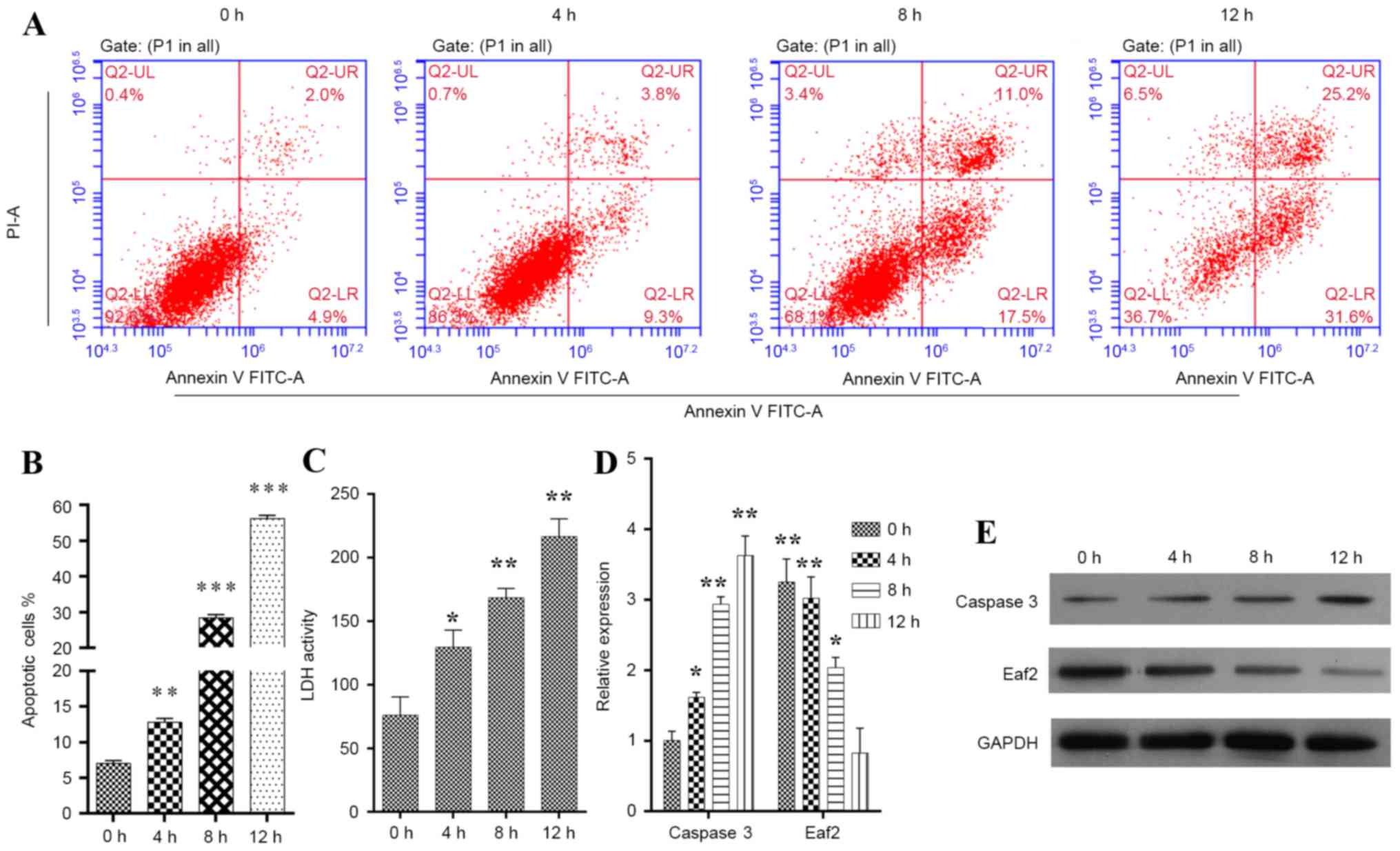
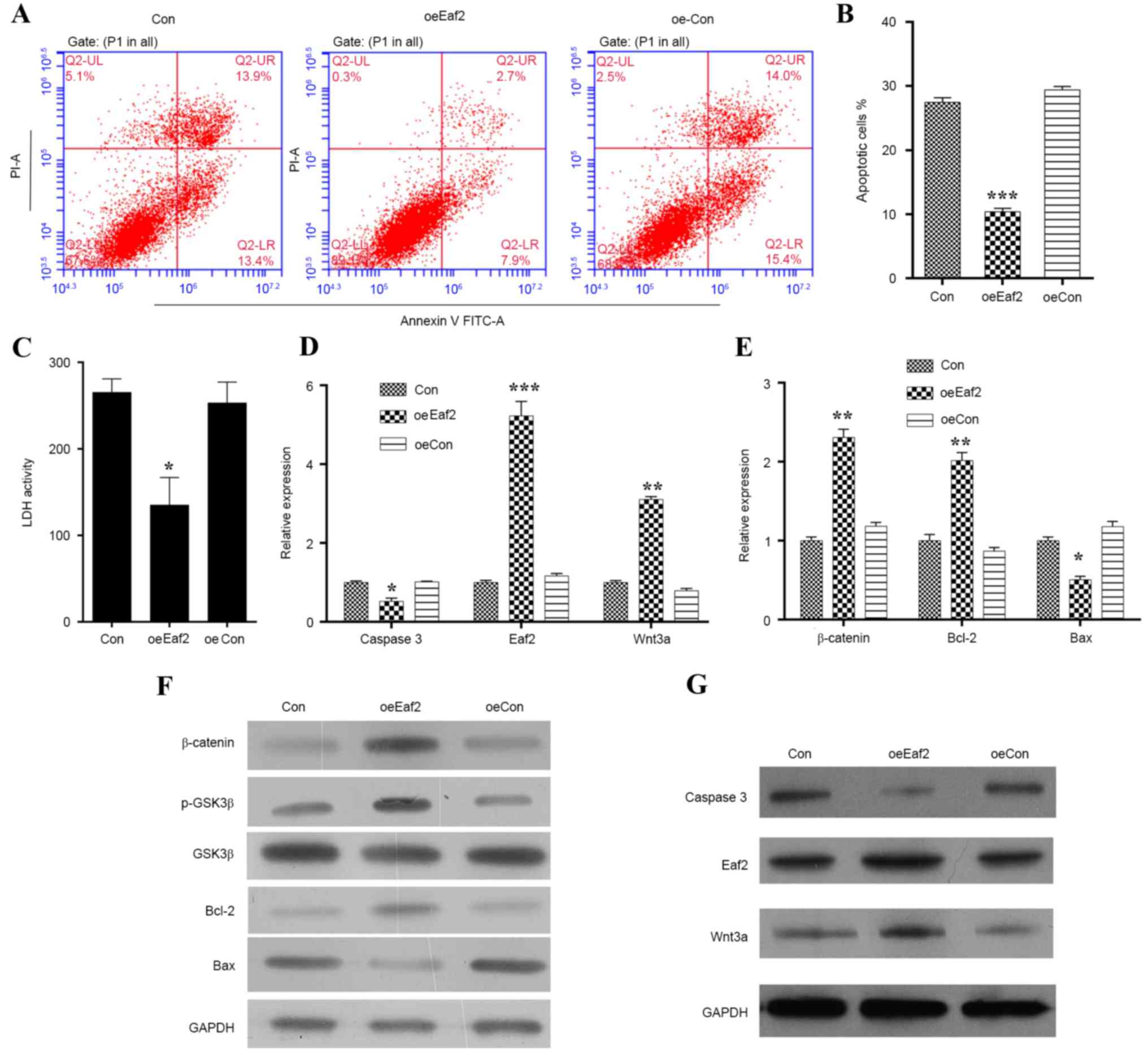
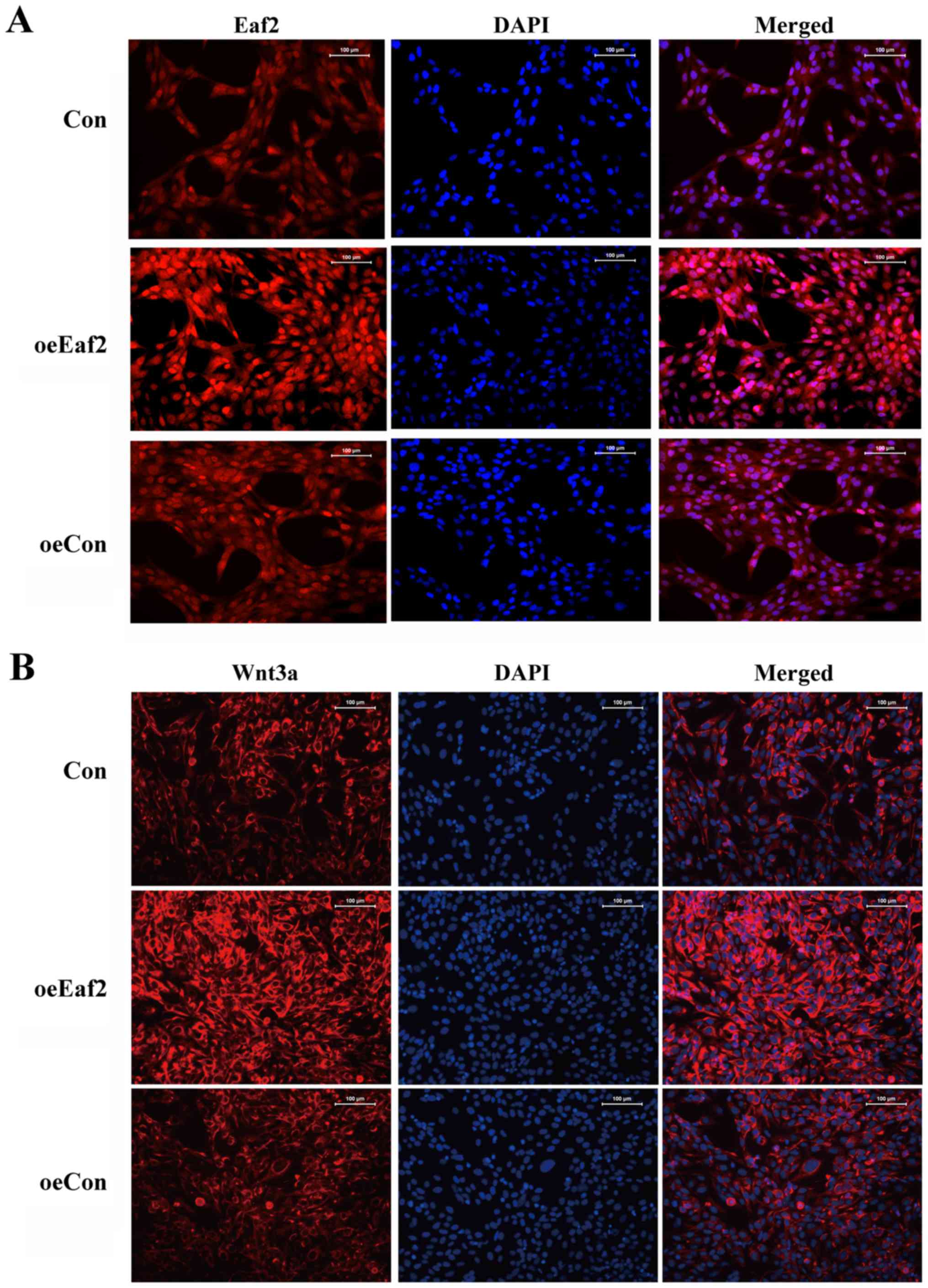
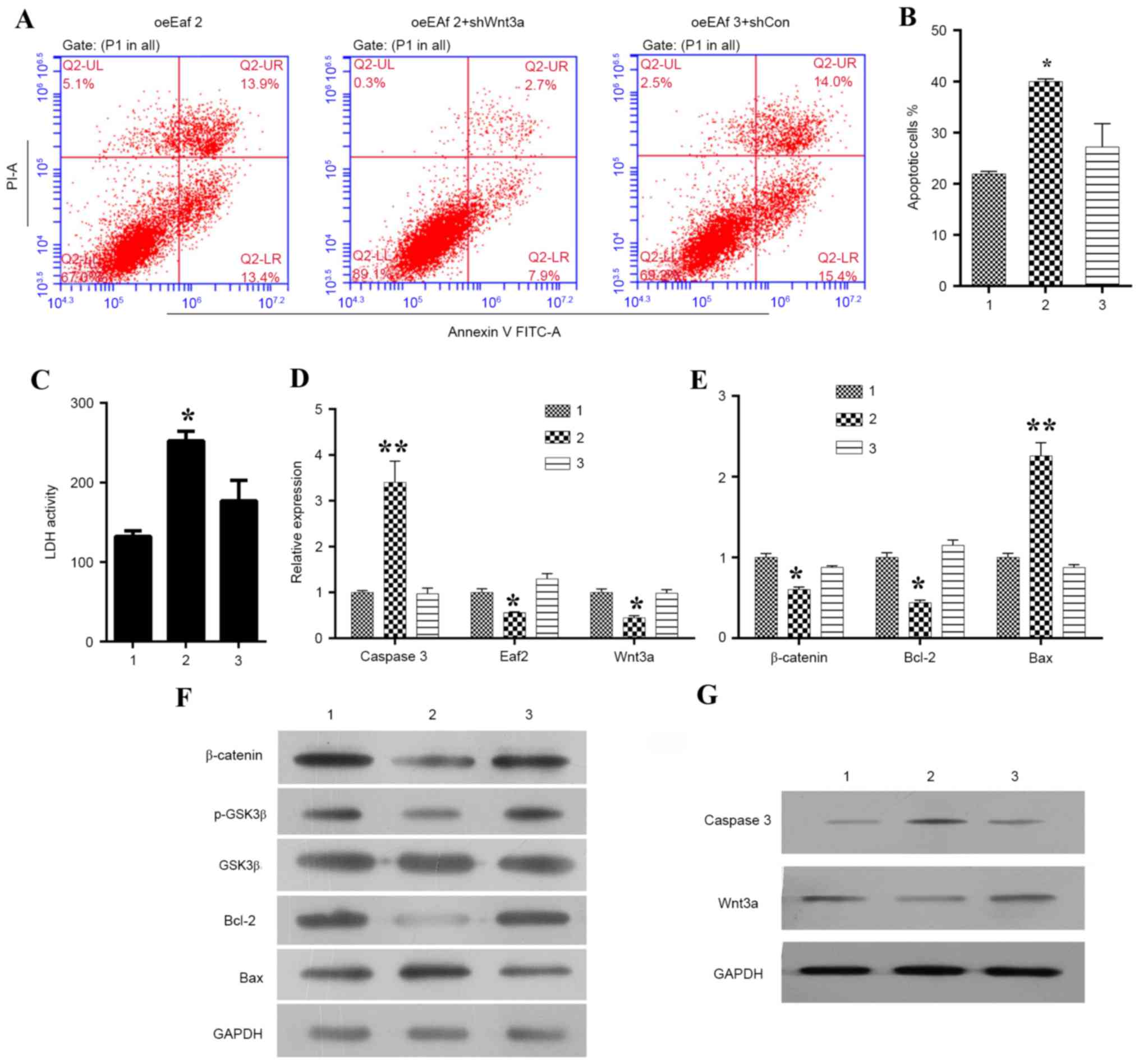
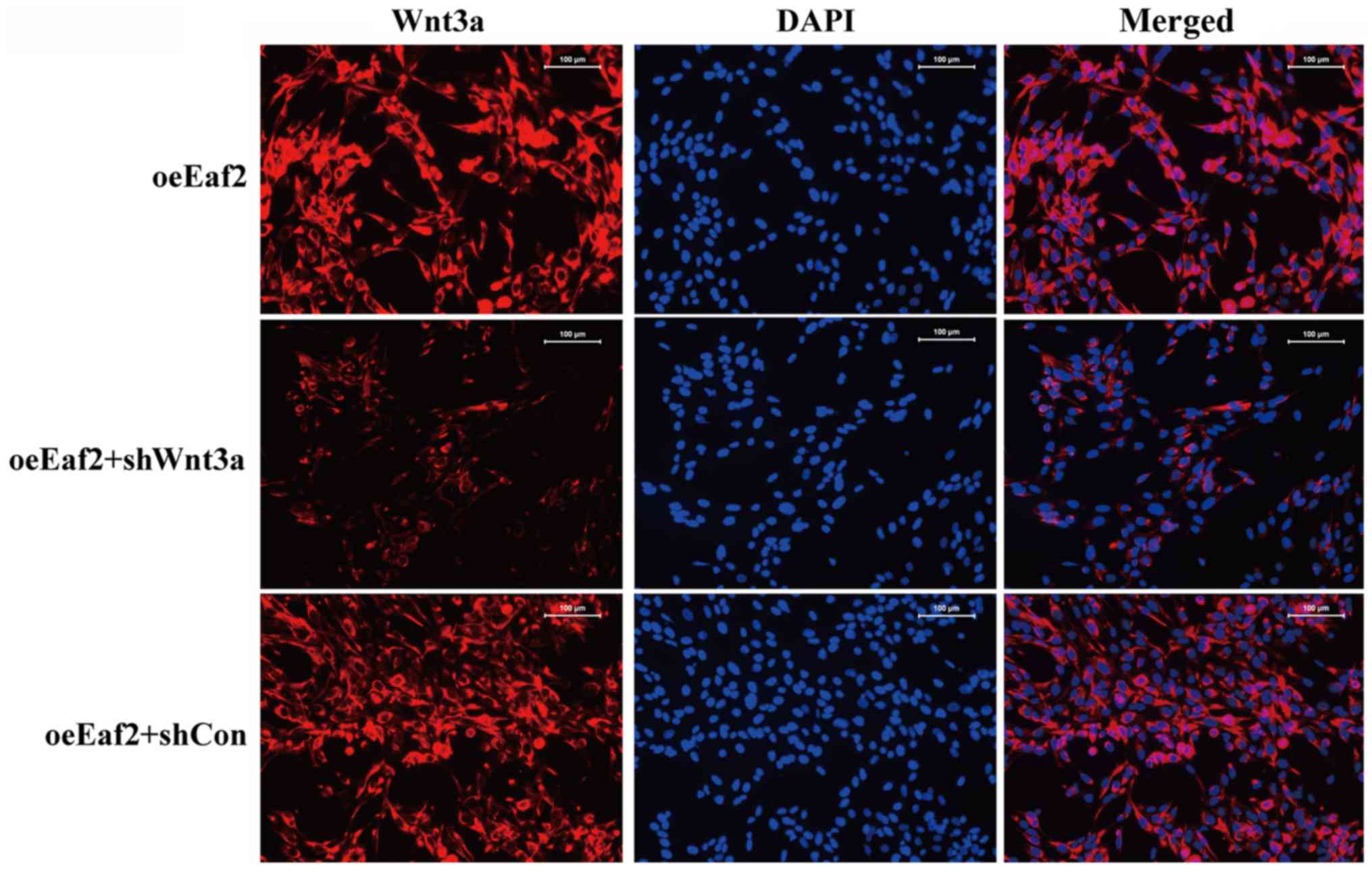
|
1
|
Wormstone IM, Collison DJ, Hansom SP and
Duncan G: A focus on the human lens in vitro. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 21:215–221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pascolini D and Mariotti SP: Global
estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol. 96:614–618.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang Z, Wang D, Li Y and Zhang X:
Protective effects of verapamil against H2O2-induced apoptosis in
human lens epithelial cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:553–557. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ottonello S, Foroni C, Carta A, Petrucco S
and Maraini G: Oxidative stress and age-related cataract.
Ophthalmologica. 214:78–85. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seomun Y, Kim JT, Kim HS, Park JY and Joo
CK: Induction of p21Cip1-mediated G2/M arrest in H2O2-treated lens
epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 11:764–774. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Spector A: Oxidative stress-induced
cataract: Mechanism of action. FASEB J. 9:1173–1182.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Spector A and Garner WH: Hydrogen peroxide
and human cataract. Exp Eye Res. 33:673–681. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simone F, Luo RT, Polak PE, Kaberlein JJ
and Thirman MJ: ELL-associated factor 2 (EAF2), a functional
homolog of EAF1 with alternative ELL binding properties. Blood.
101:2355–2362. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kong SE, Banks CA, Shilatifard A, Conaway
JW and Conaway RC: ELL-associated factors 1 and 2 are positive
regulators of RNA polymerase II elongation factor ELL. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 10094–10098. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiao W, Zhang Q, Jiang F, Pins M,
Kozlowski JM and Wang Z: Suppression of prostate tumor growth by
U19, a novel testosterone-regulated apoptosis inducer. Cancer Res.
63:4698–4704. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xiao W, Zhang Q, Habermacher G, Yang X,
Zhang AY, Cai X, Hahn J, Liu J, Pins M, Doglio L, et al: U19/Eaf2
knockout causes lung adenocarcinoma, B-cell lymphoma,
hepatocellular carcinoma and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
Oncogene. 27:1536–1544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li M, Wu X, Zhuang F, Jiang S, Jiang M and
Liu YH: Expression of murine ELL-associated factor 2 (Eaf2) is
developmentally regulated. Dev Dyn. 228:273–280. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maurus D, Héligon C, Bürger-Schwärzler A,
Brändli AW and Kühl M: Noncanonical Wnt-4 signaling and EAF2 are
required for eye development in Xenopus laevis. EMBO J.
24:1181–1191. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heisenberg CP, Tada M, Rauch GJ, Saúde L,
Concha ML, Geisler R, Stemple DL, Smith JC and Wilson SW:
Silberblick/Wnt11 mediates convergent extension movements during
zebrafish gastrulation. Nature. 405:76–81. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kilian B, Mansukoski H, Barbosa FC, Ulrich
F, Tada M and Heisenberg CP: The role of Ppt/Wnt5 in regulating
cell shape and movement during zebrafish gastrulation. Mech Dev.
120:467–476. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu JX, Hu B, Wang Y, Gui JF and Xiao W:
Zebrafish eaf1 and eaf2/u19 mediate effective convergence and
extension movements through the maintenance of wnt11 and wnt5
expression. J Biol Chem. 284:16679–16692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Clevers H: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
development and disease. Cell. 127:469–480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao XL, Song H, Chen Z and Tang X: Wnt3a
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration, and
proliferation of lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis. 18:1983–1990.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang Y, Fu R, Zhao J, Wu D, Qiao G, Li R
and Zhang J: Effects of ELL-associated factor 2 on ultraviolet
radiation-induced cataract formation in mice. Mol Med Rep.
12:6605–6611. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rasmussen JT, Deardorff MA, Tan C, Rao MS,
Klein PS and Vetter ML: Regulation of eye development by frizzled
signaling in Xenopus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:pp. 3861–3866.
2001; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai J, Liu H, Zhou J and Huang K:
Selenoprotein R protects human lens epithelial cells against
d-Galactose-induced apoptosis by regulating oxidative stress and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Int J Mol Sci. 17:2312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mao YW, Xiang H, Wang J, Korsmeyer S,
Reddan J and Li DW: Human bcl-2 gene attenuates the ability of
rabbit lens epithelial cells against H2O2-induced apoptosis through
down-regulation of the alpha B-crystallin gene. J Biol Chem.
276:43435–43445. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Takamura Y, Sugimoto Y, Kubo E, Takahashi
Y and Akagi Y: Immunohistochemical study of apoptosis of lens
epithelial cells in human and diabetic rat cataracts. Jpn J
Ophthalmol. 45:559–563. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blankenberg FG and Strauss HW: Recent
advances in the molecular imaging of programmed cell death: Part
I-pathophysiology and radiotracers. J Nucl Med. 53:1659–1662. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J and Yuan J: Caspases in apoptosis and
beyond. Oncogene. 27:6194–6206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li WC, Kuszak JR, Dunn K, Wang RR, Ma W,
Wang GM, Spector A, Leib M, Cotliar AM, Weiss M, et al: Lens
epithelial cell apoptosis appears to be a common cellular basis for
non-congenital cataract development in humans and animals. J Cell
Biol. 130:169–181. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shang YC, Wang SH, Xiong F, Zhao CP, Peng
FN, Feng SW, Li MS, Li Y and Zhang C: Wnt3a signaling promotes
proliferation, myogenic differentiation, and migration of rat bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:1761–1774.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|