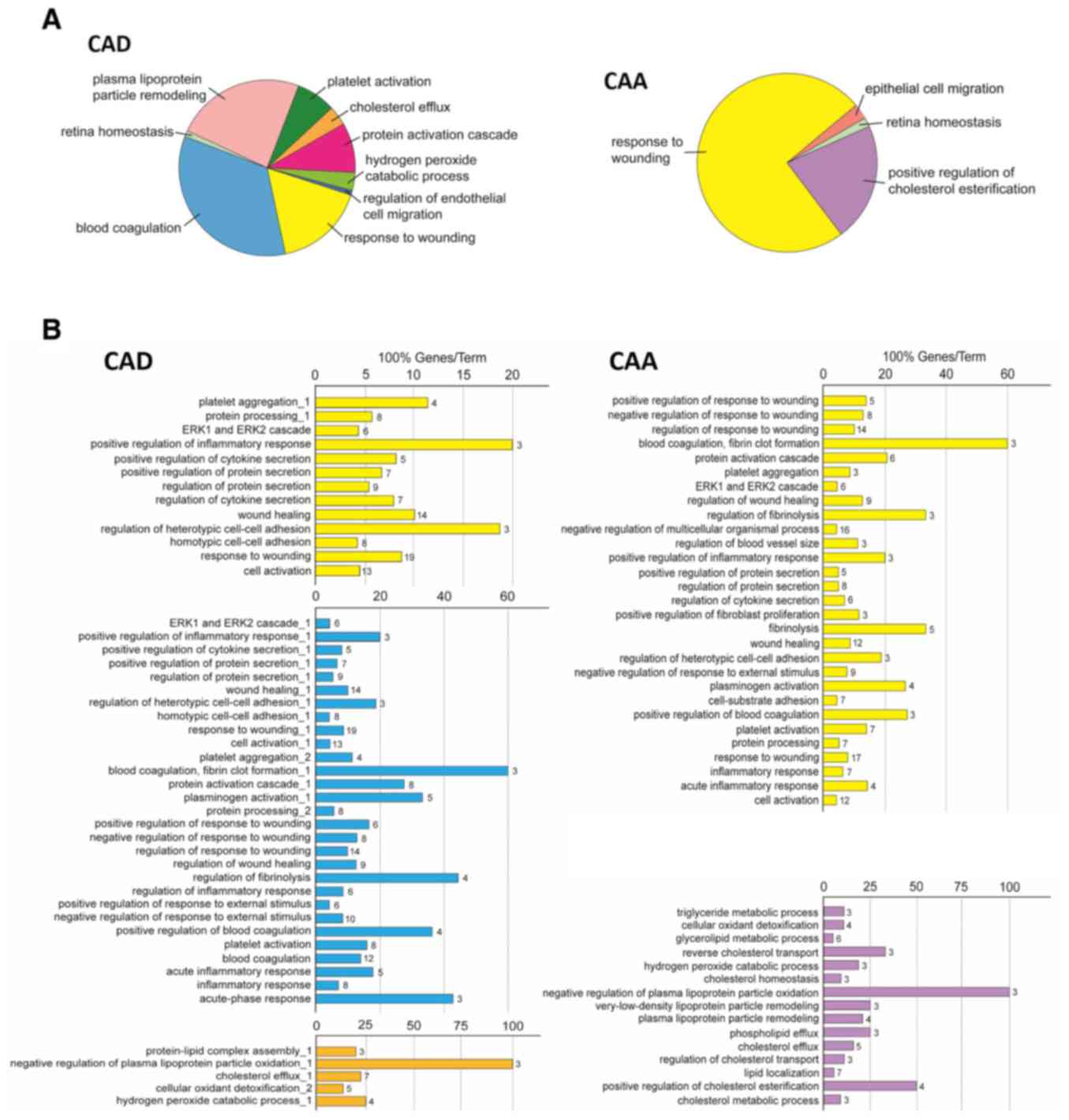
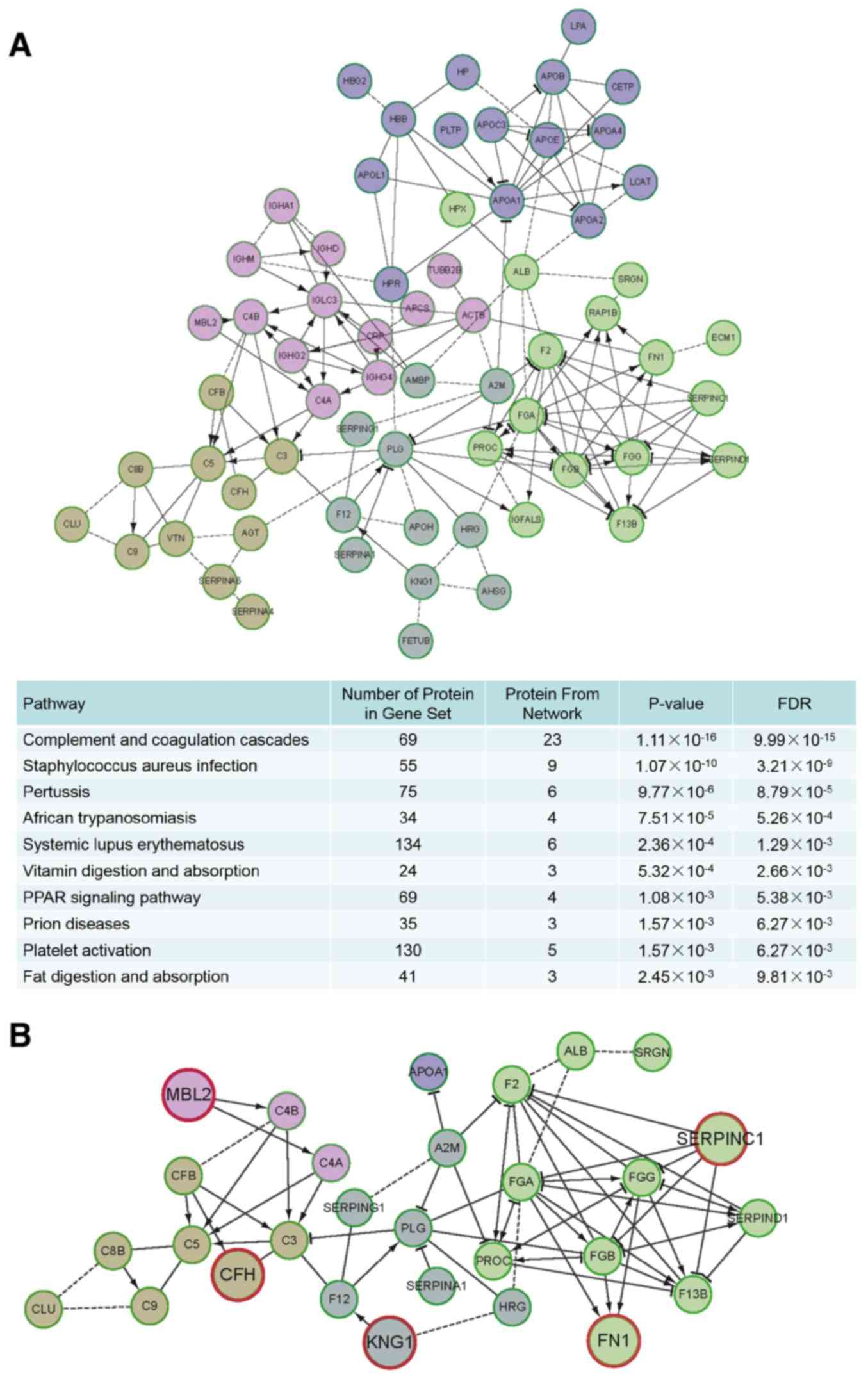
|
1
|
Kawasaki T: Acute febrile mucocutaneous
syndrome with lymphoid involvement with specific desquamation of
the fingers and toes in children. Allergy. 16:178–222. 1967.(In
Japanese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen KY, Curtis N, Dahdah N, Kowalski R,
Cheung M and Burgner DP: Kawasaki disease and cardiovascular risk:
A comprehensive review of subclinical vascular changes in the
longer term. Acta Paediatric. 105:752–761. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kato H, Koike S, Yamamoto M, Ito Y and
Yano E: Coronary aneurysms in infants and young children with acute
febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. J Pediatr. 86:892–898.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uehara R and Belay ED: Epidemiology of
Kawasaki disease in Asia, Europe, and the United States. J
Epidemiol. 22:79–85. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Singh S, Vignesh P and Burgner D: The
epidemiology of Kawasaki disease: A global update. Arch Dis Child.
100:1084–1088. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Gerber MA,
Gewitz MH, Tani LY, Burns JC, Shulman ST, Bolger AF, Ferrieri P,
Baltimore RS, et al: Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management
of Kawasaki disease: A statement for health professionals from the
committee on rheumatic fever, endocarditis and Kawasaki disease,
council on cardiovascular disease in the young, American heart
association. Circulation. 110:2747–2771. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mueller F, Knirsch W, Harpes P, Pretre R,
Valsangiacomo Buechel E and Kretschmar O: Long-term follow-up of
acute changes in coronary artery diameter caused by Kawasaki
disease: Risk factors for development of stenotic lesions. Clin Res
Cardiol. 98:501–507. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aebersold R and Mann M: Mass
spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature. 422:198–207. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Celis JE, Gromov P, Cabezón T, Moreira JM,
Ambartsumian N, Sandelin K, Rank F and Gromova I: Proteomic
characterization of the interstitial fluid perfusing the breast
tumor microenvironment: A novel resource for biomarker and
therapeutic target discovery. Mol Cell Proteomics. 3:327–344. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ray S, Reddy PJ, Jain R, Gollapalli K,
Moiyadi A and Srivastava S: Proteomic technologies for the
identification of disease biomarkers in serum: Advances and
challenges ahead. Proteomics. 11:2139–2161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ayusawa M, Sonobe T, Uemura S, Ogawa S,
Nakamura Y, Kiyosawa N, Ishii M and Harada K; Kawasaki Disease
Research Committee, : Revision of diagnostic guidelines for
Kawasaki disease (the 5th revised edition). Pediatr Int.
47:232–234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu G, Dawson E, Duong A, Haw R and Stein
L: ReactomeFIViz: A Cytoscape app for pathway and network-based
data analysis. F1000Res. 3:1462014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Komatsu H and Fujisawa T: Kawasaki disease
and infection. Nihon Rinsho. 66:278–282. 2008.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee KY, Lee HS, Hong JH, Han JW, Lee JS
and Whang KT: High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin downregulates
the activated levels of inflammatory indices except erythrocyte
sedimentation rate in acute stage of Kawasaki Disease. J Trop
Pediatr. 51:98–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Adler AC and Kodavatiganti R: Kawasaki
disease and giant coronary artery aneurysms: The role of
echocardiography from diagnosis through follow-up.
Echocardiography. 33:1245–1250. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Greco A, De Virgilio A, Rizzo MI,
Tombolini M, Gallo A, Fusconi M, Ruoppolo G, Pagliuca G,
Martellucci S and de Vincentiis M: Kawasaki disease: An evolving
paradigm. Autoimmun Rev. 14:703–709. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burns JC, Herzog L, Fabri O, Tremoulet AH,
Rodó X, Uehara R, Burgner D, Bainto E, Pierce D, Tyree M, et al:
Seasonality of Kawasaki disease: A globalperspective. PLoS One.
8:e745292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watanabe T: Kidney and urinary tract
involvement in Kawasaki disease. Int J Pediatr. 2013:8318342013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blankier S, McCrindle BW, Ito S and Yeung
RS: The role of atorvastatin in regulating the immune response
leading to vascular damage in a model of Kawasaki disease. Clin Exp
Immunol. 164:193–201. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoon KL: Update of genetic susceptibility
in patients with Kawasaki disease. Korean J Pediatr. 58:84–88.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perkins SJ, Fung KW and Khan S: Molecular
interactions between complement factor H and its heparin and
heparan sulfate ligands. Front Immunol. 5:1262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Biezeveld MH, Geissler J, Weverling GJ,
Kuipers IM, Lam J, Ottenkamp J and Kuijpers TW: Polymorphisms in
the mannose-binding lectin gene as determinants of age-defined risk
of coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. Arthritis Rheum.
54:369–376. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brunel H, Massanet R, Martinez-Perez A,
Ziyatdinov A, Martin-Fernandez L, Souto JC, Perera A and Soria JM:
The central role of KNG1 gene as a genetic determinant of
coagulation pathway-related traits: Exploring metaphenotypes. PLoS
One. 11:e01671872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weng LC, Cushman M, Pankow JS, Basu S,
Boerwinkle E, Folsom AR and Tang W: A genetic association study of
activated partial thromboplastin time in European Americans and
African Americans: The ARIC study. Hum Mol Genet. 24:2401–2408.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang W, Schwienbacher C, Lopez LM,
Ben-Shlomo Y, Oudot-Mellakh T, Johnson AD, Samani NJ, Basu S,
Gögele M, Davies G, et al: Genetic associations for activated
partial thromboplastin time and prothrombin time, their gene
expression profiles, and risk of coronary artery disease. Am J Hum
Genet. 91:152–162. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iba T and Thachil J: Is antithrombin III
for sepsis-associated disseminated intravascular coagulation really
ineffective? Intensive Care Med. 42:1193–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Simioni P, Tormene D, Spiezia L, Tognin G,
Rossetto V, Radu C and Prandoni P: Inherited thrombophilia and
venous thromboembolism. Semin Thromb Hemost. 32:700–708. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cooper PC, Coath F, Daly ME and Makris M:
The phenotypic and genetic assessment of antithrombin deficiency.
Int J Lab Hematol. 33:227–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ohtsubo H, Okada T, Nozu K, Takaoka Y,
Shono A, Asanuma K, Zhang L, Nakanishi K, Taniguchi-Ikeda M, Kaito
H, et al: Identification of mutations in FN1 leading to
glomerulopathy with fibronectin deposits. Pediatr Nephrol.
31:1459–1467. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|