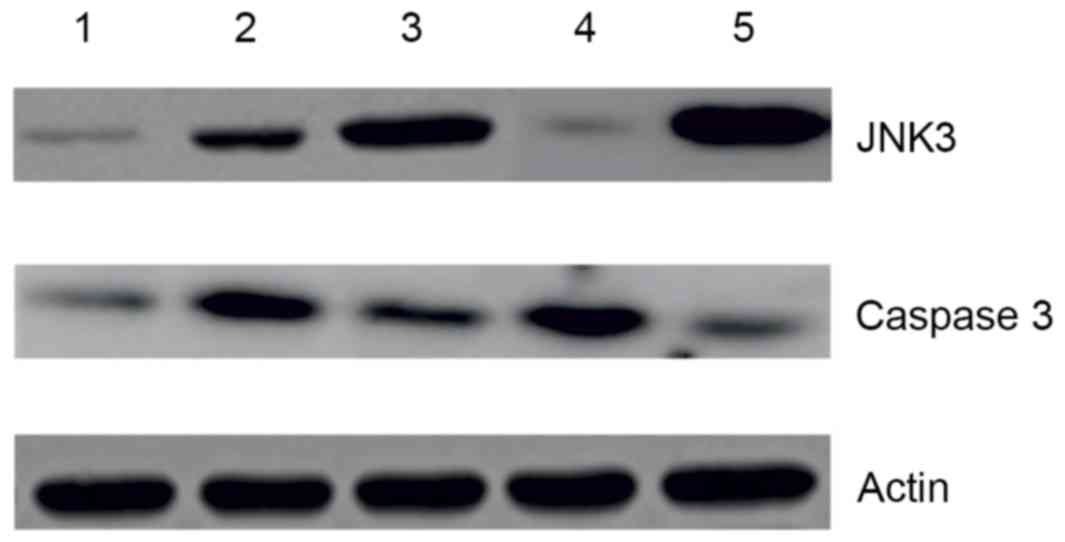
|
1
|
AlDakheel A, Kalia LV and Lang AE:
Pathogenesis-targeted, disease-modifying therapies in Parkinson
disease. Neurotherapeutics. 11:6–23. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buter TC, Van den Hout A, Matthews FE,
Larsen JP, Brayne C and Aarsland D: Dementia and survival in
Parkinson disease: A 12-year population study. Neurology.
70:1017–1022. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Crabtree D: Modulation of alpha-synuclein
metabolism and toxicity by cathepsin D. Uni Alabama Birmingham;
2012
|
|
4
|
Bennett DA, Beckett LA, Murray AM, Shannon
KM, Goetz CG, Pilgrim DM and Evans DA: Prevalence of parkinsonian
signs and associated mortality in a community population of older
people. N Engl J Med. 334:71–76. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kish SJ, Shannak K, Rajput A, Deck JH and
Hornykiewicz O: Aging produces a specific pattern of striatal
dopamine loss: Implications for the etiology of idiopathic
Parkinson's disease. J Neurochem. 58:642–648. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hornykiewicz O: Ageing and neurotoxins as
causative factors in idiopathic Parkinson's disease-a critical
analysis of the neurochemical evidence. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol
Biol Psychiatry. 13:319–328. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lang AE: Clinical trials of
disease-modifying therapies for neurodegenerative diseases: The
challenges and the future. Nat Med. 16:1223–1226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schapira AH: Recent developments in
biomarkers in Parkinson disease. Curr Opin Neurol. 26:395–400.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schapira AH and Schrag A: Parkinson
disease: Parkinson disease clinical subtypes and their
implications. Nat Rev Neurol. 7:247–248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goetz CG, Tilley BC, Shaftman SR, Stebbins
GT, Fahn S, Martinez-Martin P, Poewe W, Sampaio C, Stern MB, Dodel
R, et al: Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the
unified parkinson's disease rating scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale
presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov Disord.
23:2129–2170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian
mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways
activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol Rev. 81:807–869.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dhanasekaran DN and Reddy EP: JNK
signaling in apoptosis. Oncogene. 27:6245–6251. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bogoyevitch MA: The isoform-specific
functions of the c-Jun N-terminal Kinases (JNKs): Differences
revealed by gene targeting. Bioessays. 28:923–934. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Prediger RD, Aguiar AS Jr, Moreira EL,
Matheus FC, Castro AA, Walz R, De Bem AF, Latini A, Tasca CI,
Farina M and Raisman-Vozari R: The intranasal administration of
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP): A new rodent
model to test palliative and neuroprotective agents for Parkinson's
disease. Curr Pharm Des. 17:489–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duty S and Jenner P: Animal models of
Parkinson's disease: A source of novel treatments and clues to the
cause of the disease. Br J Pharmacol. 164:1357–1391. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su JH, Anderson AJ, Cummings BJ and Cotman
CW: Immunohistochemical evidence for apoptosis in Alzheimer's
disease. Neuroreport. 5:2529–2533. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J:
Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to
nitrocellulose sheets: Procedure and some applications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 76:pp. 4350–4354. 1979; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Vlahopoulos S and Zoumpourlis VC: JNK: A
key modulator of intracellular signaling. Biochemistry (Mosc).
69:844–854. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rabey JM, Sagi I, Huberman M, Melamed E,
Korczyn A, Giladi N, Inzelberg R, Djaldetti R, Klein C and Berecz
G; Rasagiline Study Group, : Rasagiline mesylate, a new MAO-B
inhibitor for the treatment of Parkinson's disease: A double-blind
study as adjunctive therapy to levodopa. Clin Neuropharmacol.
23:324–330. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
King KL and Cidlowski JA: Cell cycle
regulation and apoptosis 1. Annu Rev Physiol. 60:601–617. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hanyu H, Asano T, Sakurai H, Takasaki M,
Shindo H and Abe K: Magnetisation transfer measurements of the
subcortical grey and white matter in Parkinson's disease with and
without dementia and in progressive supranuclear palsy.
Neuroradiology. 43:542–546. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Donovan S: Parkinson's disease treatment
US 6620415 B2. Filed July 11, 2001; issued September 16. 2003
|
|
23
|
Wegner C and Stadelmann C: Gray matter
pathology and multiple sclerosis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
9:399–404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rathinam R, Berrier A and Alahari SK: Role
of Rho GTPases and their regulators in cancer progression. Front
Biosci (Landmark Ed). 16:2561–2571. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cellurale C, Girnius N, Jiang F,
Cavanagh-Kyros J, Lu S, Garlick DS, Mercurio AM and Davis RJ: Role
of JNK in mammary gland development and breast cancer. Cancer Res.
72:472–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bellamy CO, Malcolmson RD, Harrison DJ and
Wyllie AH: Cell death in health and disease: The biology and
regulation of apoptosis. Semin Cancer Biol. 6:3–16. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|