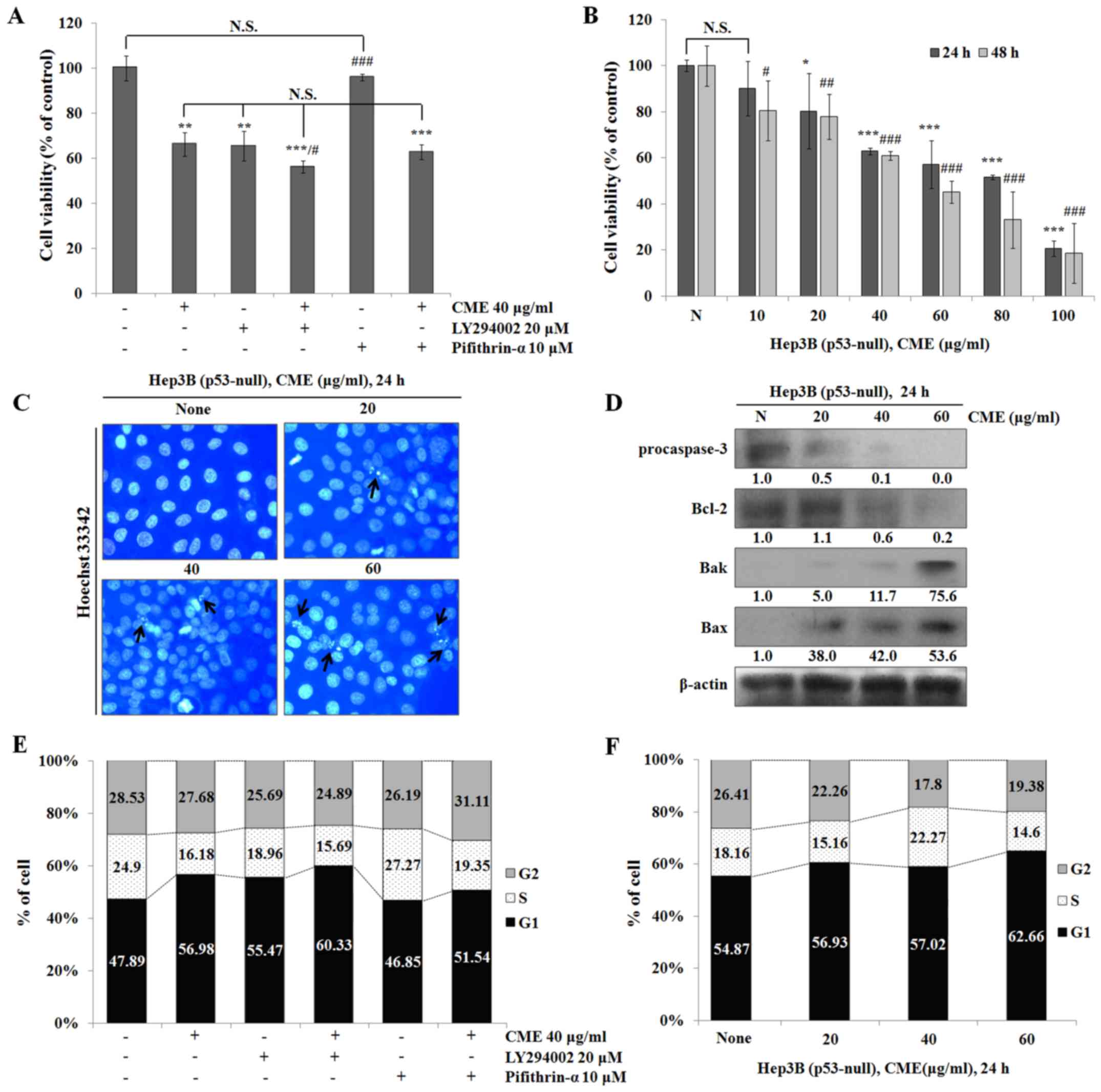
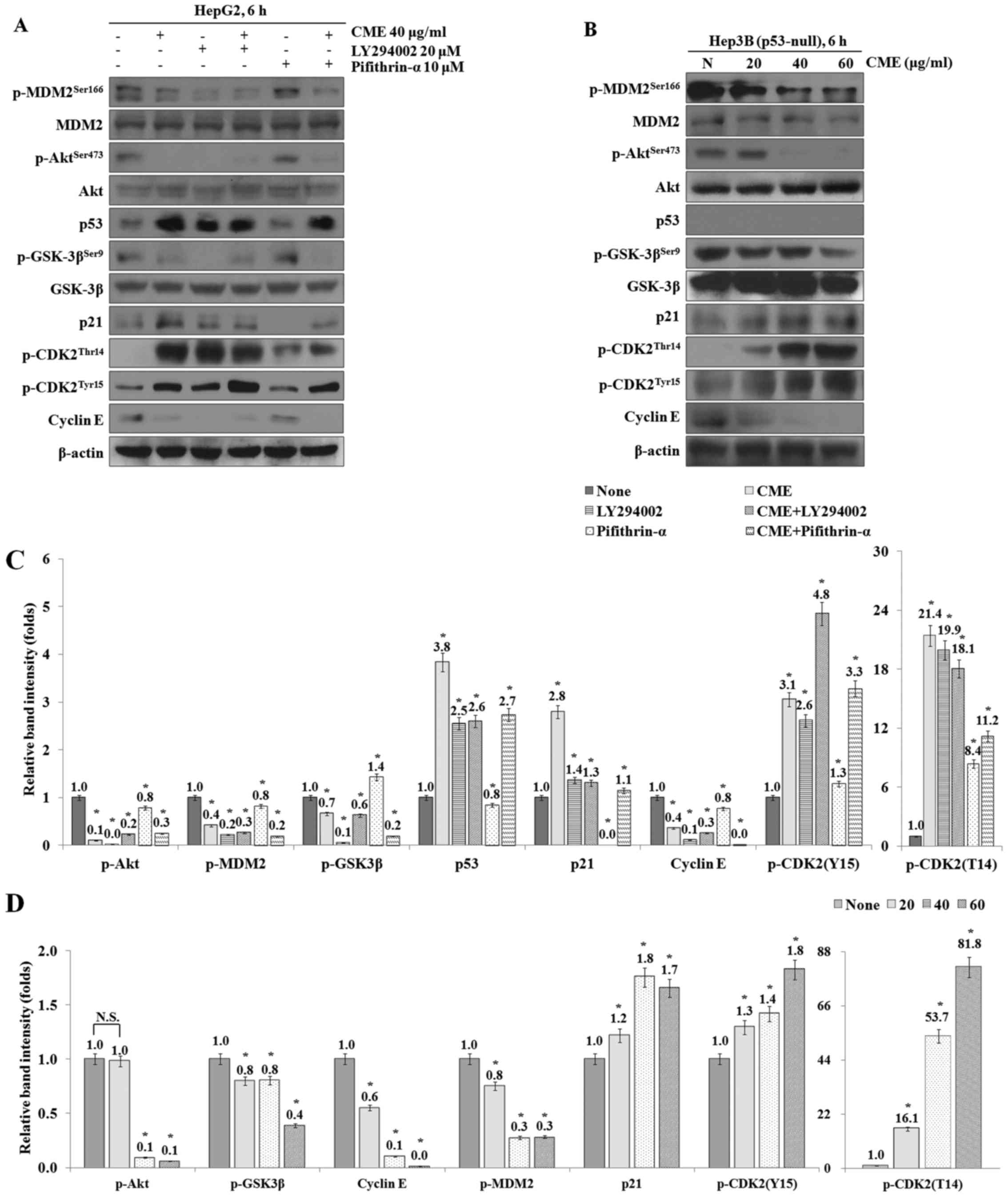
|
1
|
Wang Y, Nie H, Zhao X, Qin Y and Gong X:
Bicyclol induces cell cycle arrest and autophagy in HepG2 human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the PI3K/AKT and
Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. BMC Cancer. 16:7422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun Y, Tao C, Huang X, He H, Shi H, Zhang
Q and Wu H: Metformin induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular
carcinoma HepG2 cells by activating an AMPK/p53/miR-23a/FOXA1
pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 9:2845–2853. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Lin JP, Lee JH, Lin CC, Su
CC, Lin HJ and Chung JG: Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana
radix induce cytotoxicity and apoptosis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line (Hep3B). Anticancer Res. 27:2415–2425.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grizzi F, Franceschini B, Hamrick C,
Frezza EE, Cobos E and Chiriva-Internati M: Usefulness of
cancer-testis antigens as biomarkers for the diagnosis and
treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 5:32007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee SH, Jung DW, Kim GT, Park SY, Kim SY,
Park OJ and Kim YM: Quercetin of plants extracts regulates Sestrin2
and induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon cancer cells. J Cancer Prev.
17:244–250. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Parkash O, Kumar A and Kumar P Ajeet:
Anticancer Potential of Plants and Natural Products: A review. Am J
Pharmacol Sci. 1:104–115. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Tai Y, Sun YM, Zou X, Pan Q, Lan YD, Huo
Q, Zhu JW, Guo F, Zheng CQ, Wu CZ and Liu H: Effect of polygonatum
odoratum extract on human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cell
proliferation and apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 12:2681–2687. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park C, Jeong JS, Jeong JW, Kim SO, Kim
YJ, Kim GY, Hong SH and Choi YH: Ethanol extract of Kalopanax
septemlobus leaf inhibits HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cell
proliferation via inducing cell cycle arrest at G1 phase. Asian Pac
J Trop Med. 9:344–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Byambaragchaa M, de la Cruz J, Yang SH and
Hwang SG: Anti-metastatic potential of ethanol extract of Saussurea
involucrata against hepatic cancer in vitro. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 14:5397–5402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choi EJ and Kim GH: Antioxidant and
anticancer activity of Artemisia princeps var. orientalis extract
in HepG2 and Hep3B hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Chin J Cancer
Res. 25:536–543. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nicholson KM and Anderson NG: The protein
kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy cellular
signaling. Cell Signal. 14:381–395. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Romorini L, Garate X, Neiman G, Luzzani C,
Furmento VA, Guberman AS, Sevlever GE, Scassa ME and Miriuka SG:
AKT/GSK3β signaling pathway is critically involved in human
pluripotent stem cell survival. Sci Rep. 6:356602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thotala DK, Hallahan DE and Yazlovitskaya
EM: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibitors protect hippocampal
neurons from radiation-induced apoptosis by regulating MDM2-p53
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 19:387–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Watcharasit P, Bijur GN, Song L, Zhu J,
Chen X and Jope RS: Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta (GSK3beta) binds
to and promotes the actions of p53. J Biol Chem. 278:48872–48879.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tan J, Zhuang L, Leong HS, Iyer NG, Liu ET
and Yu Q: Pharmacologic Mmodulation of glycogen synthase
kinase-3beta promotes p53-dependent apoptosis through a direct
Bax-mediated mitochondrial pathway in colorectal cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 65:9012–9020. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meng J, Zhang HH, Zhou CX, Li C, Zhang F
and Mei QB: The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A
induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells
via p53-dependent and -independent pathways. Oncol Rep. 28:384–388.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang R, Wang Y, Li J, Jin H, Song S and
Huang S: The Chinese herb isolate yuanhuacine (YHL-14) induces G2/M
arrest in human cancer cells by up-regulating p21 protein
expression through an p53 protein-independent cascade. J Biol Chem.
289:6394–6403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang G, Liu J, Ren B, Tang Y, Owusu L, Li
M, Zhang J, Liu L and Li W: Anti-tumor effects of osthole on
ovarian cancer cells in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. 193:368–376. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang LL, Wang MC, Chen LG and Wang CC:
Cytotoxic activity of coumarins from the fruits of Cnidium monnieri
on leukemia cell lines. Planta Med. 69:1091–1095. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhu YP: Chinese Material Medica:
Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Applications. Harwood Academic
Publishers; Amsterdam: pp. 6241998
|
|
22
|
Li HB and Chen F: Simultaneous separation
and purification of five bioactive coumarins from the Chinese
medicinal plant Cnidium monnieri by high-speed counter-current
chromatography. J Sep Sci. 28:268–272. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao T, Pan H, Feng Y, Li H and Zhao Y:
Petroleum ether extract of Chenopodium album L. prevents cell
growth and induces apoptosis of human lung cancer cells. Exp Ther
Med. 12:3301–3307. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Zhang Q, Peng X, Zhou C, Zhong Y,
Chen X, Qiu Y, Jin M, Gong M and Kong D: Stellettin B induces G1
arrest, apoptosis and autophagy in Hhuman non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cells via blocking PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Sci Rep.
6:270712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chien SY, Wu YC, Chung JG, Yang JS, Lu HF,
Tsou MF, Wood WG, Kuo SJ and Chen DR: Quercetin-induced apoptosis
acts through mitochondrial- and caspase-3-dependent pathways in
human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 28:493–503.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Degli Esposti M and Dive C: Mitochondrial
membrane permeabilisation by Bax/Bak. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
304:455–461. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rössig L, Badorff C, Holzmann Y, Zeiher AM
and Dimmeler S: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 couples AKT-dependent
signaling to the regulation of p21Cip1 degradation. J Biol Chem.
277:9684–9689. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kulikov R, Boehme KA and Blattner C:
Glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent phosphorylation of Mdm2
regulates p53 abundance. Mol Cell Biol. 25:7170–7180. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abbas T and Dutta A: p21 in cancer:
Intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:400–414. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Z, Wang H, Li M, Agrawal S, Chen X
and Zhang R: MDM2 is a negative regulator of p21WAF1/CIP1,
independent of p53. J Biol Chem. 279:16000–16006. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sutherland C: What are the bona fide GSK3
substrates? Int J Alzheimers Dis 2011. 5056072011.
|
|
32
|
Yuan L, Zhang Y, Xia J, Liu B, Zhang Q,
Liu J, Luo L, Peng Z, Song Z and Zhu R: Resveratrol induces cell
cycle arrest via a p53-independent pathway in A549 cells. Mol Med
Rep. 11:2459–2464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shen G, Xu C, Chen C, Hebbar V and Kong
AN: p53-independent G1 cell cycle arrest of human colon carcinoma
cells HT-29 by sulforaphane is associated with induction of p21CIP1
and inhibition of expression of cyclin D1. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 57:317–327. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kim EJ, Kim GT, Kim BM, Lim EG, Kim SY, Ha
SH, Kim YM and Yoo JG: Cell cycle arrest effects by artemisia annua
linné in Hep3B liver cancer cell. KSBB J. 30:175–181. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Gartel AL and Tyner AL: The role of the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 in apoptosis. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:639–649. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|