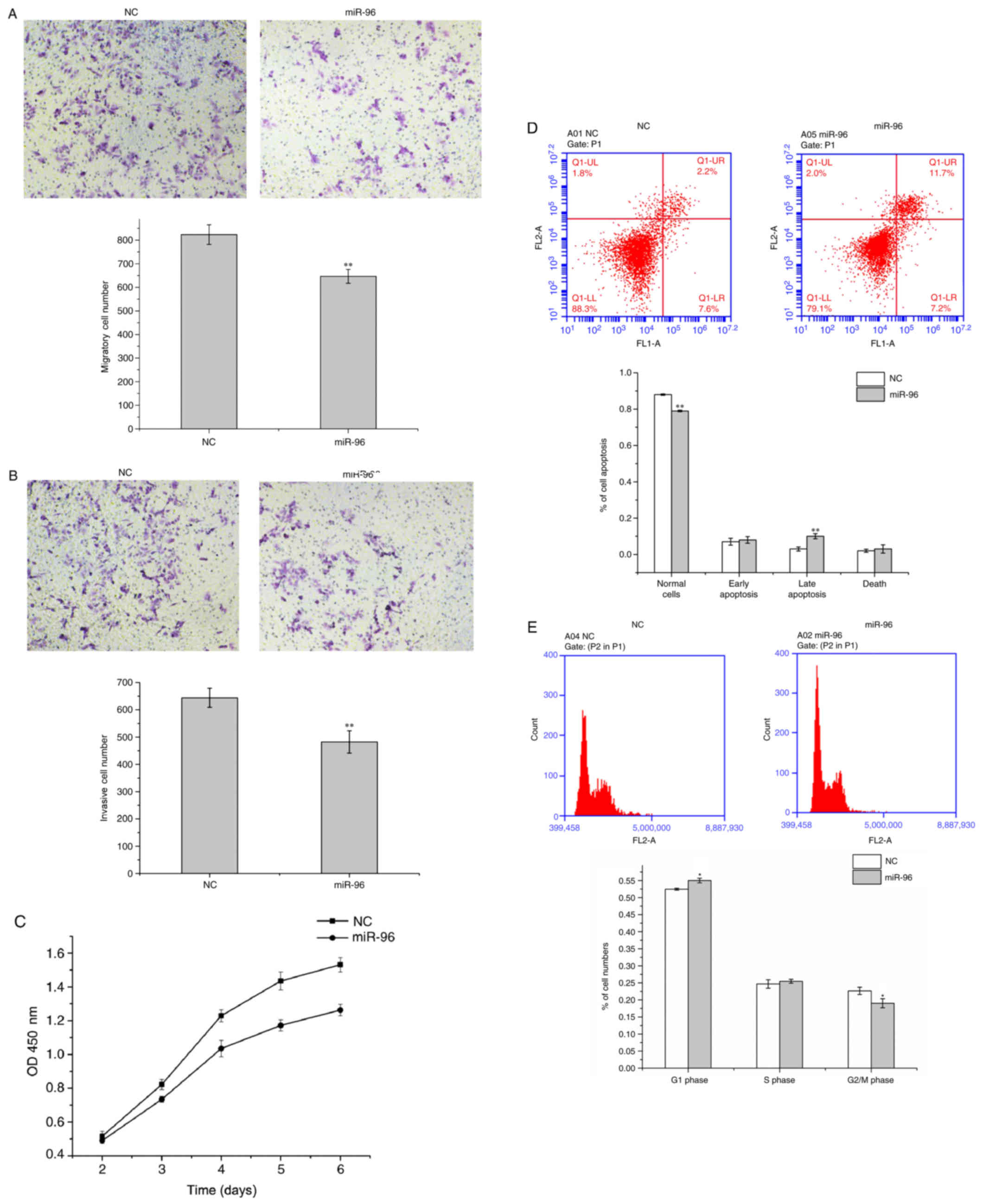
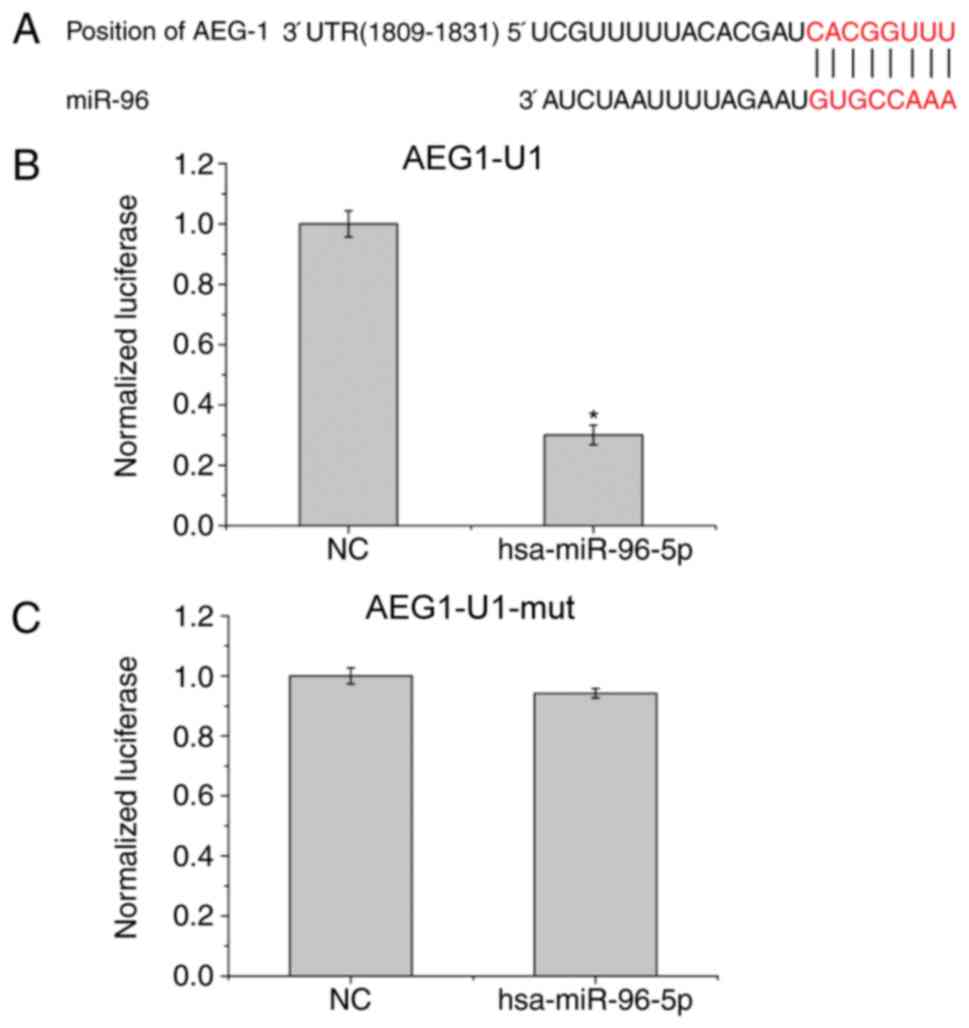
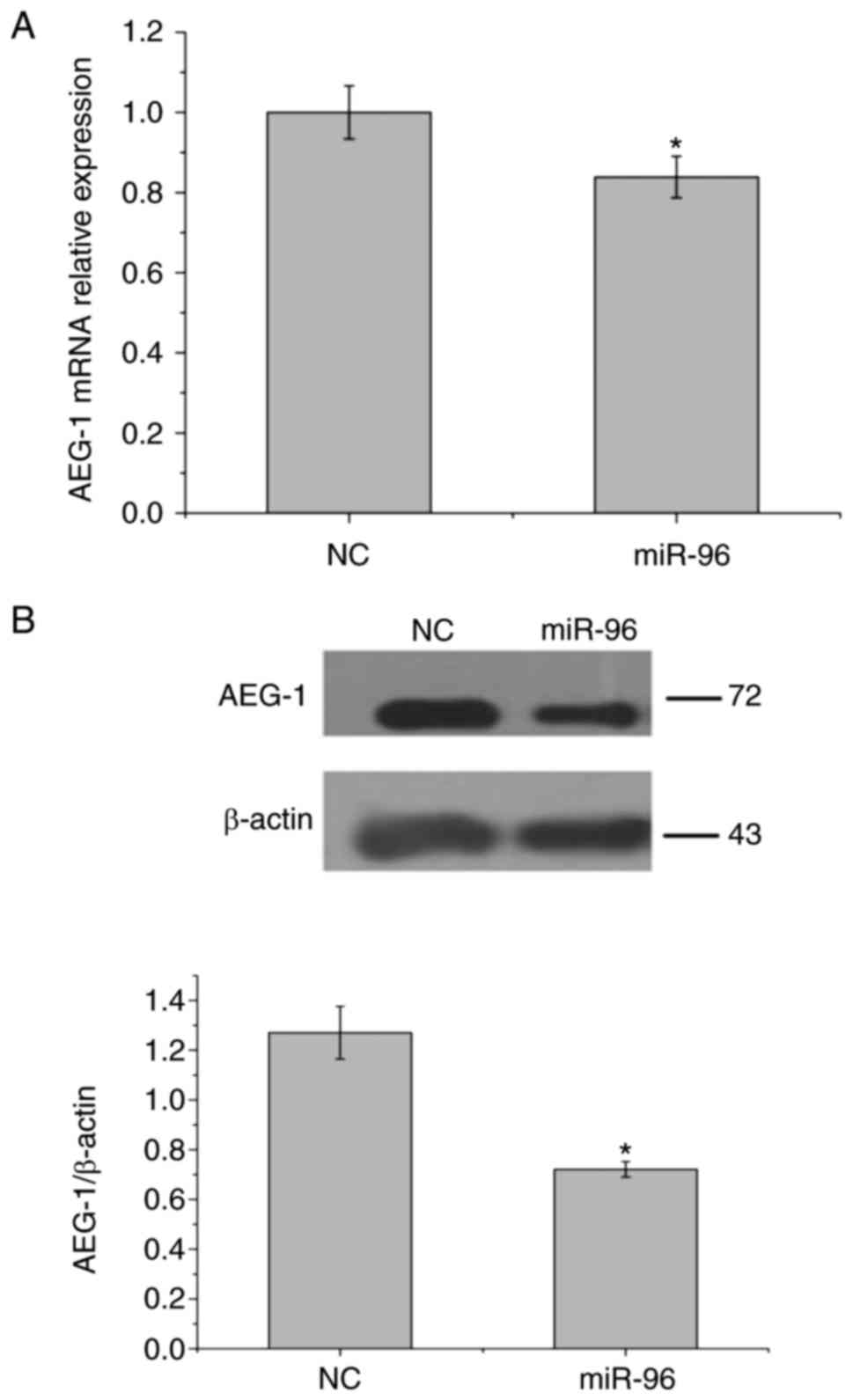
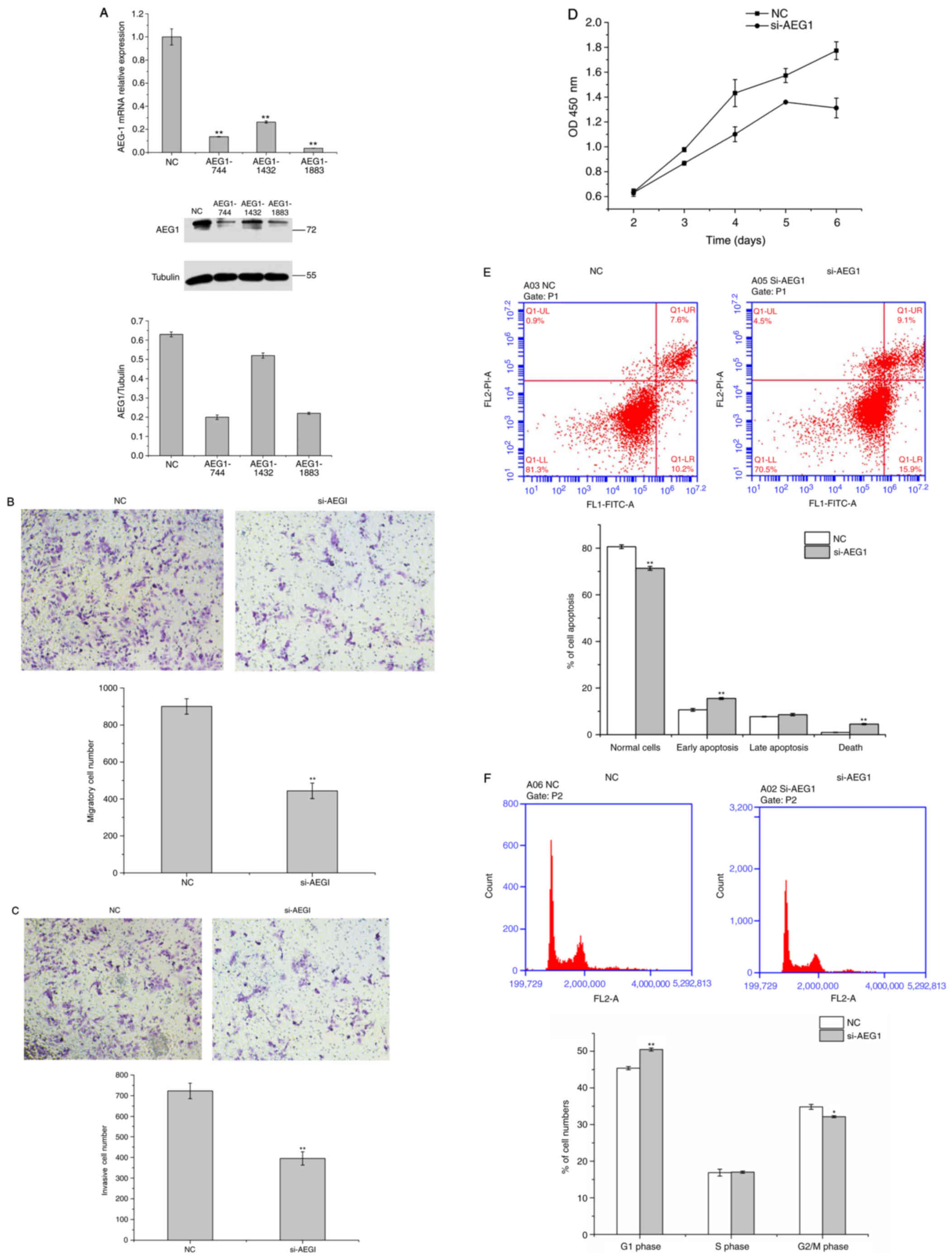
|
1
|
Rosenblum MK: The 2007 WHO classification
of nervous system tumors: Newly recognized members of the mixed
glioneuronal group. Brain Pathol. 17:308–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, Mukasa A,
Stommel JM, Stegh A, Hahn WC, Ligon KL, Louis DN, Brennan C, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: Genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perry A, Aldape KD, George DH and Burger
PC: Small cell astrocytoma: An aggressive variant that is
clinicopathologically and genetically distinct from anaplastic
oligodendroglioma. Cancer. 101:2318–2326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stummer W, van den Bent MJ and Westphal M:
Cytoreductive surgery of glioblastoma as the key to successful
adjuvant therapies: New arguments in an old discussion. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 153:1211–1218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP: New insights of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 40:643–650. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thiery JP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:442–454. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ozcan S: MiR-30 family and EMT in human
fetal pancreatic islets. Islets. 1:283–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu YN, Yin JJ, Abou-Kheir W, Hynes PG,
Casey OM, Fang L, Yi M, Stephens RM, Seng V, Sheppard-Tillman H, et
al: MiR-1 and miR-200 inhibit EMT via slug-dependent and
tumorigenesis via slug-independent mechanisms. Oncogene.
32:296–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tutar Y: miRNA and cancer; computational
and experimental approaches. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 15:4292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weeraratne SD, Amani V, Teider N,
Pierre-Francois J, Winter D, Kye MJ, Sengupta S, Archer T, Remke M,
Bai AH, et al: Pleiotropic effects of miR-183~96~182 converge to
regulate cell survival, proliferation and migration in
medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 123:539–552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ress AL, Stiegelbauer V, Winter E,
Schwarzenbacher D, Kiesslich T, Lax S, Jahn S, Deutsch A,
Bauernhofer T, Ling H, et al: MiR-96-5p influences cellular growth
and is associated with poor survival in colorectal cancer patients.
Mol Carcinog. 54:1442–1450. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su ZZ, Kang DC, Chen Y, Pekarskaya O, Chao
W, Volsky DJ and Fisher PB: Identification and cloning of human
astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with
HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid
subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene. 21:3592–3602. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Wei Y, Tong H, Chen L, Fan Y, Ji
Y, Jia W, Liu D and Wang G: MiR-302c-3p suppresses invasion and
proliferation of glioma cells via down-regulating metadherin (MTDH)
expression. Cancer Biol Ther. 16:1308–1315. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang Y, Ren GP, Xu C, Dong SF, Wang Y,
Gan Y, Zhu L and Feng TY: Expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1
(AEG-1) as a biomarker for aggressive pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 14:4792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu JQ, Zhou Q, Zhu H, Zheng FY and Chen
ZW: Overexpression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) in cervical
cancer and its correlation with angiogenesis. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:2277–2281. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang S, Wu B, Li D, Zhou W, Deng G, Zhang
K and Li Y: Knockdown of astrocyte elevated gene-1 inhibits tumor
growth and modifies microRNAs expression profiles in human
colorectal cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 444:338–345.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srivastava J, Robertson CL, Gredler R,
Siddiq A, Rajasekaran D, Akiel MA, Emdad L, Mas V, Mukhopadhyay ND,
Fisher PB and Sarkar D: Astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1)
contributes to non-thyroidal illness syndrome (NTIS) associated
with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). J Biol Chem. 290:15549–15558.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support
transcriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1987–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shin SY, Rath O, Zebisch A, Choo SM, Kolch
W and Cho KH: Functional roles of multiple feedback loops in
extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Wnt signaling pathways
that regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
70:6715–6724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Timmerman LA, Grego-Bessa J, Raya A,
Bertrán E, Pérez-Pomares JM, Díez J, Aranda S, Palomo S, McCormick
F, Izpisúa-Belmonte JC and de la Pompa JL: Notch promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition during cardiac development and
oncogenic transformation. Genes Dev. 18:99–115. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara
S, Gardner D, Maitra A, Isaacs JT, Berman DM and Beachy PA:
Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and
metastasis. Nature. 431:707–712. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang W, Qian P, Zhang X, Zhang M, Wang H,
Wu M, Kong X, Tan S, Ding K, Perry JK, et al: Autocrine/paracrine
human growth hormone-stimulated MicroRNA 96-182-183 cluster
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in breast
cancer. J Biol Chem. 290:13812–13829. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Q, Guo W, Zhang Y, Wu Y and Xiang J:
MiR-19a promotes cell proliferation and invasion by targeting RhoB
in human glioma cells. Neurosci Lett. 628:161–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Man HB, Bi WP and Man HH: Decreased
microRNA-198 expression and its prognostic significance in human
glioma. Genet Mol Res. 15:2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rapti SM, Kontos CK, Papadopoulos IN and
Scorilas A: High miR-96 levels in colorectal adenocarcinoma predict
poor prognosis, particularly in patients without distant metastasis
at the time of initial diagnosis. Tumour Biol. 37:11815–11824.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li C, Wu X, Zhang W, Li J, Liu H, Hao M,
Wang J, Zhang H, Yang G, Hao M, et al: AEG-1 promotes metastasis
through downstream AKR1C2 and NF1 in liver cancer. Oncol Res.
22:203–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gollavilli PN, Kanugula AK, Koyyada R,
Karnewar S, Neeli PK and Kotamraju S: AMPK inhibits MTDH expression
via GSK3β and SIRT1 activation: Potential role in triple negative
breast cancer cell proliferation. FEBS J. 282:3971–3985. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang B, Shen ZL, Jiang KW, Zhao G, Wang
CY, Yan YC, Yang Y, Zhang JZ, Shen C, Gao ZD, et al: MicroRNA-217
functions as a prognosis predictor and inhibits colorectal cancer
cell proliferation and invasion via an AEG-1 dependent mechanism.
BMC Cancer. 15:4372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
He W, He S, Wang Z, Shen H, Fang W, Zhang
Y, Qian W, Lin M, Yuan J, Wang J, et al: Astrocyte elevated
gene-1(AEG-1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung
cancer through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. BMC Cancer.
15:1072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou B, Yang J, Shu B, Liu K, Xue L, Su N,
Liu J and Xi T: Overexpression of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 is
associated with ovarian cancer development and progression. Mol Med
Rep. 11:2981–2990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi P, Fang C and Pang X: Astrocyte
elevated gene-1 regulates CCL3/CCR5-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via Erk1/2 and Akt signaling
in cardiac myxoma. Oncol Rep. 34:1319–1326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|