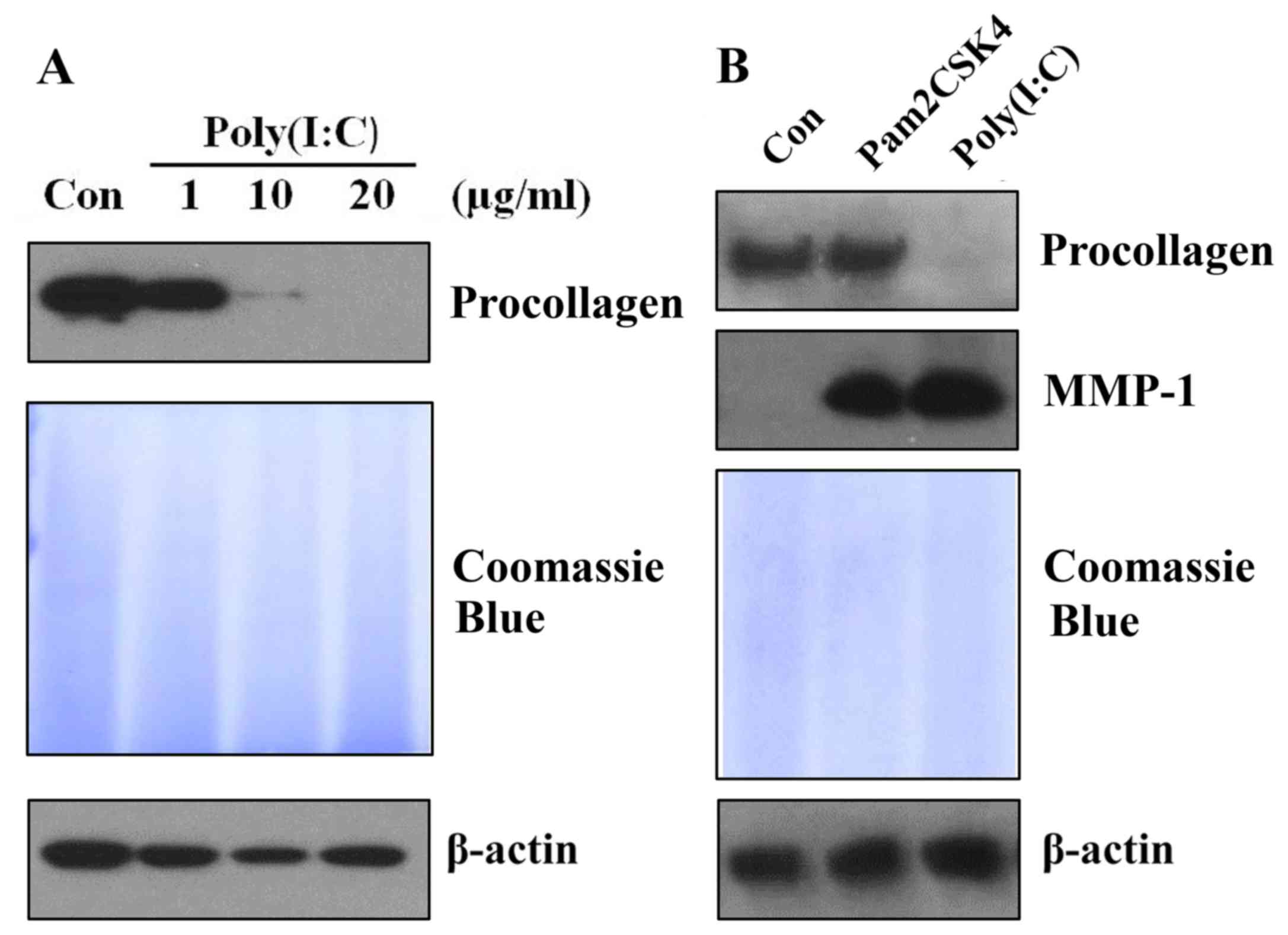
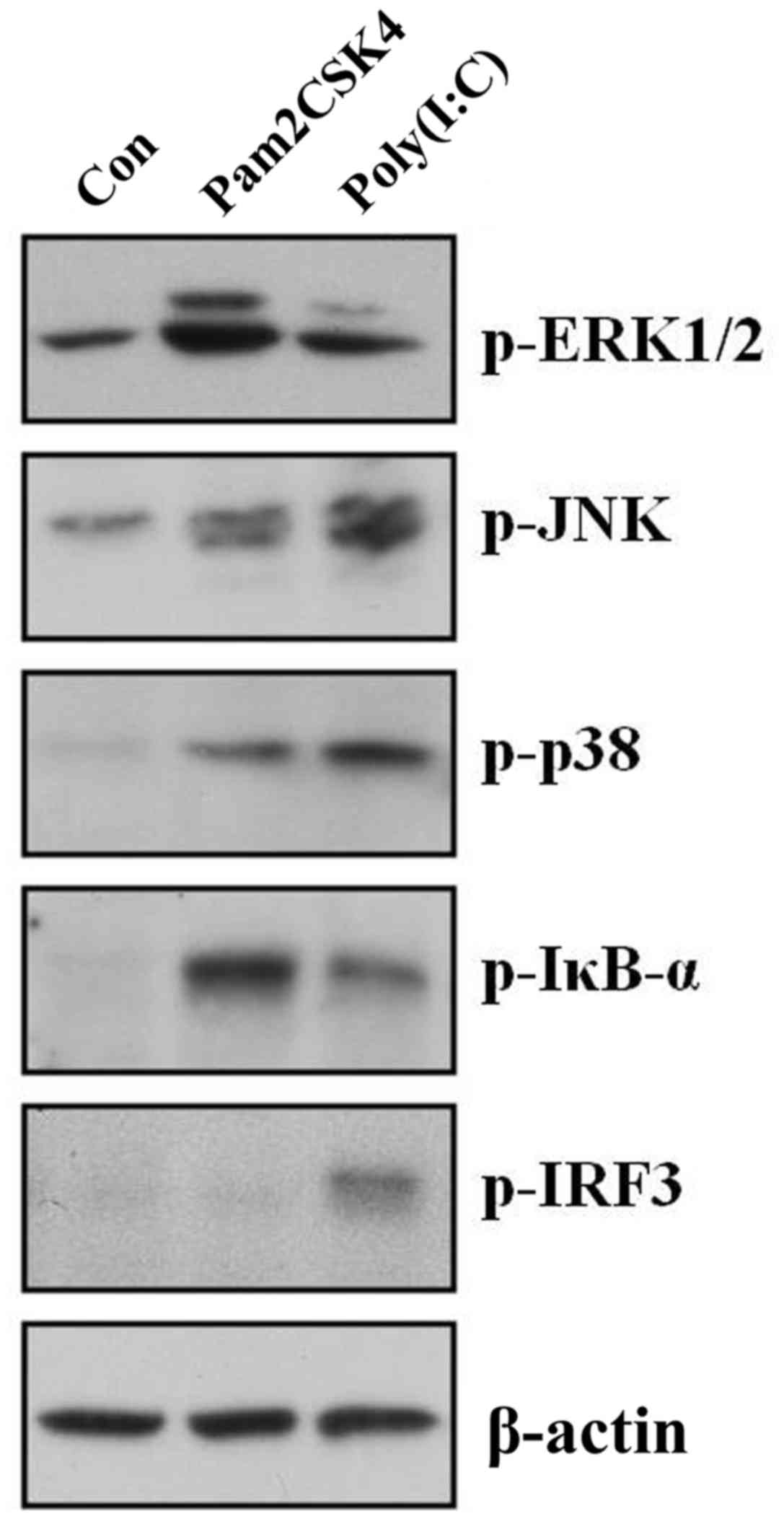
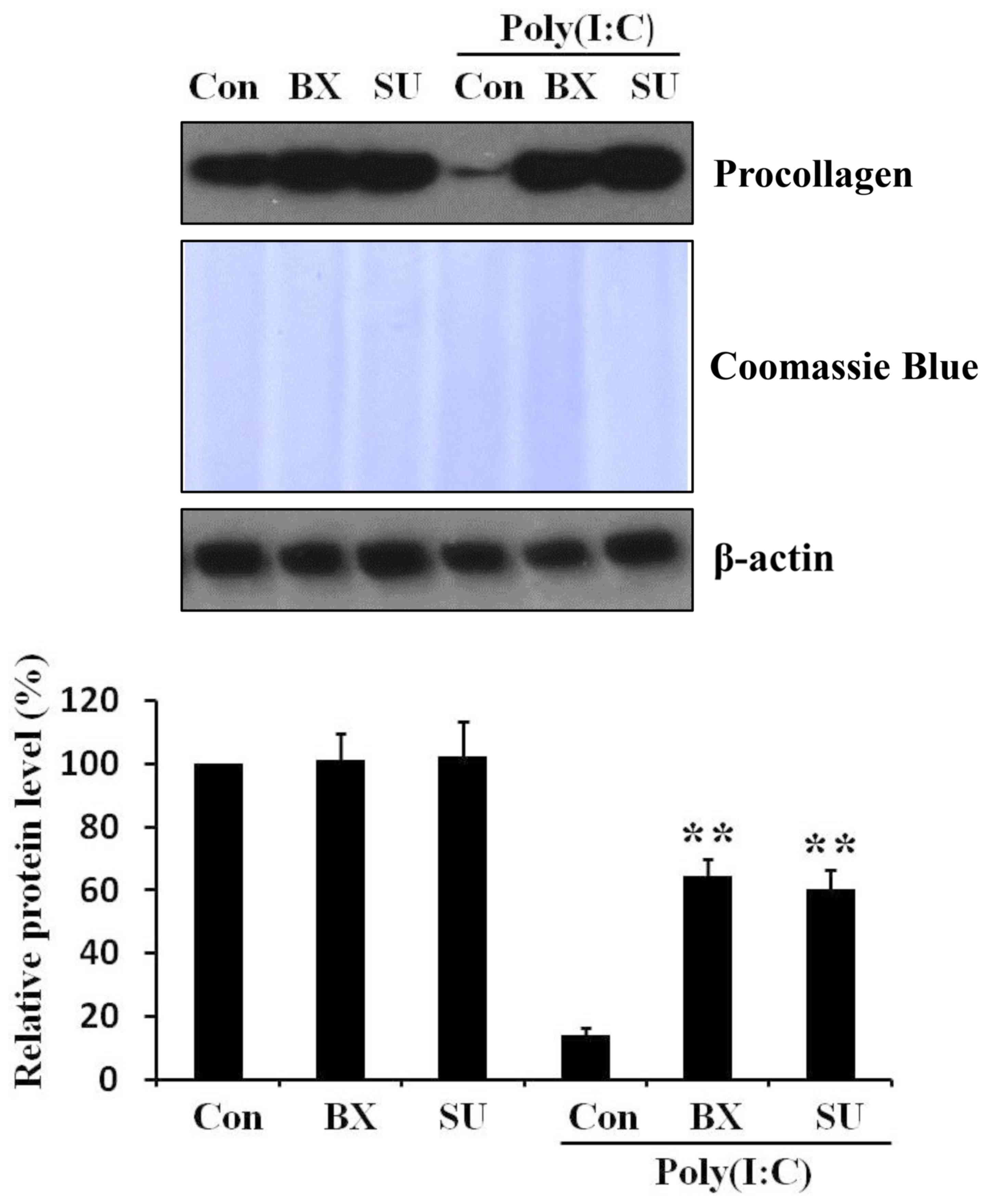
|
1
|
Chen K, Huang J, Gong W, Iribarren P,
Dunlop NM and Wang JM: Toll-like receptors in inflammation,
infection and cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 7:1271–1285. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ermertcan AT, Öztürk F and Gündüz K:
Toll-like receptors and skin. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol.
25:997–1006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Medzhitov R: Toll-like receptors and
innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:135–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller LS and Modlin RL: Toll-like
receptors in the skin. Semin Immunopathol. 29:15–26. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takeuchi O, Kaufmann A, Grote K, Kawai T,
Hoshino K, Morr M, Mühlradt PF and Akira S: Cutting edge:
Preferentially the R-stereoisomer of the mycoplasmal lipopeptide
macrophage-activating lipopeptide-2 activates immune cells through
a toll-like receptor 2- and MyD88-dependent signaling pathway. J
Immunol. 164:554–557. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takeuchi O, Sato S, Horiuchi T, Hoshino K,
Takeda K, Dong Z, Modlin RL and Akira S: Cutting edge: Role of
Toll-like receptor 1 in mediating immune response to microbial
lipoproteins. J Immunol. 169:10–14. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Mühlradt PF, Morr M,
Radolf JD, Zychlinsky A, Takeda K and Akira S: Discrimination of
bacterial lipoproteins by Toll-like receptor 6. Int Immunol.
13:933–940. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kalali BN, Köllisch G, Mages J, Müller T,
Bauer S, Wagner H, Ring J, Lang R, Mempel M and Ollert M:
Double-stranded RNA induces an antiviral defense status in
epidermal keratinocytes through TLR3-, PKR-, and
MDA5/RIG-I-mediated differential signaling. J Immunol.
181:2694–2704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanner NK and Linder P: DExD/H box RNA
helicases: From generic motors to specific dissociation functions.
Mol Cell. 8:251–262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sloane JA, Blitz D, Margolin Z and
Vartanian T: A clear and present danger: Endogenous ligands of
Toll-like receptors. Neuromolecular Med. 12:149–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lester SN and Li K: Toll-like receptors in
antiviral innate immunity. J Mol Biol. 426:1246–1264. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pattanaik D, Brown M, Postlethwaite BC and
Postlethwaite AE: Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Front
Immunol. 6:2722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rittié L and Fisher GJ: UV-light-induced
signal cascades and skin aging. Ageing Res Rev. 1:705–720. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Farina GA, York MR, Di Marzio M, Collins
CA, Meller S, Homey B, Rifkin IR, Marshak-Rothstein A, Radstake TR
and Lafyatis R: Poly(I:C) drives type I IFN- and TGFβ-mediated
inflammation and dermal fibrosis simulating altered gene expression
in systemic sclerosis. J Invest Dermatol. 130:2583–2593. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sugiura H, Ichikawa T, Koarai A,
Yanagisawa S, Minakata Y, Matsunaga K, Hirano T, Akamatsu K and
Ichinose M: Activation of Toll-like receptor 3 augments
myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
40:654–662. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee Y, Kim H, Kim S, Kim KH and Chung JH:
Activation of toll-like receptors 2, 3 or 5 induces matrix
metalloproteinase-1 and −9 expression with the involvement of MAPKs
and NF-kappaB in human epidermal keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol.
19:e44–e49. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Reimer T, Schweizer M and Jungi TW:
Stimulation-specific contribution of p38 and JNK to IFN-beta gene
expression in human macrophages. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
27:751–755. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fang F, Ooka K, Sun X, Shah R,
Bhattacharyya S, Wei J and Varga J: A synthetic TLR3 ligand
mitigates profibrotic fibroblast responses by inducing autocrine
IFN signaling. J Immunol. 191:2956–2966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kinnier CV, Martinu T, Gowdy KM, Nugent
JL, Kelly FL and Palmer SM: Innate immune activation by the viral
PAMP poly I:C potentiates pulmonary graft-versus-host disease after
allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Transpl Immunol.
24:83–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao C, Oh JH, Lee DH, Bae JS, Jin CL, Park
CH and Chung JH: Toll-like receptor family members in skin
fibroblasts are functional and have a higher expression compared to
skin keratinocytes. Int J Mol Med. 35:1443–1450. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yao C, Lee DH, Oh JH, Kim MK, Kim KH, Park
CH and Chung JH: Poly(I:C) induces expressions of MMP-1, −2, and −3
through various signaling pathways including IRF3 in human skin
fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 80:54–60. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chiappinelli KB, Strissel PL, Desrichard
A, Li H, Henke C, Akman B, Hein A, Rote NS, Cope LM, Snyder A, et
al: Inhibiting DNA methylation causes an interferon response in
cancer via dsRNA including endogenous retroviruses. Cell.
169:3612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bernard JJ, Cowing-Zitron C, Nakatsuji T,
Muehleisen B, Muto J, Borkowski AW, Martinez L, Greidinger EL, Yu
BD and Gallo RL: Ultraviolet radiation damages self noncoding RNA
and is detected by TLR3. Nat Med. 18:1286–1290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hyde DM and Giri SN:
Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid, an interferon inducer, ameliorates
bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in mice. Exp Lung Res. 16:533–546.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hou X, Yu F, Man S, Huang D, Zhang Y, Liu
M, Ren C and Shen J: Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid attenuates
hepatic fibrosis in C57BL/6 mice with Schistosoma japonicum
infection. Acta Trop. 121:99–104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ni MM, Xu T, Wang YR, He YH, Zhou Q, Huang
C, Meng XM and Li J: Inhibition of IRF3 expression reduces
TGF-β1-induced proliferation of hepatic stellate cells. J Physiol
Biochem. 72:9–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu P, Bailey-Bucktrout S, Xi Y, Xu D, Du
D, Zhang Q, Xiang W, Liu J, Melton A, Sheppard D, et al: Innate
antiviral host defense attenuates TGF-β function through
IRF3-mediated suppression of Smad signaling. Mol Cell. 56:723–737.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|