|
1
|
Borgmann J, Tüttelmann F, Dworniczak B,
Röpke A, Song HW, Kliesch S, Wilkinson MF, Laurentino S and Gromoll
J: The human RHOX gene cluster: Target genes and functional
analysis of gene variants in infertile men. Hum Mol Genet.
15:4898–4910. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Zhuang X, Huang J, Jin X, Yu Y, Li J, Qiao
J and Liu P: Chromosome aberrations and spermatogenic disorders in
mice with Robertsonian translocation (11; 13). Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:7735–7743. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ishizuka M, Ohtsuka E, Inoue A, Odaka M,
Ohshima H, Tamura N, Yoshida K, Sako N, Baba T, Kashiwabara S, et
al: Abnormal spermatogenesis and male infertility in testicular
zinc finger protein Zfp318-knockout mice. Dev Growth Differ.
58:600–608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Diao R, Fok KL, Chen H, Yu MK, Duan Y,
Chung CM, Li Z, Wu H, Li Z, Zhang H, et al: Deficient human
β-defensin 1 underlies male infertility associated with poor sperm
motility and genital tract infection. Sci Transl Med.
6:249ra1082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miyamoto T, Tsujimura A, Miyagawa Y, Koh
E, Namiki M and Sengoku K: Male infertility and its causes in
human. Adv Urol. 2012:3845202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ji ZY, Sha YW, Ding L and Li P: Genetic
factors contributing to human primary ciliary dyskinesia and male
infertility. Asian J Androl. 19:515–520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
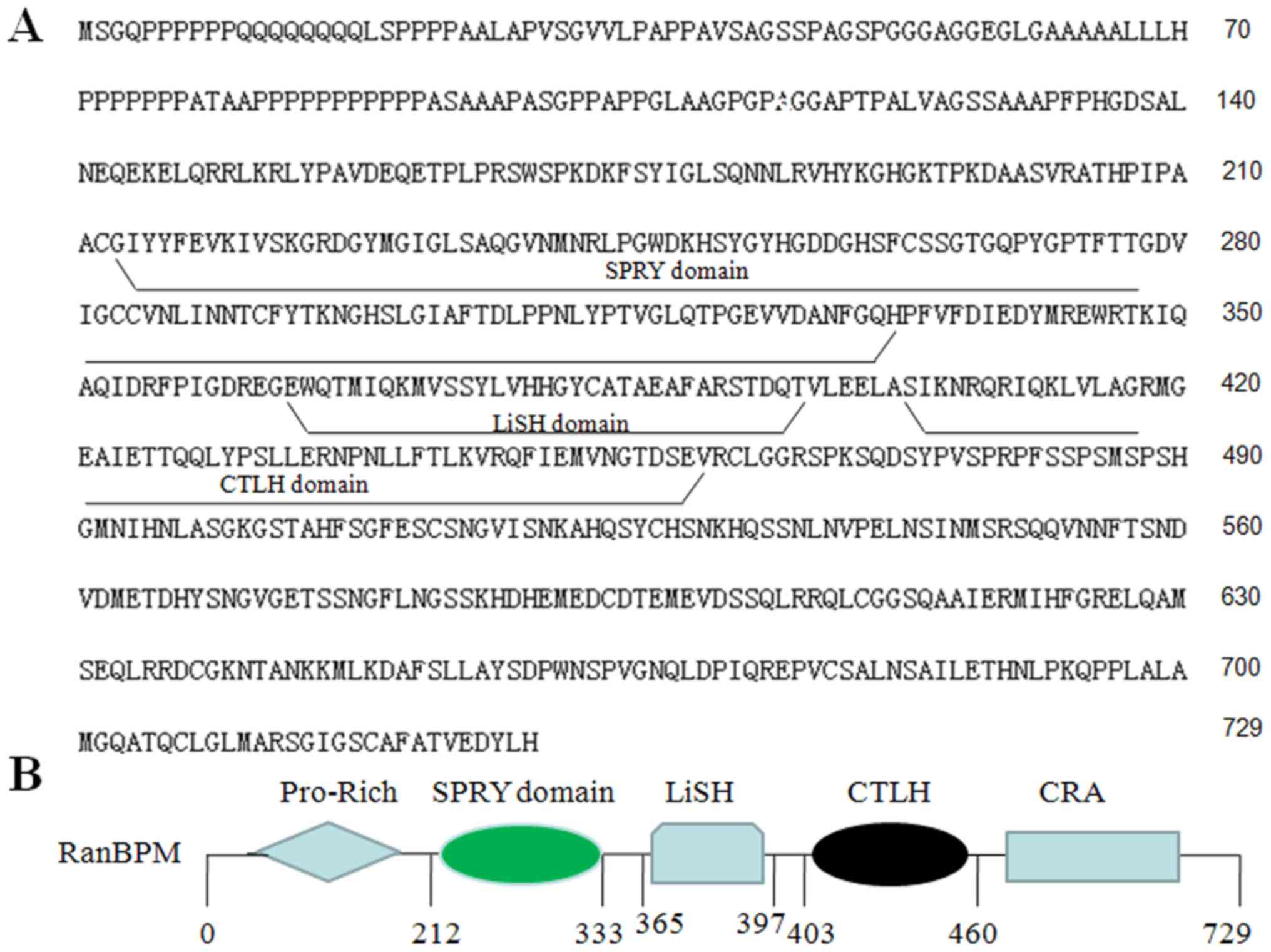
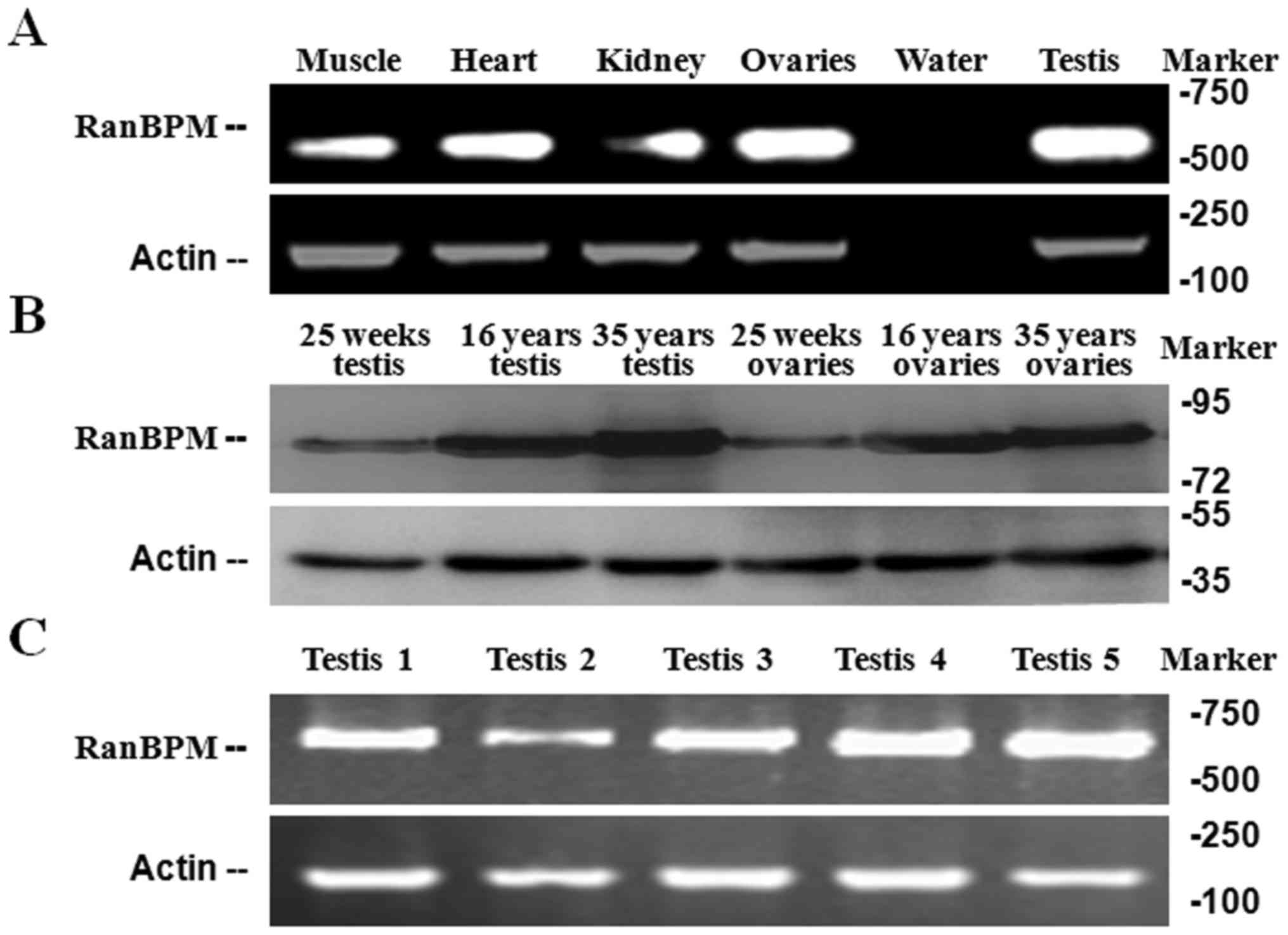
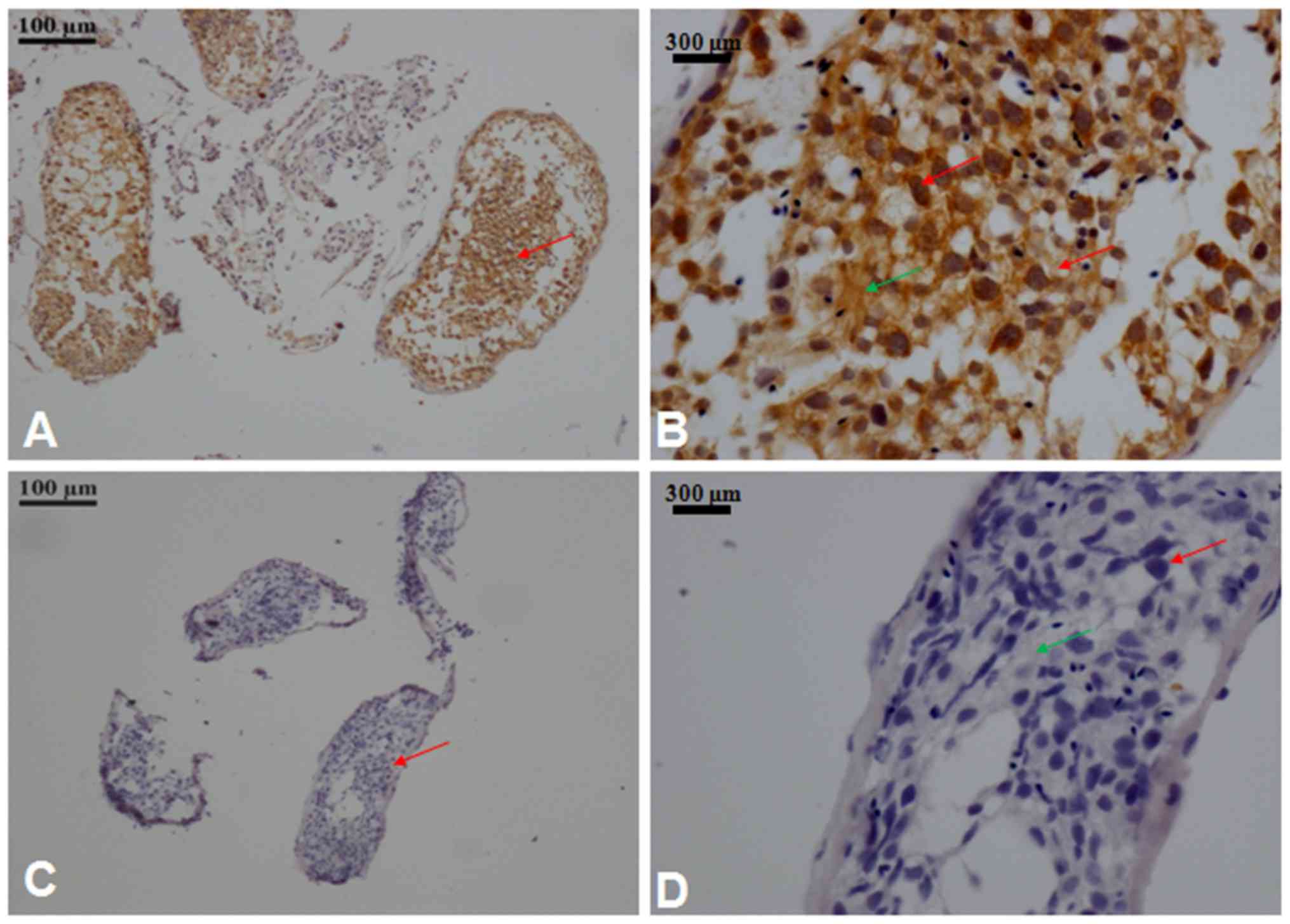
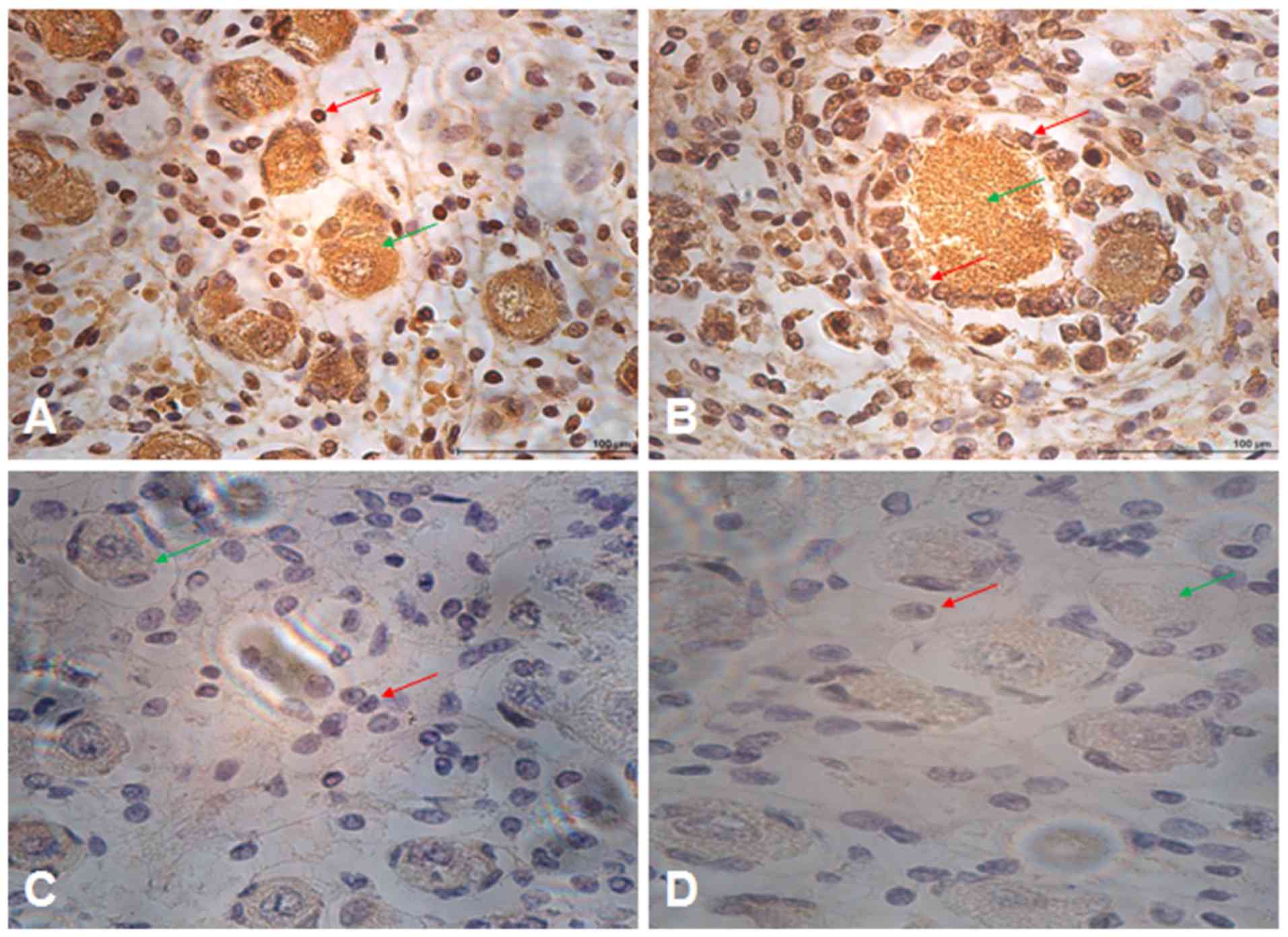
Puverel S, Barrick C, Dolci S, Coppola V
and Tessarollo L: RanBPM is essential for mouse spermatogenesis and
oogenesis. Development. 138:2511–2521. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ponting C, Schultz J and Bork P: SPRY
domains in ryanodine receptors (Ca(2+)-release channels). Trends
Biochem Sci. 22:193–194. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Perfetto L, Gherardini PF, Davey NE,
Diella F, Helmer-Citterich M and Cesareni G: Exploring the
diversity of SPRY/B30.2-mediated interactions. Trends Biochem Sci.
38:38–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Menon RP, Gibson TJ and Pastore A: The C
terminus of fragile X mental retardation protein interacts with the
multi-domain Ran-binding protein in the microtubule-organising
centre. J Mol Biol. 343:43–53. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Emes RD and Ponting CP: A new sequence
motif linking lissencephaly, Treacher Collins and
oral-facial-digital type 1 syndromes, microtubule dynamics and cell
migration. Hum Mol Genet. 10:2813–2820. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim MH, Cooper DR, Oleksy A, Devedjiev Y,
Derewenda U, Reiner O, Otlewski J and Derewenda ZS: The structure
of the N-terminal domain of the product of the lissencephaly gene
Lis1 and its functional implications. Structure. 12:987–998. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gerlitz G, Darhin E, Giorgio G, Franco B
and Reiner O: Novel functional features of the Lis-H domain: Role
in protein dimerization, half-life and cellular localization. Cell
Cycle. 4:1632–1640. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nishitani H, Hirose E, Uchimura Y,
Nakamura M, Umeda M, Nishii K, Mori N and Nishimoto T: Full-sized
RanBPM cDNA encodes a protein possessing a long stretch of proline
and glutamine within the N-terminal region, comprising a large
protein complex. Gene. 272:25–33. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kobayashi N, Yang J, Ueda A, Suzuki T,
Tomaru K, Takeno M, Okuda K and Ishigatsubo Y: RanBPM, Muskelin,
p48EMLP, p44CTLH, and the armadillo-repeat proteins ARMC8alpha and
ARMC8beta are components of the CTLH complex. Gene. 396:236–247.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Umeda M, Nishitani H and Nishimoto T: A
novel nuclear protein, Twa1, and Muskelin comprise a complex with
RanBPM. Gene. 303:47–54. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salemi LM, Almawi AW, Lefebvre KJ and
Schild-Poulter C: Aggresome formation is regulated by RanBPM
through an interaction with HDAC6. Biol Open. 3:418–430. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brunkhorst A, Karlén M, Shi J, Mikolajczyk
M, Nelson MA, Metsis M and Hermanson O: A specific role for the
TFIID subunit TAF4 and RanBPM in neural progenitor differentiation.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 29:250–258. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang Y, Paramasivam M, Girgenti MJ,
Walikonis RS, Bianchi E and LoTurco JJ: RanBPM regulates the
progression of neuronal precursors through M-phase at the surface
of the neocortical ventricular zone. Dev Neurobiol. 70:1–15.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Togashi H, Schmidt EF and Strittmatter SM:
RanBPM contributes to Semaphorin3A signaling through plexin-A
receptors. J Neurosci. 26:4961–4969. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kramer S, Ozaki T, Miyazaki K, Kato C,
Hanamoto T and Nakagawara A: Protein stability and function of p73
are modulated by a physical interaction with RanBPM in mammalian
cultured cells. Oncogene. 24:938–944. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hafizi S, Gustafsson A, Stenhoff J and
Dahlbäck B: The Ran binding protein RanBPM interacts with Axl and
Sky receptor tyrosine kinases. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
37:2344–2356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Valiyaveettil M, Bentley AA, Gursahaney P,
Hussien R, Chakravarti R, Kureishy N, Prag S and Adams JC: Novel
role of the muskelin-RanBP9 complex as a nucleocytoplasmic mediator
of cell morphology regulation. J Cell Biol. 182:727–739. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zou Y, Lim S, Lee K, Deng X and Friedman
E: Serine/threonine kinase Mirk/Dyrk1B is an inhibitor of
epithelial cell migration and is negatively regulated by the Met
adaptor Ran-binding protein M. J Biol Chem. 278:49573–49581. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Poirier MB, Laflamme L and Langlois MF:
Identification and characterization of RanBPM, a novel coactivator
of thyroid hormone receptors. J Mol Endocrinol. 36:313–325. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bai D, Chen H and Huang BR: RanBPM is a
novel binding protein for p75NTR. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
309:552–557. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mikolajczyk M, Shi J, Vaillancourt RR,
Sachs NA and Nelson M: The cyclin-dependent kinase 11(p46) isoform
interacts with RanBPM. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 310:14–18. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhuang XJ, Shi YQ, Xu B, Chen L, Tang WH,
Huang J, Lian Y, Liu P and Qiao J: SLX2 interacting with BLOS2 is
differentially expressed during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation.
Cell Cycle. 13:2231–2237. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhuang XJ, Tang WH, Feng X, Liu CY, Zhu
JL, Yan J, Liu DF, Liu P and Qiao J: Trim27 interacts with Slx2, is
associated with meiotic processes during spermatogenesis. Cell
Cycle. 15:2576–2584. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhuang XJ, Lu YQ, Zhang M, Lu SS and Lu
KH: Microisolation and microcloning of bovine X-chromosomes for
identification of sorted buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) spermatozoa.
Anim Reprod Sci. 126:32–36. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhuang XJ, Tang WH, Liu CY, Zhu JL, Feng
X, Yan J, Lian Y, Liu P and Qiao J: Identification and
characterization of Xlr5c as a novel nuclear localization protein
in mouse germ cells. PLoS One. 10:e01300872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi YQ, Liao SY, Zhuang XJ and Han CS:
Mouse Fem1b interacts with and induces ubiquitin-mediated
degradation of Ankrd37. Gene. 485:153–159. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhuang XJ, Hou XJ, Liao SY, Wang XX, Cooke
HJ, Zhang M and Han C: SLXL1, a novel acrosomal protein, interacts
with DKKL1 and is involved in fertilization in mice. PLoS One.
6:e208662011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi YQ, Zhuang XJ, Xu B, Hua J, Liao SY,
Shi Q, Cooke HJ and Han C: SYCP3-like X-linked 2 is expressed in
meiotic germ cells and interacts with synaptonemal complex central
element protein 2 and histone acetyltransferase TIP60. Gene.
527:352–359. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Denti S, Sirri A, Cheli A, Rogge L,
Innamorati G, Putignano S, Fabbri M, Pardi R and Bianchi E: RanBPM
is a phosphoprotein that associates with the plasma membrane and
interacts with the integrin LFA-1. J Biol Chem. 279:13027–13034.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D, Li Z, Messing EM and Wu G:
Activation of Ras/Erk pathway by a novel MET-interacting protein
RanBPM. J Biol Chem. 277:36216–36222. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Murrin LC and Talbot JN: RanBPM, a
scaffolding protein in the immune and nervous systems. J
Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2:290–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yin YX, Sun ZP, Huang SH, Zhao L, Geng Z
and Chen ZY: RanBPM contributes to TrkB signaling and regulates
brain-derived neurotrophic factor-induced neuronal morphogenesis
and survival. J Neurochem. 114:110–121. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tang X, Zhang J, Cai Y, Miao S, Zong S,
Koide SS and Wang L: Sperm membrane protein (hSMP-1) and RanBPM
complex in the microtubule-organizing centre. J Mol Med (Berl).
82:383–388. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|