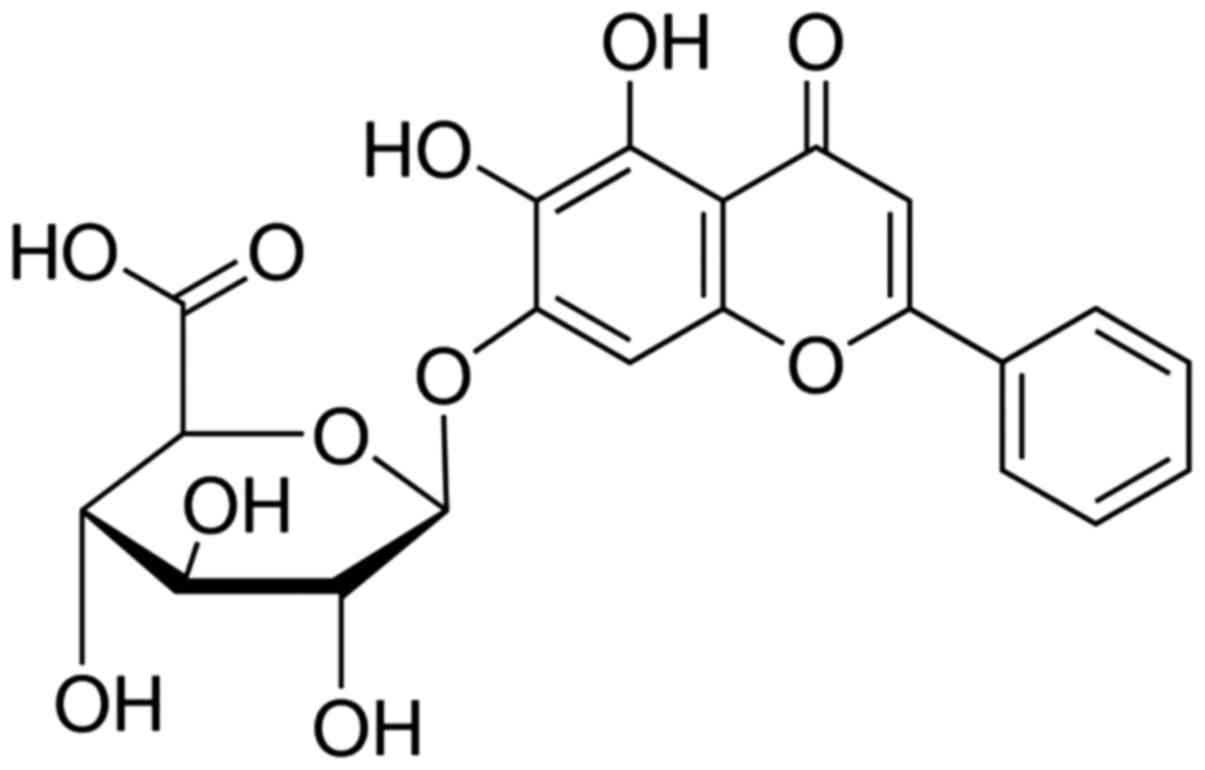
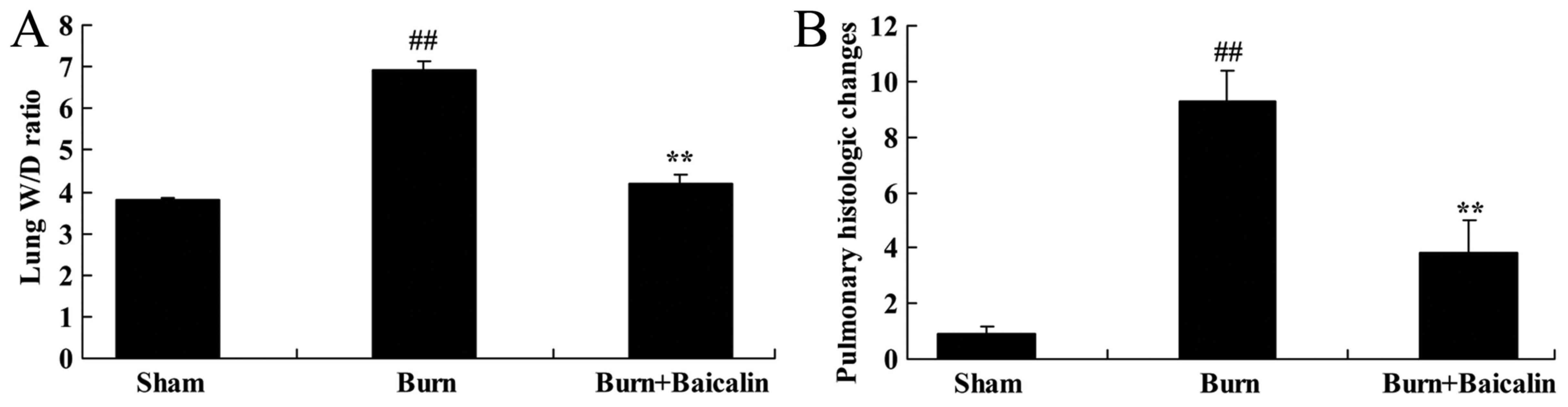
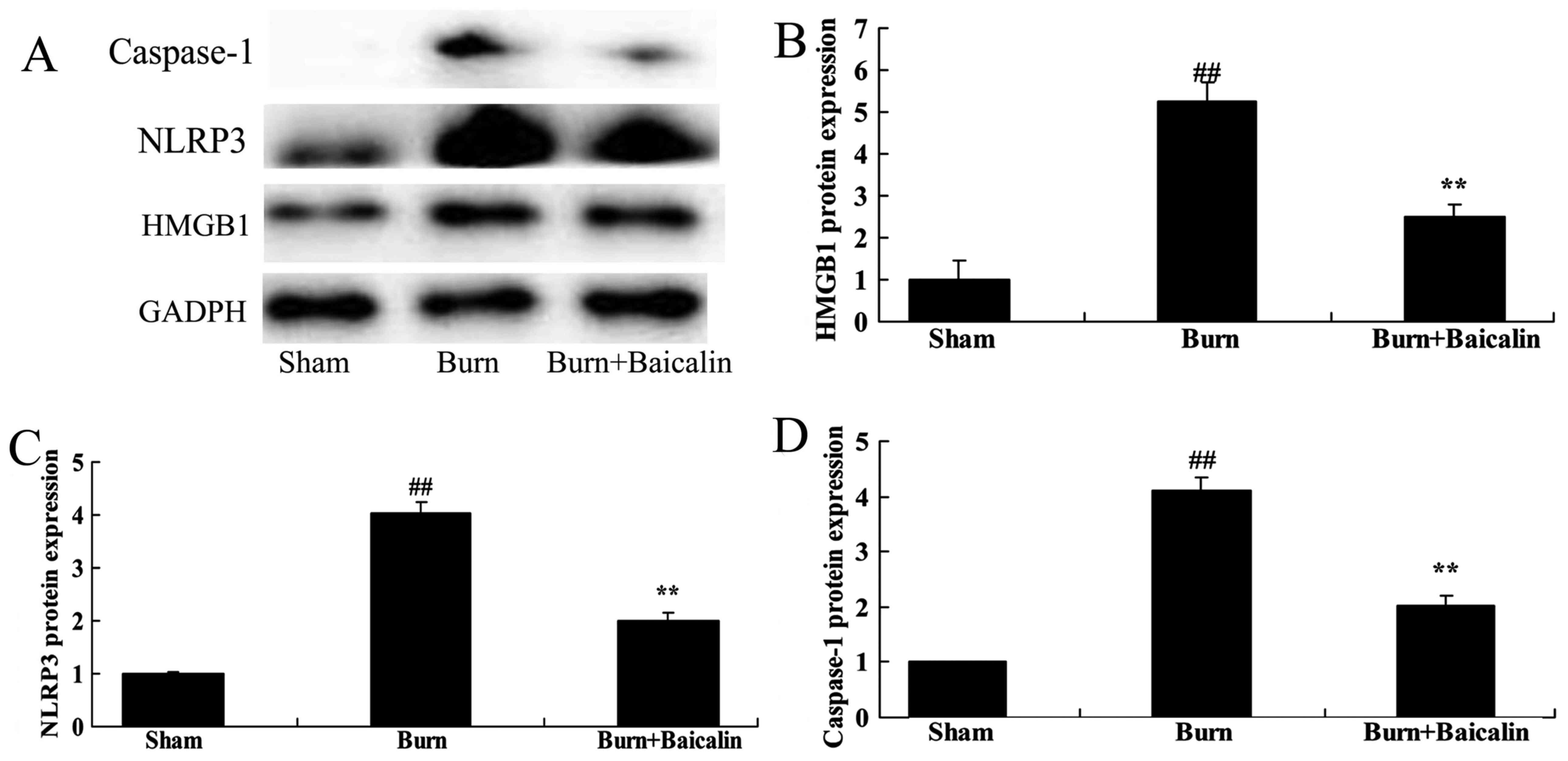
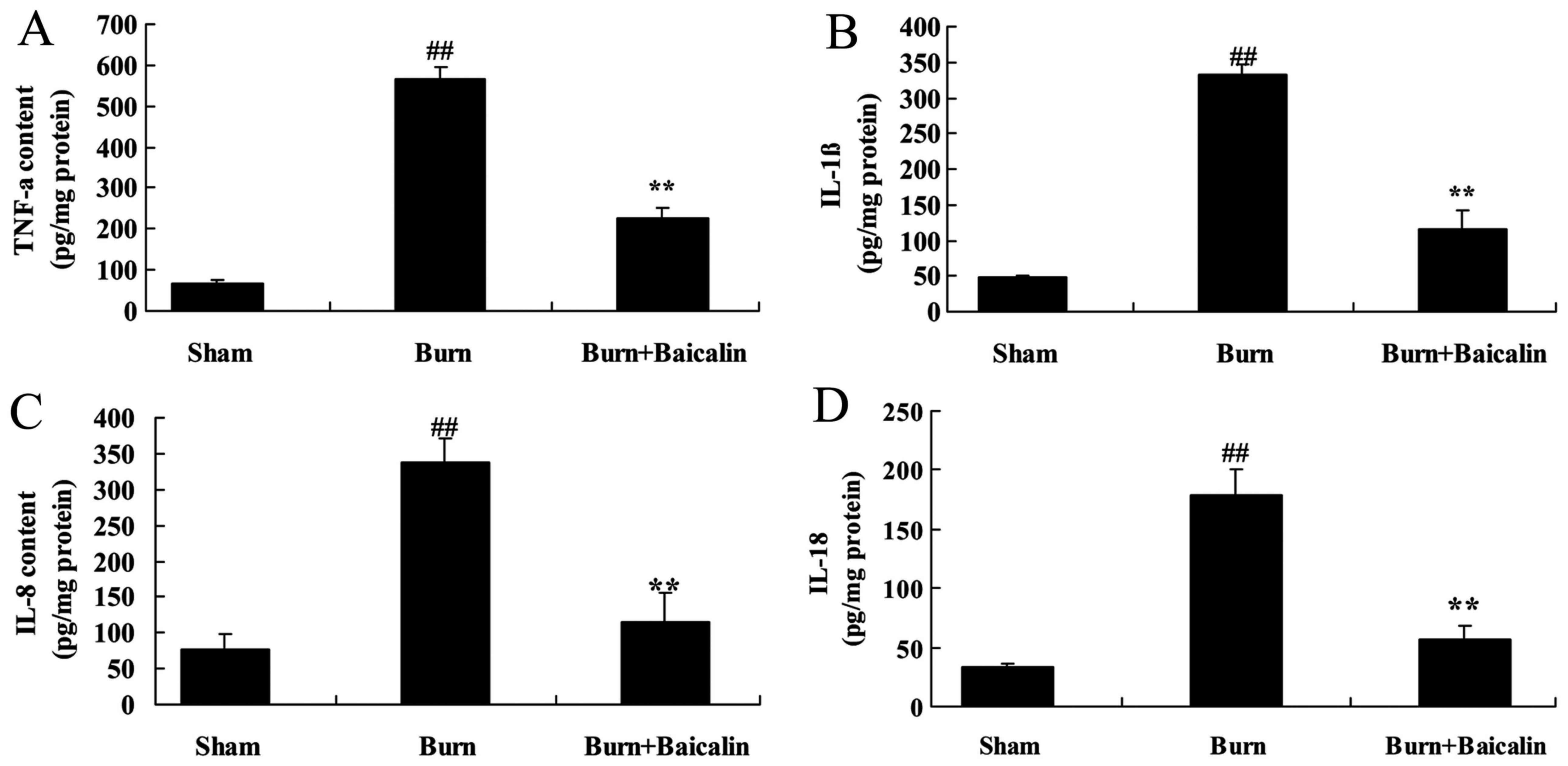
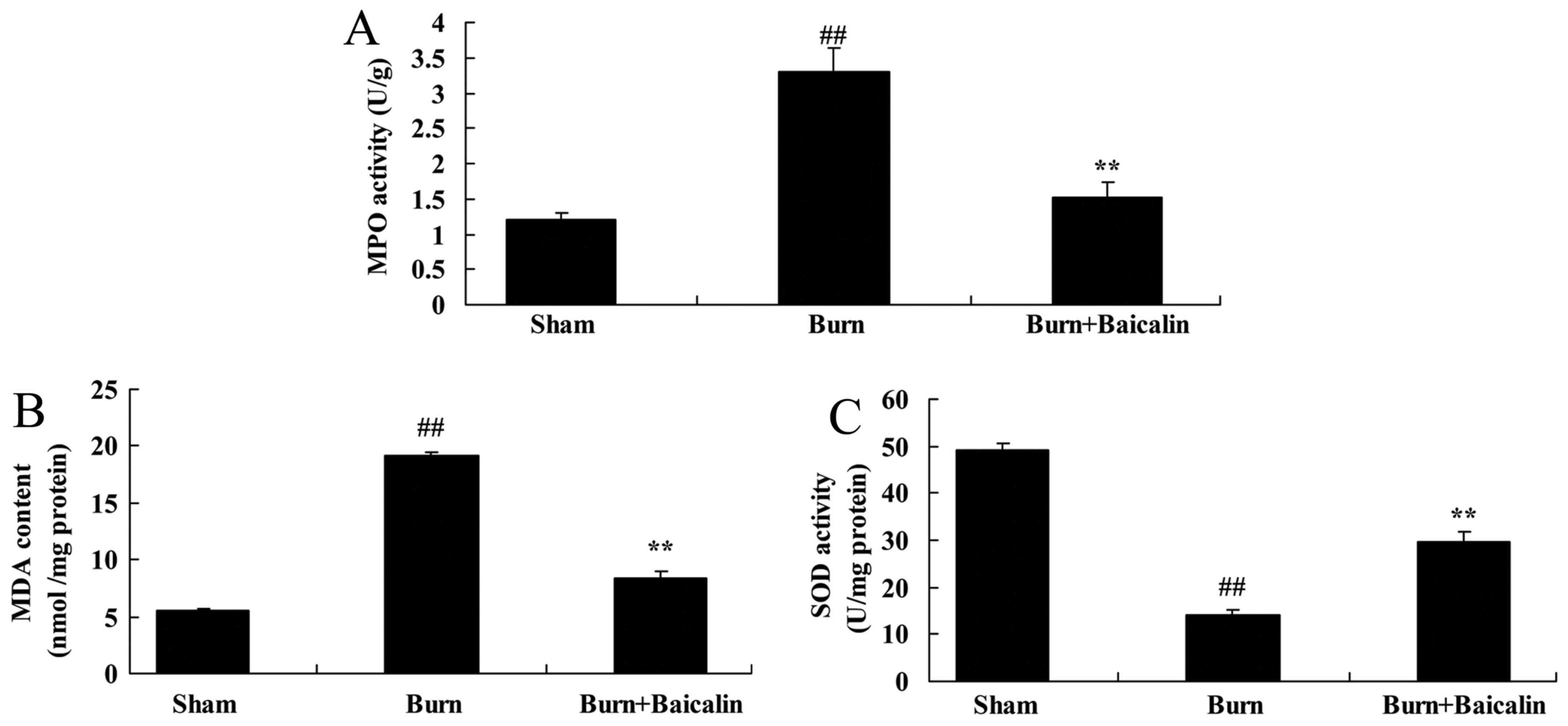
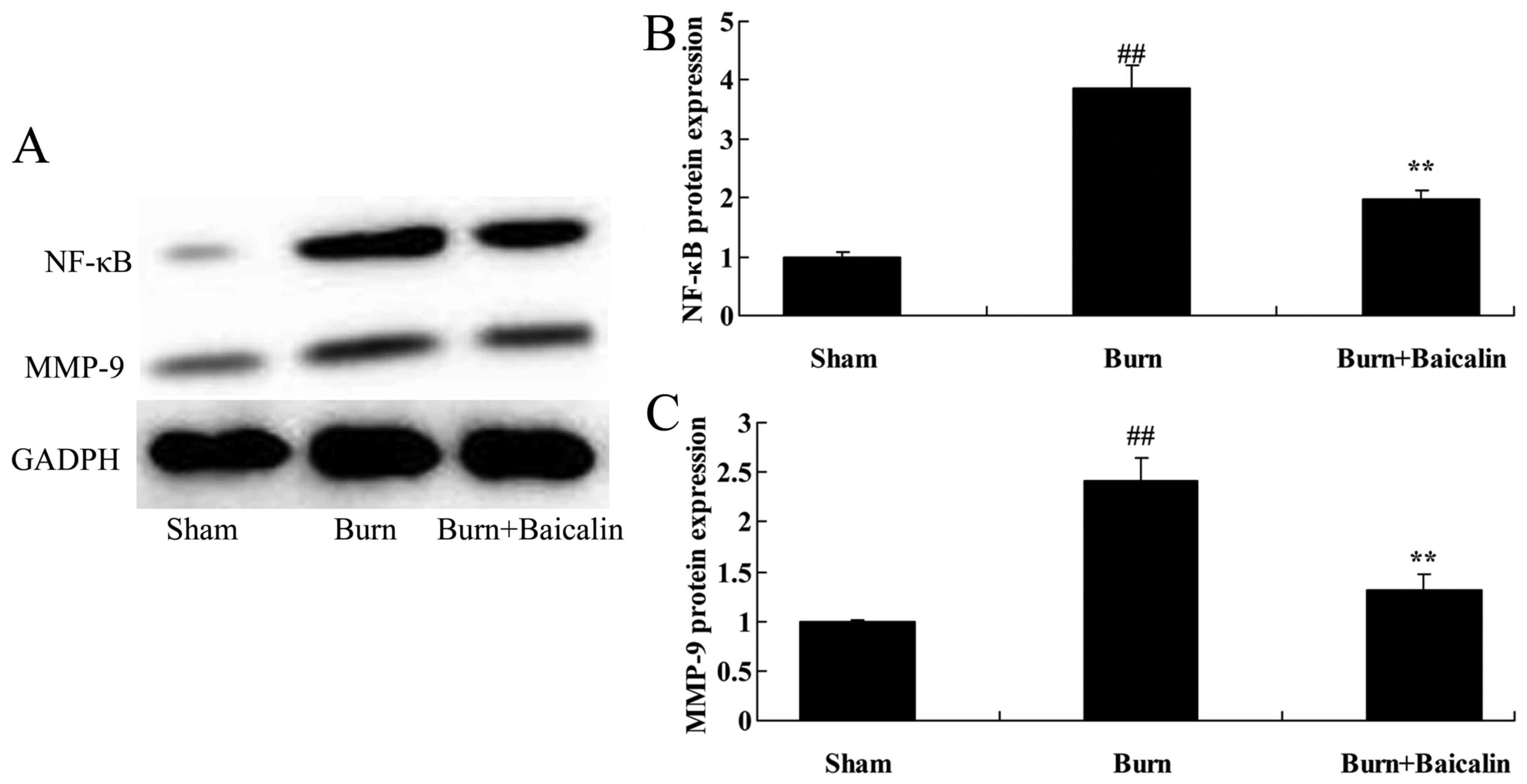
|
1
|
Sun R, Li Y, Chen W, Zhang F and Li T:
Total ginsenosides synergize with ulinastatin against septic acute
lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:7385–7390. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Patel BK, Wolfe KS, Pohlman AS, Hall JB
and Kress JP: Effect of noninvasive ventilation delivered by helmet
vs face mask on the rate of endotracheal intubation in patients
with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A randomized clinical
trial. JAMA. 315:2435–2441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang Z and Ni H: Prediction model for
critically ill patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome.
PLoS One. 10:e01206412015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shah HA, Dritsaki M, Pink J and Petrou S:
Psychometric properties of Patient Reported Outcome Measures
(PROMs) in patients diagnosed with Acute Respiratory Distress
Syndrome (ARDS). Health Qual Life Outcomes. 14:152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yin N, Peng Z, Li B, Xia J, Wang Z, Yuan
J, Fang L and Lu X: Isoflurane attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Am J Transl Res.
8:2033–2046. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang S, Zhao J, Wang H, Liang Y, Yang N
and Huang Y: Blockage of P2×7 attenuates acute lung injury in mice
by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome. Int Immunopharmacol. 27:38–45.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jiang W, Li M, He F, Bian Z, Liu J, He Q,
Wang X, Sun T and Zhu L: Dopamine D1 receptor agonist A-68930
inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and protects rats from
spinal cord injury-induced acute lung injury. Spinal Cord.
54:951–956. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang LL, Xiao N, Liu J, Liu K, Liu B, Li P
and Qi LW: Differential regulation of baicalin and scutellarin on
AMPK and Akt in promoting adipose cell glucose disposal. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:598–606. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan S, Wang Y, Liu P, Chen A, Chen M, Yao
D, Xu X, Wang L and Huang X: Baicalin attenuates hypoxia-induced
pulmonary arterial hypertension to improve hypoxic cor pulmonale by
reducing the activity of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway and MMP-9.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:25464022016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Craig TR, Duffy MJ, Shyamsundar M,
McDowell C, O'Kane CM, Elborn JS and McAuley DF: A randomized
clinical trial of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme a reductase
inhibition for acute lung injury (The HARP Study). Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 183:620–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qiu ZQ and Zhao K: Expression of ERCC1,
RRM1 and LRP in non-small cell lung cancers and their influence on
chemotherapeutic efficacy of gemcitabine concomitant with
nedaplatin. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7303–7307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoeboer SH, Groeneveld AB, van der Heijden
M and Oudemans-van Straaten HM: Serial inflammatory biomarkers of
the severity, course and outcome of late onset acute respiratory
distress syndrome in critically ill patients with or at risk for
the syndrome after new-onset fever. Biomark Med. 9:605–616. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Onorati F, Santini F, Mariscalco G,
Bertolini P, Sala A, Faggian G and Mazzucco A: Leukocyte filtration
ameliorates the inflammatory response in patients with mild to
moderate lung dysfunction. Ann Thorac Surg. 92:111–121. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Samransamruajkit R, Jiraratanawong K,
Siritantiwat S, Chottanapan S, Deelodejanawong J, Sritippayawan S,
Prapphal N and Poovorawan Y: Potent inflammatory cytokine response
following lung volume recruitment maneuvers with HFOV in pediatric
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol.
30:197–203. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Wei Y, Luo Q, Xu F, Zhao Z, Zhang
H, Lu L, Sun J, Liu F, Du X, et al: Baicalin attenuates
inflammation in mice with OVA-induced asthma by inhibiting NF-κB
and suppressing CCR7/CCL19/CCL21. Int J Mol Med. 38:1541–1548.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chao W, Deng JS, Huang SS, Li PY, Liang YC
and Huang GJ: 3,4-dihydroxybenzalacetone attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury via
down-regulation of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities through suppressing
ROS-mediated MAPK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 50:77–86. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He W, Jiang J, Yu ZQ and Zhou JH: Novel
5-hydroxy, 5-substituted benzenesulfonamide
pyrimidine-2,4,6-triones attenuate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury via inhibition of the gelatinases, MMP-2 and MMP-9.
Drug Dev Res. 77:251–257. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizushina Y, Shirasuna K, Usui F, Karasawa
T, Kawashima A, Kimura H, Kobayashi M, Komada T, Inoue Y, Mato N,
et al: NLRP3 protein deficiency exacerbates hyperoxia-induced
lethality through Stat3 protein signaling independent of
interleukin-1β. J Biol Chem. 290:5065–5077. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo YP, Jiang L, Kang K, Fei DS, Meng XL,
Nan CC, Pan SH, Zhao MR and Zhao MY: Hemin inhibits NLRP3
inflammasome activation in sepsis-induced acute lung injury,
involving heme oxygenase-1. Int Immunopharmacol. 20:24–32. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fukumoto J, Fukumoto I, Parthasarathy PT,
Cox R, Huynh B, Ramanathan GK, Venugopal RB, Allen-Gipson DS,
Lockey RF and Kolliputi N: NLRP3 deletion protects from
hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
305:C182–C189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu S, Xu L, Li S, Qiu Y, Liu Y, Wu Z, Ye
C, Hou Y and Hu CA: Baicalin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome and
nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling during Haemophilus
parasuis infection. Vet Res. 47:802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|