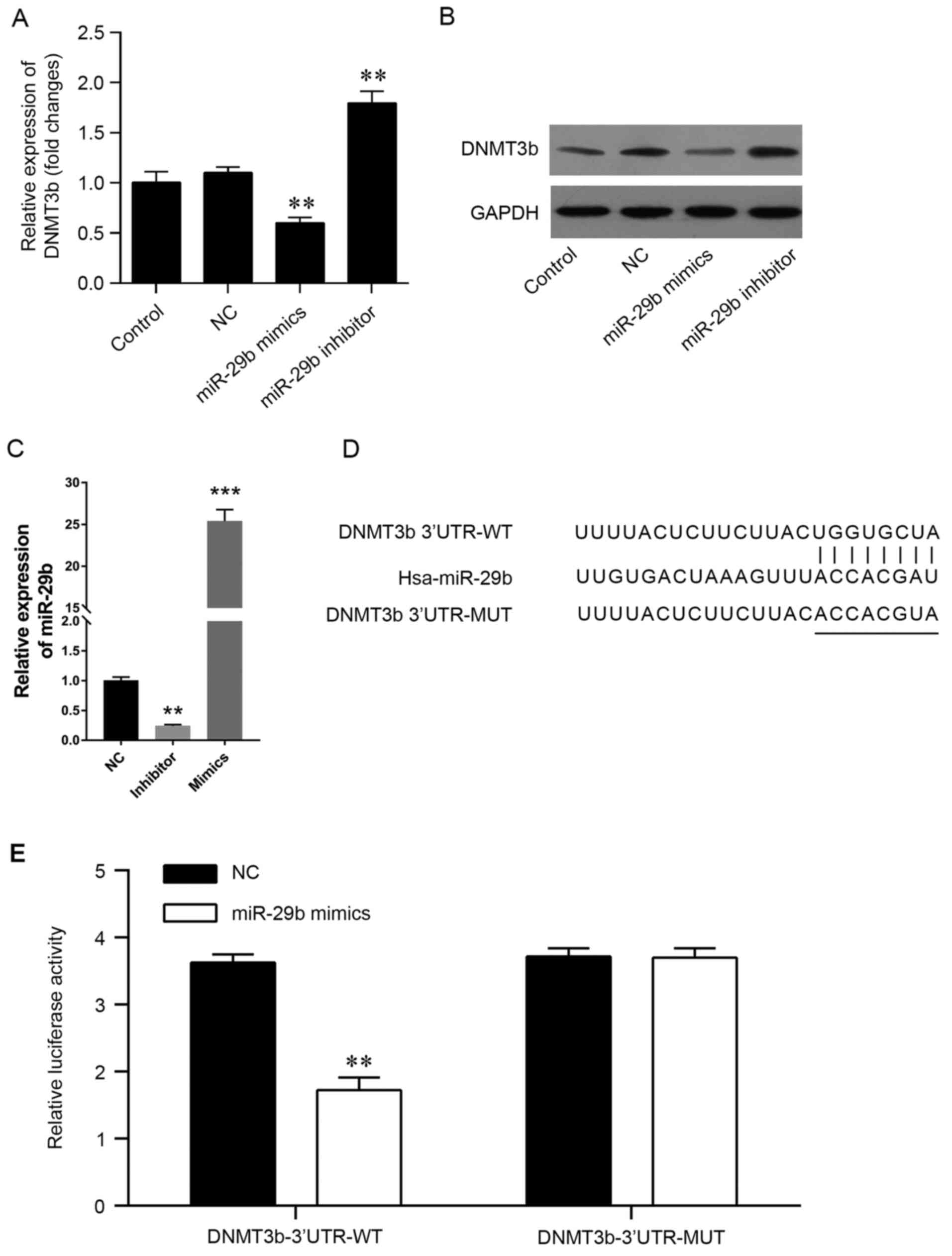
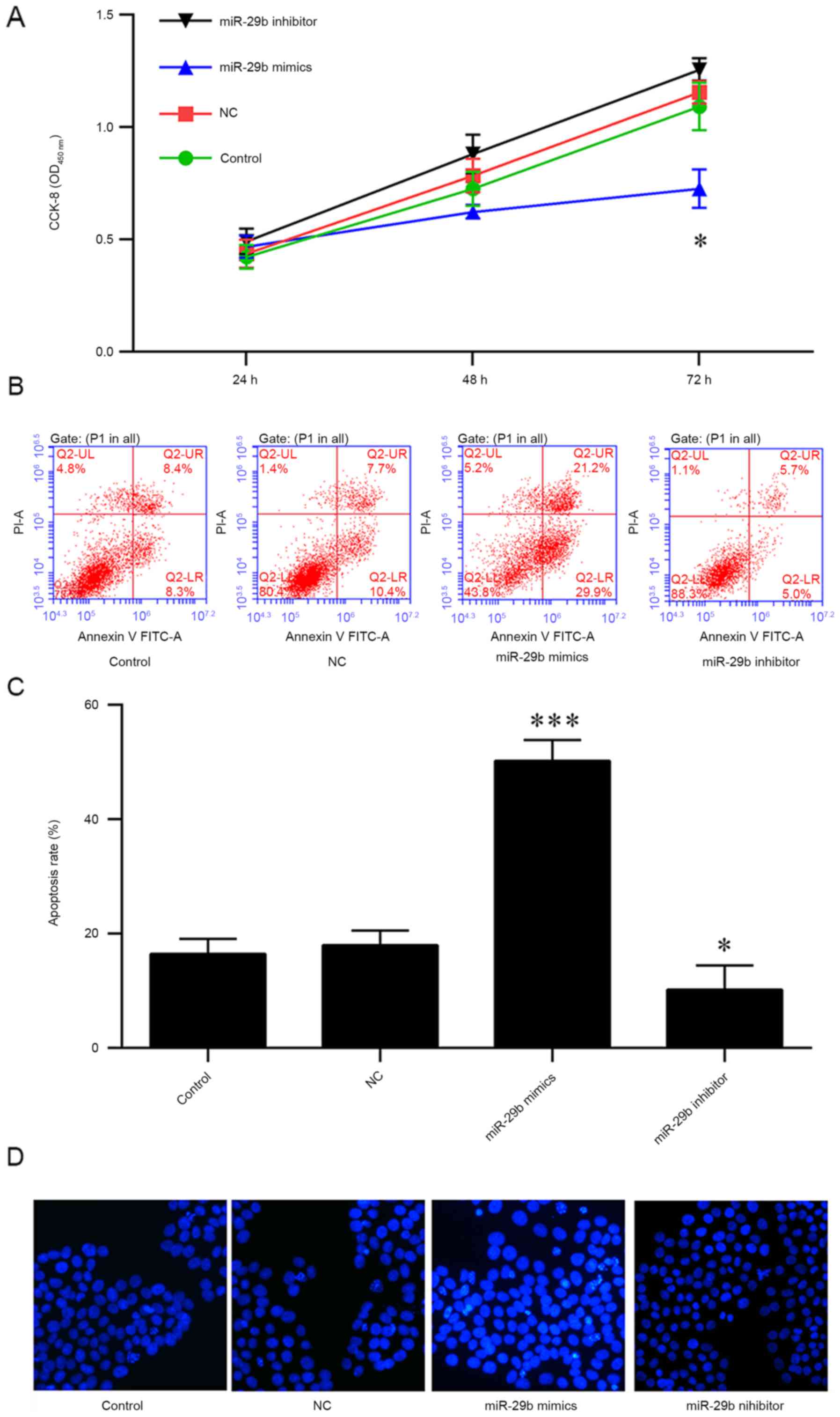
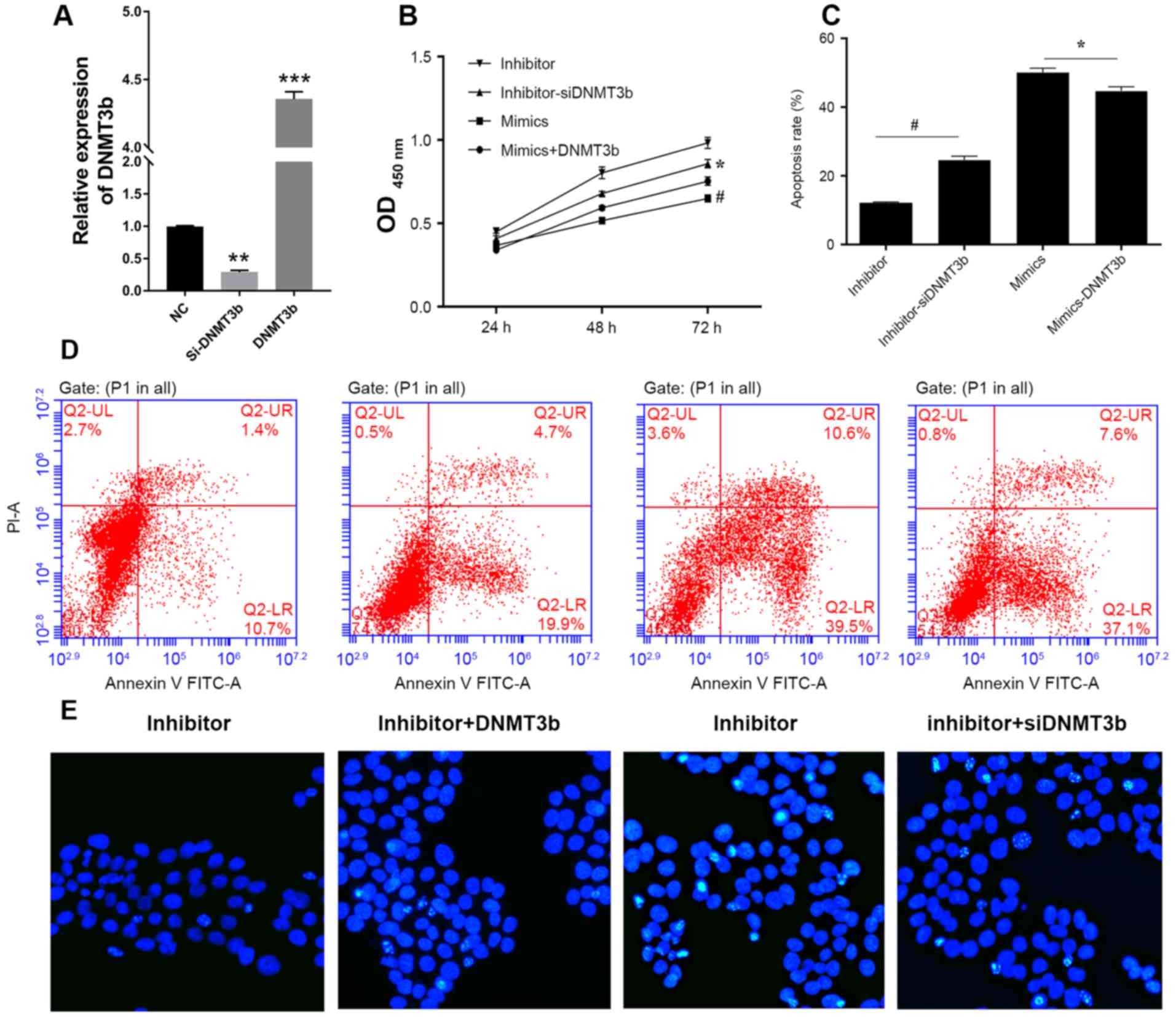
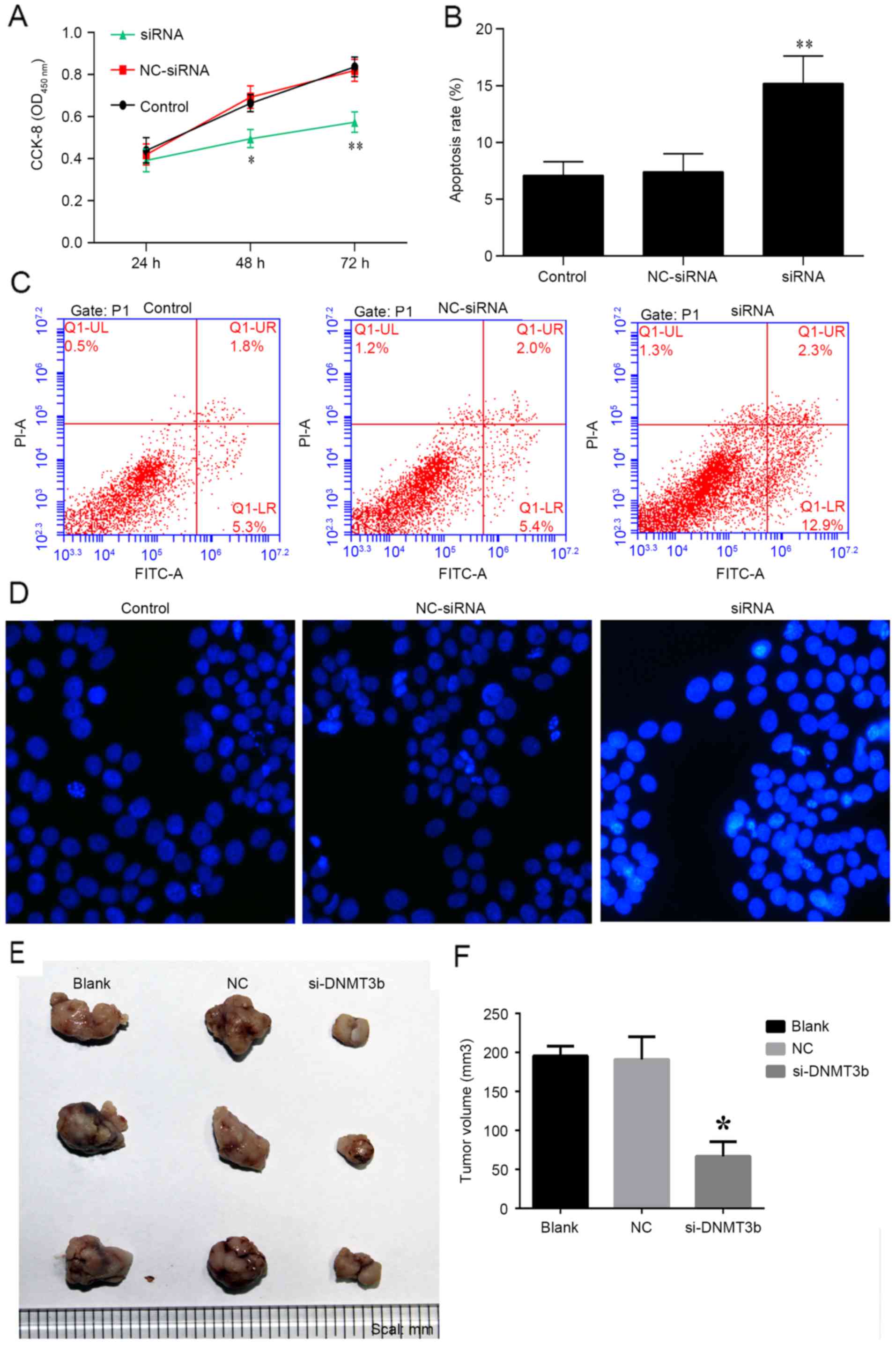
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Demir IE, Friess H and Ceyhan GO: Neural
plasticity in pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:649–659. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Falasca M, Kim M and Casari I: Pancreatic
cancer: Current research and future directions. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1865:123–132. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Subramaniam D, Thombre R, Dhar A and Anant
S: DNA methyltransferases: A novel target for prevention and
therapy. Front Oncol. 4:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hamidi T, Singh AK and Chen T: Genetic
alterations of DNA methylation machinery in human diseases.
Epigenomics. 7:247–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Eads CA, Danenberg KD, Kawakami K, Saltz
LB, Danenberg PV and Laird PW: CpG island hypermethylation in human
colorectal tumors is not associated with DNA methyltransferase
overexpression. Cancer Res. 59:2302–2306. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patra SK, Patra A, Zhao H and Dahiya R:
DNA methyltransferase and demethylase in human prostate cancer. Mol
Carcinog. 33:163–171. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Girault I, Tozlu S, Lidereau R and Biéche
I: Expression analysis of DNA methyltransferases 1, 3A and 3B in
sporadic breast carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4415–4422.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buchi F, Spinelli E, Masala E, Gozzini A,
Sanna A, Bosi A, Ferrari G and Santini V: Proteomic analysis
identifies differentially expressed proteins in AML1/ETO acute
myeloid leukemia cells treated with DNMT inhibitors azacitidine and
decitabine. Leuk Res. 36:607–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao J, Wang L, Xu J, Zheng J, Man X, Wu H,
Jin J, Wang K, Xiao H, Li S and Li Z: Aberrant DNA
methyltransferase expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
development and progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:862013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tan M, Wu J and Cai Y: Suppression of Wnt
signaling by the miR-29 family is mediated by demethylation of
WIF-1 in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
438:673–679. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niederwieser C, Kohlschmidt J, Volinia S,
Whitman SP, Metzeler KH, Eisfeld AK, Maharry K, Yan P, Frankhouser
D, Becker H, et al: Prognostic and biologic significance of DNMT3B
expression in older patients with cytogenetically normal primary
acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 29:567–575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Melo SA and Esteller M: Dysregulation of
microRNAs in cancer: Playing with fire. FEBS Lett. 585:2087–2099.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amodio N, Rossi M, Raimondi L, Pitari MR,
Botta C, Tagliaferri P and Tassone P: miR-29s: A family of
epi-miRNAs with therapeutic implications in hematologic
malignancies. Oncotarget. 6:12837–12861. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Amodio N, Leotta M, Bellizzi D, Di Martino
MT, D'Aquila P, Lionetti M, Fabiani F, Leone E, Gullà AM, Passarino
G, et al: DNA-demethylating and anti-tumor activity of synthetic
miR-29b mimics in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 3:1246–1258. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garzon R, Liu S, Fabbri M, Liu Z, Heaphy
CE, Callegari E, Schwind S, Pang J, Yu J, Muthusamy N, et al:
MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor
suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting
directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood. 113:6411–6418.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fabbri M, Garzon R, Cimmino A, Liu Z,
Zanesi N, Callegari E, Liu S, Alder H, Costinean S,
Fernandez-Cymering C, et al: MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant
methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltransferases 3A
and 3B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 15805–15810. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guzman EA, Xu Q, Pitts TP, Mitsuhashi KO,
Baker C, Linley PA, Oestreicher J, Tendyke K, Winder PL, Suh EM and
Wright AE: Leiodermatolide, a novel marine natural product, has
potent cytotoxic and antimitotic activity against cancer cells,
appears to affect microtubule dynamics, and exhibits antitumor
activity. Int J Cancer. 139:2116–2126. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Arundhathi A, Chuang WH, Chen JK, Wang SE,
Shyr YM, Chen JY, Liao WN, Chen HW, Teng YM, Pai CC and Wang CH:
Prorenin receptor acts as a potential molecular target for
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma diagnosis. Oncotarget. Jul
13–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Su MJ, Aldawsari H and Amiji M: Pancreatic
cancer cell exosome-mediated macrophage reprogramming and the role
of microRNAs 155 and 125b2 transfection using nanoparticle delivery
systems. Sci Rep. 6:301102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang D, Shi S, Xu J, Zhang B, Qin Y, Ji
S, Xu W, Liu J, Liu L, Liu C, et al: New insights into perineural
invasion of pancreatic cancer: More than pain. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1865:111–122. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang C, Bian Z, Wei D and Zhang JG:
miR-29b regulates migration of human breast cancer cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 352:197–207. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kobayashi Y, Absher DM, Gulzar ZG, Young
SR, McKenney JK, Peehl DM, Brooks JD, Myers RM and Sherlock G: DNA
methylation profiling reveals novel biomarkers and important roles
for DNA methyltransferases in prostate cancer. Genome Res.
21:1017–1027. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Robaina MC, Mazzoccoli L, Arruda VO, Reis
FR1, Apa AG, de Rezende LM and Klumb CE: Deregulation of DNMT1,
DNMT3B and miR-29 s in Burkitt lymphoma suggests novel contribution
for disease pathogenesis. Exp Mol Pathol. 98:200–207. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang JJ, Zhu Y, Wu JL, Liang WB, Zhu R,
Xu ZK, Du Q and Miao Y: Association of increased DNA
methyltransferase expression with carcinogenesis and poor prognosis
in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. 14:116–124.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu H, Wang B, Lin J and Zhao L:
microRNA-29b: An emerging player in human cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:9059–9064. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan B, Guo Q, Fu FJ, Wang Z, Yin Z, Wei YB
and Yang JR: The role of miR-29b in cancer: Regulation, function,
and signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 8:539–548. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|