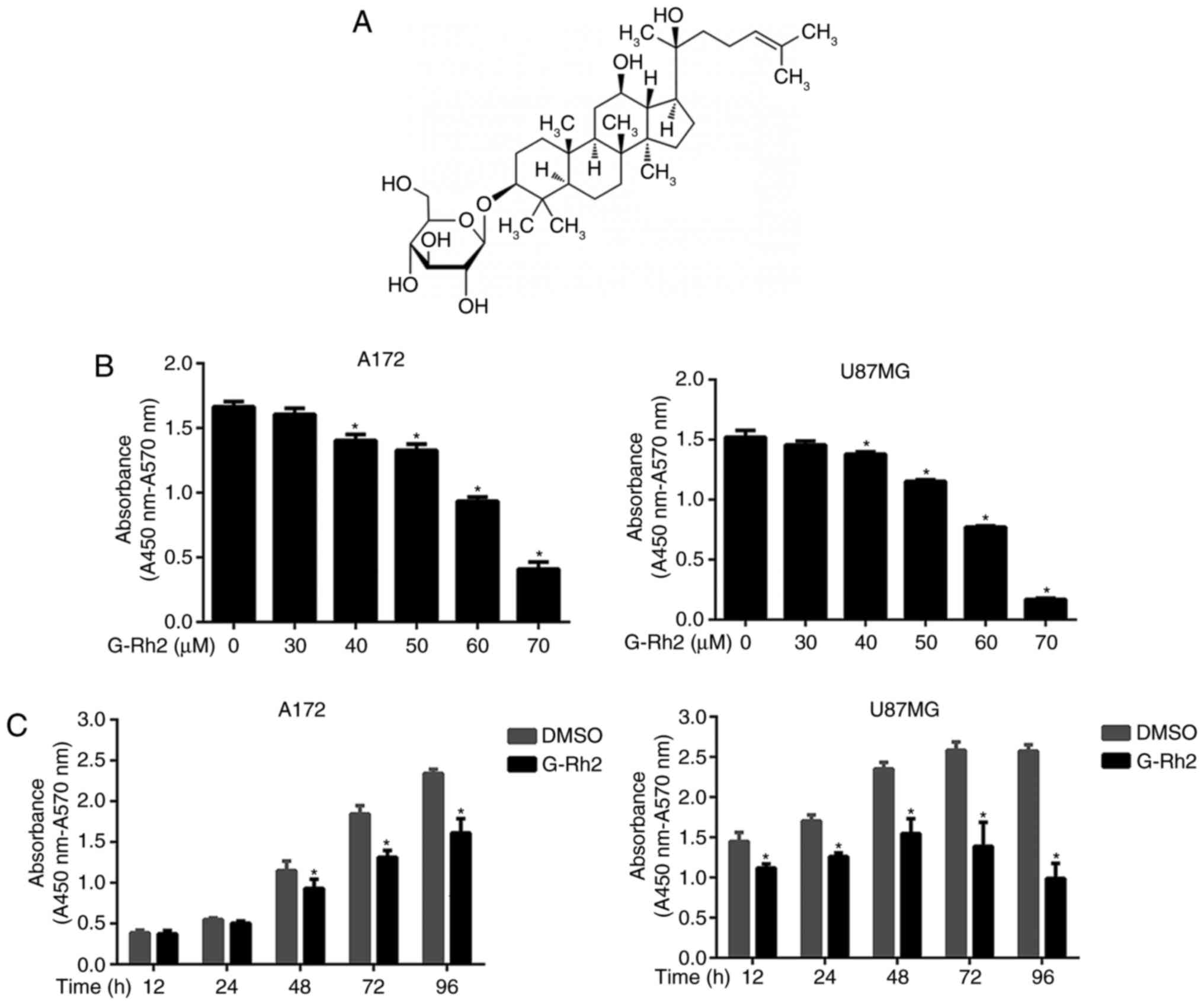
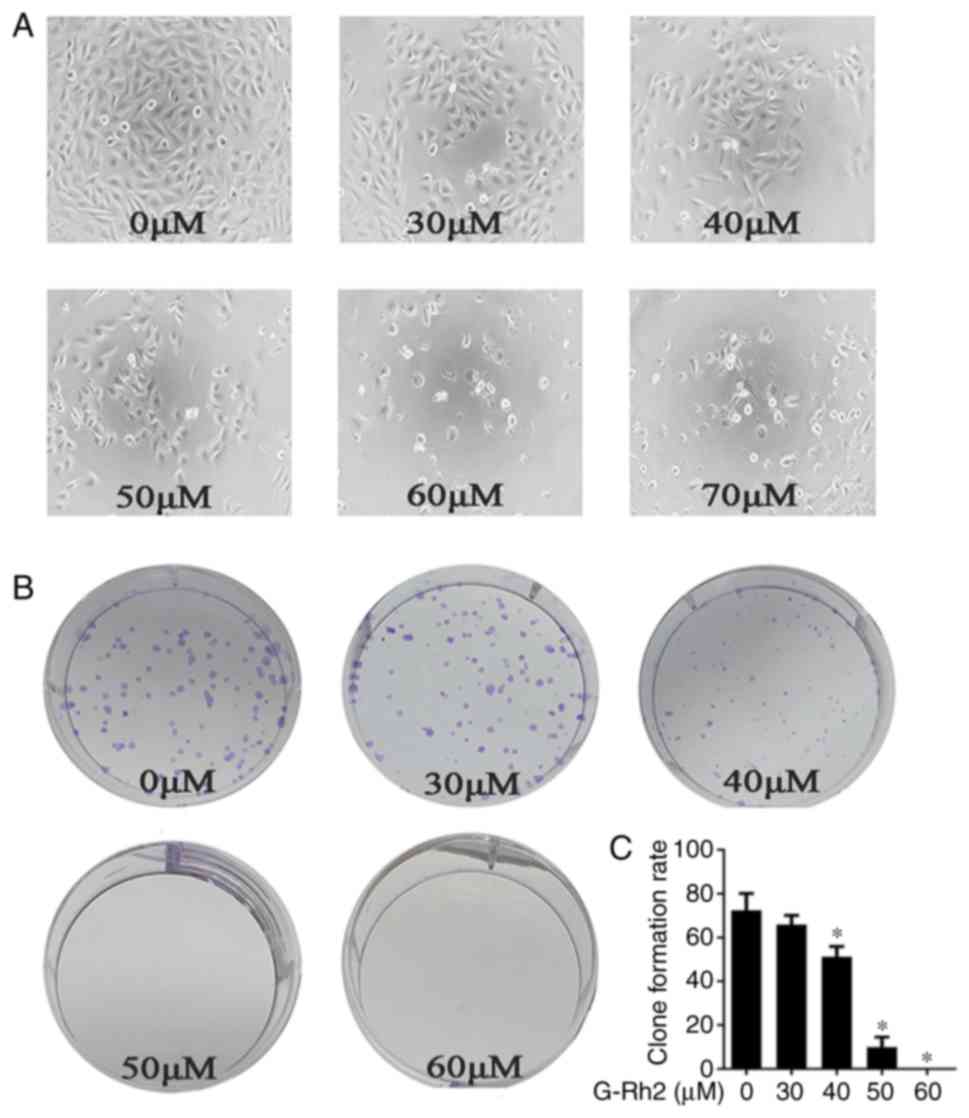
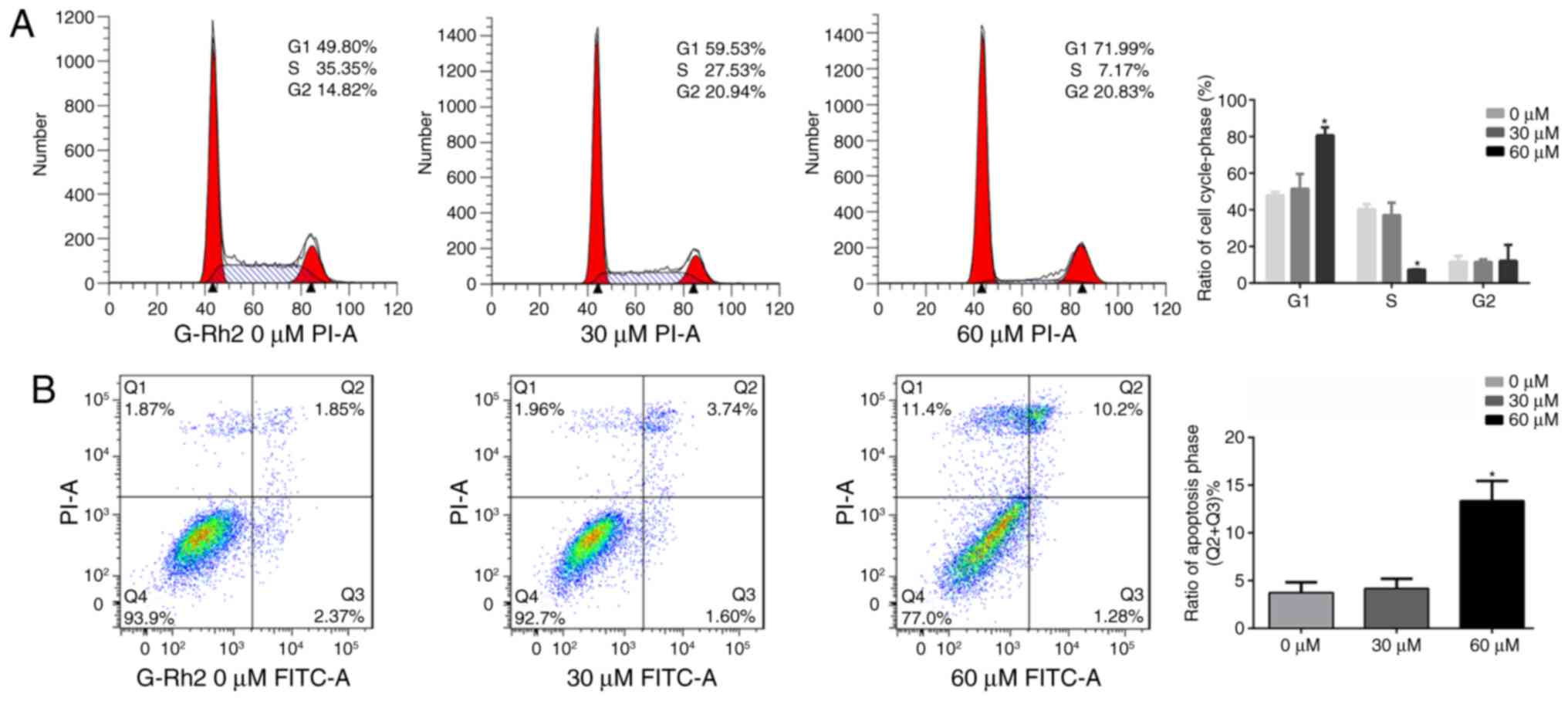
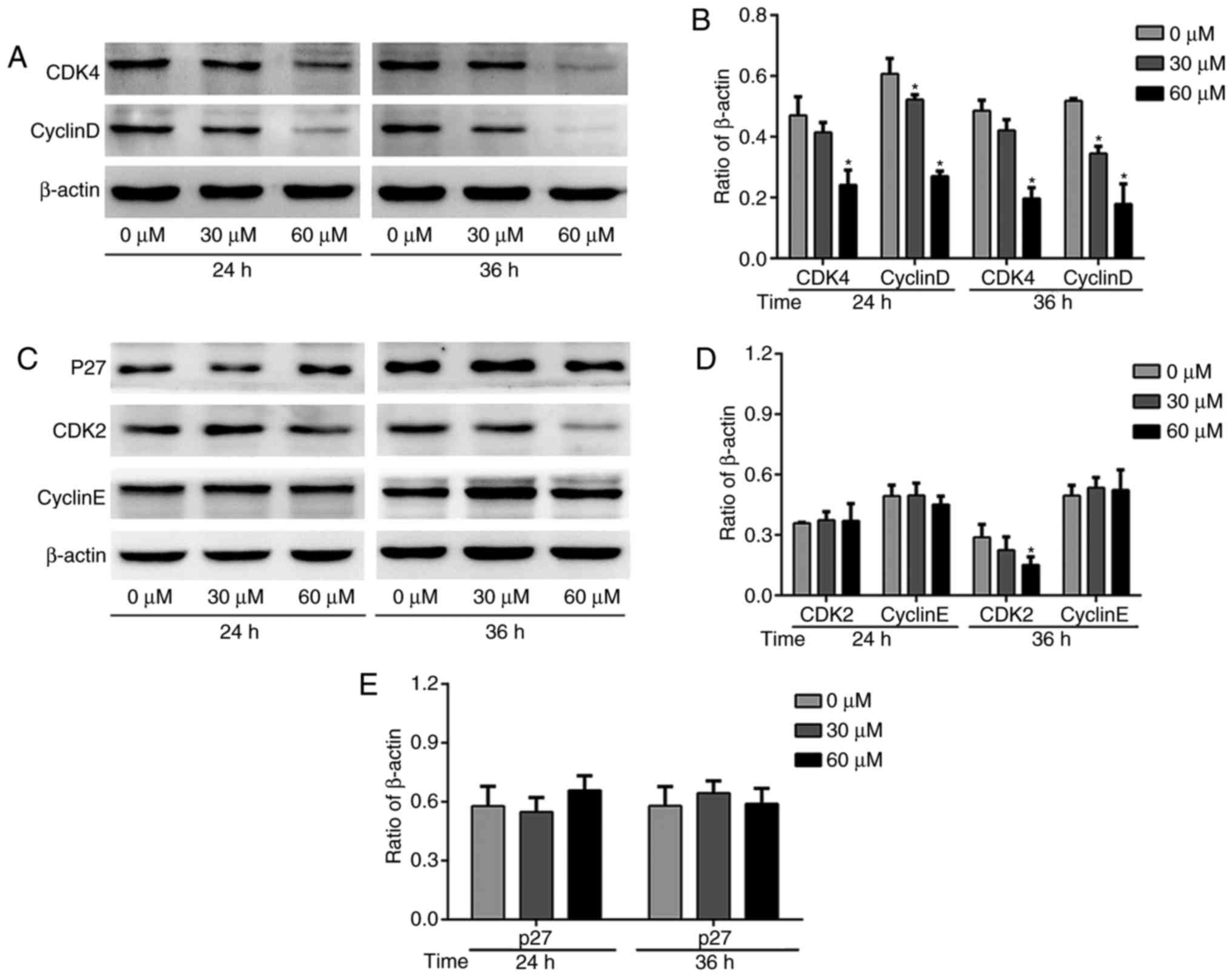
|
1
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I,
Fisher JL, Langer CE, Pekmezci M, Schwartzbaum JA, Turner MC, Walsh
KM, et al: The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A ‘state of the
science’ review. Neuro-Oncol. 16:896–913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang H, Xu T, Jiang Y, Xu H, Yan Y, Fu D
and Chen J: The challenges and the promise of molecular targeted
therapy in malignant gliomas. Neoplasia. 17:239–255. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gu Y, Wang GJ, Sun JG, Jia YW, Wang W, Xu
MJ, Lv T, Zheng YT and Sai Y: Pharmacokinetic characterization of
ginsenoside Rh2, an anticancer nutrient from ginseng, in rats and
dogs. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:2257–2268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bahrke MS and Morgan WR: Evaluation of the
ergogenic properties of ginseng: An update. Sports Med. 29:113–133.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jin Y, Kotakadi VS, Ying L, Hofseth AB,
Cui X, Wood PA, Windust A, Matesic LE, Pena EA, Chiuzan C, et al:
American ginseng suppresses inflammation and DNA damage associated
with mouse colitis. Carcinogenesis. 29:2351–2359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shen CY, Jiang JG, Yang L, Wang DW and Zhu
W: Anti-ageing active ingredients from herbs and nutraceuticals
used in traditional Chinese medicine: Pharmacological mechanisms
and implications for drug discovery. Br J Pharmacol. 174:1395–1425.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cui X, Jin Y, Poudyal D, Chumanevich AA,
Davis T, Windust A, Hofseth A, Wu W, Habiger J, Pena E, et al:
Mechanistic insight into the ability of American ginseng to
suppress colon cancer associated with colitis. Carcinogenesis.
31:1734–1741. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li B, Zhao J, Wang CZ, Searle J, He TC,
Yuan CS and Du W: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces apoptosis and
paraptosis-like cell death in colorectal cancer cells through
activation of p53. Cancer Lett. 301:185–192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park HM, Kim SJ, Kim JS and Kang HS:
Reactive oxygen species mediated ginsenoside Rg3- and Rh2-induced
apoptosis in hepatoma cells through mitochondrial signaling
pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2736–2741. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo XX, Li Y, Sun C, Jiang D, Lin YJ, Jin
FX, Lee SK and Jin YH: p53-dependent Fas expression is critical for
Ginsenoside Rh2 triggered caspase-8 activation in HeLa cells.
Protein Cell. 5:224–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park EK, Lee EJ, Lee SH, Koo KH, Sung JY,
Hwang EH, Park JH, Kim CW, Jeong KC, Park BK and Kim YN: Induction
of apoptosis by the ginsenoside Rh2 by internalization of lipid
rafts and caveolae and inactivation of Akt. Br J Pharmacol.
160:1212–1223. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu S, Chen M, Li P, Wu Y, Chang C, Qiu Y,
Cao L, Liu Z and Jia C: Ginsenoside rh2 inhibits cancer stem-like
cells in skin squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:499–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hengstschläger M, Braun K, Soucek T,
Miloloza A and Hengstschläger-Ottnad E: Cyclin-dependent kinases at
the G1-S transition of the mammalian cell cycle. Mutat Res.
436:1–9. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giacinti C and Giordano A: RB and cell
cycle progression. Oncogene. 25:5220–5227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Munro S, Carr SM and La Thangue NB:
Diversity within the pRb pathway: Is there a code of conduct.
Oncogene. 31:4343–4352. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lapenna S and Giordano A: Cell cycle
kinases as therapeutic targets for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
8:547–566. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chung KS, Cho SH, Shin JS, Kim DH, Choi
JH, Choi SY, Rhee YK, Hong HD and Lee KT: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces
cell cycle arrest and differentiation in human leukemia cells by
upregulating TGF-β expression. Carcinogenesis. 34:331–340. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Gao Y, Ma W, Guo W, Zhou G, Cheng T
and Liu Y: EGFR signaling-dependent inhibition of glioblastoma
growth by ginsenoside Rh2. Tumor Biol. 35:5593–5598. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Plumb JA: Cell sensitivity assays:
Clonogenic assay. Methods Mol Med. 88:159–164. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Diaz-Moralli S, Tarrado-Castellarnau M,
Miranda A and Cascante M: Targeting cell cycle regulation in cancer
therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 138:255–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burris HA III: Overcoming acquired
resistance to anticancer therapy: Focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:829–842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shaw TK, Mandal D, Dey G, Pal MM, Paul P,
Chakraborty S, Ali KA, Mukherjee B, Bandyopadhyay AK and Mandal M:
Successful delivery of docetaxel to rat brain using experimentally
developed nanoliposome: A treatment strategy for brain tumor. Drug
Deliv. 24:346–357. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen F, Deng ZY, Zhang B, Xiong ZX, Zheng
SL, Tan CL and Hu JN: Esterification of Ginsenoside Rh2 enhanced
its cellular uptake and antitumor activity in human HepG2 cells. J
Agric Food Chem. 64:253–261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaluzova M, Bouras A, Machaidze R and
Hadjipanayis CG: Targeted therapy of glioblastoma stem-like cells
and tumor non-stem cells using cetuximab-conjugated iron-oxide
nanoparticles. Oncotarget. 6:8788–8806. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Choi S, Kim TW and Singh SV: Ginsenoside
Rh2-mediated G1 phase cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer
cells is caused by p15Ink4B and p27Kip1-dependent inhibition of
cyclin-dependent kinases. Pharm Res. 26:2280–2288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng CC, Yang SM, Huang CY, Chen JC,
Chang WM and Hsu SL: Molecular mechanisms of ginsenoside
Rh2-mediated G1 growth arrest and apoptosis in human lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 55:531–540.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Viana-Pereira M, Lopes JM, Little S,
Milanezi F, Basto D, Pardal F, Jones C and Reis RM: Analysis of
EGFR overexpression, EGFR gene amplification and the EGFRvIII
mutation in portuguese high-grade gliomas. Anticancer Res.
28:913–920. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hill MM and Hemmings BA: Inhibition of
protein kinase B/Akt: Implications for cancer therapy. Pharmacol
Ther. 93:243–251. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoeli-Lerner M and Toker A: Akt/PKB
signaling in cancer: A function in cell motility and invasion. Cell
Cycle. 5:603–605. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gallia GL, Tyler BM, Hann CL, Siu IM,
Giranda VL, Vescovi AL, Brem H and Riggins GJ: Inhibition of Akt
inhibits growth of glioblastoma and glioblastoma stem-like cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 8:386–393. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chautard E, Ouédraogo ZG, Biau J and
Verrelle P: Role of Akt in human malignant glioma: From oncogenesis
to tumor aggressiveness. J Neurooncol. 117:205–215. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mayer IA and Arteaga CL: The PI3K/AKT
pathway as a target for cancer treatment. Annu Rev Med. 67:11–28.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lv Q, Rong N, Liu LJ, Xu XL, Liu JT, Jin
FX and Wang CM: Antitumoral activity of (20R)- and
(20S)-Ginsenoside Rh2 on transplanted hepatocellular carcinoma in
mice. Planta Med. 82:705–711. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|