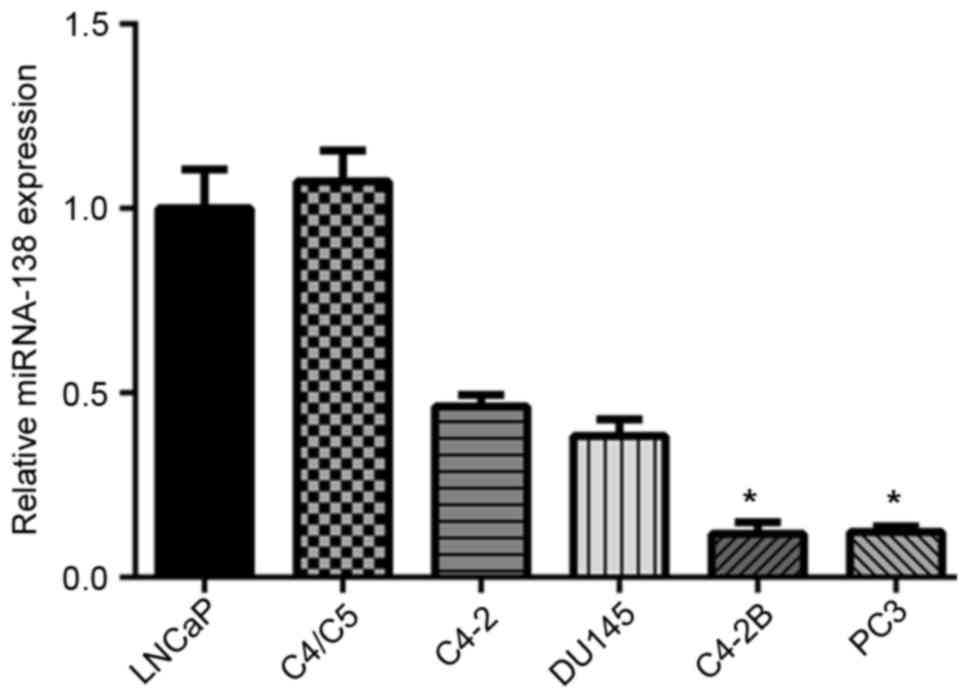
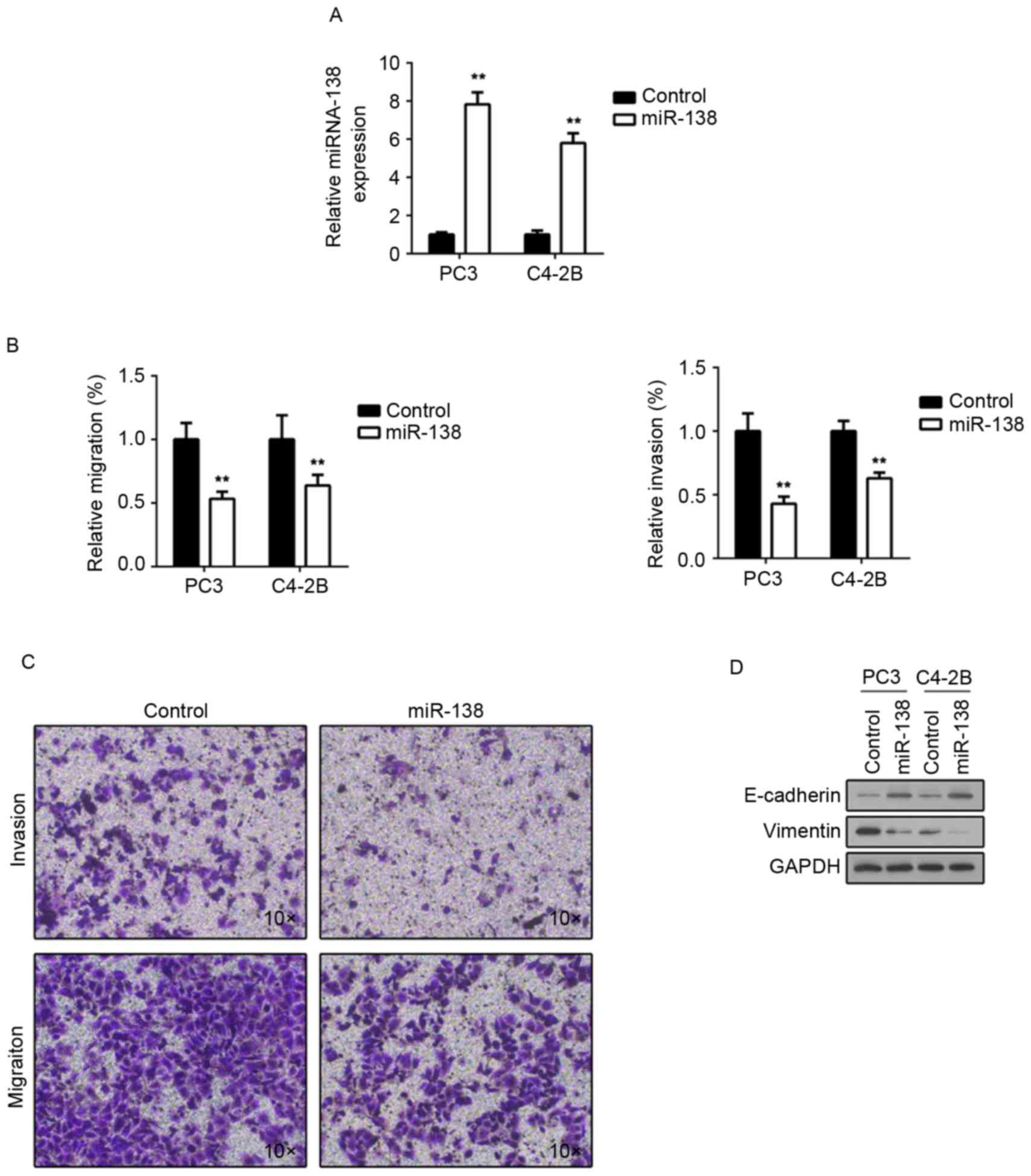
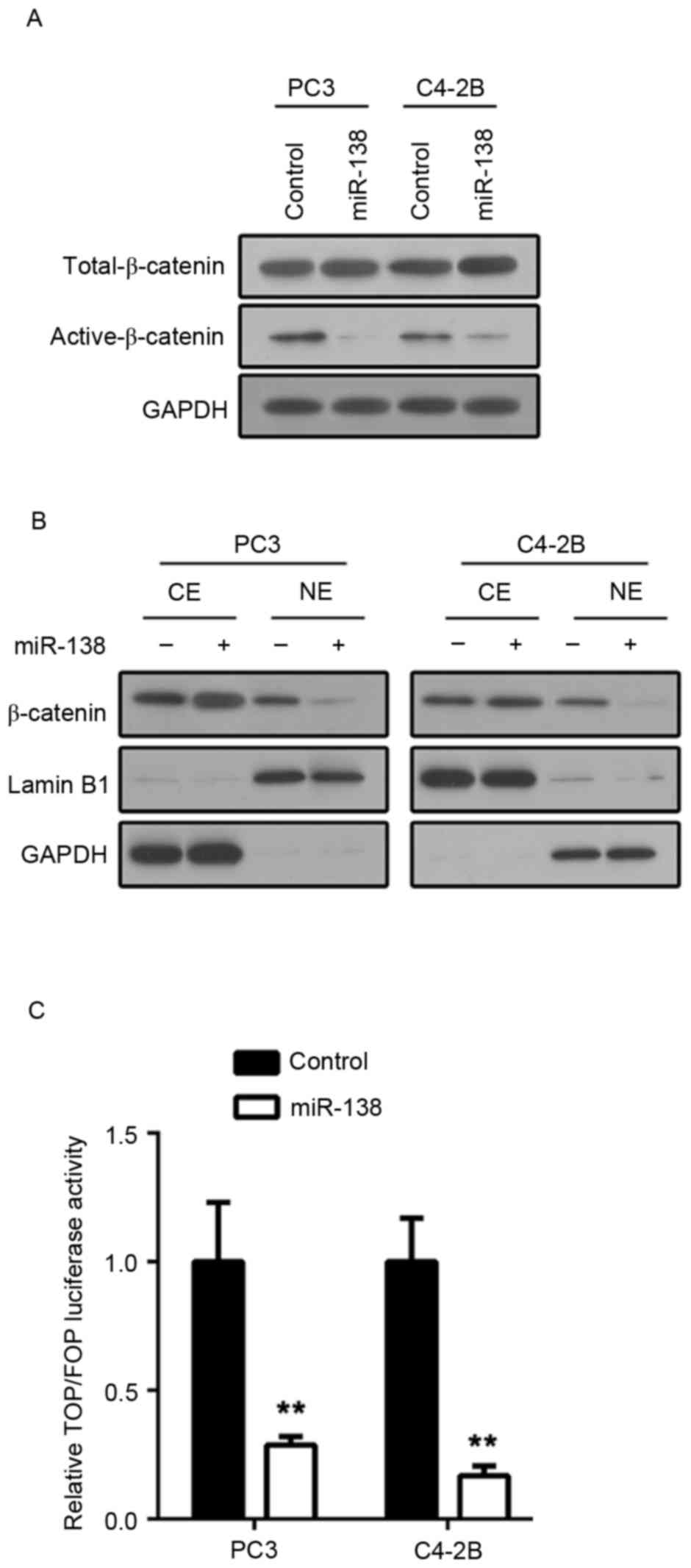
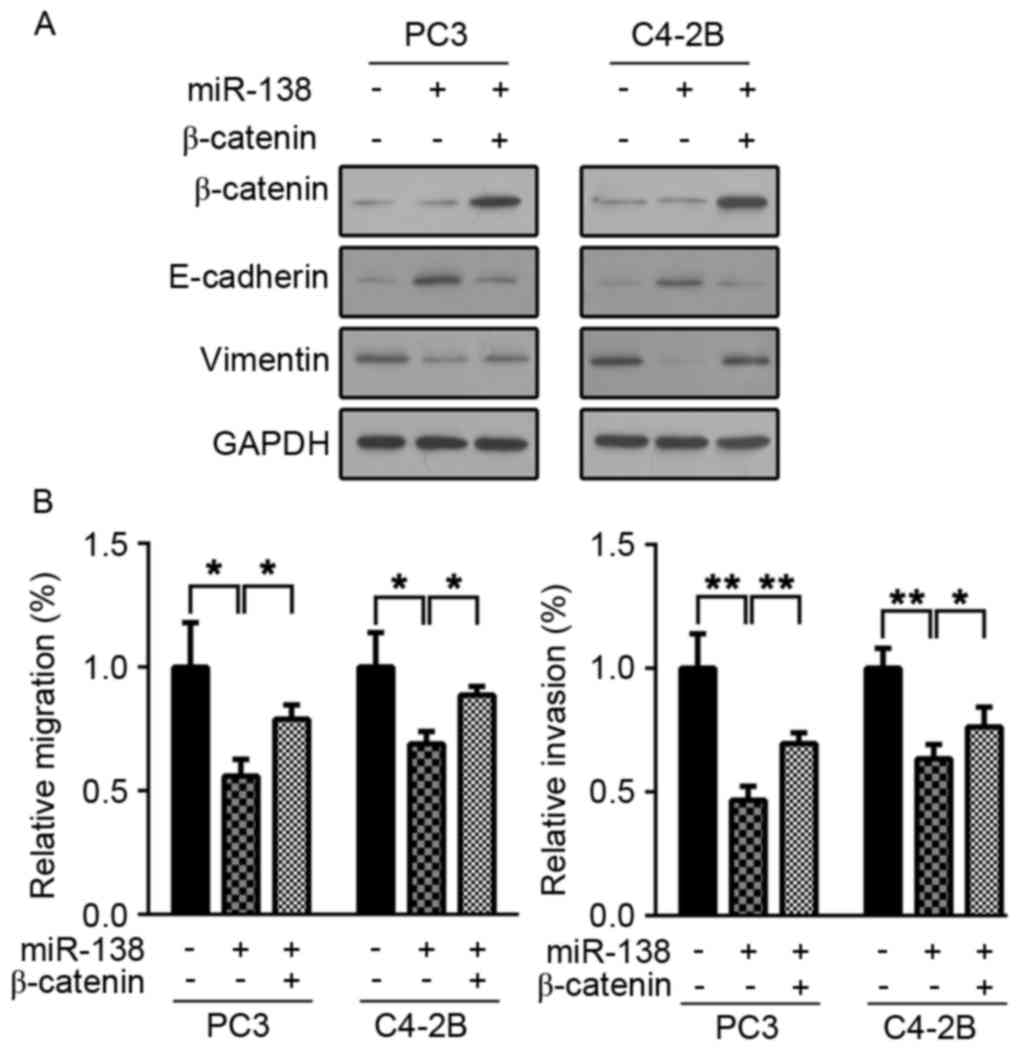
|
1
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hess KR, Varadhachary GR, Taylor SH, Wei
W, Raber MN, Lenzi R and Abbruzzese JL: Metastatic patterns in
adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 106:1624–1633. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sturge J, Caley MP and Waxman J: Bone
metastasis in prostate cancer: Emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 8:357–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Corn PG, Wang F, McKeehan WL and Navone N:
Targeting fibroblast growth factor pathways in prostate cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 19:5856–5866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schoenborn JR, Nelson P and Fang M:
Genomic profiling defines subtypes of prostate cancer with the
potential for therapeutic stratification. Clin Cancer Res.
19:4058–4066. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam
WL, Thomson AM, Lim B and Rigoutsos I: A pattern-based method for
the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their
corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 126:1203–1217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Jiang L, Wang A, Yu J, Shi F and
Zhou X: MicroRNA-138 suppresses invasion and promotes apoptosis in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Lett.
286:217–222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiang L, Dai Y, Liu X, Wang C, Wang A,
Chen Z, Heidbreder CE, Kolokythas A and Zhou X: Identification and
experimental validation of G protein alpha inhibiting activity
polypeptide 2 (GNAI2) as a microRNA-138 target in tongue squamous
cell carcinoma. Hum Genet. 129:189–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamasaki T, Seki N, Yamada Y, Yoshino H,
Hidaka H, Chiyomaru T, Nohata N, Kinoshita T, Nakagawa M and
Enokida H: Tumor suppressive microRNA-138 contributes to cell
migration and invasion through its targeting of vimentin in renal
cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 41:805–817. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Zhang H, Zhao M, Lv Z, Zhang X,
Qin X, Wang H, Wang S, Su J, Lv X, et al: MiR-138 inhibits tumor
growth through repression of EZH2 in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:56–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nguyen DX, Chiang AC, Zhang XH, Kim JY,
Kris MG, Ladanyi M, Gerald WL and Massagué J: WNT/TCF signaling
through LEF1 and HOXB9 mediates lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.
Cell. 138:51–62. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: The hallmarks
of cancer. Cell. 100:57–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Doolan G, Benke G and Giles G: An update
on occupation and prostate cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:501–516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Han RF, Ji X, Dong XG, Xiao RJ, Liu YP,
Xiong J and Zhang QP: An epigenetic mechanism underlying
doxorubicin induced EMT in the human BGC-823 gastric cancer cell.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4271–4274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu MM, Mao GX, Liu J, Li JC, Huang H, Liu
YF and Liu JH: Low expression of the FoxO4 gene may contribute to
the phenomenon of EMT in non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:4013–4018. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Byles V, Zhu L, Lovaas JD, Chmilewski LK,
Wang J, Faller DV and Dai Y: SIRT1 induces EMT by cooperating with
EMT transcription factors and enhances prostate cancer cell
migration and metastasis. Oncogene. 31:4619–4629. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hance MW, Dole K, Gopal U, Bohonowych JE,
Jezierska-Drutel A, Neumann CA, Liu H, Garraway IP and Isaacs JS:
Secreted Hsp90 is a novel regulator of the epithelial to
mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate cancer. J Biol Chem.
287:37732–37744. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen CL, Mahalingam D, Osmulski P, Jadhav
RR, Wang CM, Leach RJ, Chang TC, Weitman SD, Kumar AP, Sun L, et
al: Single-cell analysis of circulating tumor cells identifies
cumulative expression patterns of EMT-related genes in metastatic
prostate cancer. Prostate. 73:813–826. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zurita AJ, Bischoff FZ, Gorlov I, Mayer
JN, Pircher TJ, Mikolajezyk S, Logothetis C and Lin SH: Cadherin-11
(Cad11) for detection of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
circulating prostate cancer (PCa) cells. J Clin Oncol.
31:e220472013.
|
|
26
|
Yu CY, Liang GB, Du P and Liu YH: Lgr4
promotes glioma cell proliferation through activation of Wnt
signaling. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4907–4911. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yuan JB, Yang LY, Tang ZY, Zu XB and Qi L:
Down-regulation of EZH2 by RNA interference inhibits proliferation
and invasion of ACHN cells via the Wnt/β- catenin pathway. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:6197–6201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arcaroli JJ, Quackenbush KS, Purkey A,
Powell RW, Pitts TM, Bagby S, Tan AC, Cross B, McPhillips K, Song
EK, et al: Tumours with elevated levels of the Notch and Wnt
pathways exhibit efficacy to PF-03084014, a γ-secretase inhibitor,
in a preclinical colorectal explant model. Br J Cancer.
109:667–675. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan Z, Zhu Z, Wang J, Sun J, Chen Y, Yang
G, Chen W and Deng Y: Synthesis, characterization, and evaluation
of a novel inhibitor of WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol
Cancer. 12:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Basu D, Lettan R, Damodaran K, Strellec S,
Reyes-Mugica M and Rebbaa A: Identification, mechanism of action,
and antitumor activity of a small molecule inhibitor of hippo,
TGF-β, and Wnt signaling pathways. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1457–1467.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jiang Y, Dai J, Zhang H, Sottnik JL,
Keller JM, Escott KJ, Sanganee HJ, Yao Z, McCauley LK and Keller
ET: Activation of the Wnt pathway through AR79, a GSK3β inhibitor,
promotes prostate cancer growth in soft tissue and bone. Mol Cancer
Res. 11:1597–1610. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|