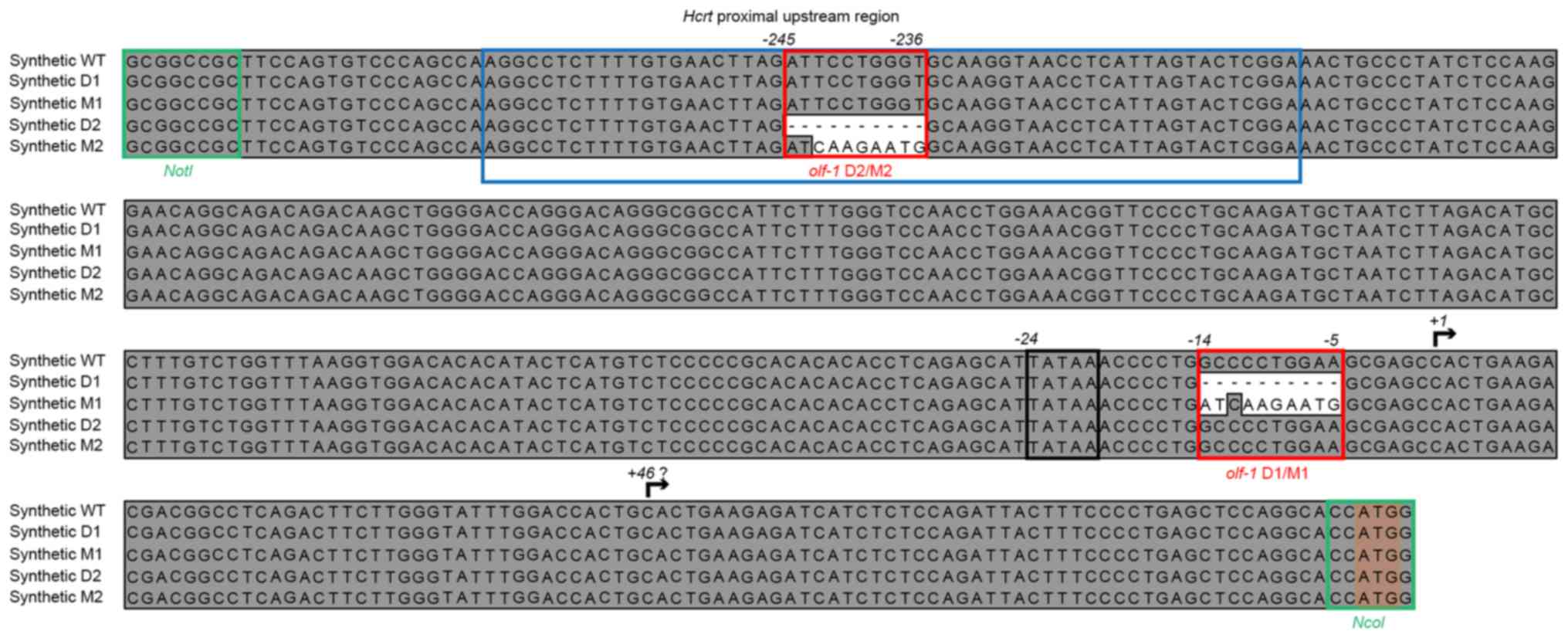
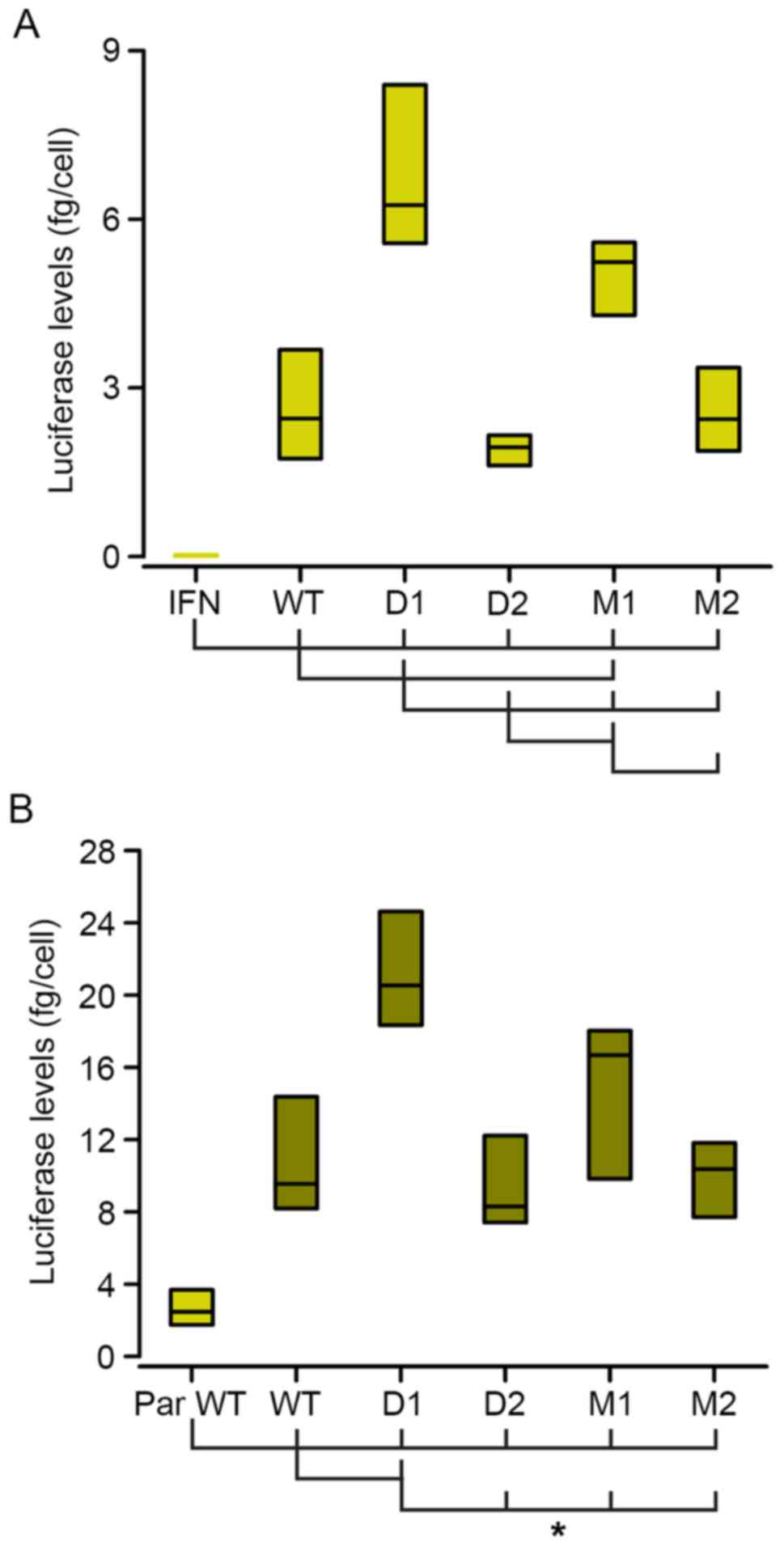
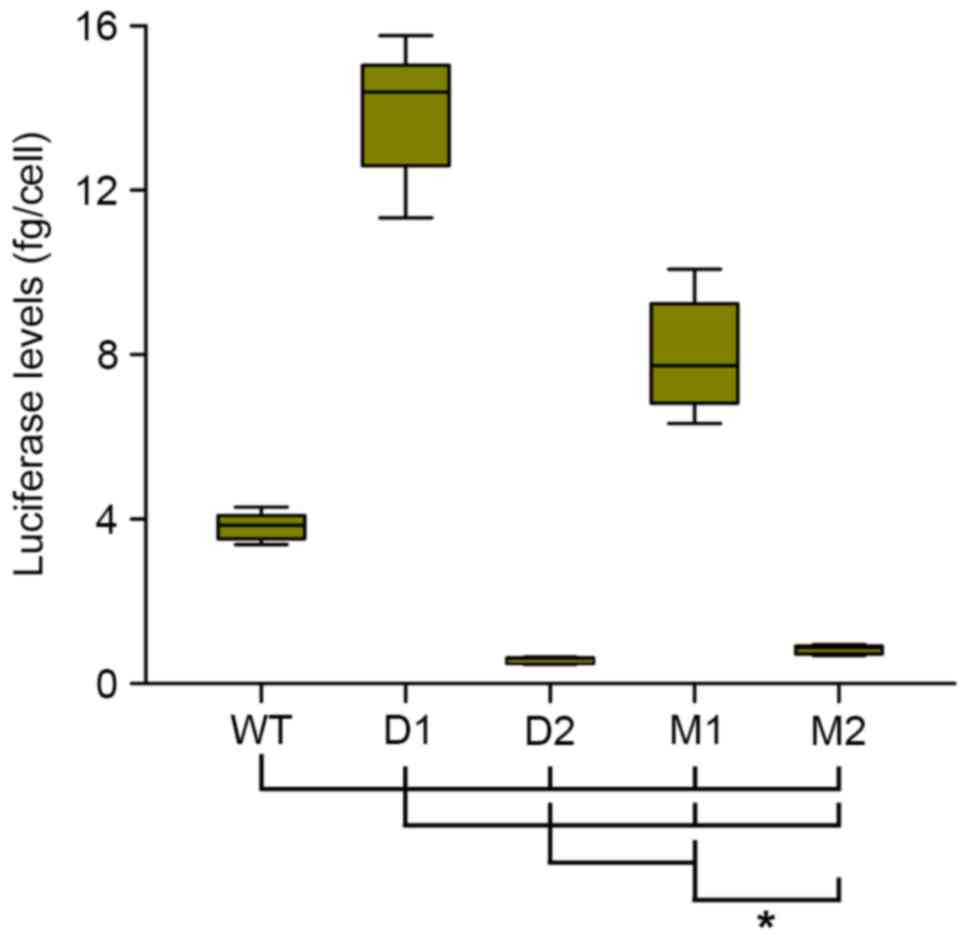
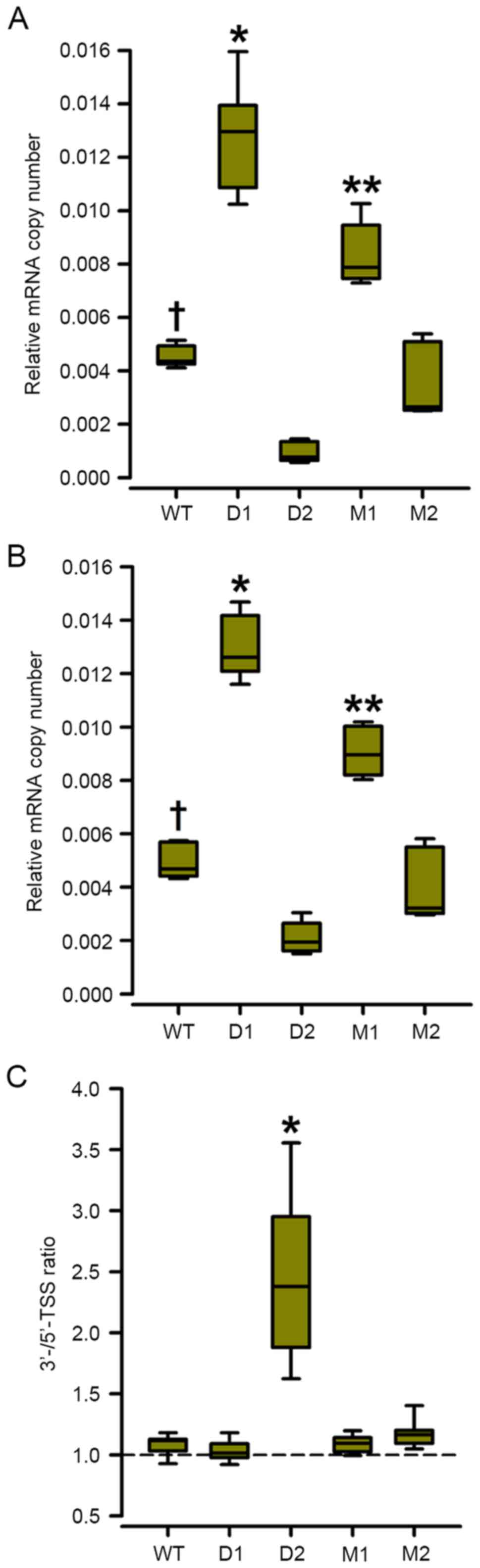
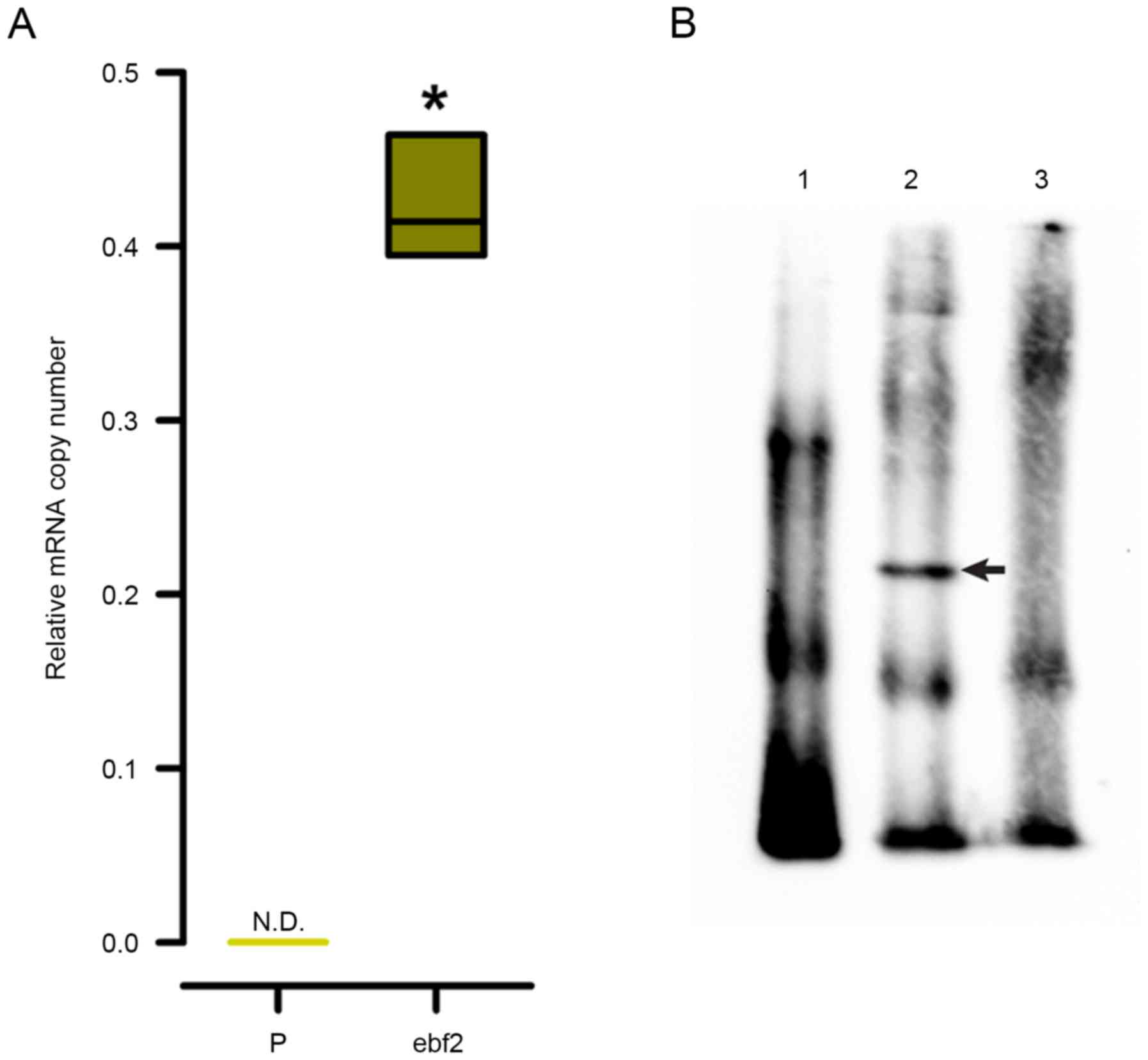
|
1
|
de Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X,
Foye PE, Danielson PE, Fukuhara C, Battenberg EL, Gautvik VT,
Bartlett FS II, et al: The hypocretins: Hypothalamus-specific
peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:pp. 322–327. 1998; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki
I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richarson JA, Kozlowski GP,
Wilson S, et al: Orexins and orexin receptors: A family of
hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that
regulate feeding behavior. Cell. 92:573–585. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Routh VH, Hao L, Santiago AM, Sheng Z and
Zhou C: Hypothalamic glucose sensing: Making ends meet. Front Syst
Neurosci. 8:2362014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tsujino N and Sakurai T: Role of orexin in
modulating arousal, feeding, and motivation. Front Behav Neurosci.
7:282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nuñez A, Rodrigo-Angulo ML, Andrés ID and
Garzón M: Hypocretin/orexin neuropeptides: Participation in the
control of sleep-wakefulness cycle and energy homeostasis. Curr
Neuropharmacol. 7:50–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ohno K and Sakurai T: Orexin neuronal
circuitry: Role in the regulation of sleep and wakefulness. Front
Neuroendocrinol. 29:70–87. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsuki T and Sakurai T: Orexins and
orexin receptors: From molecules to integrative physiology. Results
Probl Cell Differ. 46:27–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cai XJ, Widdowson PS, Harrold J, Wilson S,
Buckingham RE, Arch JR, Tadayyon M, Clapham JC, Wilding J and
Williams G: Hypothalamic orexin expression: Modulation by blood
glucose and feeding. Diabetes. 48:2132–2137. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Griffond B, Risold PY, Jacquemard C,
Colard C and Fellmann D: Insulin-induced hypoglycemia increases
preprohypocretin (orexin) mRNA in the rat lateral hypothalamic
area. Neurosci Lett. 262:77–80. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wagner D, Salin-Pascual R, Greco MA and
Shiromani PJ: Distribution of hypocretin-containing neurons in the
lateral hypothalamus and C-fos-immunoreactive neurons in the VLPO.
Sleep Res Online. 3:35–42. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sakurai T, Nagata R, Yamanaka A, Kawamura
H, Tsujino N, Muraki Y, Kageyama H, Kunita S, Takahashi S, Goto K,
et al: Input of orexin/hypocretin neurons revealed by a genetically
encoded tracer in mice. Neuron. 46:297–308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tanaka S, Kodama T, Nonaka T, Toyoda H,
Arai M, Fukazawa M, Honda Y, Honda M and Mignot E: Transcriptional
regulation of the hypocretin/orexin gene by NR6A1. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 403:178–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sakurai T, Moriguchi T, Furuya K, Kajiwara
N, Nakamura T, Yanagisawa M and Goto K: Structure and function of
human prepro-orexin gene. J Biol Chem. 274:17771–17776. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cunningham F, Amode MR, Barrell D, Beal K,
Billis K, Brent S, Carvalho-Silva D, Clapham P, Coates G,
Fitzgerald S, et al: Ensembl 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 43(Database
issue): D662–D669. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waleh NS, Apte-Deshpande A, Terao A, Ding
J and Kilduff TS: Modulation of the promoter region of
prepro-hypocretin by alpha-interferon. Gene. 262:123–128. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moriguchi T, Sakurai T, Takahashi S, Goto
K and Yamamoto M: The human prepro-orexin gene regulatory region
that activates gene expression in the lateral region and represses
it in the medial regions of the hypothalamus. J Biol Chem.
277:16985–16992. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanaka S: Transcriptional regulation of
the hypocretin/orexin gene. Vitam Horm. 89:75–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Honda M, Eriksson KS, Zhang S, Tanaka S,
Lin L, Salehi A, Hesla PE, Maehlen J, Gaus SE, Yanagisawa M, et al:
IGFBP3 colocalizes with and regulates hypocretin (orexin). PLoS
One. 4:e42542009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Silva JP, von Meyenn F, Howell J, Thorens
B, Wolfrum C and Stoffel M: Regulation of adaptive behaviour during
fasting by hypothalamic Foxa2. Nature. 462:646–650. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
De La Herrán-Arita AK, Zomosa-Signoret VC,
Millán-Aldaco DA, Palomero-Rivero M, Guerra-Crespo M, Drucker-Colín
R and Vidaltamayo R: Aspects of the narcolepsy-cataplexy syndrome
in O/E3-null mutant mice. Neuroscience. 183:134–143. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang SS, Lewcock JW, Feinstein P,
Mombaerts P and Reed RR: Genetic disruptions of O/E2 and O/E3 genes
reveal involvement in olfactory receptor neuron projection.
Development. 131:1377–1388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garcia-Dominguez M, Poquet C, Garel S and
Charnay P: Ebf gene function is required for coupling neuronal
differentiation and cell cycle exit. Development. 130:6013–6025.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Croci L, Chung SH, Masserdotti G, Gianola
S, Bizzoca A, Gennarini G, Corradi A, Rossi F, Hawkes R and
Consalez GG: A key role for the HLH transcription factor
EBF2COE2,O/E-3 in Purkinje neuron migration and cerebellar cortical
topography. Development. 133:2719–2729. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chuang SM, Wang Y, Wang Q, Liu KM and Shen
Q: Ebf2 marks early cortical neurogenesis and regulates the
generation of cajal-retzius neurons in the developing cerebral
cortex. Dev Neurosci. 33:479–493. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roby YA, Bushey MA, Cheng LE, Kulaga HM,
Lee SJ and Reed RR: Zfp423/OAZ mutation reveals the importance of
Olf/EBF transcription activity in olfactory neuronal maturation. J
Neurosci. 32:13679–13688. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burt J, Alberto CO, Parsons MP and
Hirasawa M: Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the
lateral hypothalamus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
301:R572–R580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tanno S, Terao A, Okamatsu-Ogura Y and
Kimura K: Hypothalamic prepro-orexin mRNA level is inversely
correlated to the non-rapid eye movement sleep level in high-fat
diet-induced obese mice. Obes Res Clin Pract. 7:e251–e257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arafat AM, Kaczmarek P, Skrzypski M,
Pruszyńska-Oszmałek E, Kołodziejski P, Adamidou A, Ruhla S,
Szczepankiewicz D, Sassek M, Billert M, et al: Glucagon regulates
orexin A secretion in humans and rodents. Diabetologia.
57:2108–2116. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iwasa T, Matsuzaki T, Munkhzaya M,
Tungalagsuvd A, Kuwahara A, Yasui T and Irahara M: Developmental
changes in the hypothalamic mRNA levels of prepro-orexin and orexin
receptors and their sensitivity to fasting in male and female rats.
Int J Dev Neurosci. 46:51–54. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Justinussen JL, Holm A and Kornum BR: An
optimized method for measuring hypocretin-1 peptide in the mouse
brain reveals differential circadian regulation of hypocretin-1
levels rostral and caudal to the hypothalamus. Neuroscience.
310:354–361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Leri F, Cummins E and Kreek MJ:
Individual differences in gene expression of vasopressin, D2
receptor, POMC and orexin: Vulnerability to relapse to
heroin-seeking in rats. Physiol Behav. 139:127–135. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dalal J, Roh JH, Maloney SE, Akuffo A,
Shah S, Yuan H, Wamsley B, Jones WB, de Guzman Strong C, Gray PA,
et al: Translational profiling of hypocretin neurons identifies
candidate molecules for sleep regulation. Genes Dev. 27:565–578.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Merkle FT, Gandhi AV, Gagnon JA,
Woods IG, Chiu CN, Shimogori T, Schier AF and Prober DA:
Evolutionarily conserved regulation of hypocretin neuron
specification by Lhx9. Development. 142:1113–1124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Szabó NE, Zhao T, Cankaya M, Theil T, Zhou
X and Alvarez-Bolado G: Role of neuroepithelial Sonic hedgehog in
hypothalamic patterning. J Neurosci. 29:6989–7002. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|