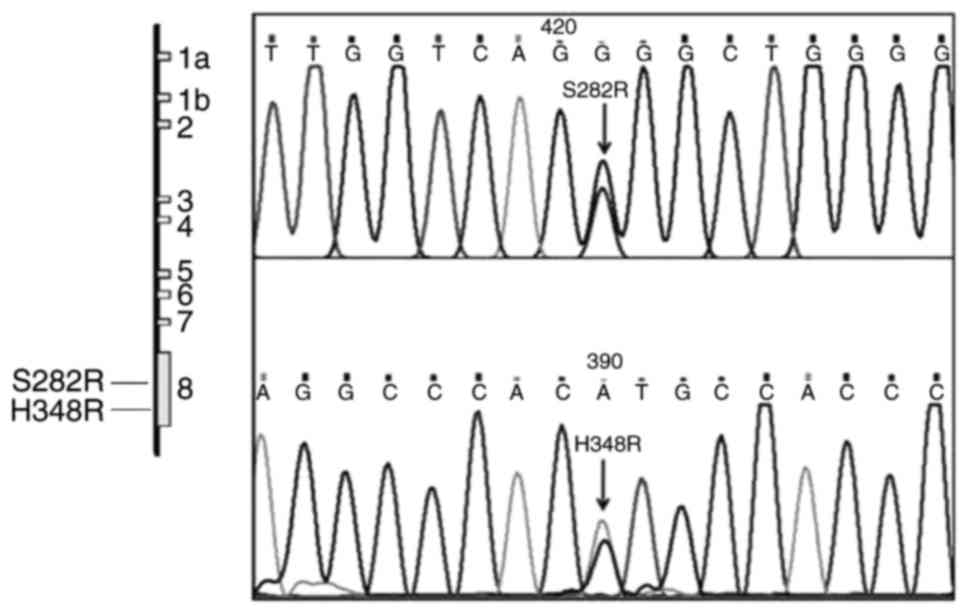
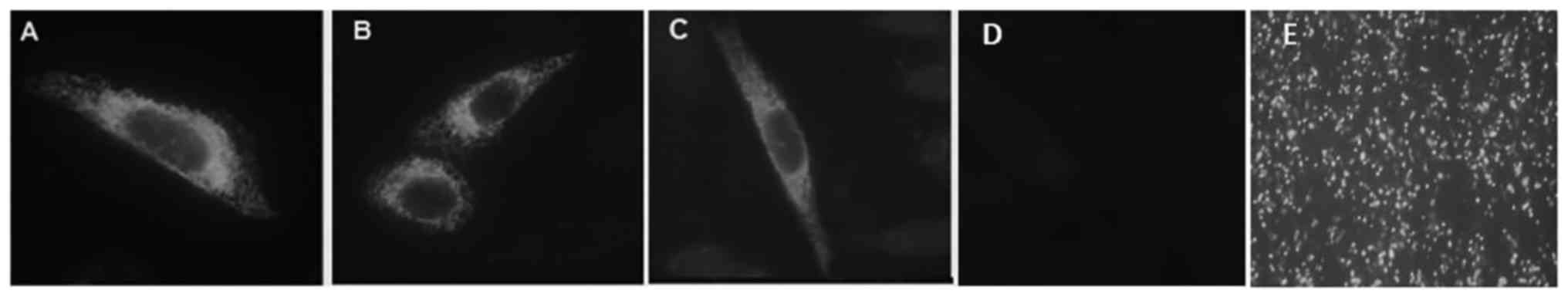
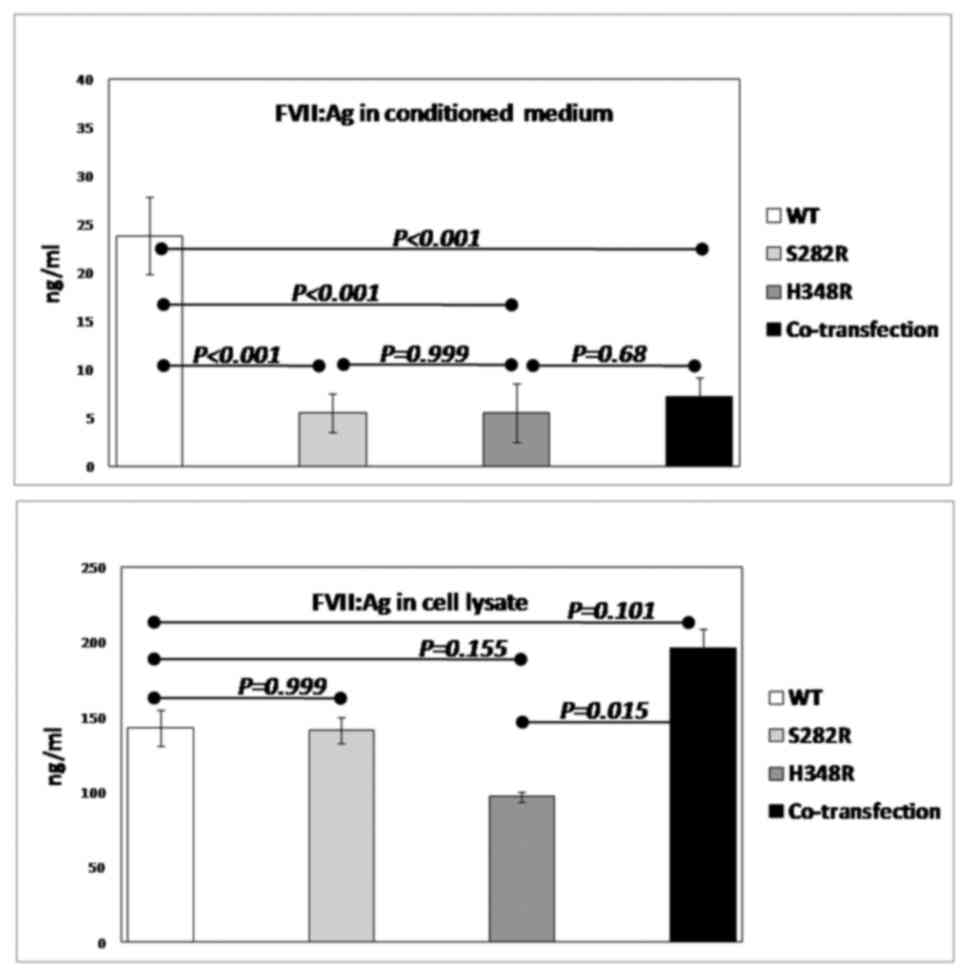
|
1
|
Hellstern P, Beeck H, Fellhauer A, Fischer
A and Faller-Stöckl B: Measurement of factor VII and of activated
factor VII in healthy individuals and in prothrombin complex
concentrates. Thromb Res. 86:493–504. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Millar DS, Kemball-Cook G, McVey JH,
Tuddenham EG, Mumford AD, Attock GB, Reverter JC, Lanir N, Parapia
LA, Reynaud J, et al: Molecular analysis of the genotype-phenotype
relationship in factor VII deficiency. Hum Genet. 107:327–342.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tanaka R, Nakashima D, Suzuki A, Miyawaki
Y, Fujimori Y, Yamada T, Takagi A, Murate T, Yamamoto K, Katsumi A,
et al: Impaired secretion of carboxyl-terminal truncated factor VII
due to an F7 nonsense mutation associated with FVII deficiency.
Thromb Res. 125:262–266. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O'Hara PJ, Grant FJ, Haldeman BA, Gray CL,
Insley MY, Hagen FS and Murray MJ: Nucleotide sequence of the gene
coding for human factor VII, a vitamin K-dependent protein
participating in blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 84:pp.
5158–5162. 1987; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagaizumi K, Inaba H, Suzuki T, Hatta Y,
Hagiwara T, Amano K, Arai M and Fukutake K: Two double heterozygous
mutations in the F7 gene show different manifestations. Br J
Haematol. 119:1052–1058. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shahbazi S: Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
among coagulation factor genes. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 19:344–349.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mariani G and Bernardi F: Factor VII
deficiency. Semin Thromb Hemos. 35:400–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mariani G, Herrmann FH, Dolce A, Batorova
A, Etro D, Peyvandi F, Wulff K, Schved JF, Auerswald G, Ingerslev
J, et al: Clinical phenotypes and factor VII genotype in congenital
factor VII deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 93:481–487. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu N, Aldea S, Francois D, Cherqui-Michel
M, Giansily-Blaizot M and Fischler M: Recombinant activated factor
VII for a patient with factor VII deficiency undergoing urgent
intracerebral haematoma evacuation with underlying cavernous
angioma. Br J Anaesth. 103:858–860. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ahmed RP, Biswas A, Kannan M, Bhattacharya
M, Geisen C, Seifried E, Oldenburg J and Saxena R: First report of
a FVII-deficient Indian patient carrying double heterozygous
mutations in the FVII gene. Thromb Res. 115:535–536. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peyvandi F, Jenkins PV, Mannucci PM,
Billio A, Zeinali S, Perkins SJ and Perry DJ: Molecular
characterisation and three-dimensional structural analysis of
mutations in 21 unrelated families with inherited factor VII
deficiency. Thromb Haemost. 84:250–257. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma W, Shi X, Lu S, Wu L and Wang Y:
Hypoxia-induced overexpression of DEC1 is regulated by HIF-1α in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 30:2957–2962. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang P, Xue D, Zhang Y, Ye L, Liu Y,
Makale M, Kesari S, Edgington TS and Liu C: The extrinsic
coagulation cascade and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in
macrophages: A potential therapeutic opportunity for
atherosclerotic thrombosis. Thromb Res. 133:657–666. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Quintavalle G, Riccardi F, Rivolta GF,
Martorana D, Di Perna C, Percesepe A and Tagliaferri A; Ad-Hoc
Study Group, : F7 gene variants modulate protein levels in a large
cohort of patients with factor VII deficiency. Results from a
genotype-phenotype study. Thromb Haemost. 117:1455–1464. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Girolami A, Cosi E, Ferrari S, Girolami B
and Lombardi AM: Bleeding manifestations in heterozygotes with
congenital FVII deficiency: A comparison with unaffected family
members during a long observation period. Hematology. 22:375–379.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hunault M, Arbini AA, Carew JA, Peyvandi F
and Bauer KA: Characterization of two naturally occurring mutations
in the second epidermal growth factor-like domain of factor VII.
Blood. 93:1237–1244. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Branchini A, Ferrarese M, Lombardi S, Mari
R, Bernardi F and Pinotti M: Differential functional readthrough
over homozygous nonsense mutations contributes to the bleeding
phenotype in coagulation factor VII deficiency. J Thromb Haemost.
14:1994–2000. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hao X, Cheng X, Ye J, Wang Y, Yang L, Wang
M and Jin Y: Severe coagulation factor VII deficiency caused by a
novel homozygous mutation (p. Trp284Gly) in loop 140s. Blood Coagul
Fibrinolysis. 27:461–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
D'Andrea G, Bossone A, Lupone MR, Peyvandi
F, Maisto G, Perricone F, Grandone E and Margaglione M: Molecular
characterization of a factor VII deficient patient supports the
importance of the second epidermal growth factor-like domain.
Haematologica. 89:979–984. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|