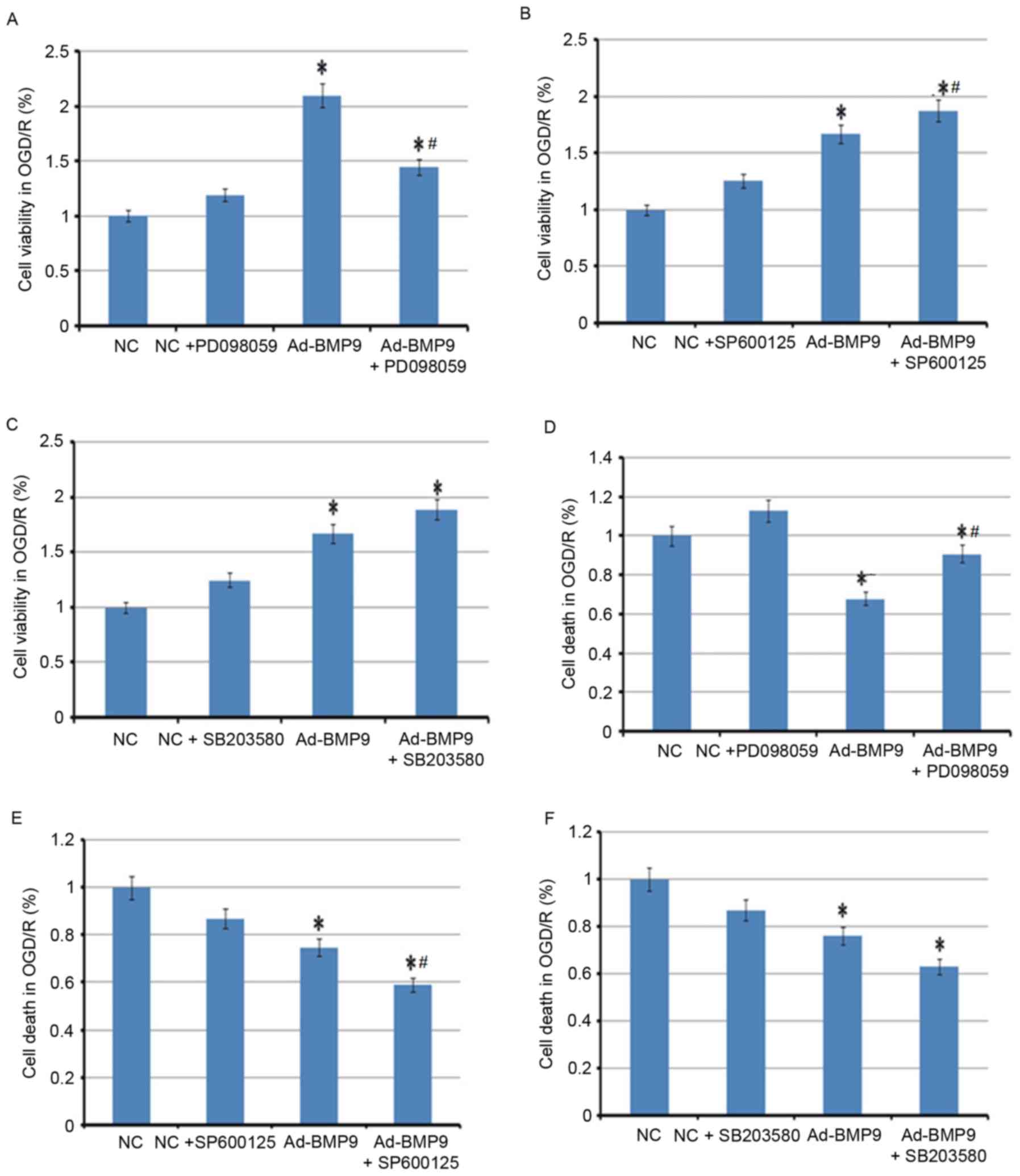
|
1
|
Roger VL, Go AS, Lloyd-Jones DM, Adams RJ,
Berry JD, Brown TM, Carnethon MR, Dai S, de Simone G, Ford ES, et
al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2011 update: A report from
the American Heart Association. Circulation. 123:e18–e209. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stoll G, Kleinschnitz C and Nieswandt B:
Molecular mechanisms of thrombus formation in ischemic stroke:
Novel insights and targets for treatment. Blood. 112:3555–3562.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Deb P, Sharma S and Hassan KM:
Pathophysiologic mechanisms of acute ischemic stroke: An overview
with emphasis on therapeutic significance beyond thrombolysis.
Pathophysiology. 17:197–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sanderson TH, Reynolds CA, Kumar R,
Przyklenk K and Hüttemann M: Molecular mechanisms of
ischemia-reperfusion injury in brain: Pivotal role of the
mitochondrial membrane potential in reactive oxygen species
generation. Mol Neurobiol. 47:9–23. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang M, Li YJ, Ding Y, Zhang HN, Sun T,
Zhang K, Yang L, Guo YY, Liu SB, Zhao MG and Wu YM: Silibinin
prevents autophagic cell death upon oxidative stress in cortical
neurons and cerebral ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Mol Neurobiol.
53:932–943. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reddi AH: Regulation of cartilage and bone
differentiation by bone morphogenetic proteins. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 4:850–855. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu A and Niswander LA: Bone morphogenetic
protein signalling and vertebrate nervous system development. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 6:945–954. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chalazonitis A and Kessler JA: Pleiotropic
effects of the bone morphogenetic proteins on development of the
enteric nervous system. Dev Neurobiol. 72:843–856. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang R, Pei H, Ru L, Li H and Liu G: Bone
morphogenetic protein 7 upregulates the expression of nestin and
glial fibrillary acidic protein in rats with cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biomed Rep. 1:895–900. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y and Morikawa M: Bone
morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem.
147:35–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu JH, Zhang TZ, Zhao YY, Wang JK and Yuan
ZG: Protective effects of recombinant human bone morphogenetic
protein-7 on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J
Neurosci. 123:375–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pei H, Cao D, Guo Z, Liu G, Guo Y and Lu
C: Bone morphogenetic protein-7 ameliorates cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion injury via inhibiting oxidative stress and neuronal
apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 14:23441–23453. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Chang CF, Morales M, Chou J, Chen
HL, Chiang YH, Lin SZ, Cadet JL, Deng X, Wang JY, et al: Bone
morphogenetic protein-6 reduces ischemia-induced brain damage in
rats. Stroke. 32:2170–2178. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schnitzler AC, Mellott TJ, Lopez-Coviella
I, Tallini YN, Kotlikoff MI, Follettie MT and Blusztajn JK: BMP9
(bone morphogenetic protein 9) induces NGF as an
autocrine/paracrine cholinergic trophic factor in developing basal
forebrain neurons. J Neurosci. 30:8221–8228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao C, Wu N, Deng F, Zhang H, Wang N,
Zhang W, Chen X, Wen S, Zhang J, Yin L, et al: Adenovirus-mediated
gene transfer in mesenchymal stem cells can be significantly
enhanced by the cationic polymer polybrene. PLoS One. 9:e929082014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Germano SM,
Nishimura MC, Davis RL and Bartkowski HM: Evaluation of
2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride as a stain for detection and
quantification of experimental cerebral infarction in rats. Stroke.
17:1304–1308. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen H, Tian M, Jin L, Jia H and Jin Y:
PUMA is invovled in ischemia/reperfusion-induced apoptosis of mouse
cerebral astrocytes. Neuroscience. 284:824–832. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dong YF, Chen ZZ, Zhao Z, Yang DD, Yan H,
Ji J and Sun XL: Potential role of microRNA-7 in the
anti-neuroinflammation effects of nicorandil in astrocytes induced
by oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Neuroinflammation. 13:602016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH and Iadecola C: The
science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron.
67:181–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lo EH: Experimental models, neurovascular
mechanisms and translational issues in stroke research. Br J
Pharmacol. 153 Suppl 1:S396–S405. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
López-Coviella I, Berse B, Krauss R, Thies
RS and Blusztajn JK: Induction and maintenance of the neuronal
cholinergic phenotype in the central nervous system by BMP-9.
Science. 289:313–316. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lopez-Coviella I, Follettie MT, Mellott
TJ, Kovacheva VP, Slack BE, Diesl V, Berse B, Thies RS and
Blusztajn JK: Bone morphogenetic protein 9 induces the
transcriptome of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:pp. 6984–6989. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luan L, Yang X, Zhou C, Wang K and Qin L:
Post-hypoxic and ischemic neuroprotection of BMP-7 in the cerebral
cortex and caudate-putamen tissue of rat. Acta Histochem.
117:148–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fong D, Bisson M, Laberge G, Mcmanus S,
Grenier G, Faucheux N and Roux S: Bone morphogenetic protein-9
activates Smad and ERK pathways and supports human osteoclast
function and survival in vitro. Cell Signal. 25:717–728. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye G, Li C, Xiang X, Chen C, Zhang R, Yang
X, Yu X, Wang J, Wang L, Shi Q and Weng Y: Bone morphogenetic
protein-9 induces PDLSCs osteogenic differentiation through the ERK
and p38 signal pathways. Int J Med Sci. 11:1065–1072. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kovalska M, Kovalska L, Pavlikova M,
Janickova M, Mikuskova K, Adamkov M, Kaplan P, Tatarkova Z and
Lehotsky J: Intracellular signaling MAPK pathway after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Neurochem Res. 37:1568–1577. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu YM, Wang CC, Chen L, Qian LB, Ma LL,
Yu J, Zhu MH, Wen CY, Yu LN and Yan M: Both PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2
pathways participate in the protection by dexmedetomidine against
transient focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Brain
Res. 1494:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang PR, Wang JS, Zhang C, Song XF, Tian N
and Kong LY: Huang-Lian-Jie-Du-Decotion induced protective
autophagy against the injury of cerebral ischemia/reperfusion via
MAPK-mTOR signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:270–280. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang S, Yuan Y, Jiao S, Luo Q and Yu J:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide protects rats from cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury via a mechanism of action in the MAPK
pathway. Biomed Rep. 4:699–703. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gong J, Sun F, Li Y, Zhou X, Duan Z, Duan
F, Lei Z, Chen H, Qi S and Shen J: Momordica charantia
polysaccharides could protect against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury through inhibiting oxidative stress mediated c-Jun
N-terminal kinase 3 signaling pathway. Neuropharmacology.
91:123–134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang W, Tang L, Yong L and Yong W:
Biochanin a protects against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in
rats via inhibition of p38-mediated inflammatory responses. J
Neurol Sci. 348:121–125. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|