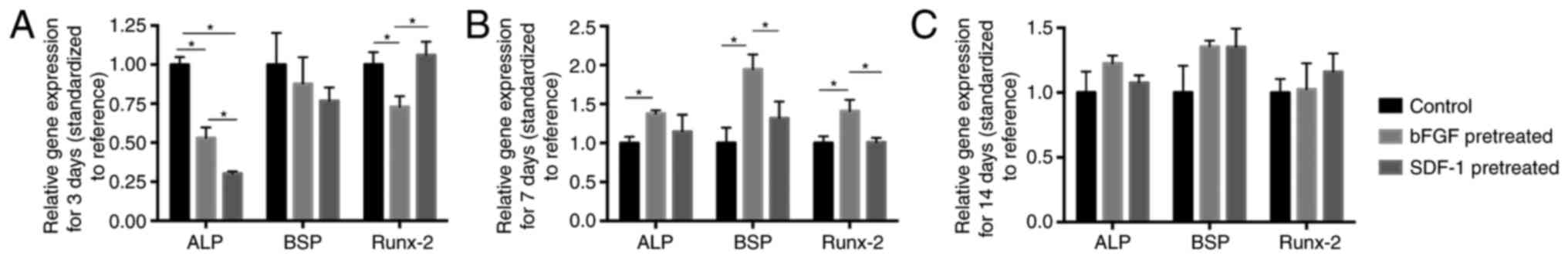
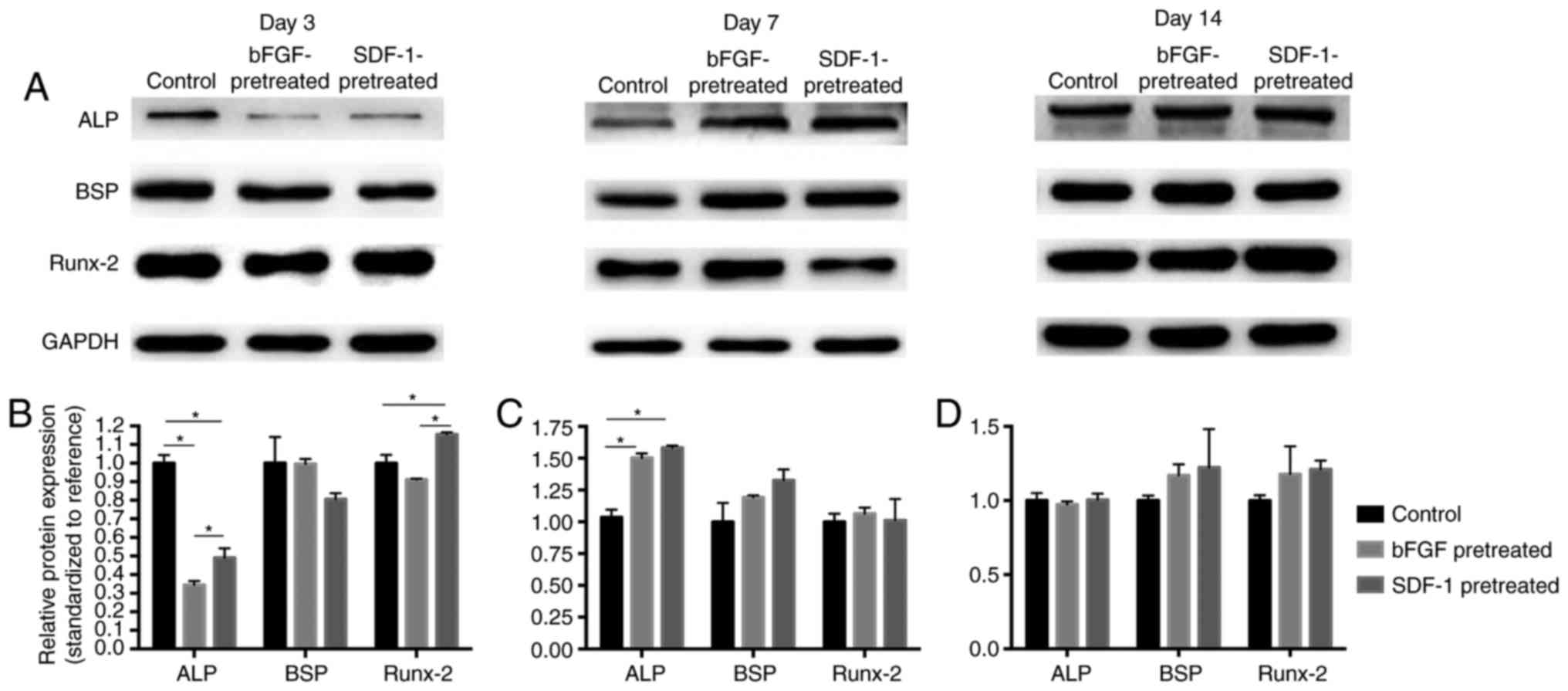
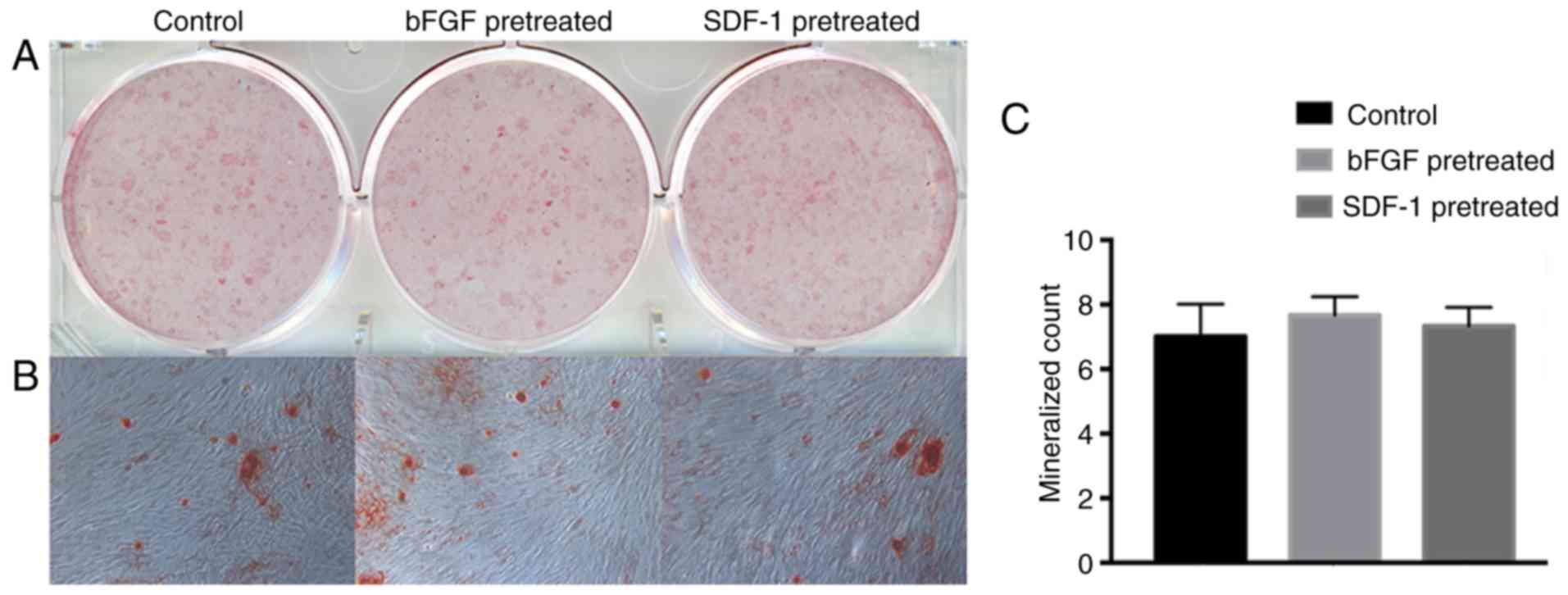
|
1
|
Flemming TF: Periodontitis. Ann
Periodontol. 4:32–38. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Villar CC and Cochran DL: Regeneration of
periodontal tissues: Guided tissue regeneration. Dent Clin North
Am. 54:73–92. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Melcher AH: On the repair potential of
periodontal tissues. J Periodontol. 47:256–260. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Langer R and Vacanti JP: Tissue
engineering. Science. 260:920–926. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sengupta D, Waldman SD and Li S: From in
vitro to in situ tissue engineering. Ann Biomed Eng. 42:1537–1545.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakahara T, Nakamura T, Kobayashi E, Inoue
M, Shigeno K, Tabata Y, Eto K and Shimizu Y: Novel approach to
regeneration of periodontal tissues based on in situ tissue
engineering: Effects of controlled release of basic fibroblast
growth factor from a sandwich membrane. Tissue Eng. 9:153–162.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shao Z, Zhang X, Pi Y, Wang X, Jia Z, Zhu
J, Wang X, Jia Z, Zhu J, Dai L, et al: Polycaprolactone electrospun
mesh conjugated with an MSC affinity peptide for MSC homing in
vivo. Biomaterials. 33:3375–3387. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shafiq M, Lee SH, Jung Y and Kim SH:
Strategies for recruitment of stem cells to treat myocardial
infarction. Curr Pharm Des. 21:1584–1597. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee CH, Cook JL, Mendelson A, Moioli EK,
Yao H and Mao JJ: Regeneration of the articular surface of the
rabbit synovial joint by cell homing: A proof of concept study.
Lancet. 376:440–448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Li M, Du L, Yang P and Ge S: Local
administration of stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes stem cell
recruitment and bone regeneration in a rat periodontal bone defect
model. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 53:83–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vanden Berg-Foels WS: In situ tissue
regeneration: Chemoattractants for endogenous stem cell
recruitment. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 20:28–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Du L, Yang P and Ge S: Stromal
cell-derived factor-1 significantly induces proliferation,
migration, and collagen type I expression in a human periodontal
ligament stem cell subpopulation. J Periodontol. 83:379–388. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rehimi R, Khalida N, Yusuf F, Dai F,
Morosan-Puopolo G and Brand-Saberi B: Stromal-derived factor-1
(SDF-1)expression during early chick development. Int J Dev Biol.
52:87–92. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Baggiolini M: Chemokines and leukocyte
traffic. Nature. 392:565–568. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu X, Huang Y, Collin-Osdoby P and Osdoby
P: Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (SDF-1) recruits osteoclast
precursors by inducing chemotaxis, matrix metalloproteinase-9
(MMP-9) activity, and collagen transmigration. J Bone Miner Res.
18:1404–1418. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wynn RF, Hart CA, Corradi-Perini C,
O'Neill L, Evans CA, Wraith JE, Fairbairn LJ and Bellantuono I: A
small proportion of mesenchymal stem cells strongly expresses
functionally active CXCR4 receptor capable of promoting migration
to bone marrow. Blood. 104:2643–2645. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kucia M, Ratajczak J, Reca R,
Janowska-Wieczorek A and Ratajczak MZ: Tissue-specific muscle,
neural and liver stem/progenitor cells reside in the bone marrow,
respond to an SDF-1 gradient and are mobilized into peripheral
blood during stress and tissue injury. Blood Cells Mol Dis.
32:52–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Abbott JD, Huang Y, Liu D, Hickey R,
Krause DS and Giordano FJ: Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays
a critical role in stem cell recruitment to the heart after
myocardial infarction but is not sufficient to induce homing in the
absence of injury. Circulation. 110:3300–3305. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ji JF, He BP, Dheen ST and Tay SS:
Interactions of chemokines and chemokine receptors mediate the
migration of mesenchymal stem cells to the impaired site in the
brain after hypoglossal nerve injury. Stem Cells. 22:415–427. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji W, Yang F, Ma J, Bouma MJ, Boerman OC,
Chen Z, van den Beucken JJ and Jansen JA: Incorporation of stromal
cell-derived factor-1alpha in PCL/gelatin electrospun membranes for
guided bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 34:735–745. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu J, Chen Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Kang Q, Ho
K, Chai Y and Li G: Effect of SDF-1/Cxcr4 signaling antagonist
AMD3100 on bone mineralization in distraction osteogenesis. Calcif
Tissue Int. 100:641–652. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ratanavaraporn J, Furuya H, Kohara H and
Tabata Y: Synergistic effects of the dual release of stromal
cell-derived factor-1 and bone morphogenetic protein-2 from
hydrogels on bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 32:2797–2811. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thevenot PT, Nair AM, Shen J, Lotfi P, Ko
CY and Tang L: The effect of incorporation of SDF-1alpha into PLGA
scaffolds on stem cell recruitment and the inflammatory response.
Biomaterials. 31:3997–4008. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grzibovskis M, Urtane I and Pilmane M:
Specific signaling molecule expression in periodontal ligaments in
different age groups: Pilot study. Stomatologija. 13:117–122.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Osathanon T, Nowwarote N and Pavasant P:
Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits mineralization but induces
neuronal differentiation by human dental pulp stem cells through a
FGFR and PLCgamma signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem. 112:1807–1816.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Narong S and Leelawat K: Basic fibroblast
growth factor induces cholangio-carcinoma cell migration via
activation of the MEK1/2 pathway. Oncol Lett. 2:821–825.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Horikoshi-Ishihara H, Tobita M, Tajima S,
Tanaka R, Oshita T, Tabata Y and Mizuno H: Coadministration of
adipose-derived stem cells and control-released basic fibroblast
growth factor facilitates angiogenesis in a murine ischemic hind
limb model. J Vasc Surg. 64:1825–1834.e1. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu H, Yang A, Du J, Li D, Liu M, Ding F,
Gu X and Liu Y: Basic fibroblast growth factor is a key factor that
induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards cells with
Schwann cell phenotype. Neurosci Lett. 559:82–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ikeda M, Uemura T, Takamatsu K, Okada M,
Kazuki K, Tabata Y, Ikada Y and Nakamura H: Acceleration of
peripheral nerve regeneration using nerve conduits in combination
with induced pluripotent stem cell technology and a basic
fibroblast growth factor drug delivery system. J Biomed Mater Res
A. 102:1370–1378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Y, Tsai YT, Hsu CW, Erol D, Yang J, Wu
WH, Davis RJ, Egli D and Tsang SH: Long-term safety and efficacy of
human-induced pluripotent stem cell (iPS) grafts in a preclinical
model of retinitis pigmentosa. Mol Med. 18:1312–1319. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Levenstein ME, Ludwig TE, Xu RH, Llanas
RA, VanDenHeuvel-Kramer K, Manning D and Thomson JA: Basic
fibroblast growth factor support of human embryonic stem cell
self-renewal. Stem Cells. 24:568–574. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Du M, Zhu T, Duan X, Ge S, Li N, Sun Q and
Yang P: Acellular dermal matrix loading with bFGF achieves similar
acceleration of bone regeneration to BMP-2 via differential effects
on recruitment, proliferation and sustained osteodifferentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 70:62–70.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schmidt A, Ladage D, Schinköthe T,
Klausmann U, Ulrichs C, Klinz FJ, Brixius K, Arnhold S, Desai B,
Mehlhorn U, et al: Basic fibroblast growth factor controls
migration in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells.
24:1750–1758. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tasso R, Gaetani M, Molino E, Cattaneo A,
Monticone M, Bachi A and Cancedda R: The role of bFGF on the
ability of MSC to activate endogenous regenerative mechanisms in an
ectopic bone formation model. Biomaterials. 33:2086–2096. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
de Sousa Abreu R, Penalva LO, Marcotte EM
and Vogel C: Global signatures of protein and mRNA expression
levels. Mol Biosyst. 5:1512–1526. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
de Klerk E and 't Hoen PA: Alternative
mRNA transcription, processing, and translation: Insights from RNA
sequencing. Trends Genet. 31:128–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kitamura M, Nakashima K, Kowashi Y, Fujii
T, Shimauchi H, Sasano T, Furuuchi T, Fukuda M, Noguchi T,
Shibutani T, et al: Periodontal tissue regeneration using
fibroblast growth factor-2: Randomized controlled phase II clinical
trial. PLoS One. 3:e26112008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hosogane N, Huang Z, Rawlins BA, Liu X,
Boachie-Adjei O, Boskey AL and Zhu W: Stromal derived factor-1
regulates bone morphogenetic protein 2-induced osteogenic
differentiation of primary mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 42:1132–1141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang S, Shen Y, Yuan X, Chen K, Guo X,
Chen Y, Niu Y, Li J, Xu RH, Yan X, et al: Dissecting signaling
pathways that govern self-renewal of rabbit embryonic stem cells. J
Biol Chem. 283:35929–35940. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sukarawan W, Nowwarote N, Kerdpon P,
Pavasant P and Osathanon T: Effect of basic fibroblast growth
factor on pluripotent marker expression and colony forming unit
capacity of stem cells isolated from human exfoliated deciduous
teeth. Odontology. 102:160–166. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu J, Huang GT, He W, Wang P, Tong Z, Jia
Q, Dong L, Niu Z and Ni L: Basic fibroblast growth factor enhances
stemness of human stem cells from the apical papilla. J Endod.
38:614–622. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ponte AL, Marais E, Gallay N, Langonné A,
Delorme B, Hérault O, Charbord P and Domenech J: The in vitro
migration capacity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells:
Comparison of chemokine and growth factor chemotactic activities.
Stem Cells. 25:1737–1745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen FM, Zhang M and Wu ZF: Toward
delivery of multiple growth factors in tissue engineering.
Biomaterials. 31:6279–6308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kempen DH, Lu L, Heijink A, Hefferan TE,
Creemers LB, Maran A, Yaszemski MJ and Dhert WJ: Effect of local
sequential VEGF and BMP-2 delivery on ectopic and orthotopic bone
regeneration. Biomaterials. 30:2816–2825. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kimura Y and Tabata Y: Controlled release
of stromal-cell-derived factor-1 from gelatin hydrogels enhances
angiogenesis. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 21:37–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hankenson KD, Dishowitz M, Gray C and
Schenker M: Angiogenesis in bone regeneration. Injury. 42:556–561.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|