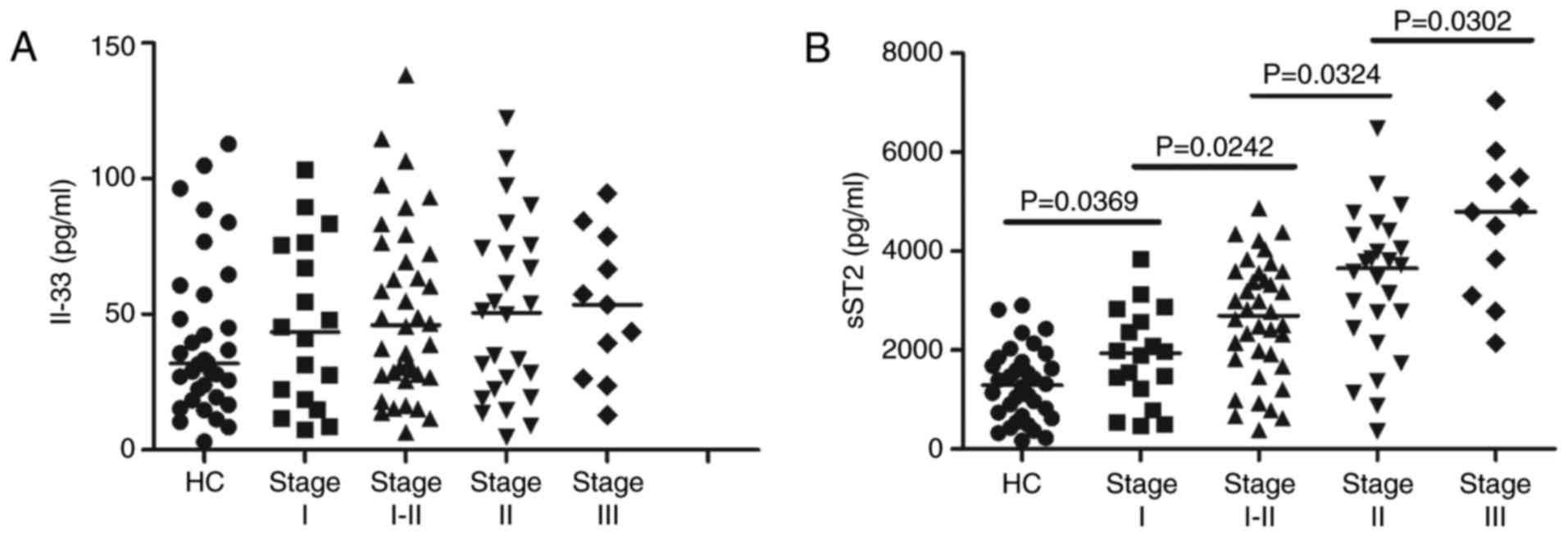
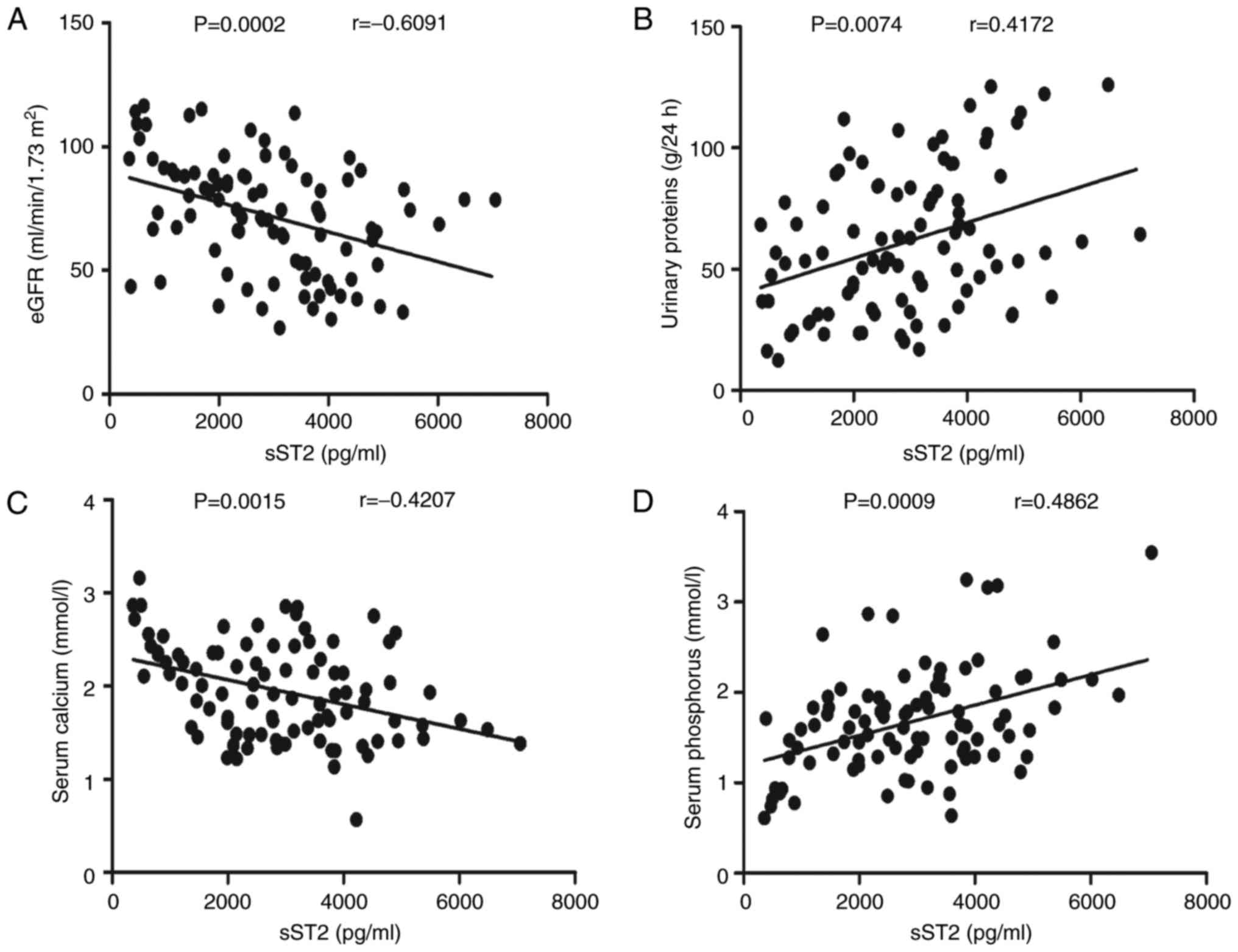
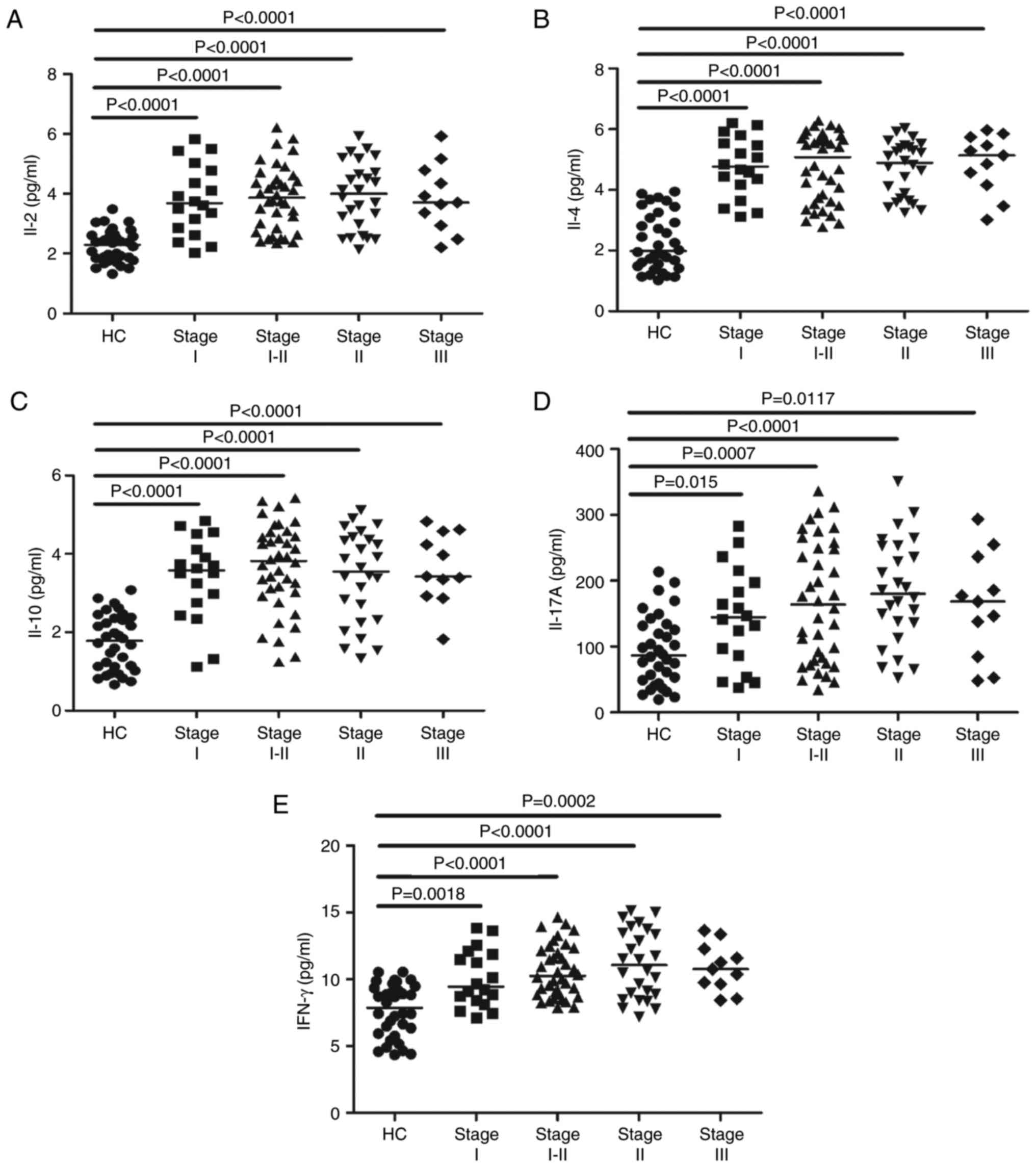
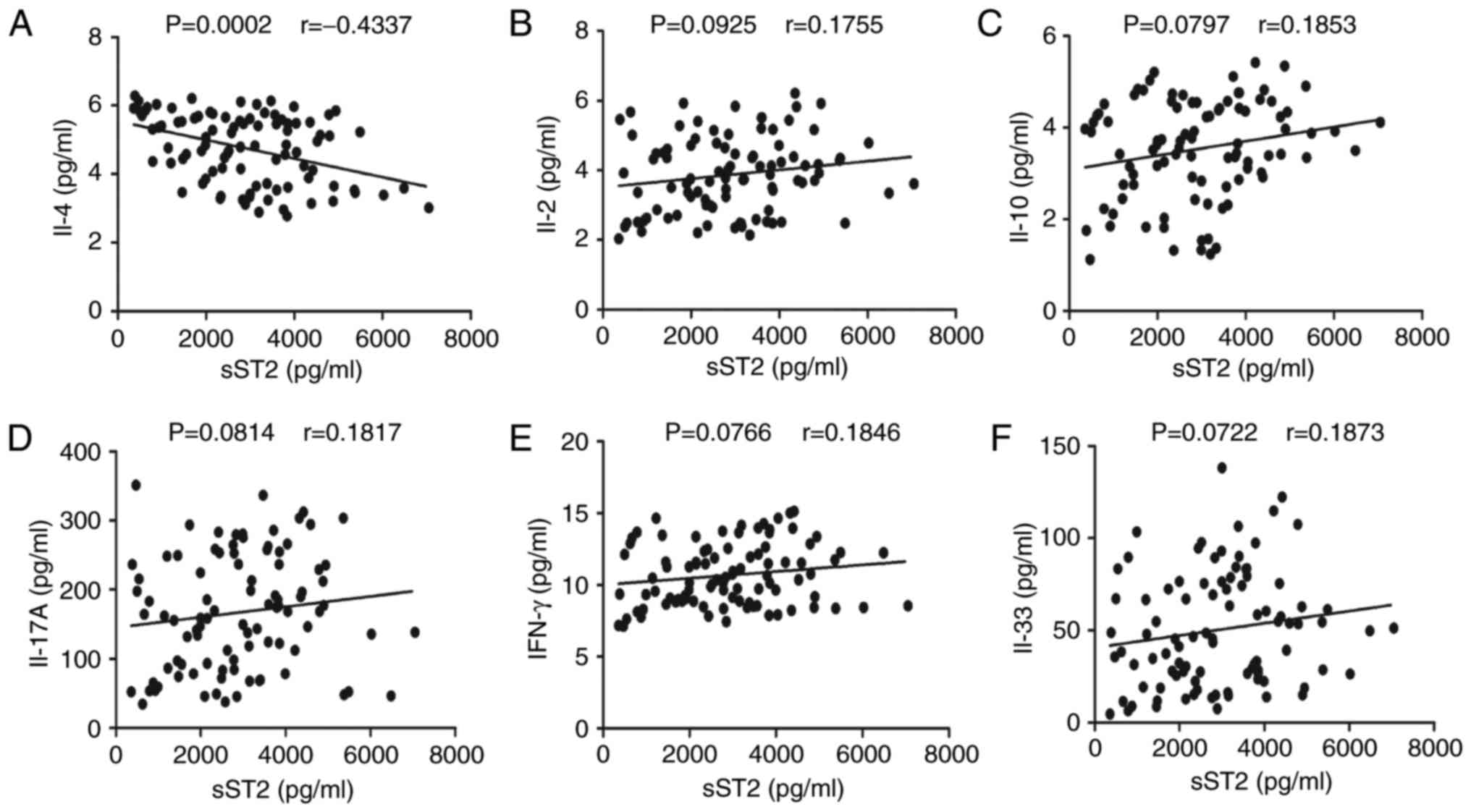
|
1
|
Glassock RJ: The pathogenesis of
idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A 50-year odyssey. Am J Kidney
Dis. 56:157–167. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ronco P and Debiec H: Pathogenesis of
membranous nephropathy: Recent advances and future challenges. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 8:203–213. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cattran D: Management of membranous
nephropathy: When and what for treatment. J Am Soc Nephrol.
16:1188–1194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cattran DC: Idiopathic membranous
glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 59:1983–1994. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Honkanen E, Törnroth T and Grönhagen-Riska
C: Natural history, clinical course and morphological evolution of
membranous nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 7 Suppl 1:S35–S41.
1992.
|
|
6
|
Glassock RJ: The treatment of idiopathic
membranous nephropathy: A dilemma or a conundrum? Am J Kidney Dis.
44:562–566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y,
Murphy E, McClanahan TK, Zurawski G, Moshrefi M, Qin J, Li X, et
al: IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1
receptorrelated protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated
cytokines. Immunity. 23:479–490. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alves-Filho JC, Sônego F, Souto FO,
Freitas A, Verri WA Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M, Basile-Filho A,
McKenzie AN, Xu D, Cunha FQ and Liew FY: Interleukin-33 attenuates
sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat
Med. 16:708–712. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Löhning M, Stroehmann A, Coyle AJ, Grogan
JL, Lin S, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Levinson D, Radbruch A and Kamradt
T: T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells,
independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10,
and important for Th2 effector function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:pp. 6930–6935. 1998; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sanada S, Hakuno D, Higgins LJ, Schreiter
ER, McKenzie AN and Lee RT: IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical
biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J
Clin Invest. 117:1538–1549. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Palmer G, Talabot-Ayer D, Lamacchia C, Toy
D, Seemayer CA, Viatte S, Finckh A, Smith DE and Gabay C:
Inhibition of interleukin-33 signaling attenuates the severity of
experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 60:738–749. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pastorelli L, De Salvo C, Cominelli MA,
Vecchi M and Pizarro TT: Novel cytokine signaling pathways in
inflammatory bowel disease: Insight into the dichotomous functions
of IL-33 during chronic intestinal inflammation. Therap Adv
Gastroenterol. 4:311–323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mok MY, Huang FP, Ip WK, Lo Y, Wong FY,
Chan EY, Lam KF and Xu D: Serum levels of IL-33 and soluble ST2 and
their association with disease activity in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:520–527. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kalavrizioti D, Gerolymos M, Rodi M,
Kalliakmani P, Provatopoulou S, Eleftheriadis T, Mouzaki A and
Goumenos DS: T helper (Th)-cytokines in the urine of patients with
primary glomerulonephritis treated with immunosuppressive drugs:
Can they predict outcome? Cytokine. 76:260–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuroki A, Iyoda M, Shibata T and Sugisaki
T: Th2 cytokines increase and stimulate B cells to produce IgG4 in
idiopathic membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int. 68:302–310. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morgan E, Varro R, Sepulveda H, Ember JA,
Apgar J, Wilson J, Lowe L, Chen R, Shivraj L, Agadir A, et al:
Cytometric bead array: A multiplexed assay platform with
applications in various areas of biology. Clin Immunol.
110:252–266. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tárnok A, Hambsch J, Chen R and Varro R:
Cytometric bead array to measure six cytokines in twenty-five
microliters of serum. Clin Chem. 49:1000–1002. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Barksby HE, Lea SR, Preshaw PM and Taylor
JJ: The expanding family of interleukin-1 cytokines and their role
in destructive inflammatory disorders. Clin Exp Immunol.
149:217–225. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liew FY, Pitman NI and McInnes IB:
Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1
family. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:103–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Cai Y, Ji H, Feng J, Ayana DA, Niu
J and Jiang Y: Serum IL-33 levels are associated with liver damage
in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
32:248–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang Z, Liang Y, Xi W, Li C and Zhong R:
Association of increased serum IL-33 levels with clinical and
laboratory characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus in
Chinese population. Clin Exp Med. 11:75–80. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A and
Tominaga S: Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic
airway inflammation. J Biol Chem. 282:26369–26380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dinarello CA: An IL-1 family member
requires caspase-1 processing and signals through the ST2 receptor.
Immunity. 23:461–462. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brunner M, Krenn C, Roth G, Moser B,
Dworschak M, Jensen-Jarolim E, Spittler A, Sautner T, Bonaros N,
Wolner E, et al: Increased levels of soluble ST2 protein and IgG1
production in patients with sepsis and trauma. Intensive Care Med.
30:1468–1473. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimpo M, Morrow DA, Weinberg EO, Sabatine
MS, Murphy SA, Antman EM and Lee RT: Serum levels of the
interleukin-1 receptor family member ST2 predict mortality and
clinical outcome in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation.
109:2186–2190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mueller T, Dieplinger B, Gegenhuber A,
Poelz W, Pacher R and Haltmayer M: Increased plasma concentrations
of soluble ST2 are predictive for 1-year mortality in patients with
acute destabilized heart failure. Clin Chem. 54:752–756. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rodrigues-Díez R, Aroeira LS, Orejudo M,
Bajo MA, Heffernan JJ, Rodrigues-Díez RR, Rayego-Mateos S, Ortiz A,
Gonzalez-Mateo G, López-Cabrera M, et al: IL-17A is a novel player
in dialysis-induced peritoneal damage. Kindey Int. 86:303–315.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Griesenauer B and Paczesny S: The
ST2/IL-33 axis in immune cells during inflammatory diseases. Front
Immunol. 8:4752017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hayakawa H, Hayakawa M, Kume A and
Tominaga S: Soluble ST2 blocks IL-33 signaling in allergic airway
inflammation. J Biol Chem. 282:26369–26380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yin H, Li XY, Liu T, Yuan BH, Zhang BB, Hu
SL, Gu HB, Jin XB and Zhu JY: Adenovirus-mediated delivery of
soluble ST2 attenuates ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice.
Clin Exp Immunol. 170:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Prunotto M, Carnevali ML, Candiano G,
Murtas C, Bruschi M, Corradini E, Trivelli A, Magnasco A, Petretto
A, Santucci L, et al: Autoimmunity in membranous nephropathy
targets aldose reductase and SOD2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:507–519.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lavi-Moshayoff V, Wasserman G, Meir T,
Silver J and Naveh-Many T: PTH increases FGF23 gene expression and
mediates the high-FGF23 levels of experimental kidney failure: A
bone parathyroid feedback loop. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
299:F882–F889. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shimada T, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki Y, Muto T,
Hino R, Takeuchi Y, Fujita T, Nakahara K, Fukumoto S and Yamashita
T: FGF-23 is a potent regulator of vitamin D metabolism and
phosphate homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 19:429–435. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Torres VE: Treatment strategies and
clinical trial design in ADPKD. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 17:190–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bao YS, Na SP, Zhang P, Jia XB, Liu RC, Yu
CY, Mu SH and Xie RJ: Characterization of interleukin-33 and
Soluble ST2 in serum and their association with disease severity in
patients with chronic kidney disease. J Clin Immunol. 32:587–594.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|