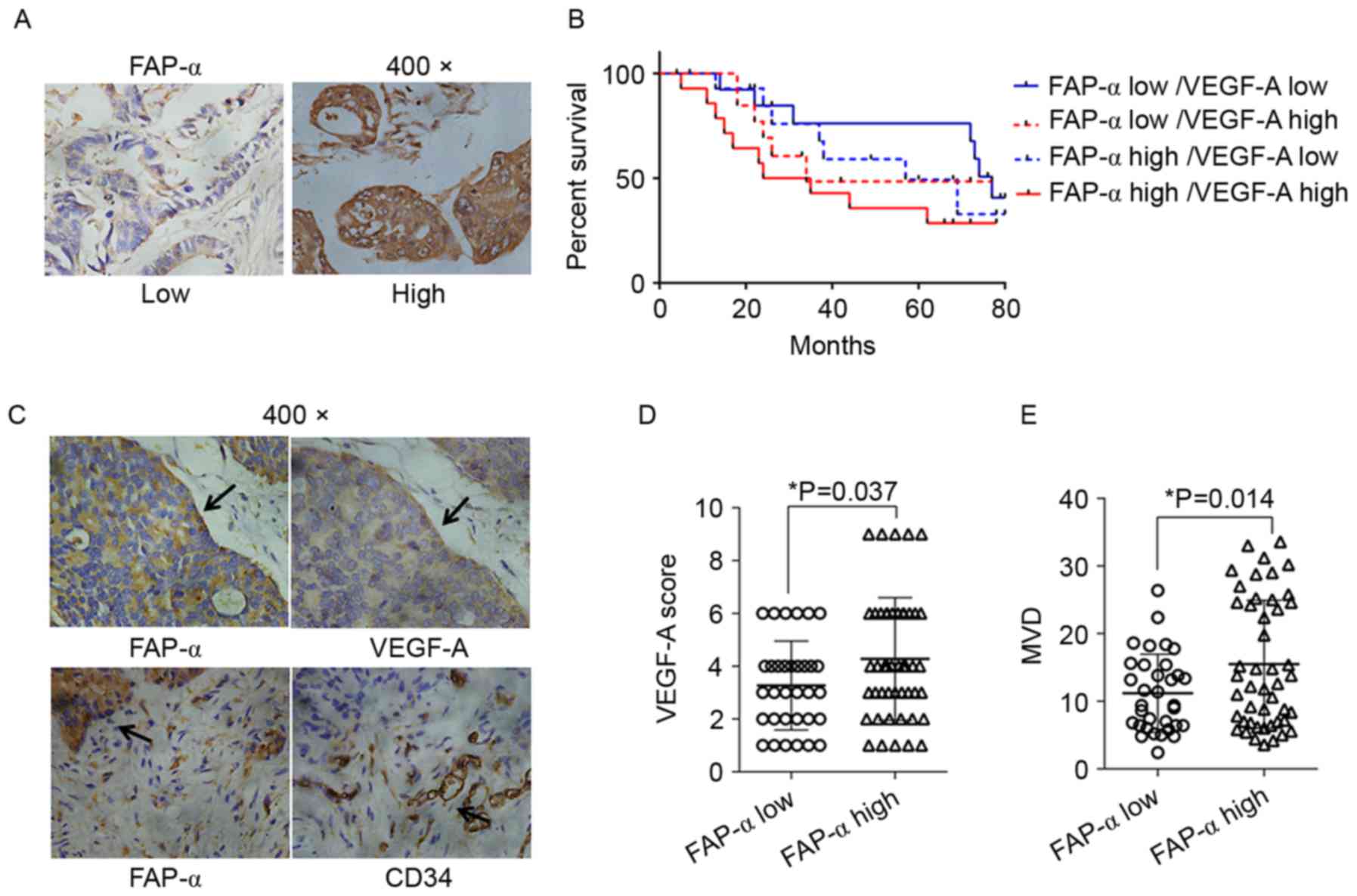
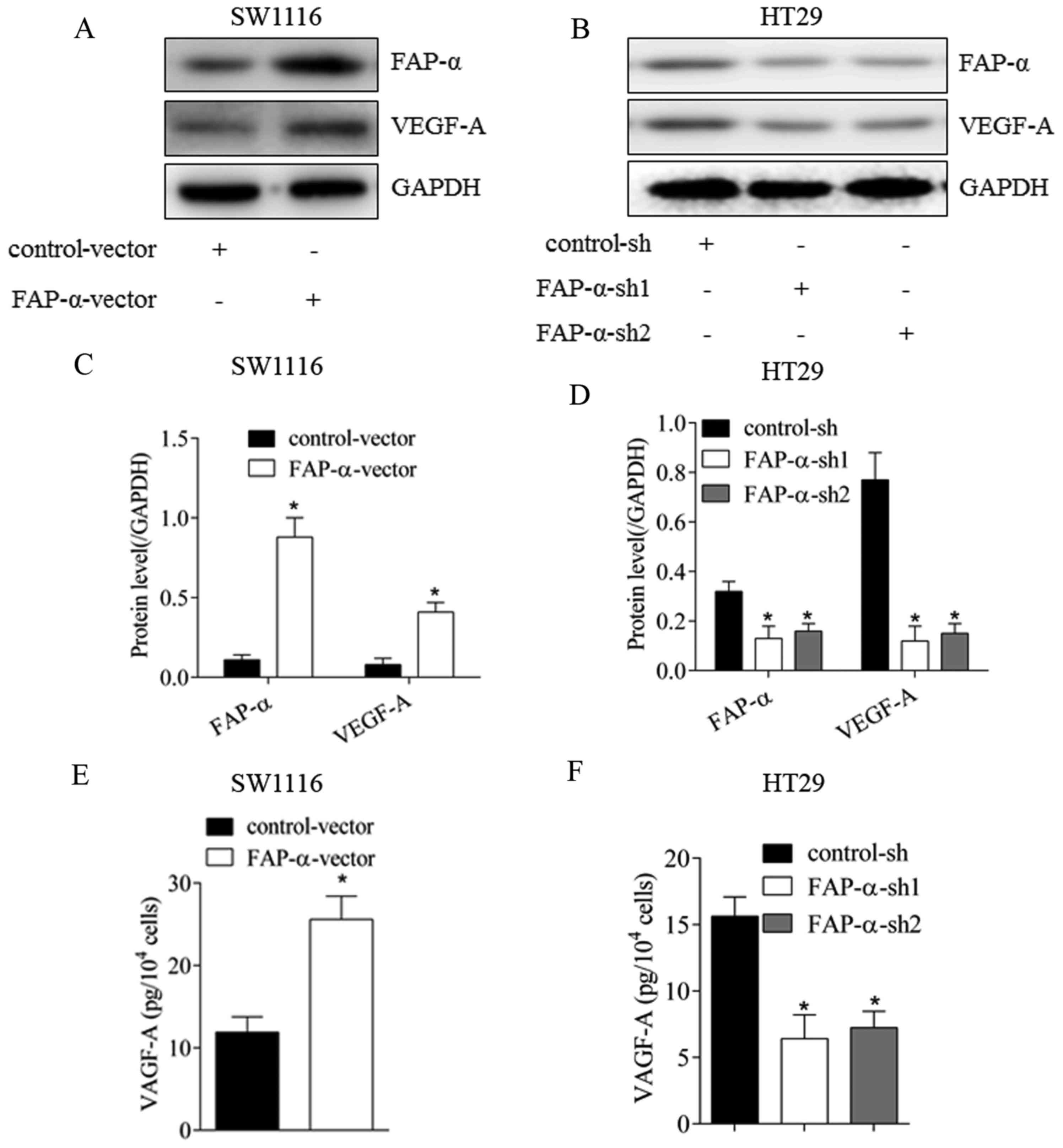
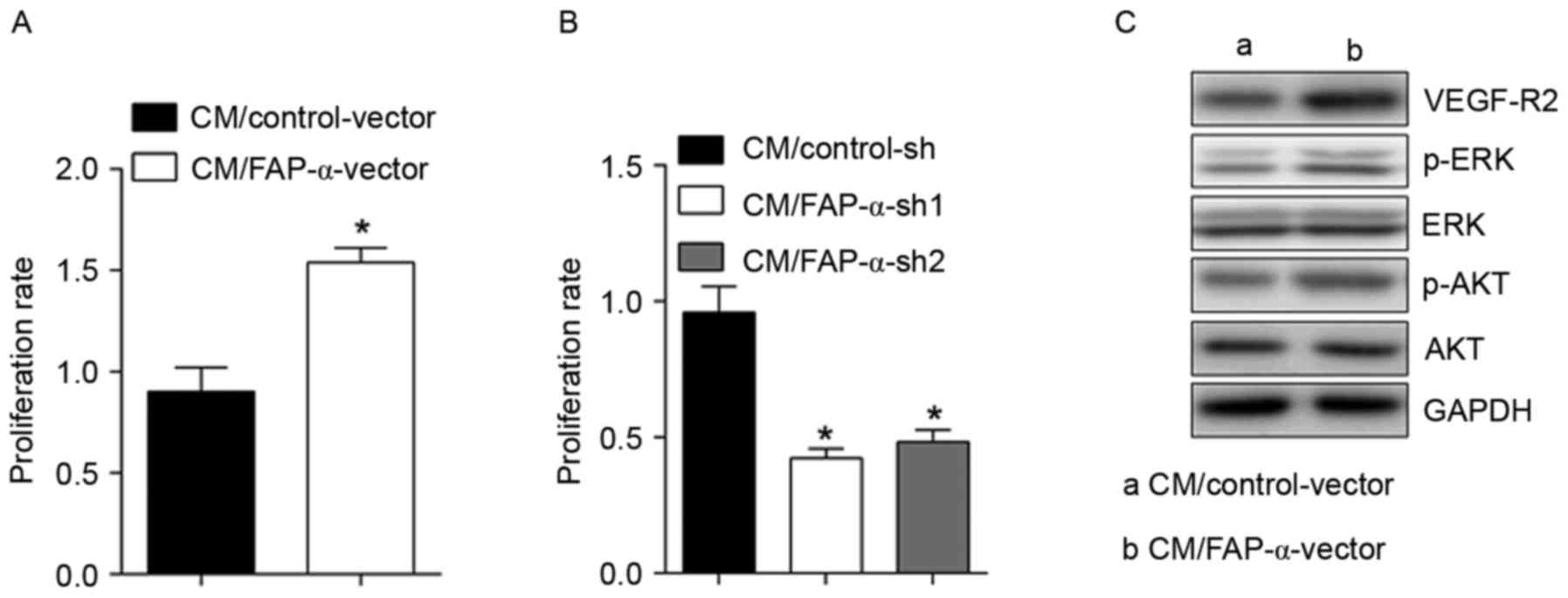
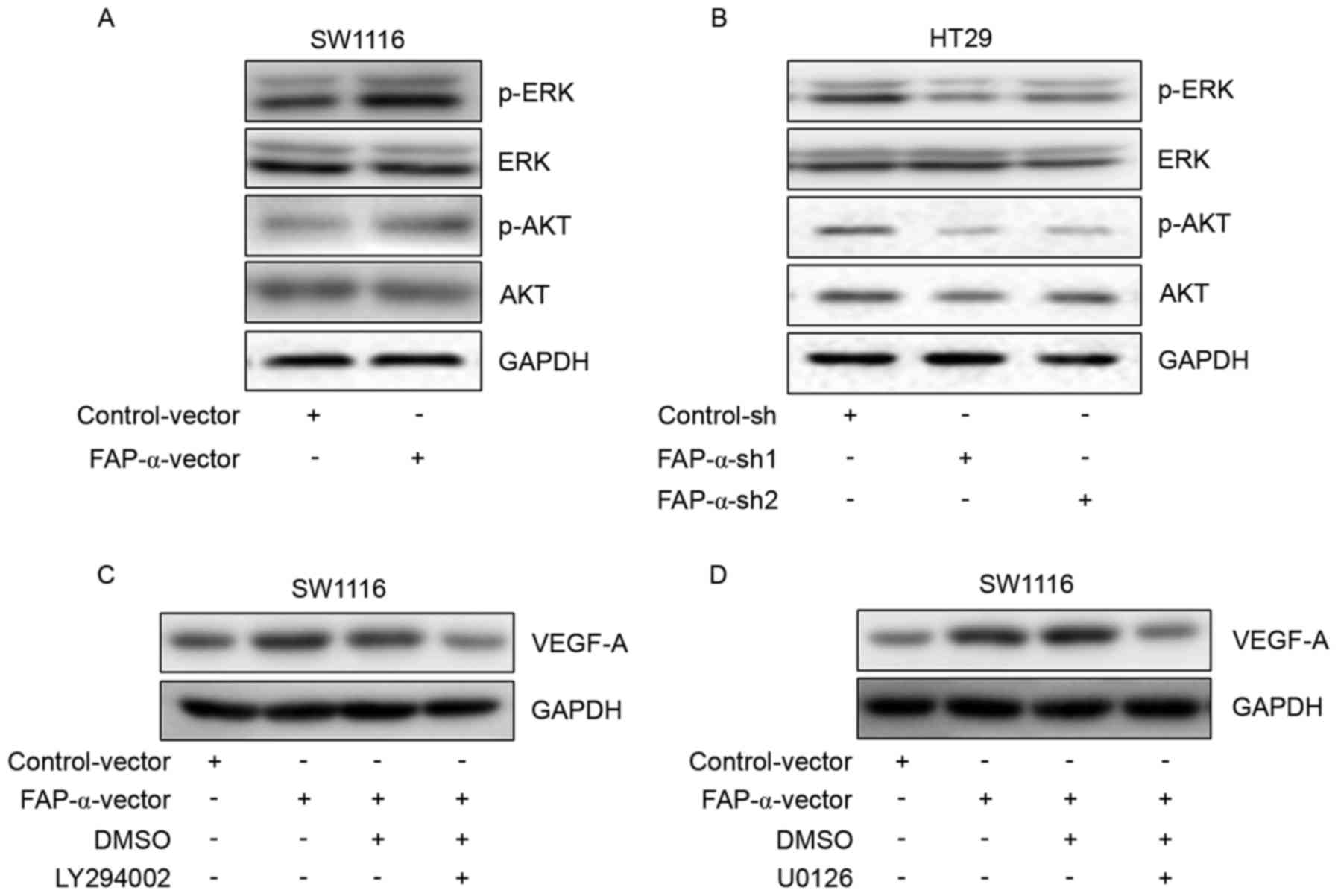
|
1
|
Hubbard JM: Management of colorectal
cancer in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 32:97–111. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arcaroli JJ, Tai WM, McWilliams R, Bagby
S, Blatchford PJ, Varella-Garcia M, Purkey A, Quackenbush KS, Song
EK, Pitts TM, et al: A NOTCH1 gene copy number gain is a prognostic
indicator of worse survival and a predictive biomarker to a Notch1
targeting antibody in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:195–205.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dickinson KJ and Blackmon SH: Results of
pulmonary resection: Colorectal carcinoma. Thorac Surg Clin.
26:41–47. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuijer A, Furnée EJ and Smakman N:
Combined surgery for primary colorectal cancer and synchronous
pulmonary metastasis: A pilot experience in two patients. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 28:15–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Zhao Q, Wang J and He X:
MicroRNA-10a influences osteoblast differentiation and angiogenesis
by regulating β-catenin expression. Cell Physiol Biochem.
37:2194–2208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salem A and O'Connor JP: Assessment of
tumor angiogenesis: Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and
beyond. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 24:45–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Yan L, Sharifian M,
Ren X, Liu S, Kim G, Gayther SA, Pejovic T and Lawrenson K: Stromal
expression of fibroblast activation protein alpha (FAP) predicts
platinum resistance and shorter recurrence in patients with
epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Microenviron. 8:23–31. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang Y, Wang S and Kelly T: Seprase
promotes rapid tumor growth and increased microvessel density in a
mouse model of human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 64:2712–2716. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng JD, Dunbrack RL Jr, Valianou M,
Rogatko A, Alpaugh RK and Weiner LM: Promotion of tumor growth by
murine fibroblast activation protein, a serine protease, in an
animal model. Cancer Res. 62:4767–4772. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwasa S, Jin X, Okada K, Mitsumata M and
Ooi A: Increased expression of seprase, a membrane-type serine
protease, is associated with lymph node metastasis in human
colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 199:91–98. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB,
Colpaert C, Marson LP, Gion M, Beliën JA, de Waal RM, Van Marck E,
Magnani E, et al: Second international consensus on the methodology
and criteria of evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid
human tumours. Eur J Cancer. 38:1564–1579. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kelly T1, Huang Y, Simms AE and Mazur A:
Fibroblast activation protein-α: A key modulator of the
microenvironment in multiple pathologies. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
297:83–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang Y, Simms AE, Mazur A, Wang S, León
NR, Jones B, Aziz N and Kelly T: Fibroblast activation protein-α
promotes tumor growth and invasion of breast cancer cells through
non-enzymatic functions. Clin Exp Metastasis. 28:567–579. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wikberg ML, Edin S, Lundberg IV, Van
Guelpen B, Dahlin AM, Rutegård J, Stenling R, Oberg A and Palmqvist
R: High intratumoral expression of fibroblast activation protein
(FAP) in colon cancer is associated with poorer patient prognosis.
Tumour Biol. 34:1013–1020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schauer IG, Sood AK, Mok S and Liu J:
Cancer-associated fibroblasts and their putative role in
potentiating the initiation and development of epithelial ovarian
cancer. Neoplasia. 13:393–405. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kelly T, Kechelava S, Rozypal TL, West KW
and Korourian S: Seprase, a membrane-bound protease, is
overexpressed by invasive ductal carcinoma cells of human breast
cancers. Mod Pathol. 11:855–863. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi M, Yu DH, Chen Y, Zhao CY, Zhang J,
Liu QH, Ni CR and Zhu MH: Expression of fibroblast activation
protein in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its
clinicopathological significance. World J Gastroenterol.
18:840–846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mori Y, Kono K, Matsumoto Y, Fujii H,
Yamane T, Mitsumata M and Chen WT: The expression of a type II
transmembrane serine protease (Seprase) in human gastric carcinoma.
Oncology. 67:411–419. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang H, Wu Q, Liu Z, Luo X, Fan Y, Liu Y,
Zhang Y, Hua S, Fu Q, Zhao M, et al: Downregulation of FAP
suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT
and Ras-ERK signaling in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death
Dis. 5:e11552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kennedy A, Dong H, Chen D and Chen WT:
Elevation of seprase expression and promotion of an invasive
phenotype by collagenous matrices in ovarian tumor cells. Int J
Cancer. 124:27–35. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jin X, Iwasa S, Okada K, Mitsumata M and
Ooi A: Expression patterns of seprase, a membrane serine protease,
in cervical carcinoma and cervical intraepithelial neoplasm.
Anticancer Res. 23:3195–3198. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia J, Martin TA and Jiang WG: FAP-α
(fibroblast activation protein-α) is involved in the control of
human breast cancer cell line growth and motility via the FAK
pathway. BMC Cell Biol. 15:162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lai D, Ma L and Wang F: Fibroblast
activation protein regulates tumor-associated fibroblasts and
epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 41:541–550. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin J, Yun D, Tao Li, Yalei L, Yudong W,
Yan Z, Xinliang Z and Wei L: Differential expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor-A, -C and -D for the diagnosis and
prognosis of cancer patients with malignant effusions. Oncol Lett.
10:667–674. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhao H, Wu Y, Chen Y and Liu H: Clinical
significance of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and VEGF-A in
osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 20:1233–1243. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gheorghescu AK, Tywoniuk B, Duess J,
Buchete NV and Thompson J: Exposure of chick embryos to cadmium
changes the extra-embryonic vascular branching pattern and alters
expression of VEGF-A and VEGF-R2. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
289:79–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Adeoye OO, Bouthors V, Hubbell MC,
Williams JM and Pearce WJ: VEGF receptors mediate hypoxic
remodeling of adult ovine carotid arteries. J Appl Physiol (1985).
117:777–787. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
D'Amico MA, Ghinassi B, Izzicupo P, Di
Ruscio A and Di Baldassarre A: IL-6 activates PI3K and PKCζ
signaling and determines cardiac differentiation in rat embryonic
H9c2 cells. J Cell Physiol. 231:576–586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ge C, Cawthorn WP, Li Y, Zhao G,
Macdougald OA and Franceschi RT: Reciprocal control of osteogenic
and adipogenic differentiation by ERK/MAP kinase phosphorylation of
Runx2 and PPARγ transcription factors. J Cell Physiol. 231:587–596.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ishii M, Nakahara T, Ikeuchi S and
Nishimura M: β-amyrin induces angiogenesis in vascular endothelial
cells through the Akt/endothelial nitric oxide synthase signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:676–682. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|