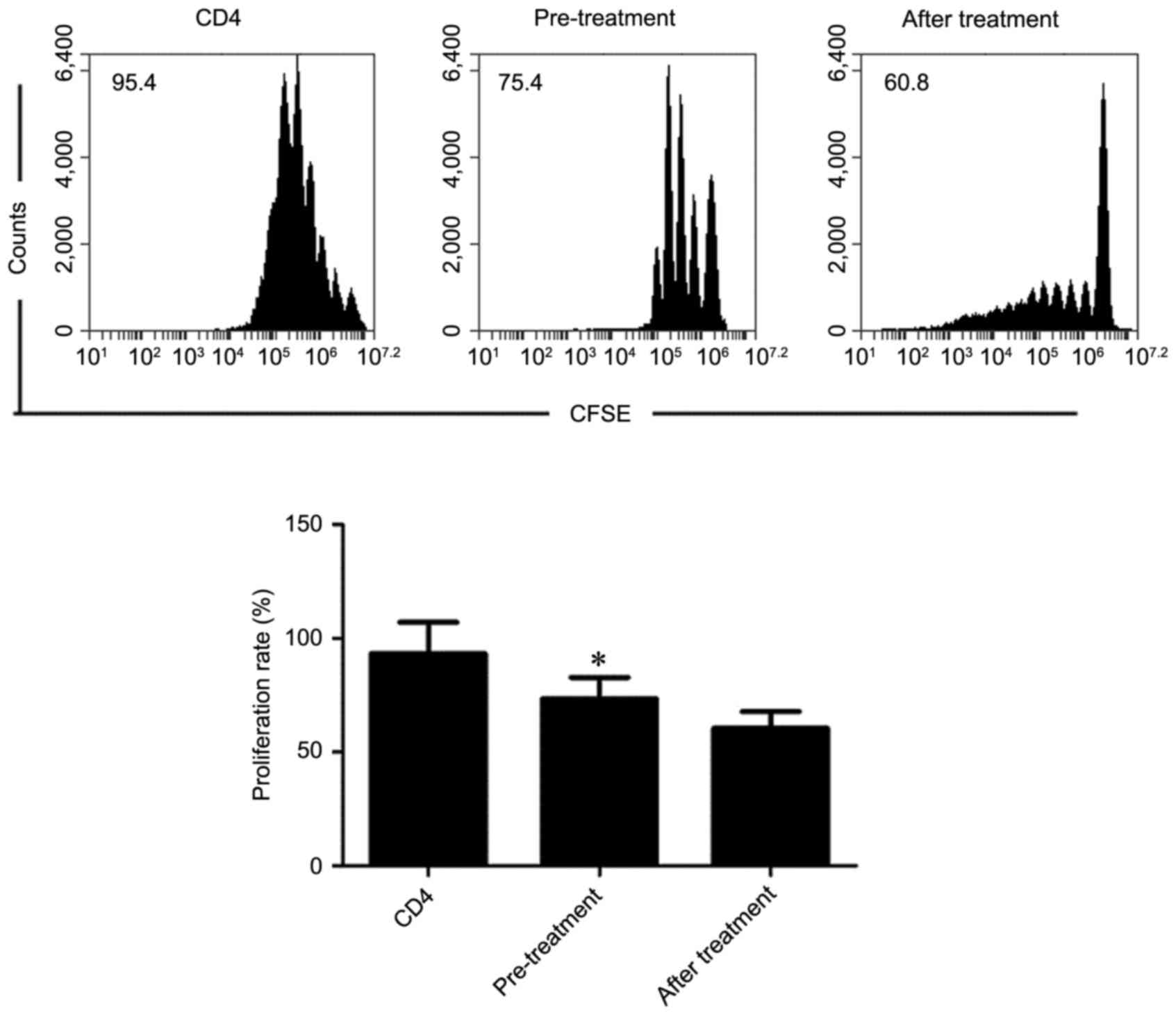
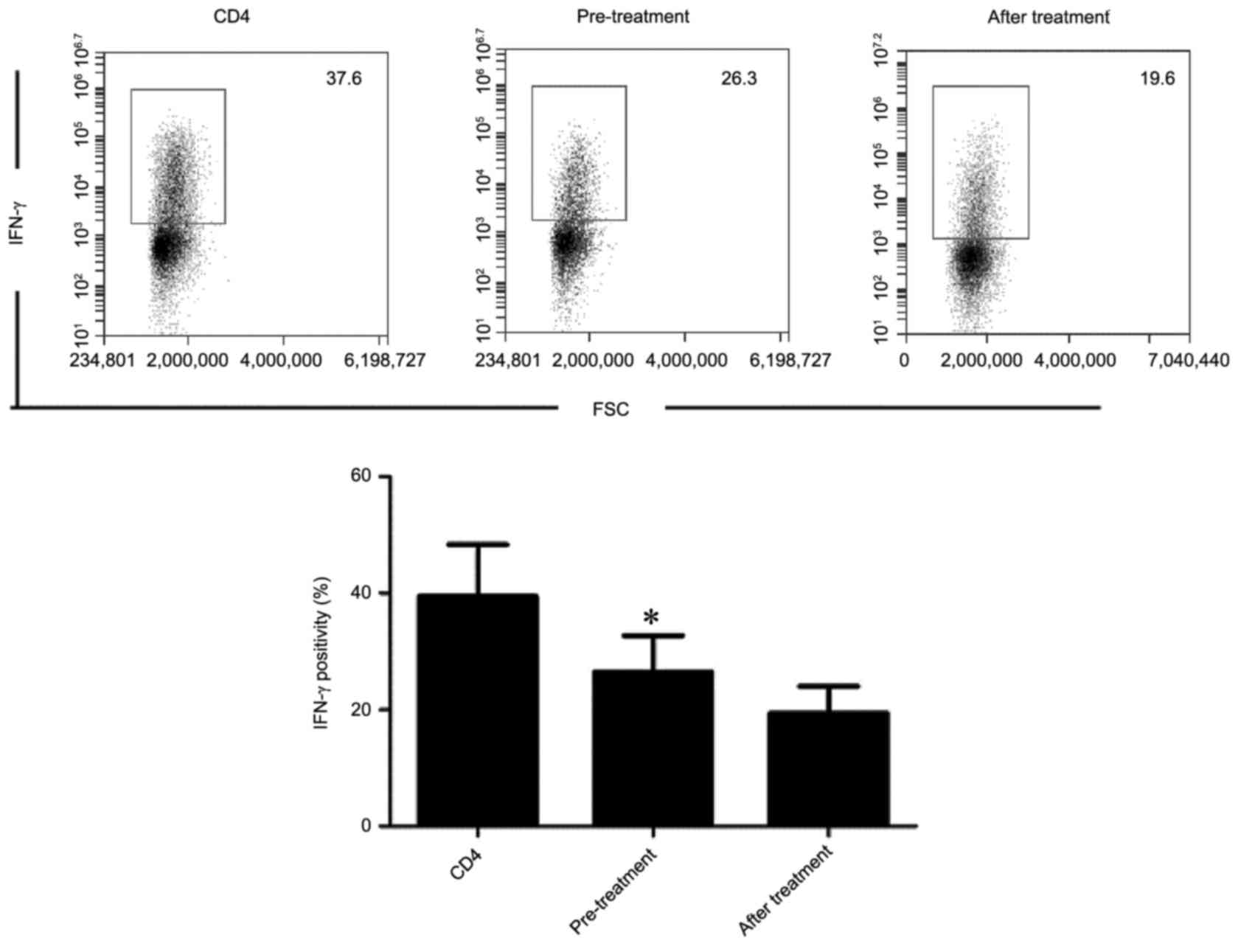
|
1
|
Vanderpump MPJ: The epidemiology of
thyroid disease. Br Med Bull. 99:39–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mao C, Wang S, Xiao Y, Xu J, Jiang Q, Jin
M, Jiang X, Guo H, Ning G and Zhang Y: Impairment of regulatory
capacity of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells mediated by dendritic cell
polarization and hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. J Immunol.
186:4734–4743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klatka M, Kaszubowska L, Grywalska E,
Wasiak M, Szewczyk L, Foerster J, Cyman M and Rolinski J: Treatment
of Graves' disease with methimazole in children alters the
proliferation of Treg cells and CD3+ T lymphocytes. Folia Histochem
Cytobiol. 52:69–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hamari S, Kirveskoski T, Glumoff V,
Kulmala P, Simell O, Knip M and Veijola R: Analyses of regulatory
CD4+ CD25+ FOXP3+ T cells and observations from peripheral T cell
subpopulation markers during the development of type 1 diabetes in
children. Scand J Immunol. 83:279–287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Legorreta-Haquet MV, Chávez-Rueda K,
Chávez-Sánchez L, Cervera-Castillo H, Zenteno-Galindo E,
Barile-Fabris L, Burgos-Vargas R, Álvarez-Hernández E and
Blanco-Favela F: Function of treg cells decreased in patients with
systemic lupus erythematosus due to the effect of prolactin.
Medicine (Baltimore). 95:e23842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu Y, Tian W, Zhang LL, Liu H, Yin GP, He
BS and Mao XM: Function of regulatory T-cells improved by
dexamethasone in Graves' disease. Eur J Endocrinol. 166:641–646.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Saitoh O and Nagayama Y: Regulation of
Graves' hyperthyroidism with naturally occurring CD4+CD25+
regulatory T cells in a mouse model. Endocrinology. 147:2417–2422.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nagayama Y, Horie I, Saitoh O, Nakahara M
and Abiru N: CD4+CD25+ naturally occurring regulatory T cells and
not lymphopenia play a role in the pathogenesis of iodide-induced
autoimmune thyroiditis in NOD-H2h4 mice. J Autoimmun. 29:195–202.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mao C, Wang S, Xiao Y, Xu J, Jiang Q, Jin
M, Jiang X, Guo H, Ning G and Zhang Y: Impairment of regulatory
capacity of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells mediated by dendritic
cell polarization and hyperthyroidism in Graves' disease. J
Immunol. 186:4734–4743. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He K, Hu Y and Mao X: Abnormal proportions
of immune regulatory cells and their subsets in peripheral blood of
patients with Graves' disease. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
30:1190–1193. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lantz M, Calissendorff J, Träisk F,
Tallstedt L, Planck T, Törring O, Hallengren B and Åsman P:
Adjuvant treatment of graves' disease with diclofenac: Safety,
effects on ophthalmopathy and antibody concentrations. Eur Thyroid
J. 5:50–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JF, Gao J, Zhang D, Wang ZH and Zhu
JY: CD4+Foxp3+ regulatory T cells converted by rapamycin from
peripheral CD4+CD25(−) naive T cells display more potent regulatory
ability in vitro. Chin Med J (Engl). 123:942–948. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singhal N, Praveen VP, Bhavani N, Menon
AS, Menon U, Abraham N, Kumar H, JayKunmar RV, Nair V, Sundaram S
and Sundaram P: Technetium uptake predicts remission and relapse in
Grave's disease patients on antithyroid drugs for at least 1 year
in South Indian subjects. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 20:157–161.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Allencherril J and Birnbaum I: Heart
failure in thyrotoxic cardiomopathy: Extracorporeal membrane
oxygenation treatment for graves' disease. J Extra Corpor Technol.
47:231–232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kaaroud H, Oueslati I, Harzallah A, Ben
Nacef I, Khiari K and Ben Hamida F: Benzylthiouracil induced ANCA
associated glomerulonephritis in patients with graves' disease.
Tunis Med. 93:696–701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sasazuki T, Inoko H, Morishima S and
Morishima Y: Gene map of the HLA region, graves' disease and
hshimoto thyroiditis, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.
Adv Immunol. 129:175–249. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Côté-Bigras S, Tran V, Turcotte S,
Rola-Pleszczynski M, Verrerult J and Rottembourg D: Impaired immune
regulation after radioiodine therapy for Graves' disease and the
protective effect of Methimazole. Endocrine. 52:587–596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wei Y, Zheng D, Li X, Zhou W, Qian Y, Ming
C and Shi B: Infusion of dendritic cells carrying donor lymphocytes
treated with 8-methoxypsoralen and ultraviolet A light induces
CD19+IL-10+ regulatory B cells and promotes skin allograft
survival. Transplant Proc. 46:pp. 3641–3646. 2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li Q, Guo Z, Xu X, Xia X and Cao X:
Pulmonary stromal cells induce the generation of regulatory DC
attenuating T-cell-mediated lung inflammation. Eur J Immunol.
38:2751–2761. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng G, Wang HY, Peng W, Kiniwa Y, Seo KH
and Wang RF: Tumor-infiltrating gammadelta T cells suppress T and
dendritic cell function via mechanisms controlled by a unique
toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Immunity. 27:334–348. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mao XM, Li HQ, Li Q, Li DM, Xie XJ, Yin
GP, Zhang P, Xu XH, Wu JD, Chen SW and Wang SK: Prevention of
relapse of Graves' disease by treatment with an intrathyroid
injection of dexamethasone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:4984–4991.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|