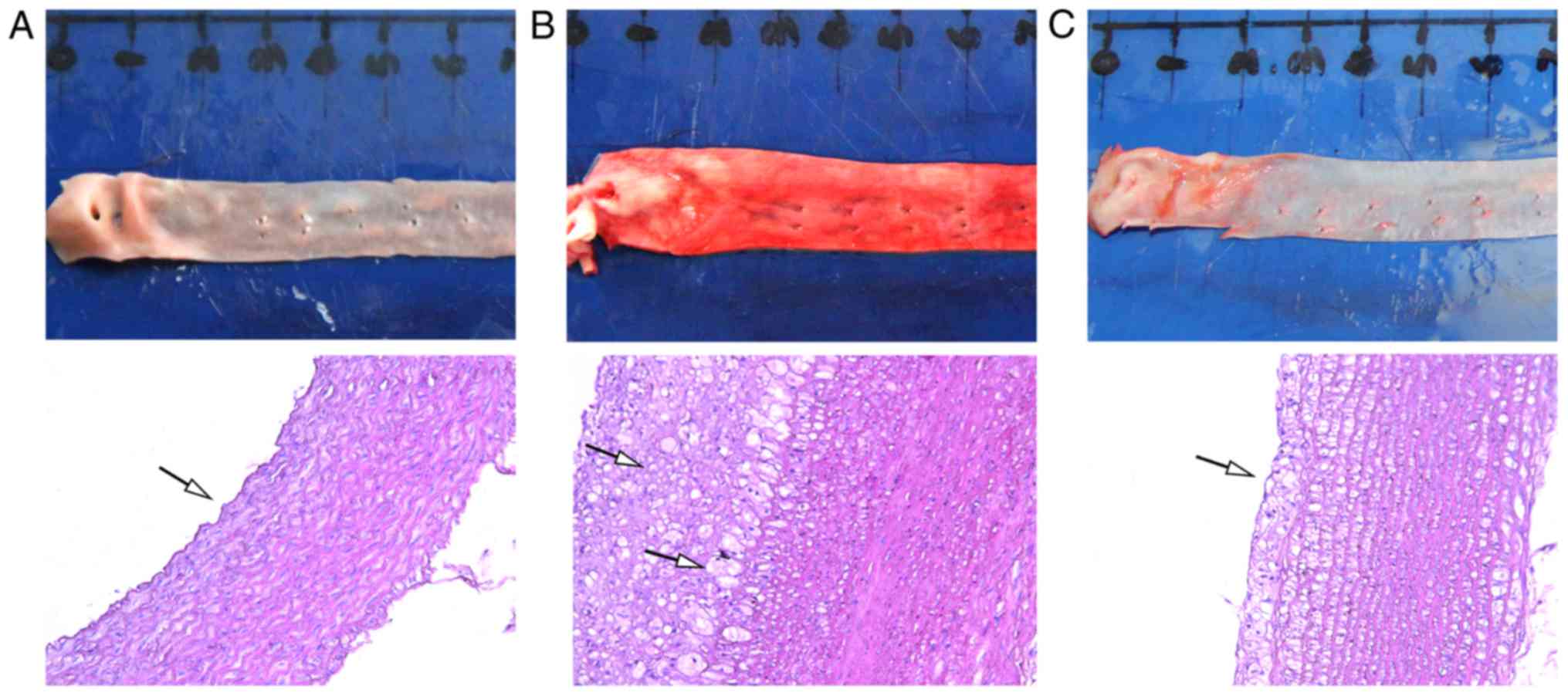
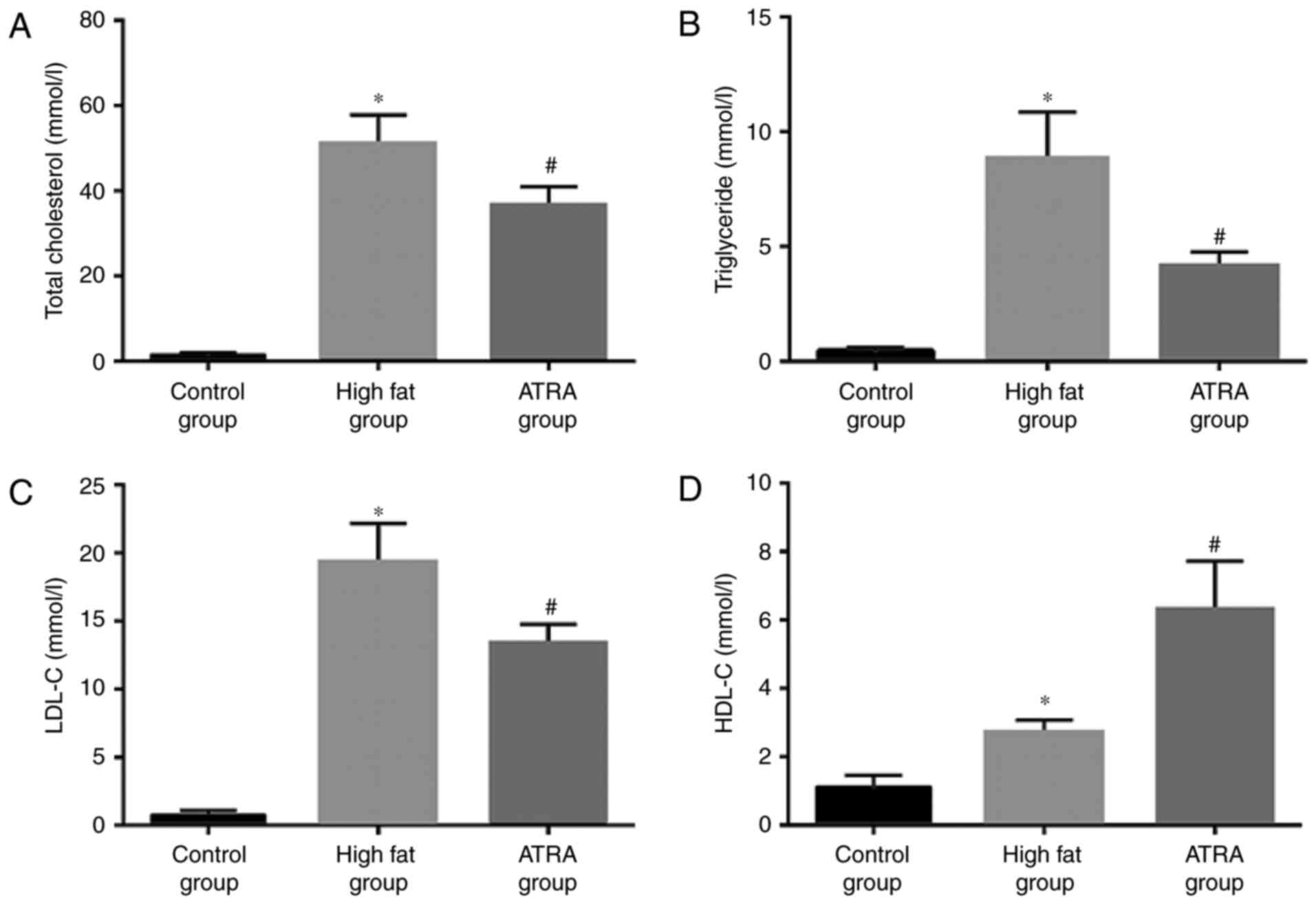
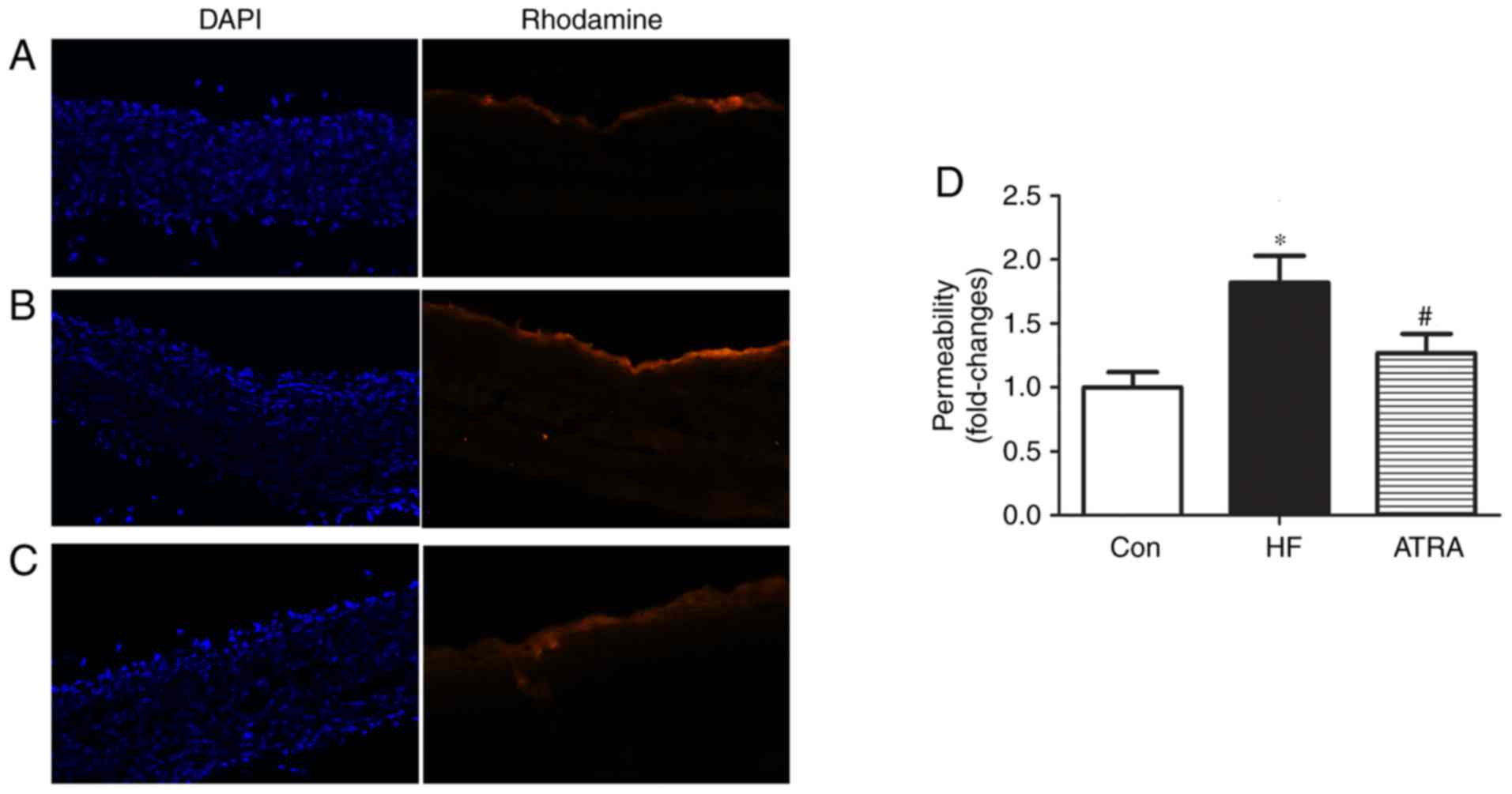
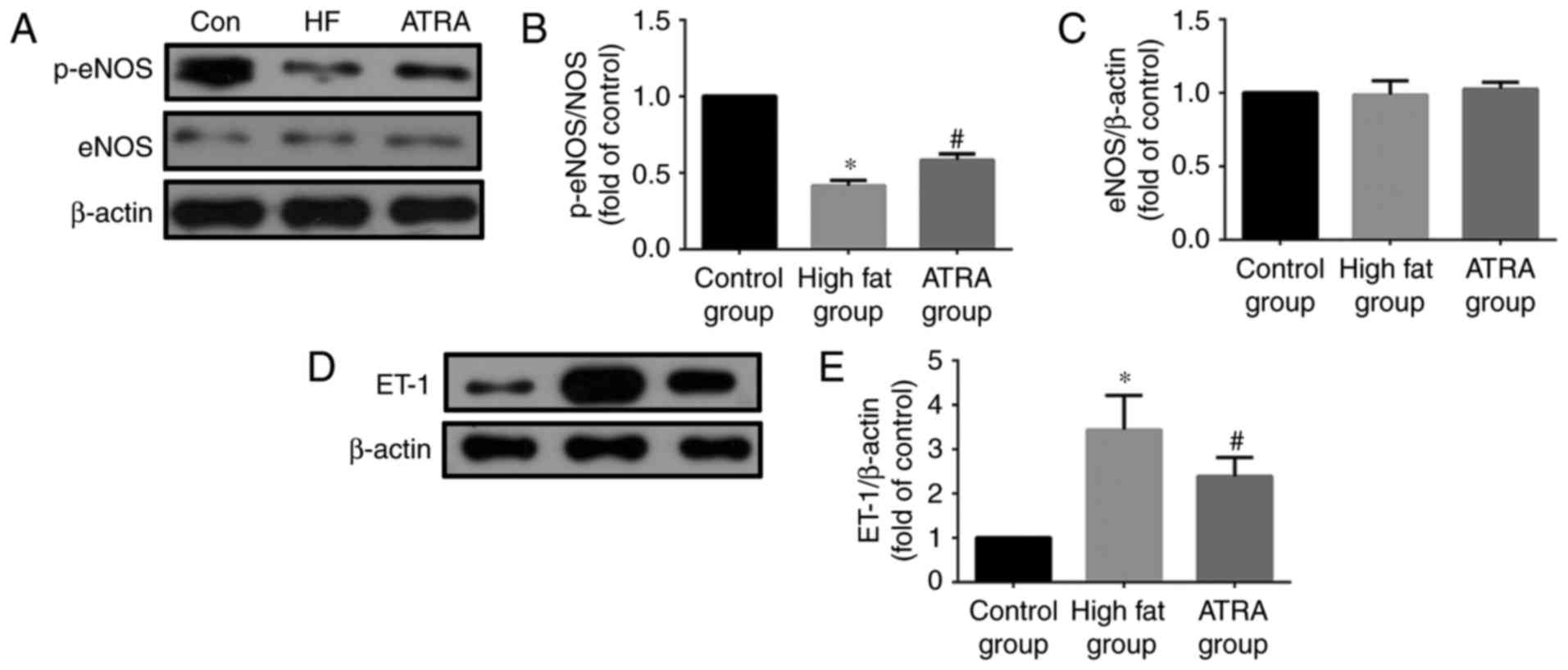
|
1
|
Bays HE: ‘Sick fat,’ metabolic disease,
and atherosclerosis. Am J Med. 122 Suppl 1:S26–S37. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bennett MR: Life and death in the
atherosclerotic plaque. Curr Opin Lipidol. 21:422–426. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baumgartner C, Brandl J, Münch G and
Ungerer M: Rabbit models to study atherosclerosis and its
complications-Transgenic vascular protein expression in vivo. Prog
Biophys Mol Biol. 121:131–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Genasetti A, Vigetti D, Viola M, Karousou
E, Moretto P, Rizzi M, Bartolini B, Clerici M, Pallotti F, De Luca
G and Passi A: Hyaluronan and human endothelial cell behavior.
Connect Tissue Res. 49:120–123. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Itakura H, Yokoyama M, Matsuzaki M, Saito
Y, Origasa H, Ishikawa Y, Oikawa S, Sasaki J, Hishida H, Kita T, et
al: Relationships between plasma fatty acid composition and
coronary artery disease. J Atheroscler Thromb. 18:99–107. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Libby P, Lichtman AH and Hansson GK:
Immune effector mechanisms implicated in atherosclerosis: From mice
to humans. Immunity. 38:1092–1104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harjes U, Bensaad K and Harris AL:
Endothelial cell metabolism and implications for cancer therapy. Br
J Cancer. 107:1207–1212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Fu L, Gao Q and Ma D: Valsartan
alleviates atherosclerotic lesions in pulmonary arteries of rabbits
via an endothelium-dependent mechanism. Acta Cardiol. 65:23–29.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo DX, Cheng J, Xiong Y, Li J, Xia C, Xu
C, Wang C, Zhu B, Hu Z and Liao DF: Static pressure drives
proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells via caveolin-1/ERK1/2
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:1693–1697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gkaliagkousi E and Ferro A: Nitric oxide
signalling in the regulation of cardiovascular and platelet
function. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:1873–1897. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang B and Rizzo V: TNF-alpha potentiates
protein-tyrosine nitration through activation of NADPH oxidase and
eNOS localized in membrane rafts and caveolae of bovine aortic
endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 292:H954–H962.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Atochin DN and Huang PL: Endothelial
nitric oxide synthase transgenic models of endothelial dysfunction.
Pflugers Arch. 460:965–974. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bkaily G, Avedanian L, Al-Khoury J,
Provost C, Nader M, D'Orléans-Juste P and Jacques D: Nuclear
membrane receptors for ET-1 in cardiovascular function. Am J
Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 300:R251–R263. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Noy N: Between death and survival:
Retinoic acid in regulation of apoptosis. Annu Rev Nutr.
30:201–217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou B, Pan Y, Hu Z, Wang X, Han J, Zhou
Q, Zhai Z and Wang Y: All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorated high fat
diet-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits by inhibiting platelet
activation and inflammation. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012:2596932012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Libby P: Inflammation in atherosclerosis.
Nature. 420:868–874. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng Z, Li X, Diao S, et al: Effect of
all-trans retinoic acid on the atherosclerotic plaque and
inflammatory response in carotid artery of rabbits. J Guangdong
Pharm Univ. 32:639–642. 2016.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Wang X, Han J, Hu Z, et al: Effects of all
trans retinoic acid on vascular endothelial function in
atherosclerotic rabbits. Acta Univ Med Anhui. 47:150–153. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu HQ, Zhou Q, Jiang ZK, Gui SY and Wang
Y: Association of aorta intima permeability with myosin light chain
kinase expression in hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Mol Cell
Biochem. 347:209–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hansson GK: Inflammation, atherosclerosis,
and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1685–1695. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mizuno Y, Jacob RF and Mason RP:
Inflammation and the development of atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 18:1–358. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bilbija D, Elmabsout AA, Sagave J, Haugen
F, Bastani N, Dahl CP, Gullestad L, Sirsjö A, Blomhoff R and Valen
G: Expression of retinoic acid target genes in coronary artery
disease. Int J Mol Med. 33:677–686. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grace VM, Siddikuzzaman and Rimashree B:
Liposome encapsulated all trans retinoic acid (ATRA) has enhanced
immunomodulatory and inflammation reducing activities in mice
model. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 15:196–205. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reriani M, Raichlin E, Prasad A, Mathew V,
Pumper GM, Nelson RE, Lennon R, Rihal C, Lerman LO and Lerman A:
Long-term administration of endothelin receptor antagonist improves
coronary endothelial function in patients with early
atherosclerosis. Circulation. 122:958–966. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wågsater D, Jatta K, Ocaya P, Dimberg J
and Sirsjo A: Expression of IL-1beta, IL-1 receptor type I and IL-1
receptor antagonist in human aortic smooth muscle cells: Effects of
all-trans-retinoic acid. J Vasc Res. 43:377–382. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yanagisawa A and Lefer AM: Vasoactive
effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on isolated vascular smooth
muscle. Basic Res Cardiol. 82:186–196. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Granger JP, Abram S, Stec D, Chandler D
and LaMarca B: Endothelin, the kidney, and hypertension. Curr
Hypertens Rep. 8:298–303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li MW, Mian MO, Barhoumi T, Rehman A, Mann
K, Paradis P and Schiffrin EL: Endothelin-1 overexpression
exacerbates atherosclerosis and induces aortic aneurysms in
apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:2306–2315. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W and Li Y: Regulation of dHAND protein
expression by all-trans retinoic acid through ET-1/ETAR signaling
in H9c2 cells. J Cell Biochem. 99:478–484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu YR, Li PW, Suo JJ, Sun Y, Zhang BA, Lu
H, Zhu HC and Zhang GB: Catalpol provides protective effects
against cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury in gerbils. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 66:1265–1270. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan XB, Peng TC and Huang D: Correlations
between plasma endothelin-1 levels and breakthrough pain in
patients with cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3703–3706.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu Y, Buikema H, van Gilst WH and Henning
RH: Caveolae and endothelial dysfunction: Filling the caves in
cardiovascular disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 585:256–260. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Salvi E, Kuznetsova T, Thijs L, Lupoli S,
Stolarz-Skrzypek K, D'Avila F, Tikhonoff V, De Astis S, Barcella M,
Seidlerová J, et al: Target sequencing, cell experiments, and a
population study establish endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS)
gene as hypertension susceptibility gene. Hypertension. 62:844–852.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Böger RH: When the endothelium cannot say
‘NO’ anymore. ADMA, an endogenous inhibitor of NO synthase,
promotes cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart J. 24:1901–1902. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Facemire CS, Nixon AB, Griffiths R,
Hurwitz H and Coffman TM: Vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2 controls blood pressure by regulating nitric oxide
synthase expression. Hypertension. 54:652–658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yoon JJ, Lee YJ, Han BH, Choi ES, Kho MC,
Park JH, Ahn YM, Kim HY, Kang DG and Lee HS: Protective effect of
betulinic acid on early atherosclerosis in diabetic
apolipoprotein-E gene knockout mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 796:224–232.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, Cui J, Yang H, Liu W and Li Q:
Reno-protective effects of all trans retinoic acid on adriamycin
induced nephropathy in mice. J Chongqing Med Univ. 37:484–488.
2012.
|
|
39
|
Yuan LP, Chen ZW, Li F, Dong LY and Chen
FH: Protective effect of total flavones of rhododendra on ischemic
myocardial injury in rabbits. Am J Chin Med. 34:483–492. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rhee EJ, Nallamshetty S and Plutzky J:
Retinoid metabolism and its effects on the vasculature. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1821:230–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Achan V, Tran CT, Arrigoni F, Whitley GS,
Leiper JM and Vallance P: All-trans-Retinoic acid increases nitric
oxide synthesis by endothelial cells: A role for the induction of
dimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase. Circ Res. 90:764–769.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yokota J, Kawana M, Hidai C, Aoka Y,
Ichikawa K, Iguchi N, Okada M and Kasanuki H: Retinoic acid
suppresses endothelin-1 gene expression at the transcription level
in endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 159:491–496. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|