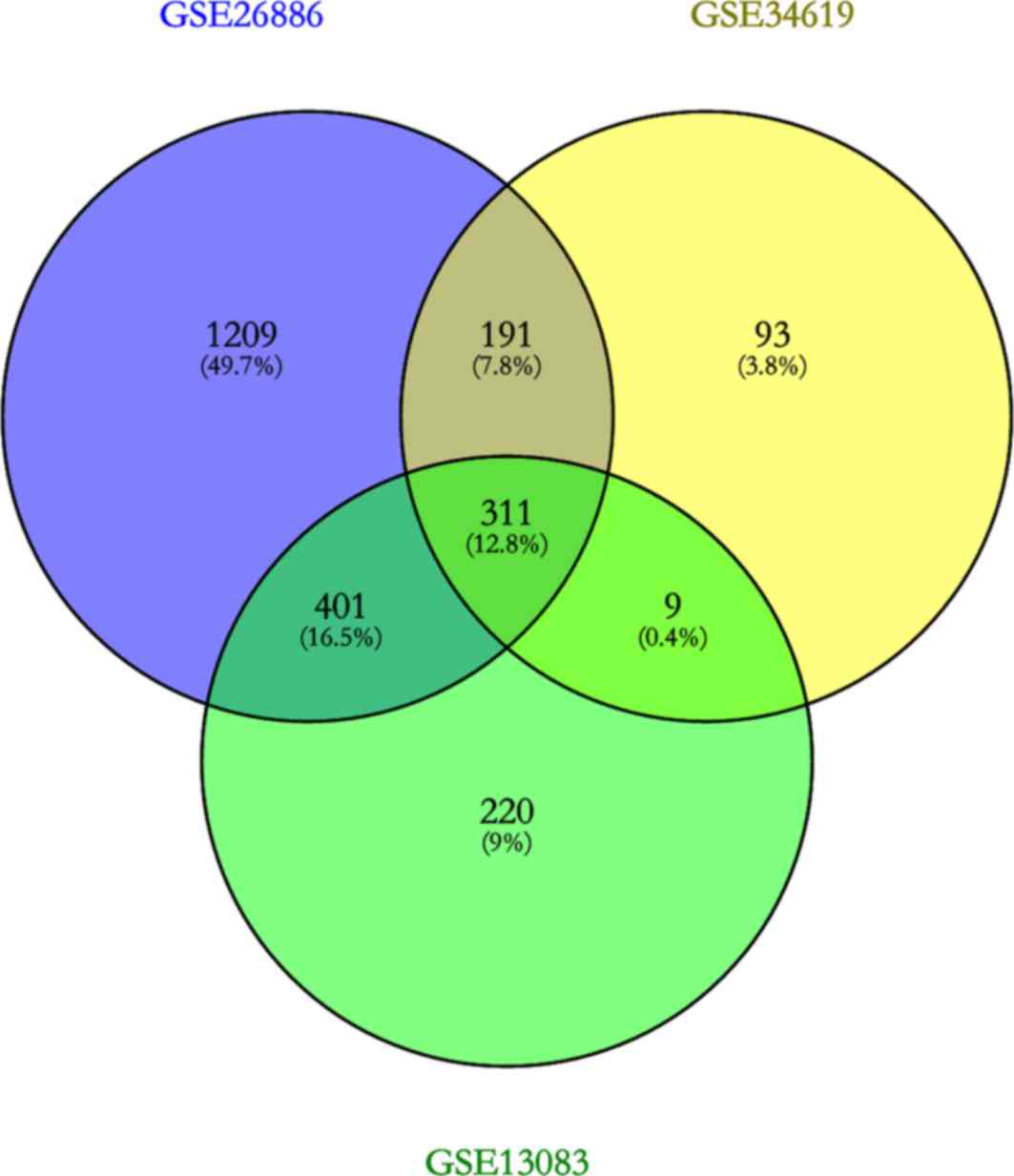
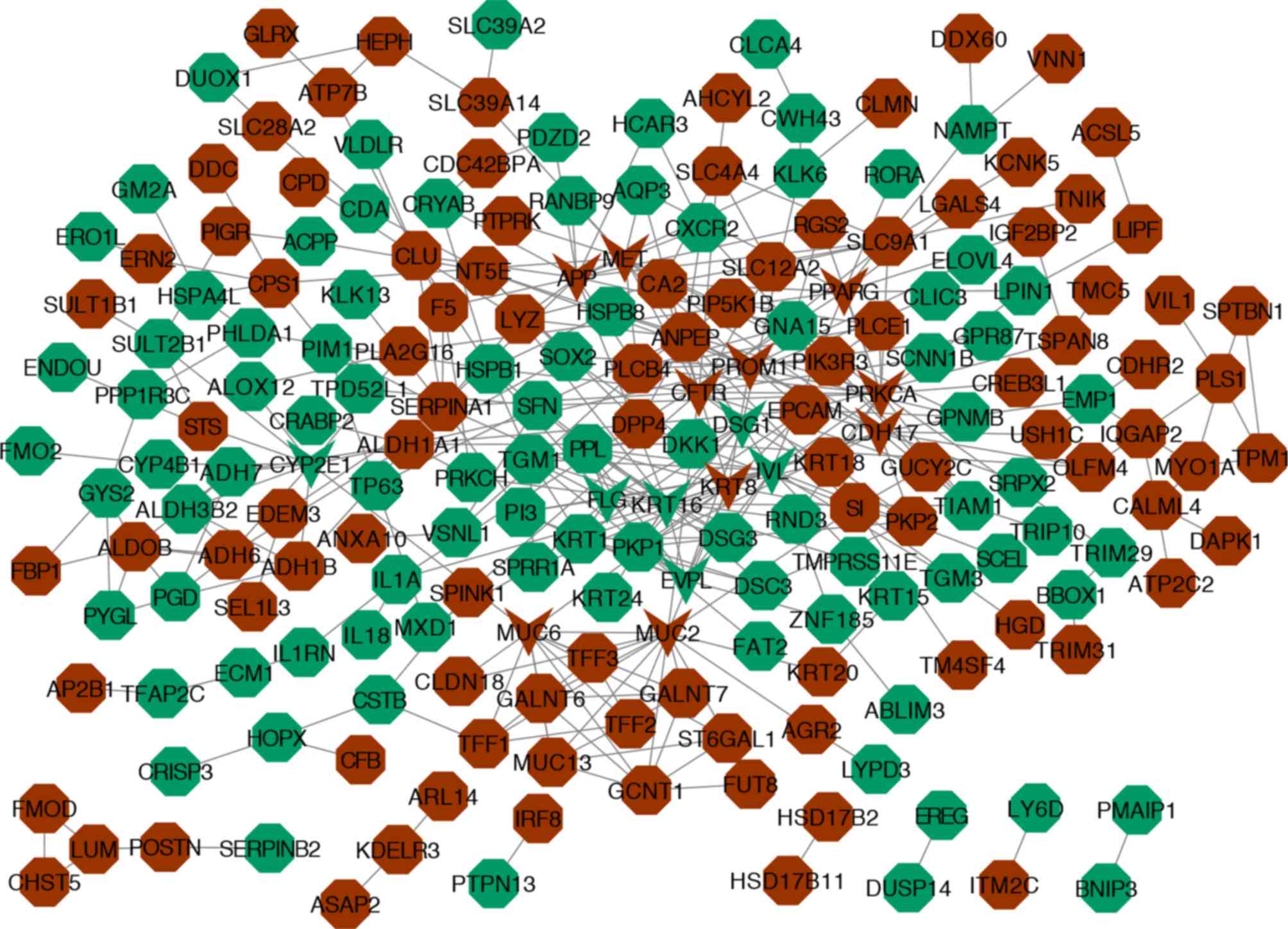
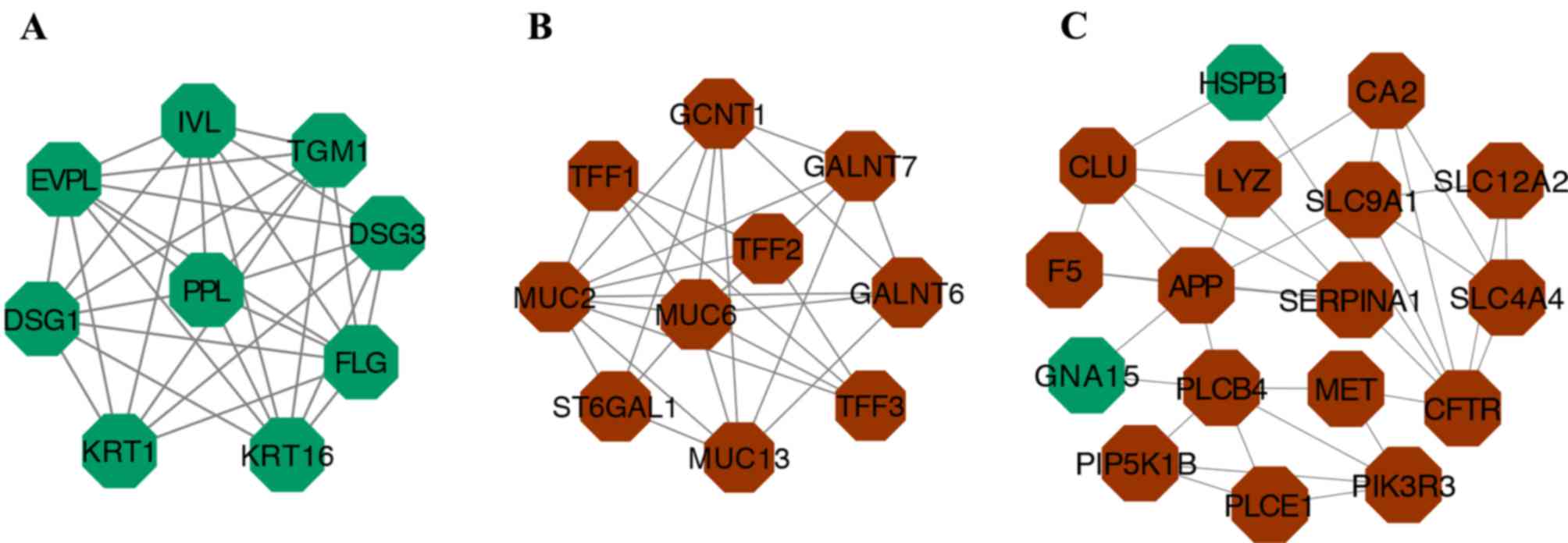
|
1
|
Falk GW, Jacobson BC, Riddell RH,
Rubenstein JH, El-Zimaity H, Drewes AM, Roark KS, Sontag SJ,
Schnell TG, Leya J, et al: Barrett's esophagus:
Prevalence-incidence and etiology-origins. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1232:1–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Solaymani-Dodaran M, Logan RF, West J,
Card T and Coupland C: Risk of oesophageal cancer in Barrett's
oesophagus and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Gut. 53:1070–1074. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tatsugami M, Ito M, Tanaka S, Yoshihara M,
Matsui H, Haruma K and Chayama K: Bile acid promotes intestinal
metaplasia and gastric carcinogenesis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 21:2101–2107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu Y, Williams VA, Gellersen O, Jones C,
Watson TJ and Peters JH: The pathogenesis of Barrett's esophagus:
Secondary bile acids upregulate intestinal differentiation factor
CDX2 expression in esophageal cells. J Gastrointest Surg.
11:827–834. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang DH, Tiwari A, Kim ME, Clemons NJ,
Regmi NL, Hodges WA, Berman DM, Montgomery EA, Watkins DN, Zhang X,
et al: Hedgehog signaling regulates FOXA2 in esophageal
embryogenesis and Barrett's metaplasia. J Clin Invest.
124:3767–3780. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Alasehirli B, Oğuz E, Oksuzler E, Koruk I,
Oztuzcu S, Ozkara E, Karakok M, Erbagcı AB and Demiryurek AT:
Investigation of intercellular adhesion molecules (ICAMs) gene
expressions in patients with Barrett's esophagus. Tumour Biol.
35:4907–4912. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kazumori H, Ishihara S, Takahashi Y, Amano
Y and Kinoshita Y: Roles of Kruppel-like factor 4 in oesophageal
epithelial cells in Barrett's epithelium development. Gut.
60:608–617. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Demiryürek S, Koruk I, Bozdag Z, Ozkara E,
Kaplan DS, Oztuzcu S, Cetinkaya A, Alasehirli B and Demiryürek AT:
Investigation of the esophageal Rho-kinase expression in patients
with Barrett's esophagus. Ultrastruct Pathol. 37:284–289. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res. 41(Database Issue):
D991–D995. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(Database Issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao F, Zuo Z, Cai G, Kang S, Gao X and Li
T: miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 37(Database Issue): D105–D110.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greer KB, Thompson CL, Brenner L,
Bednarchik B, Dawson D, Willis J, Grady WM, Falk GW, Cooper GS, Li
L and Chak A: Association of insulin and insulin-like growth
factors with Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 61:665–672. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee SW, Lien HC, Chang CS, Lee TY, Peng YC
and Yeh HZ: Association of metabolic syndrome with erosive
esophagitis and Barrett's esophagus in a Chinese population. J Chin
Med Assoc. 80:15–18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crews NR, Johnson ML, Schleck CD, Enders
FT, Wongkeesong LM, Wang KK, Katzka DA and Iyer PG: Prevalence and
predictors of gastroesophageal reflux complications in community
subjects. Dig Dis Sci. 61:3221–3228. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh S, Sharma AN, Murad MH, Buttar NS,
El-Serag HB, Katzka DA and Iyer PG: Central adiposity is associated
with increased risk of esophageal inflammation, metaplasia, and
adenocarcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:1399–1412.e7. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kendall BJ, Macdonald GA, Hayward NK,
Prins JB, Brown I, Walker N, Pandeya N, Green AC, Webb PM and
Whiteman DC: Study of Digestive Health: Leptin and the risk of
Barrett's oesophagus. Gut. 57:448–454. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thompson OM, Beresford SA, Kirk EA,
Bronner MP and Vaughan TL: Serum leptin and adiponectin levels and
risk of Barrett's esophagus and intestinal metaplasia of the
gastroesophageal junction. Obesity (Silver Spring). 18:2204–2211.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rubenstein JH, Morgenstern H, McConell D,
Scheiman JM, Schoenfeld P, Appelman H, McMahon LF Jr, Kao JY, Metko
V, Zhang M and Inadomi JM: Associations of diabetes mellitus,
insulin, leptin, and ghrelin with gastroesophageal reflux and
Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 145:1237–1244.e1-5. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cassiani RA, Mota GA, Aprile LR and Dantas
RO: Saliva transit in patients with gastroesophageal reflux
disease. Dis Esophagus. 28:673–677. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Skoczylas T, Yandrapu H, Poplawski C,
Asadi M, Wallner G and Sarosiek J: Salivary bicarbonate as a major
factor in the prevention of upper esophageal mucosal injury in
gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2411–2416. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun D, Wang X, Gai Z, Song X, Jia X and
Tian H: Bile acids but not acidic acids induce Barrett's esophagus.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1384–1392. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takahashi Y, Amano Y, Yuki T, Mishima Y,
Tamagawa Y, Uno G, Ishimura N, Sato S, Ishihara S and Kinoshita Y:
Impact of the composition of gastric reflux bile acids on Barrett's
oesophagus. Dig Liver Dis. 43:692–697. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reveiller M, Ghatak S, Toia L, Kalatskaya
I, Stein L, D'Souza M, Zhou Z, Bandla S, Gooding WE, Godfrey TE and
Peters JH: Bile exposure inhibits expression of squamous
differentiation genes in human esophageal epithelial cells. Ann
Surg. 255:1113–1120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hughes SJ, Morse MA, Weghorst CM, Kim H,
Watkins PB, Guengerich FP, Orringer MB and Beer DG: Cytochromes
P450 are expressed in proliferating cells in Barrett's metaplasia.
Neoplasia. 1:145–153. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergstrom KS and Xia L: Mucin-type
O-glycans and their roles in intestinal homeostasis. Glycobiology.
23:1026–1037. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rosekrans SL, Baan B, Muncan V and van den
Brink GR: Esophageal development and epithelial homeostasis. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 309:G216–G228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cabibi D, Caruso S, Bazan V, Castiglia M,
Bronte G, Ingrao S, Fanale D, Cangemi A, Calò V, Listì A, et al:
Analysis of tissue and circulating microRNA expression during
metaplastic transformation of the esophagus. Oncotarget.
7:47821–47830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bus P, Kestens C, Ten Kate FJ, Peters W,
Drenth JP, Roodhart JM, Siersema PD and van Baal JW: Profiling of
circulating microRNAs in patients with Barrett's esophagus and
esophageal adenocarcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 51:560–570. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Slaby O, Srovnal J, Radova L, Gregar J,
Juracek J, Luzna P, Svoboda M, Hajduch M and Ehrmann J: Dynamic
changes in microRNA expression profiles reflect progression of
Barrett's esophagus to esophageal adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis.
36:521–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wijnhoven BP, Hussey DJ, Watson DI, Tsykin
A, Smith CM and Michael MZ; South Australian Oesophageal Research
Group, : MicroRNA profiling of Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal
adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. 97:853–861. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jia Y, Guan M, Zheng Z, Zhang Q, Tang C,
Xu W, Xiao Z, Wang L and Xue Y: miRNAs in urine extracellular
vesicles as predictors of early-stage diabetic nephropathy. J
Diabetes Res. 2016:79327652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ge G, Zhang W, Niu L, Yan Y, Ren Y and Zou
Y: miR-215 functions as a tumor suppressor in epithelial ovarian
cancer through regulation of the X-chromosome-linked inhibitor of
apoptosis. Oncol Rep. 35:1816–1822. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hou Y, Zhen J, Xu X, Zhen K, Zhu B, Pan R
and Zhao C: miR-215 functions as a tumor suppressor and directly
targets ZEB2 in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett.
10:1985–1992. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xu H, Yao Y, Meng F, Qian X, Jiang X, Li
X, Gao Z and Gao L: Predictive Value of Serum miR-10b, miR-29c, and
miR-205 as promising biomarkers in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma screening. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e15582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yue X, Lan F, Hu M, Pan Q, Wang Q and Wang
J: Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic
and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J Neurosurg.
124:122–128. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vona-Davis L, Frankenberry K, Cunningham
C, Riggs DR, Jackson BJ, Szwerc MF and McFadden DW: MAPK and PI3K
inhibition reduces proliferation of Barrett's adenocarcinoma in
vitro. J Surg Res. 127:53–58. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen X, Jiang K, Fan Z, Liu Z, Zhang P,
Zheng L, Peng N, Tong J and Ji G: Aberrant expression of Wnt and
Notch signal pathways in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 36:473–483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gessner R and Tauber R: Intestinal cell
adhesion molecules. Liver-intestine cadherin. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
915:136–143. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mokrowiecka A, Zonnur S, Veits L, Musial
J, Kordek R, Lochowski M, Kozak J, Malecka-Panas E, Vieth M and
Hartmann A: Liver-intestine-cadherin is a sensitive marker of
intestinal differentiation during Barrett's carcinogenesis. Dig Dis
Sci. 58:699–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Grötzinger C, Kneifel J, Patschan D,
Schnoy N, Anagnostopoulos I, Faiss S, Tauber R, Wiedenmann B and
Gessner R: LI-cadherin: A marker of gastric metaplasia and
neoplasia. Gut. 49:73–81. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vermeer PD, Panko L, Karp P, Lee JH and
Zabner J: Differentiation of human airway epithelia is dependent on
erbB2. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 291:L175–L180. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun L, Pan J, Yu L, Liu H, Shu X, Sun L,
Lou J, Yang Z and Ran Y: Tumor endothelial cells promote metastasis
and cancer stem cell-like phenotype through elevated Epiregulin in
esophageal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2277–2288. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Amsterdam A, Shezen E, Raanan C, Slilat Y,
Ben-Arie A, Prus D and Schreiber L: Epiregulin as a marker for the
initial steps of ovarian cancer development. Int J Oncol.
39:1165–1172. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Watanabe T, Kobunai T, Yamamoto Y,
Kanazawa T, Konishi T, Tanaka T, Matsuda K, Ishihara S, Nozawa K,
Eshima K, et al: Prediction of liver metastasis after colorectal
cancer using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
analysis of 10 genes. Eur J Cancer. 46:2119–2126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|