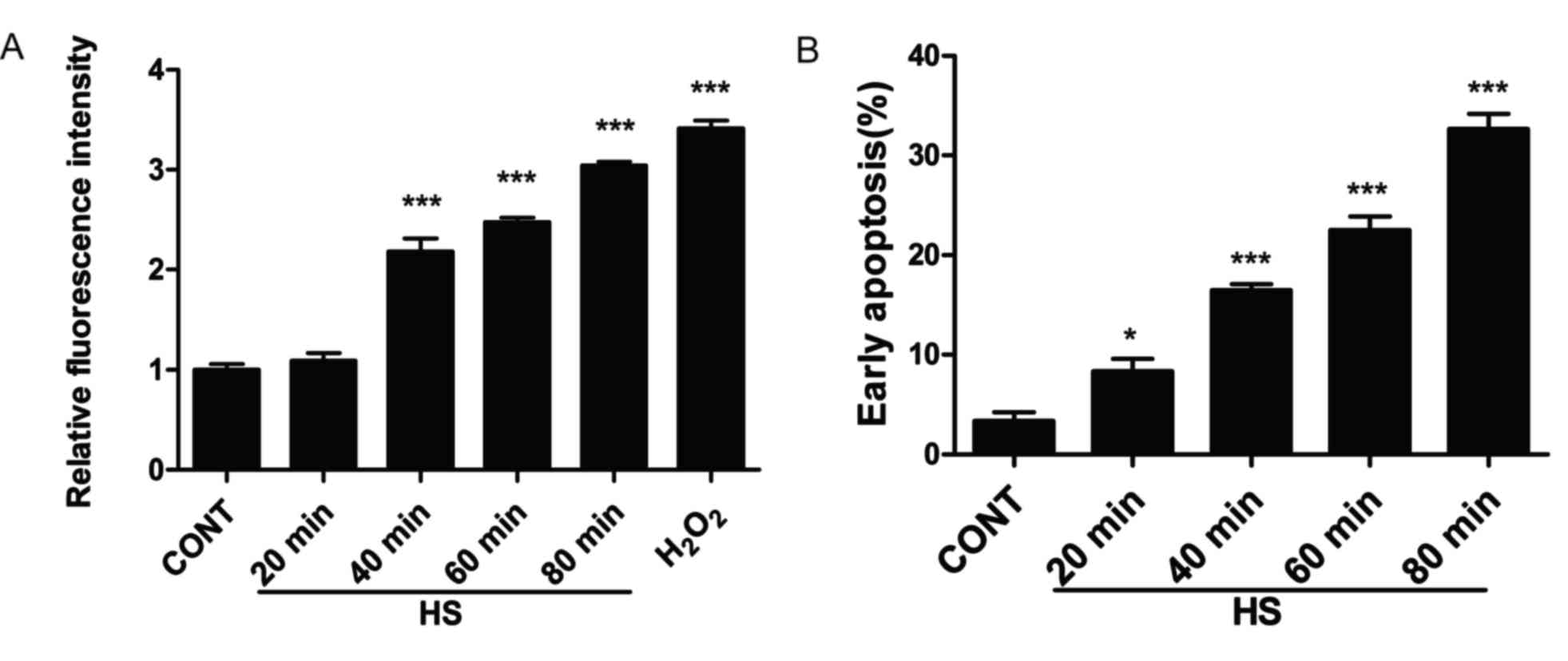
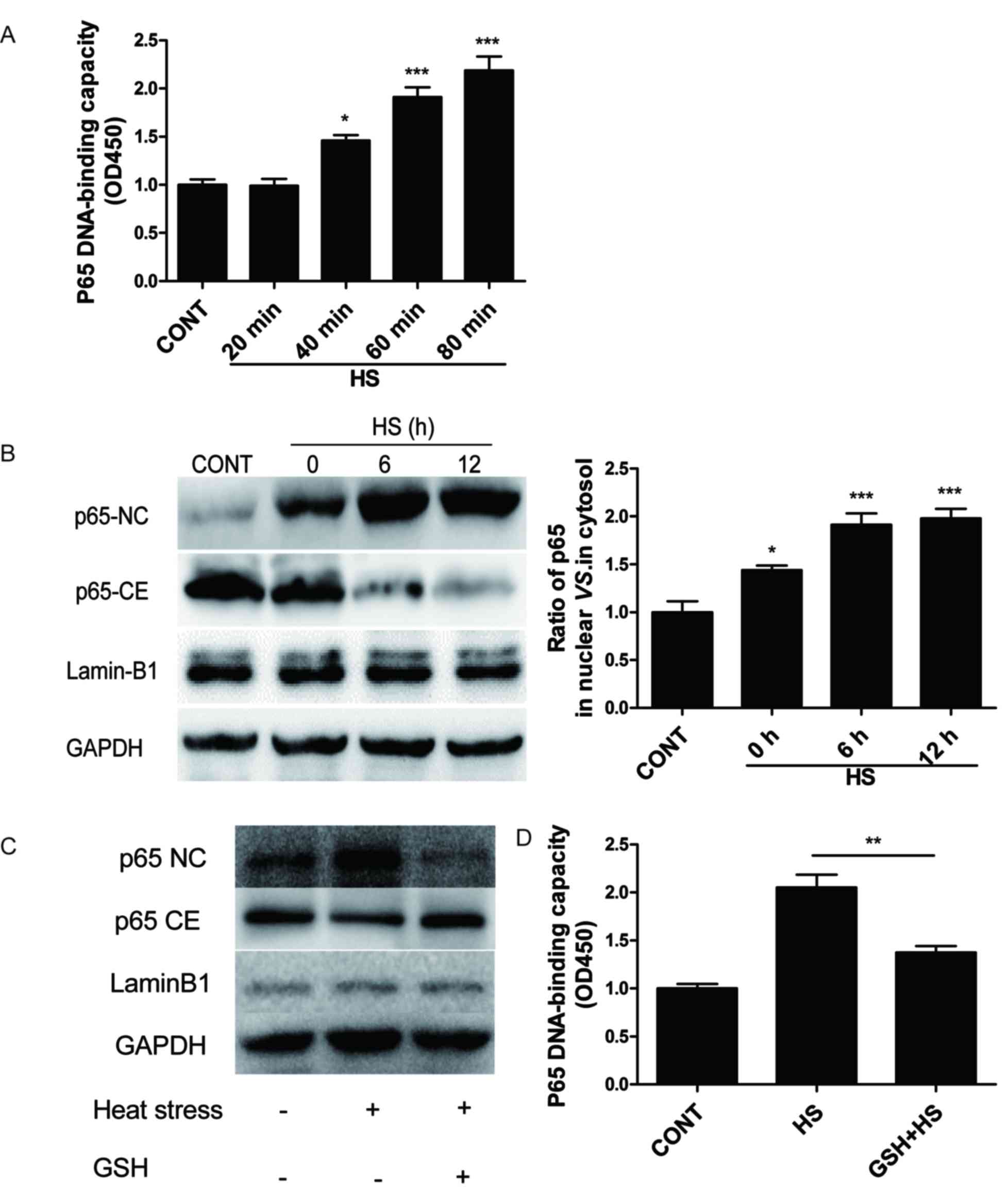
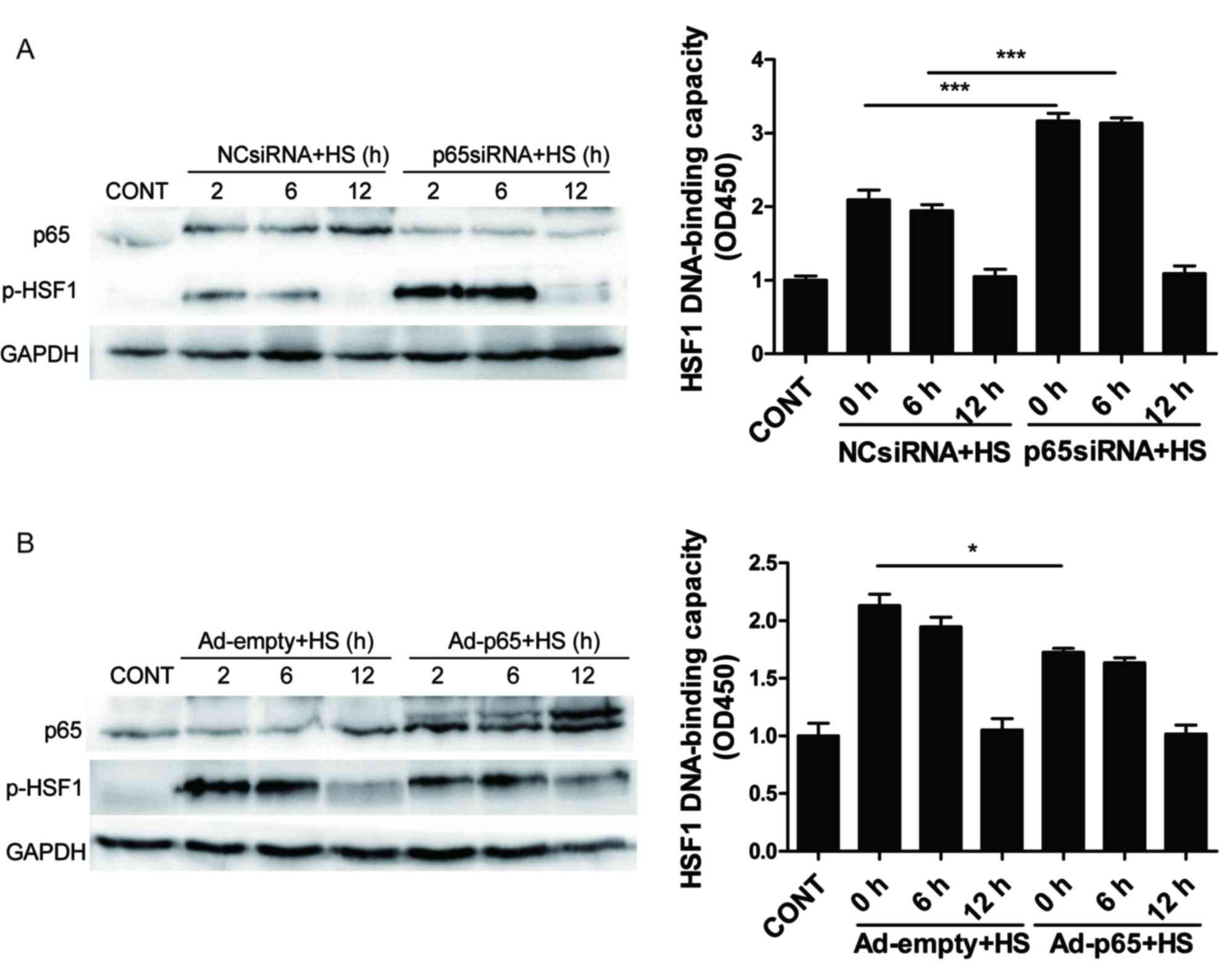
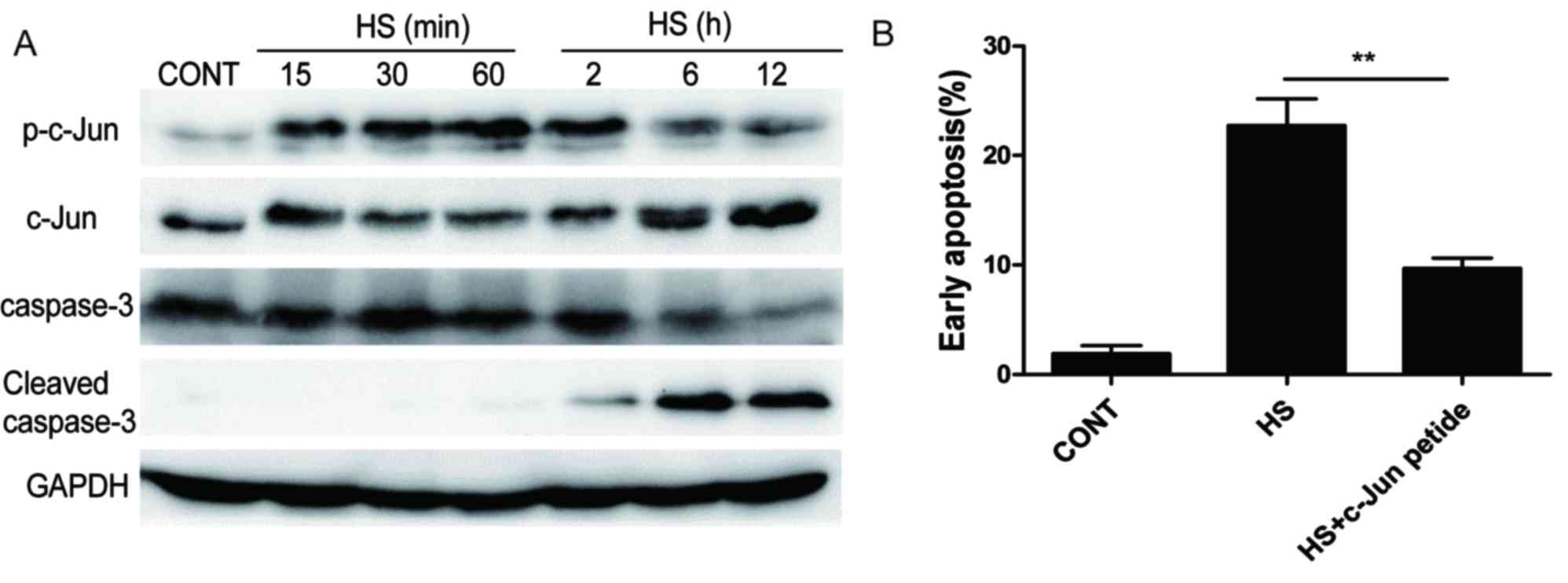
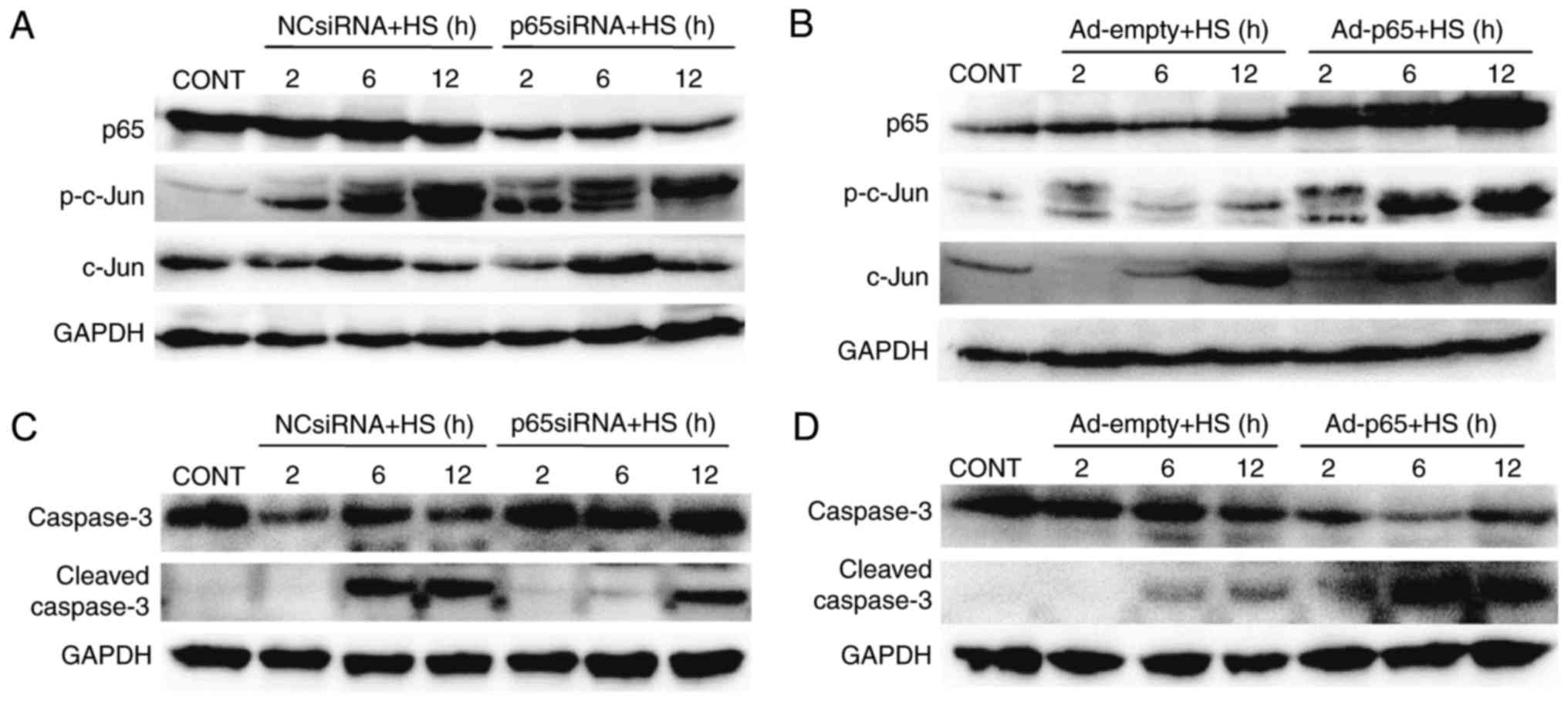
|
1
|
Bouchama A and Knochel JP: Heat stroke. N
Engl J Med. 346:1978–1988. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao Z, Liu F, Yin P, Wan C, He S, Liu X,
Zhao H, Liu T, Xu J and Guo S: Inhibition of heat-induced apoptosis
in rat small intestine and IEC-6 cells through the AKT signaling
pathway. BMC Vet Res. 9:2412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yu J, Liu F, Yin P, Zhao H, Luan W, Hou X,
Zhong Y, Jia D, Zan J, Ma W, et al: Involvement of oxidative stress
and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways in heat
stress-induced injury in the rat small intestine. Stress.
16:99–113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hsu YL, Yu HS, Lin HC, Wu KY, Yang RC and
Kuo PL: Heat shock induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen
species involving mitochondrial and death receptor pathways in
corneal cells. Exp Eye Res. 93:405–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee SJ, Yang ES, Kim SY, Kim SY, Shin SW
and Park JW: Regulation of heat shock-induced apoptosis by
sensitive to apoptosis gene protein. Free Radic Biol Med.
45:167–176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kretz-Remy C1, Munsch B and Arrigo AP:
NFkappa B-dependent transcriptional activation during heat shock
recovery. Thermolability of the NF-kappaB. Ikappa B complex. J Biol
Chem. 276:43723–43733. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kretz-Remy C, Mehlen P, Mirault ME and
Arrigo AP: Inhibition of I kappa B-alpha phosphorylation and
degradation and subsequent NF-kappa B activation by glutathione
peroxidase overexpression. J Cell Biol. 133:1083–1093. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu D, Chen M, Ren X, Ren X and Wu Y:
Leonurine ameliorates LPS-induced acute kidney injury via
suppressing ROS-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Fitoterapia.
97:148–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J
Clin Invest. 107:241–246. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pahl HL: Activators and target genes of
Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene. 18:6853–6866. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Monks NR, Biswas DK and Pardee AB:
Blocking anti-apoptosis as a strategy for cancer chemotherapy:
NF-kappaB as a target. J Cell Biochem. 92:646–650. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kasibhatla S, Brunner T, Genestier L,
Echeverri F, Mahboubi A and Green DR: DNA damaging agents induce
expression of Fas ligand and subsequent apoptosis in T lymphocytes
via the activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Mol Cell. 1:543–551.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Collins T: Endothelial nuclear
factor-kappa B and the initiation of the atherosclerotic lesion.
Lab Invest. 68:499–508. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Choi YJ, Om JY, Kim NH, Chang JE, Park JH,
Kim JY, Lee HJ, Kim SS and Chun W: Heat shock transcription
factor-1 suppresses apoptotic cell death and ROS generation in
3-nitropropionic acid-stimulated striatal cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
375:59–67. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Verma P, Pfister JA, Mallick S and D'Mello
SR: HSF1 protects neurons through a novel trimerization- and
HSP-independent mechanism. J Neurosci. 34:1599–1612. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cotto JJ, Kline M and Morimoto RI:
Activation of heat shock factor 1 DNA binding precedes
stress-induced serine phosphorylation. Evidence for a multistep
pathway of regulation. J Biol Chem. 271:3355–3358. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu L, Hu C, Huang M, Jiang M, Lu L and
Tang J: Heat shock transcription factor 1 attenuates TNFα-induced
cardiomyocyte death through suppression of NFκB pathway. Gene.
527:89–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bossy-Wetzel E, Bakiri L and Yaniv M:
Induction of apoptosis by the transcription factor c-Jun. EMBO J.
16:1695–1709. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Watson A, Eilers A, Lallemand D, Kyriakis
J, Rubin LL and Ham J: Phosphorylation of c-Jun is necessary for
apoptosis induced by survival signal withdrawal in cerebellar
granule neurons. J Neurosci. 18:751–762. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu J, Zhang J, Huang H, Li J, Yu Y, Jin
H, Li Y, Deng X, Gao J, Zhao Q and Huang C: Crucial role of c-Jun
phosphorylation at Ser63/73 mediated by PHLPP protein degradation
in the cheliensisin a inhibition of cell transformation. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 7:1270–1281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stein B, Baldwin AS Jr, Ballard DW, Greene
WC, Angel P and Herrlich P: Cross-coupling of the NF-kappa B p65
and Fos/Jun transcription factors produces potentiated biological
function. EMBO J. 12:3879–3891. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Z, Sun X, Tang J, Tang Y, Tong H, Wen
Q, Liu Y and Su L: Intestinal inflammation and tissue injury in
response to heat stress and cooling treatment in mice. Mol Med Rep.
4:437–443. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boberts GT, Ghebeh H, Chishti MA,
Al-Mohanna F, El-Sayed R, Al-Mohanna F and Bouchama A:
Microvascular injury, thrombosis, inflammation, and apoptosis in
the pathogenesis of heatstroke: A study in baboon model.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1130–1136. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lawrence T and Fong C: The resolution of
inflammation: Anti-inflammatory roles for NF-kappaB. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:519–523. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rossi A, Elia G and Santoro MG: Inhibition
of nuclear factor kappa B by prostaglandin A1: An effect associated
with heat shock transcription factor activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:pp. 746–750. 1997; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kopp E and Ghosh S: Inhibition of NF-kappa
B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science. 265:956–959. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|