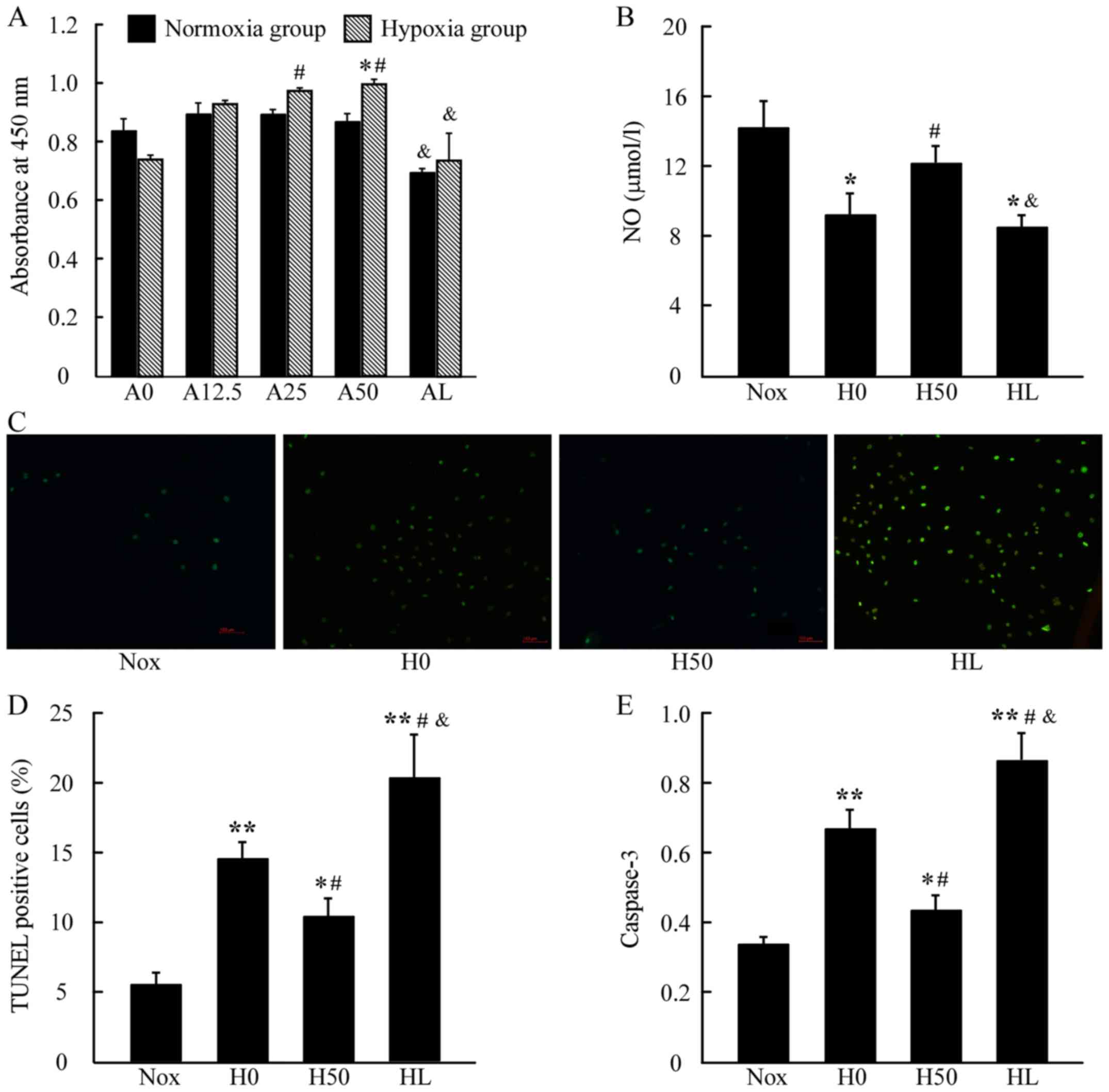
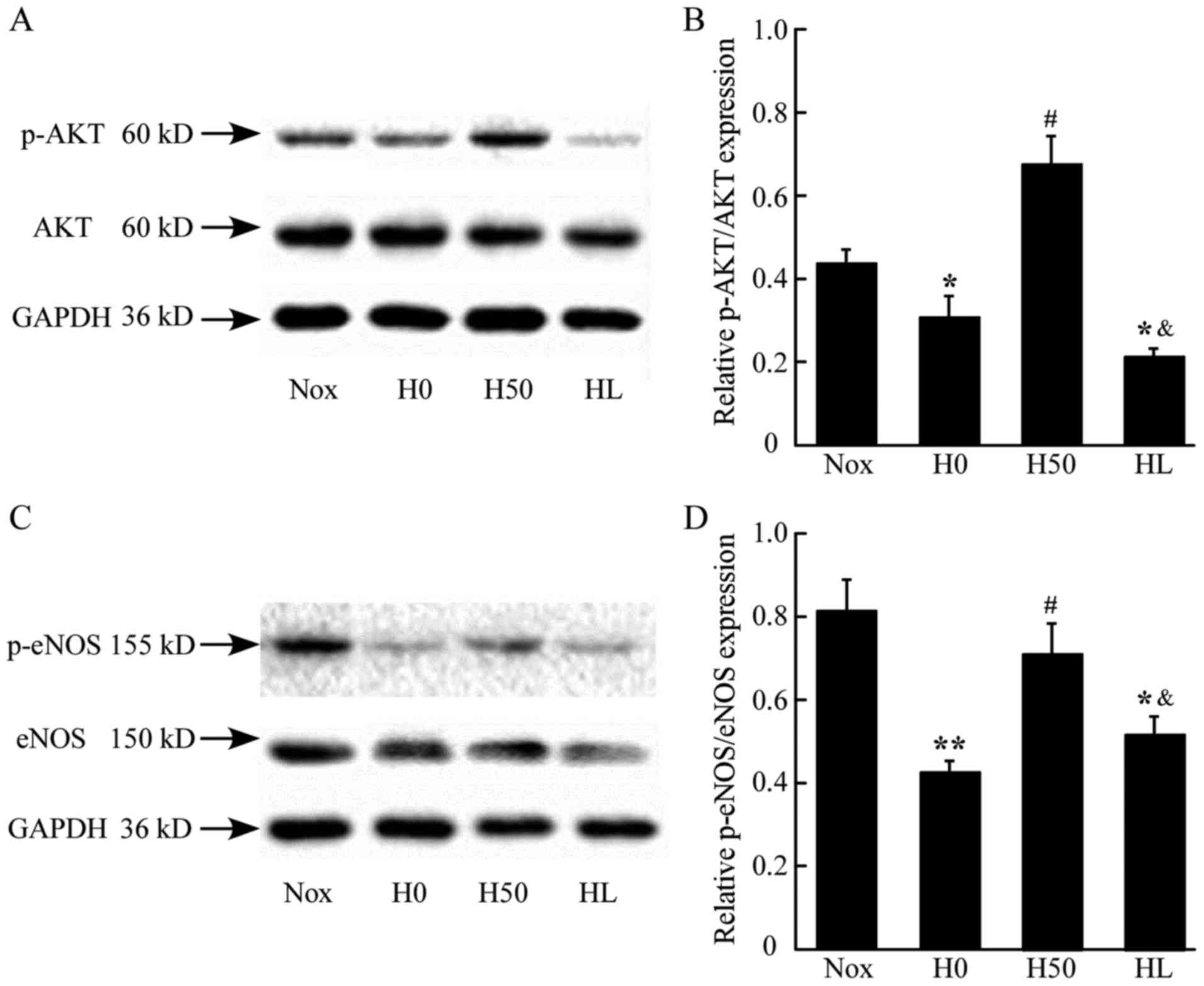
|
1
|
Rubin LJ: Primary pulmonary hypertension.
N Engl J Med. 336:111–117. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL, Stenmark
KR, MacLean MR, Lang IM, Christman BW, Weir EK, Eickelberg O,
Voelkel NF and Rabinovitch M: Cellular and molecular pathobiology
of pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 43 12 Suppl
S:13S–24S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shimoda LA, Sham JS and Sylvester JT:
Altered pulmonary vasoreactivity in the chronically hypoxic lung.
Physiol Res. 49:549–560. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu W, Koeck T, Lara AR, Neumann D,
DiFilippo FP, Koo M, Janocha AJ, Masri FA, Arroliga AC, Jennings C,
et al: Alterations of cellular bioenergetics in pulmonary artery
endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp. 1342–1347. 2007;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Campbell AI, Zhao Y, Sandhu R and Stewart
DJ: Cell-based gene transfer of vascular endothelial growth factor
attenuates monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension.
Circulation. 104:2242–2248. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao YD, Campbell AI, Robb M, Ng D and
Stewart DJ: Protective role of angiopoietin-1 in experimental
pulmonary hypertension. Circ Res. 92:984–991. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Cras TD and McMurtry IF: Nitric oxide
production in the hypoxic lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
280:L575–L582. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fulton D, Gratton JP, McCabe TJ, Fontana
J, Fujio Y, Walsh K, Franke TF, Papapetropoulos A and Sessa WC:
Regulation of endothelium-derived nitric oxide production by the
protein kinase Akt. Nature. 399:597–601. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ou J, Fontana JT, Ou Z, Jones DW, Ackerman
AW, Oldham KT, Yu J, Sessa WC and Pritchard KA Jr: Heat shock
protein 90 and tyrosine kinase regulate eNOS NO* generation but not
NO* bioactivity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 286:H561–H569.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Giaid A and Saleh D: Reduced expression of
endothelial nitric oxide synthase in the lungs of patients with
pulmonary hypertension. N Engl J Med. 333:214–221. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pullamsetti S, Kiss L, Ghofrani HA,
Voswinckel R, Haredza P, Klepetko W, Aigner C, Fink L, Muyal JP,
Weissmann N, et al: Increased levels and reduced catabolism of
asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginines in pulmonary
hypertension. FASEB J. 19:1175–1177. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo JS, Cheng CL and Koo MW: Inhibitory
effects of Centella asiatica water extract and asiaticoside on
inducible nitric oxide synthase during gastric ulcer healing in
rats. Planta Med. 70:1150–1154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yun KJ, Kim JY, Kim JB, Lee KW, Jeong SY,
Park HJ, Jung HJ, Cho YW, Yun K and Lee KT: Inhibition of
LPS-induced NO and PGE2 production by asiatic acid via NF-kappa B
inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophages: Possible involvement of the
IKK and MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 8:431–441. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dong MS, Jung SH, Kim HJ, Kim JR, Zhao LX,
Lee ES, Lee EJ, Yi JB, Lee N, Cho YB, et al: Structure-related
cytotoxicity and anti-hepatofibric effect of asiatic acid
derivatives in rat hepatic stellate cell-line, HSC-T6. Arch Pharm
Res. 27:512–517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen S, Yin ZJ, Jiang C, Ma ZQ, Fu Q, Qu R
and Ma SP: Asiaticoside attenuates memory impairment induced by
transient cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in mice through
anti-inflammatory mechanism. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 122:7–15.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang XB, Wang W, Zhu XC, Ye WJ, Cai H, Wu
PL, Huang XY and Wang LX: The potential of asiaticoside for
TGF-β1/Smad signaling inhibition in prevention and progression of
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Life Sci. 137:56–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muramatsu M, Oka M, Morio Y, Soma S,
Takahashi H and Fukuchi Y: Chronic hypoxia augments endothelin-B
receptor-mediated vasodilation in isolated perfused rat lungs. Am J
Physiol. 276:L358–L364. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Michelakis ED, McMurtry MS, Wu XC, Dyck
JR, Moudgil R, Hopkins TA, Lopaschuk GD, Puttagunta L, Waite R and
Archer SL: Dichloroacetate, a metabolic modulator, prevents and
reverses chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in rats: Role of
increased expression and activity of voltage-gated potassium
channels. Circulation. 105:244–250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng Y, Li M, Zhang Y, Shi X, Li L and
Jin M: The effects and mechanisms of mycophenolate mofetil on
pulmonary arterial hypertension in rats. Rheumatol Int. 30:341–348.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Xu F and Sehgal PB:
Aberrant cytoplasmic sequestration of eNOS in endothelial cells
after monocrotaline, hypoxia and senescence: Live-cell caveolar and
cytoplasmic NO imaging. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
292:H1373–H1389. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wilkins MR: Pulmonary hypertension: The
science behind the disease spectrum. Eur Respir Rev. 21:19–26.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Coggins MP and Bloch KD: Nitric oxide in
the pulmonary vasculature. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:1877–1885. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, He H, Rezvani
M, Ingwall JS and Dzau VJ: Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt
prevent remodeling and restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat
Med. 9:1195–1201. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Martorell L, Gentile M, Rius J, Rodríguez
C, Crespo J, Badimon L and Martínez-González J: The
hypoxia-inducible factor 1/NOR-1 axis regulates the survival
response of endothelial cells to hypoxia. Mol Cell Biol.
29:5828–5842. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pullamsetti SS, Savai R, Janssen W, Dahal
BK, Seeger W, Grimminger F, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N and Schermuly
RT: Inflammation, immunological reaction and role of infection in
pulmonary hypertension. Clin Microbiol Infect. 17:7–14. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|