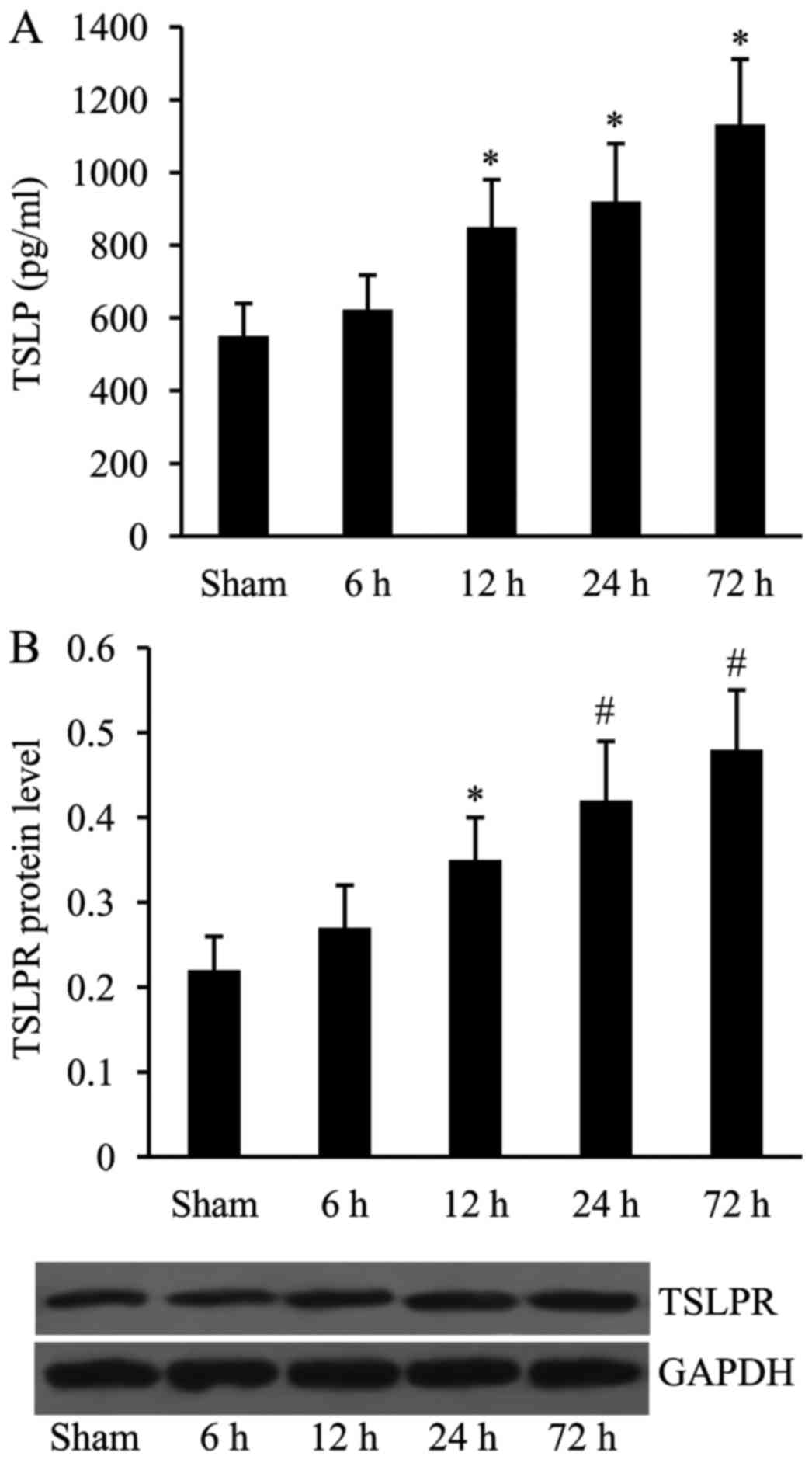
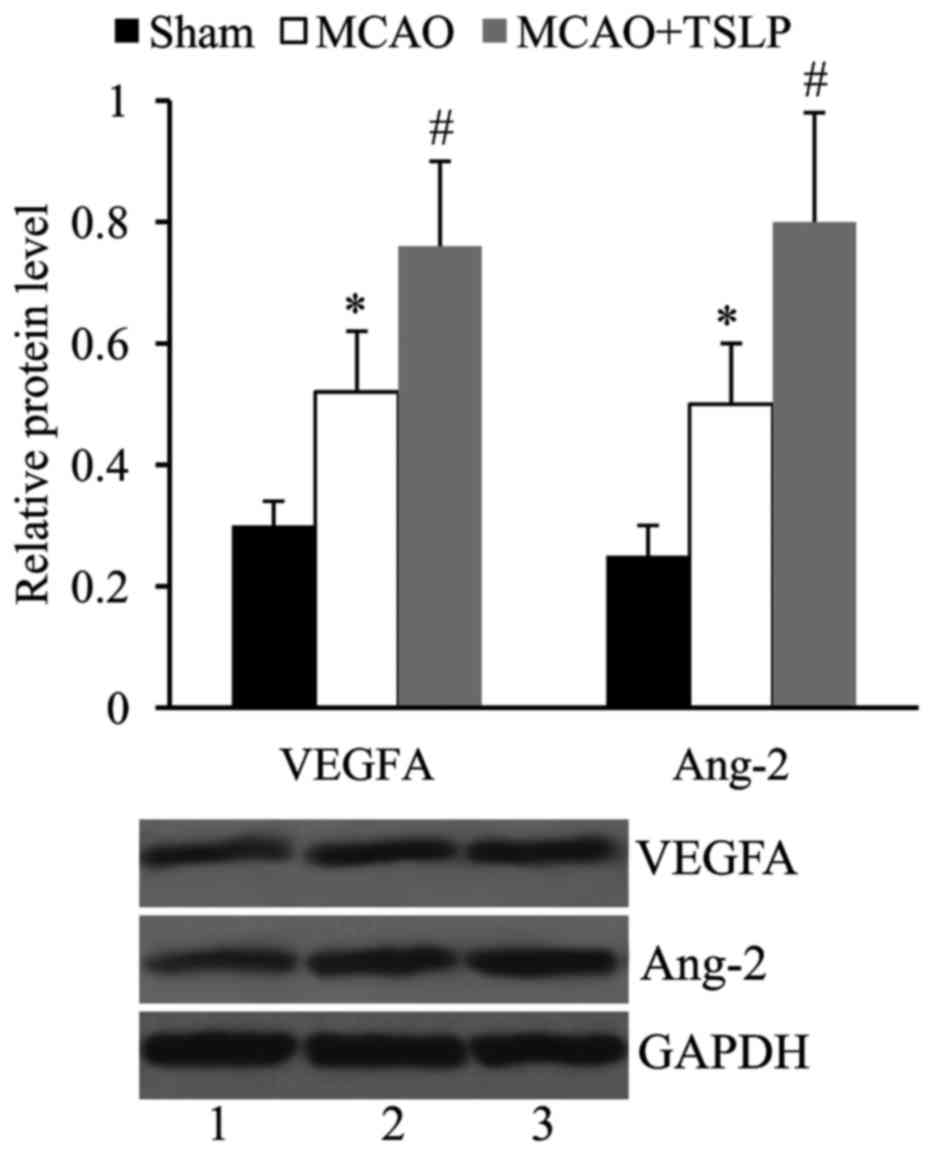
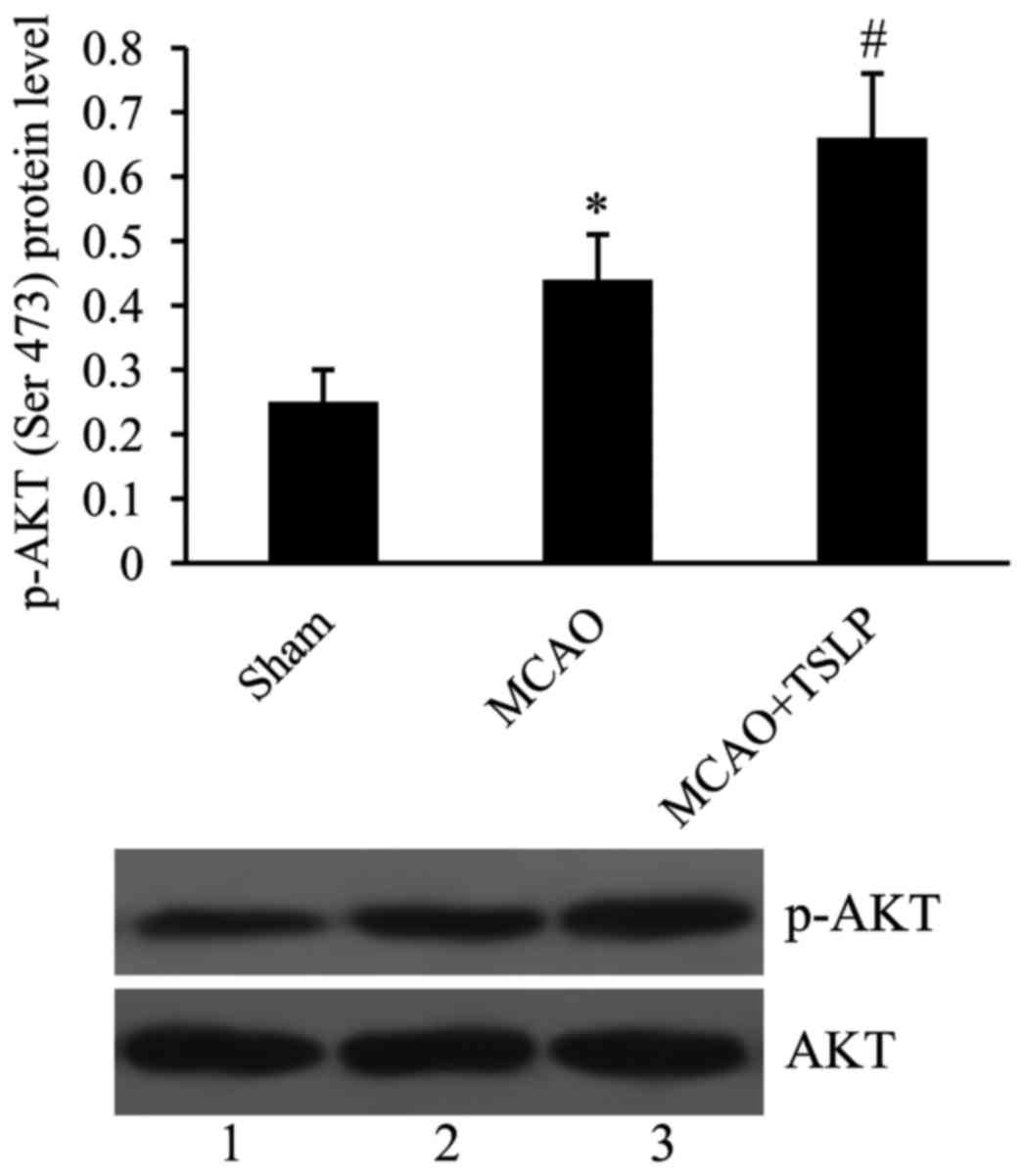
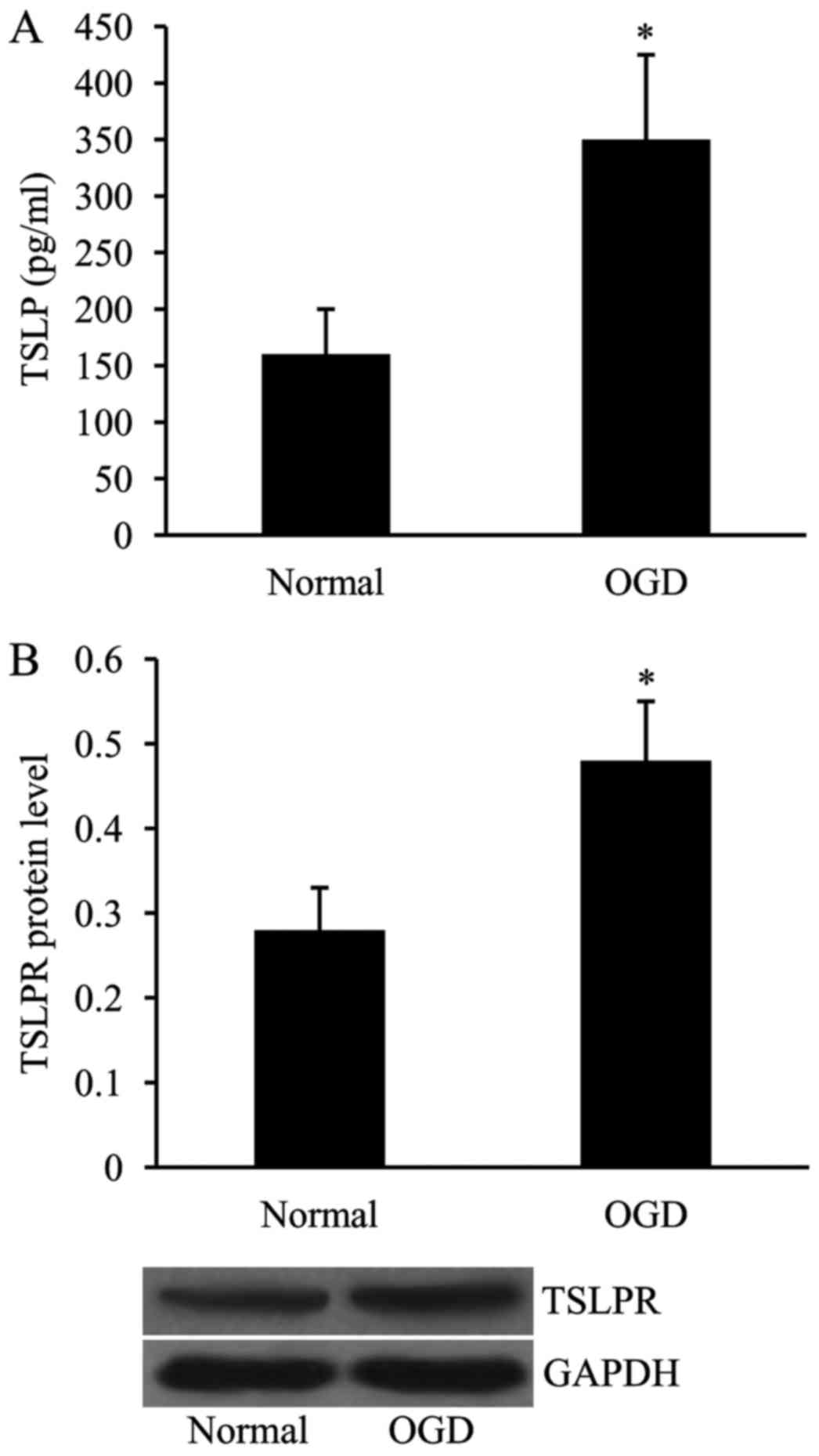
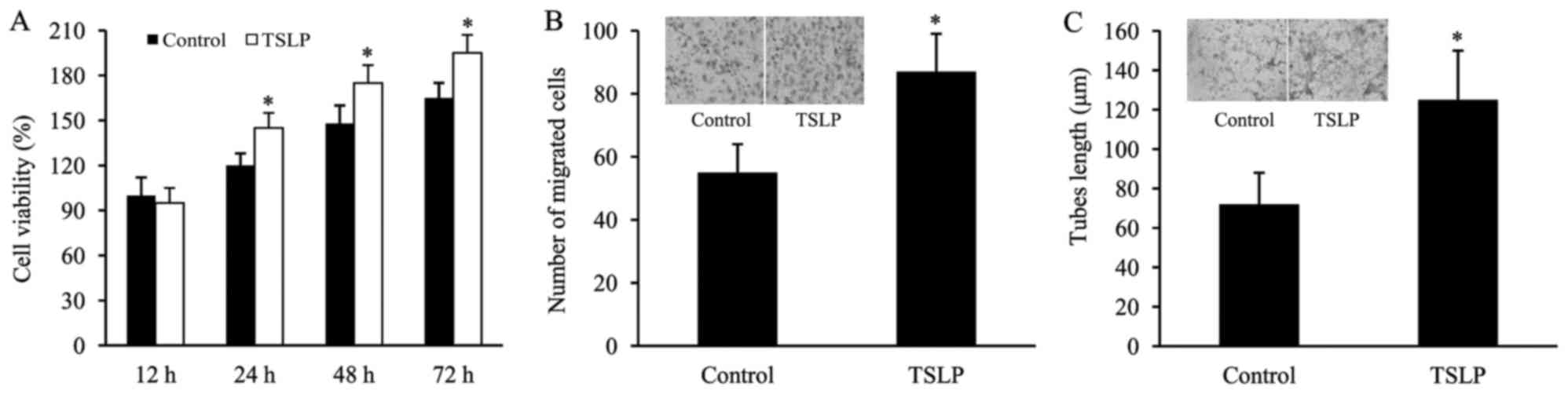
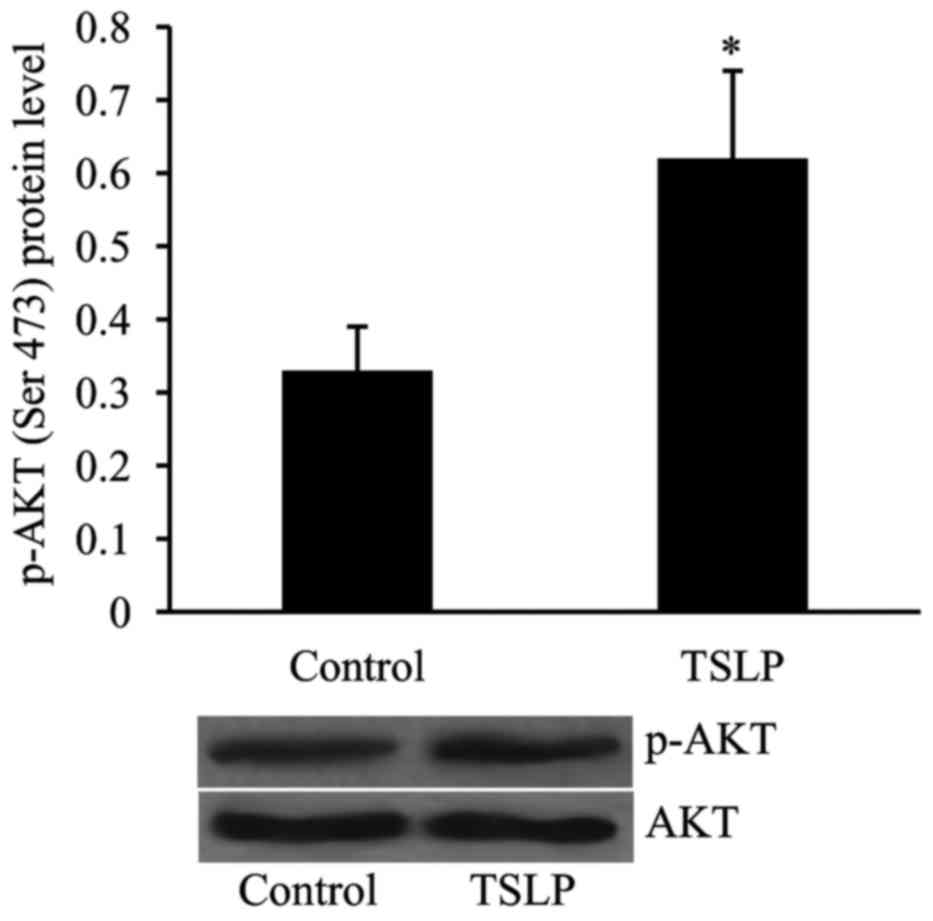
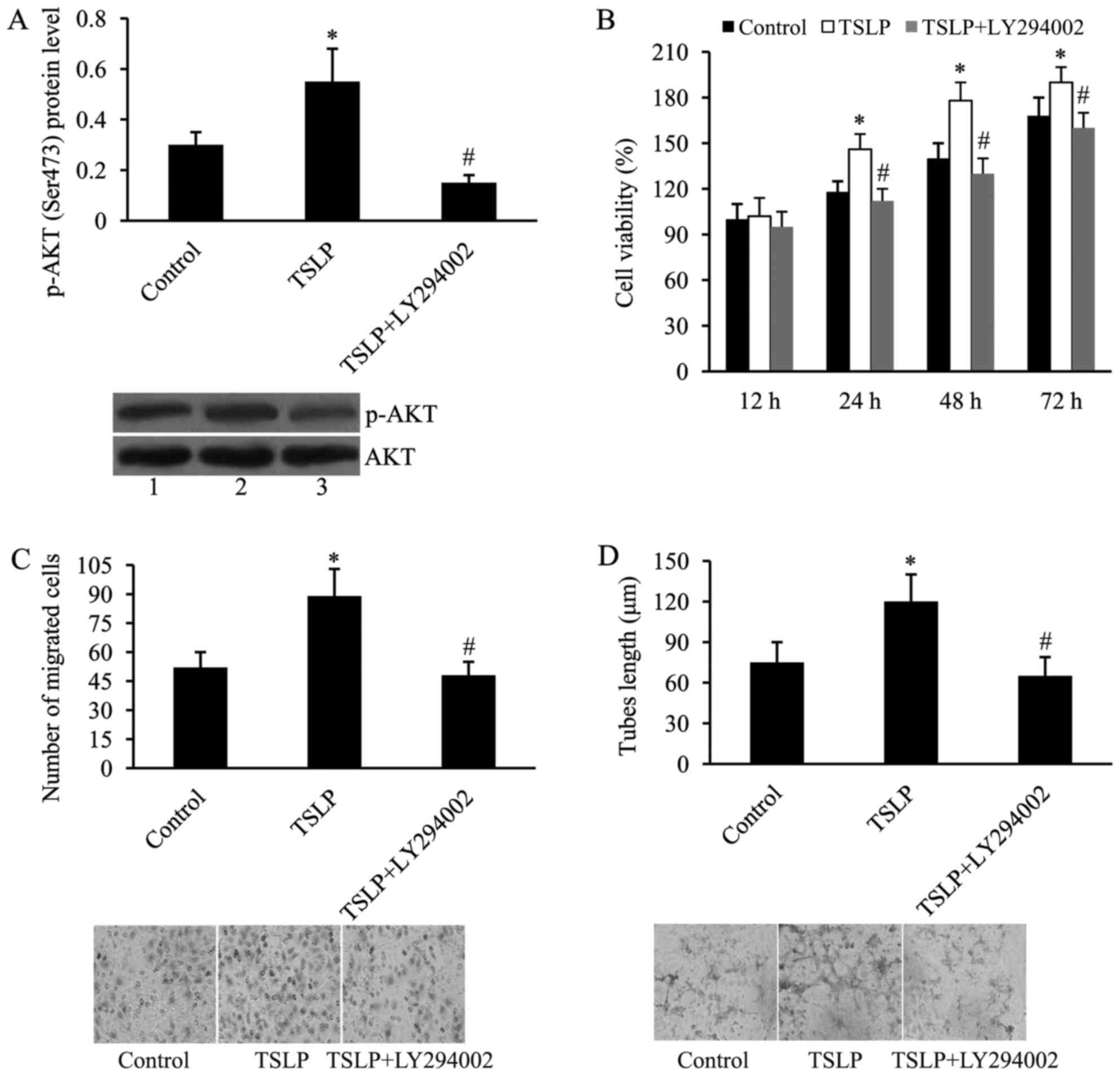
|
1
|
GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators, . Global, regional, and national age-sex specific
all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death,
1990–2013: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease
study 2013. Lancet. 385:117–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Feigin VL, Forouzanfar MH, Krishnamurthi
R, Mensah GA, Connor M, Bennett DA, Moran AE, Sacco RL, Anderson L,
Truelsen T, et al: Global and regional burden of stroke during
1990–2010: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2010.
Lancet. 383:245–254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang WZ: Neurology. 4th. People's Medical
Publishing House; Beijing: pp. 1302001
|
|
4
|
Bang OY, Saver JL, Buck BH, Alger JR,
Starkman S, Ovbiagele B, Kim D, Jahan R, Duckwiler GR, Yoon SR, et
al: Impact of collateral flow on tissue fate in acute ischaemic
stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 79:625–629. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miteff F, Levi CR, Bateman GA, Spratt N,
McElduff P and Parsons MW: The independent predictive utility of
computed tomography angiographic collateral status in acute
ischaemic stroke. Brain. 132:2231–2238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liebeskind DS, Cotsonis GA, Saver JL, Lynn
MJ, Turan TN, Cloft HJ and Chimowitz MI; Warfarin-Aspirin
Symptomatic Intracranial Disease (WASID) Investigators, :
Collaterals dramatically alter stroke risk in intracranial
atherosclerosis. Ann Neurol. 69:963–974. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Velazquez OC, Snyder R, Liu ZJ, Fairman RM
and Herlyn M: Fibroblast-dependent differentiation of human
microvaseular endothelial cells into capillary-like 3-dimensional
networks. FASEB J. 16:1316–1318. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Arai K, Jin G, Navaratna D and Lo EH:
Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes:
Neurovascular injury and angiogenic recovery after stroke. FEBS J.
276:4644–4652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lin J, Chang W, Dong J, Zhang F, Mohabeer
N, Kushwaha KK, Wang L, Su Y, Fang H and Li D: Thymic stromal
lymphopoietin over-expressed in human atherosclerosis: Potential
role in Th17 differentiation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:305–318.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao H, Li M, Wang L, Su Y, Fang H, Lin J,
Mohabeer N and Li D: Angiotensin II induces TSLP via an AT1
receptor/NF-KappaB pathway, promoting Th17 differentiation. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 30:1383–1397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu K, Zhu P, Dong Q, Zhong Y, Zhu Z, Lin
Y, Huang Y, Meng K, Ji Q, Yi G, et al: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin
attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice. J Am
Heart Assoc. 2:e0003912013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Blagoev M, Nielsen MM, Angrist M,
Chakravarti A and Pandey A: Cloning of rat thymic stromal
lymphopoietin receptor (TSLPR) and characterization of genomic
structure of murine Tslpr gene. Gene. 284:161–168. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pandey A, Ozaki K, Baumann H, Levin SD,
Puel A, Farr AG, Ziegler SF, Leonard WJ and Lodish HF: Cloning of a
receptor subunit required for signaling by thymic stromal
lymphopoietin. Nat Immunol. 1:59–64. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang W, Wang J, Wang Q, Chen G, Zhang J,
Chen T, Wan T, Zhang Y and Cao X: Identification of a novel type I
cytokine receptor CRL2 preferentially expressed by human dendritic
cells and activated monocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
281:878–883. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tonozuka Y, Fujio K, Sugiyama T, Nosaka T,
Hirai M and Kitamura T: Molecular cloning of a human novel type I
cytokine receptor related to delta1/TSLPR. Cytogenet Cell Genet.
93:23–25. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reche PA, Soumelis V, Gorman DM, Clifford
T, Liu MR, Travis M, Zurawski SM, Johnston J, Liu YJ, Spits H, et
al: Human thymic stromal lymphopoietin preferentially stimulates
myeloid cells. J Immunol. 167:336–343. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Soumelis V, Reche PA, Kanzler H, Yuan W,
Edward G, Homey B, Gilliet M, Ho S, Antonenko S, Lauerma A, et al:
Human epithelial cells trigger dendritic cell mediated allergic
inflammation by producing TSLP. Nat Immunol. 3:673–680. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He R and Geha RS: Thymic stromal
lymphopoietin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1183:13–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ziegler SF and Artis D: Sensing the
outside world: TSLP regulates barrier immunity. Nat Immunol.
11:289–293. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma P, Bian F, Wang Z, Zheng X,
Chotikavanich S, Pflugfelder SC and Li DQ: Human corneal
epithelium-derived thymic stromal lymphopoietin links the innate
and adaptive immune responses via TLRs and Th2 cytokines. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:2702–2709. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie F, Meng YH, Liu LB, Chang KK, Li H, Li
MQ and Li DJ: Cervical carcinoma cells stimulate the angiogenesis
through TSLP promoting growth and activation of vascular
endothelial cells. Am J Reprod Immunol. 70:69–79. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goldberg MP and Choi DW: Combined oxygen
and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: Calcium-dependent
and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. J Neurosci.
13:3510–3524. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brint S, Jacewicz M, Kiessling M, Tanabe J
and Pulsinelli W: Focal brain ischemia in the rat: Methods for
reproducible neocortical infarction using tandem occlusion of the
distal middle cerebral and ipsilateral common carotid arteries. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 8:474–485. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tamura A, Graham DI, McCulloch J and
Teasdale GM: Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: 1. Description of
technique and early neuropathological consequences following middle
cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1:53–60. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tamura A, Graham DI, McCulloch J and
Teasdale GM: Focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat: 2. Regional
cerebral blood flow determined by [14C]iodoantipyrine
autoradiography following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 1:61–69. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Zhang B, Tao Y, Wang Y, Wei H, Zhao
J, Huang R and Pei Z: DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects endothelial
cells against oxidative/nitrosative stress, mitochondrial damage
and subsequent cell death after oxygen glucose deprivation in
vitro. Brain Res. 1290:91–101. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Urbanek T, Kuczmik W, Basta-Kaim A and
Gabryel B: Rapamycin induces of protective autophagy in vascular
endothelial cells exposed to oxygen-glucose deprivation. Brain Res.
1553:1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dong W, Xiao S, Cheng M, Ye X and Zheng G:
Minocycline induces protective autophagy in vascular endothelial
cells exposed to an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion-induced
injury. Biomed Rep. 4:173–177. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ying S, O'Connor B, Ratoff J, Meng Q,
Mallett K, Cousins D, Robinson D, Zhang G, Zhao J, Lee TH and
Corrigan C: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin expression is increased in
asthmatic airways and correlates with expression of Th2-attracting
chemokines and disease severity. J Immunol. 174:8183–8190. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Besin G, Gaudreau S, Ménard M, Guindi C,
Dupuis G and Amrani A: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin and thymic
stromal lymphopoietin-conditioned dendritic cells induce regulatory
T-cell differentiation and protection of NOD mice against diabetes.
Diabetes. 57:2107–2117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Turcot V, Bouchard L, Faucher G, Garneau
V, Tchernof A, Deshaies Y, Pérusse L, Marceau S, Biron S,
Lescelleur O, et al: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin: An immune
cytokine gene associated with the metabolic syndrome and blood
pressure in severe obesity. Clin Sci(Lond). 123:99–109. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kitic M, Wimmer I, Adzemovic M, Kögl N,
Rudel A, Lassmann H and Bradl M: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is
expressed in the intact central nervous system and upregulated in
the myelin-degenerative central nervous system. Glia. 62:1066–1074.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu J, Wang Y, Akamatsu Y, Lee CC, Stetler
RA, Lawton MT and Yang GY: Vascular remodeling after ischemic
stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic potentials. Prog Neurobiol.
115:138–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S
and Wang JM: Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral
ischemic stroke. Stroke. 25:1794–1798. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Biel NM and Siemann DW: Targeting the
Angiopoietin-2/Tie-2 axis in conjunction with VEGF signal
interference. Cancer Lett. 380:525–533. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Everaert BR, Van Craenenbroeck EM, Hoymans
VY, Haine SE, Van Nassauw L, Conraads VM, Timmermans JP and Vrints
CJ: Current perspective of pathophysiological and interventional
effects on endothelial progenitor cell biology: Focus on
PI3K/AKT/eNOS pathway. Int J Cardiol. 144:350–366. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tokunaga E, Oki E, Egashira A, Sadanaga N,
Morita M, Kakeji Y and Maehara Y: Deregulation of the Akt pathway
in human cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:27–36. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang B, Peng Y, Dong J, Lin J, Wu C, Su Y,
Fang H, Wang L, Huang K and Li D: Human platelets express
functional thymic stromal lymphopoietin receptors: A potential role
in platelet activation in acute coronary syndrome. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 32:1741–1750. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|