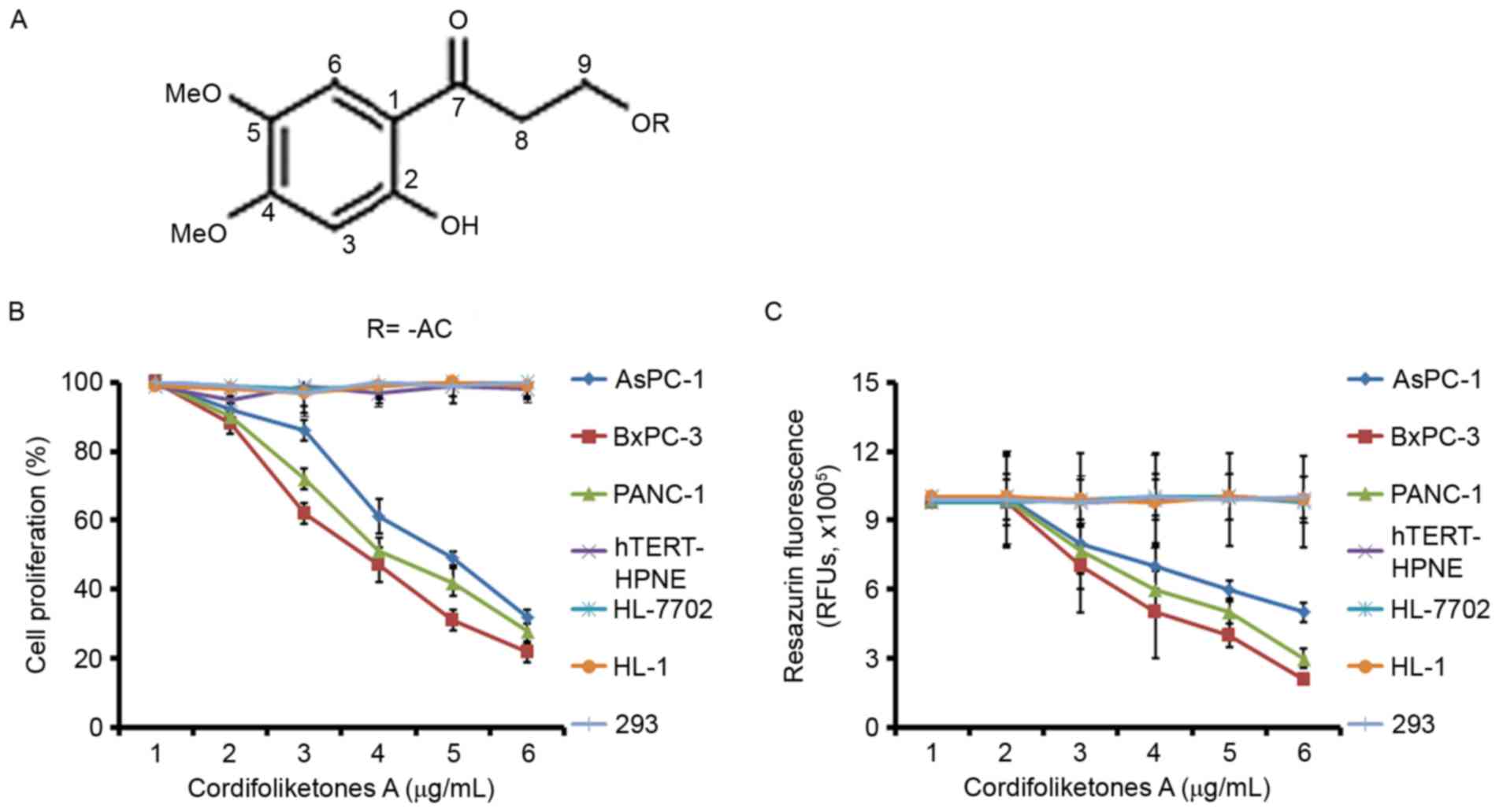
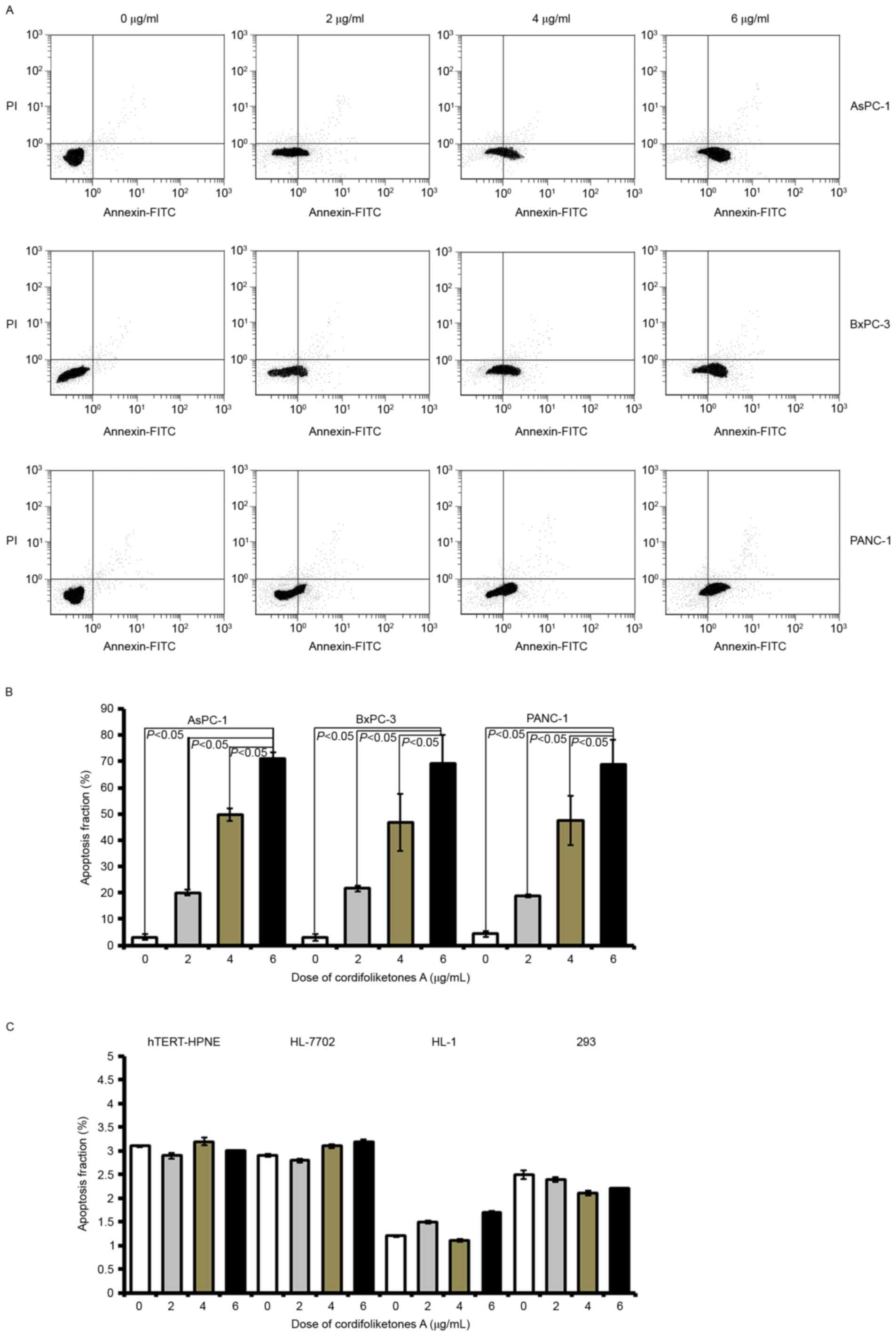
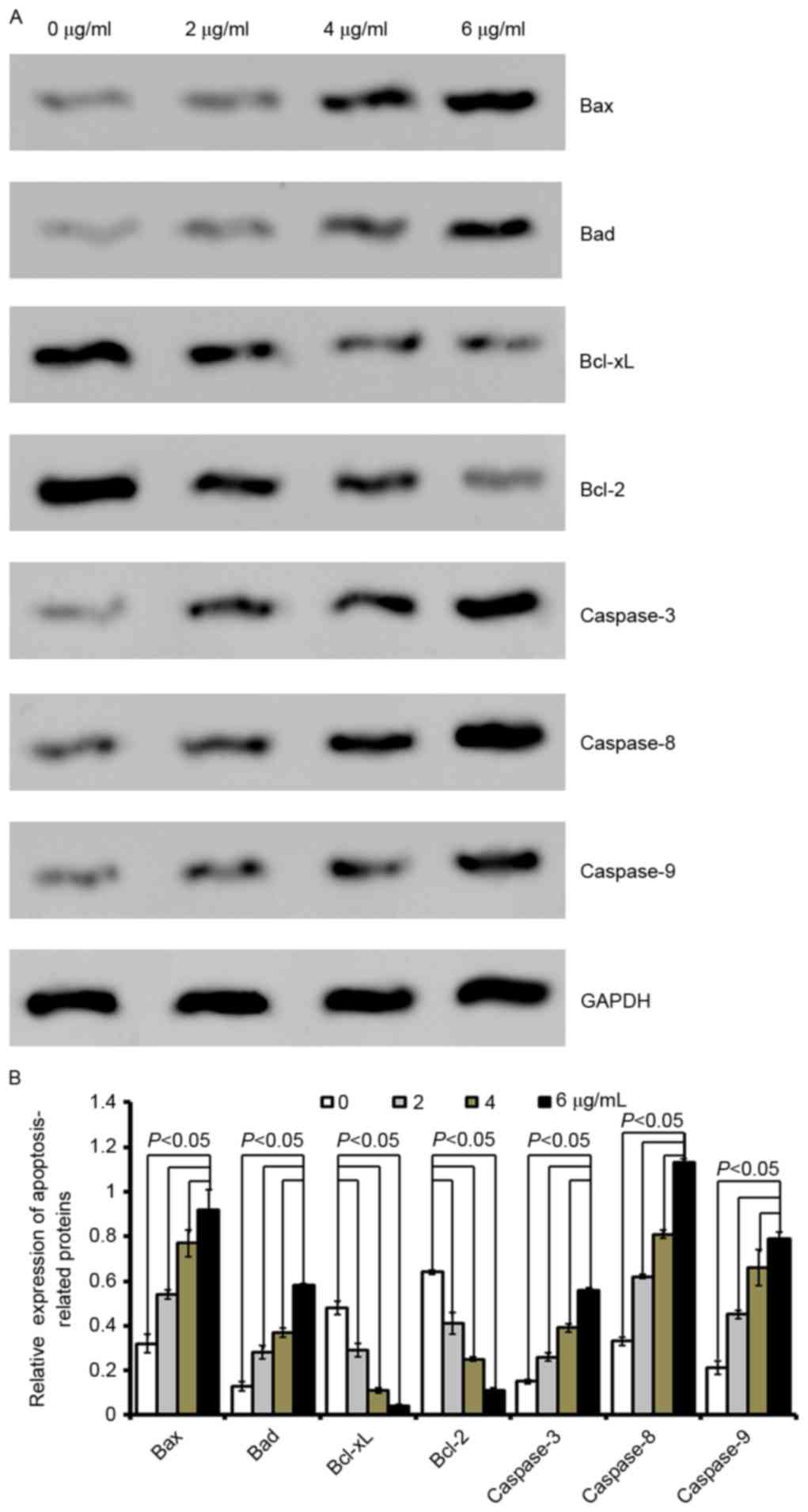
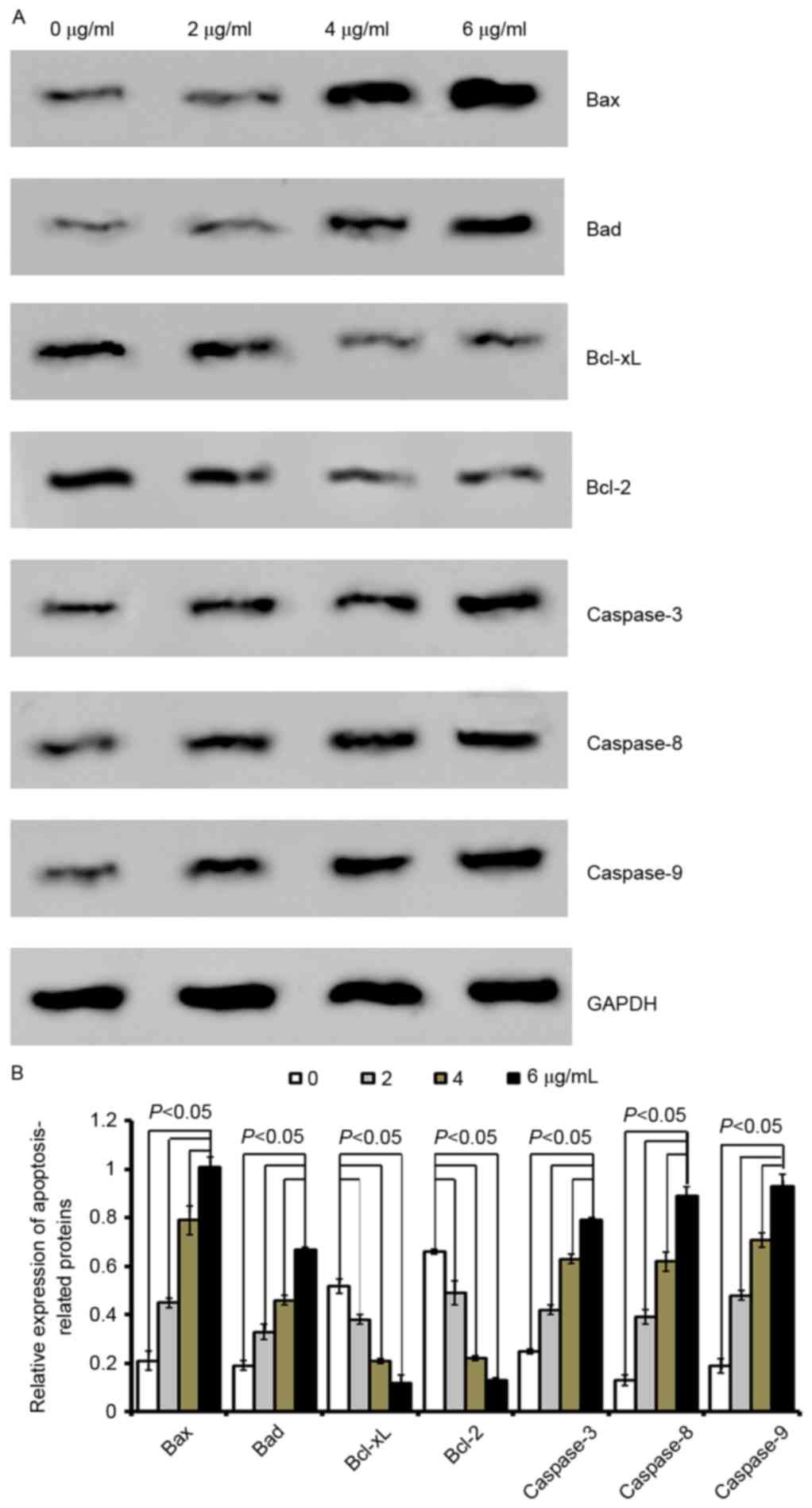
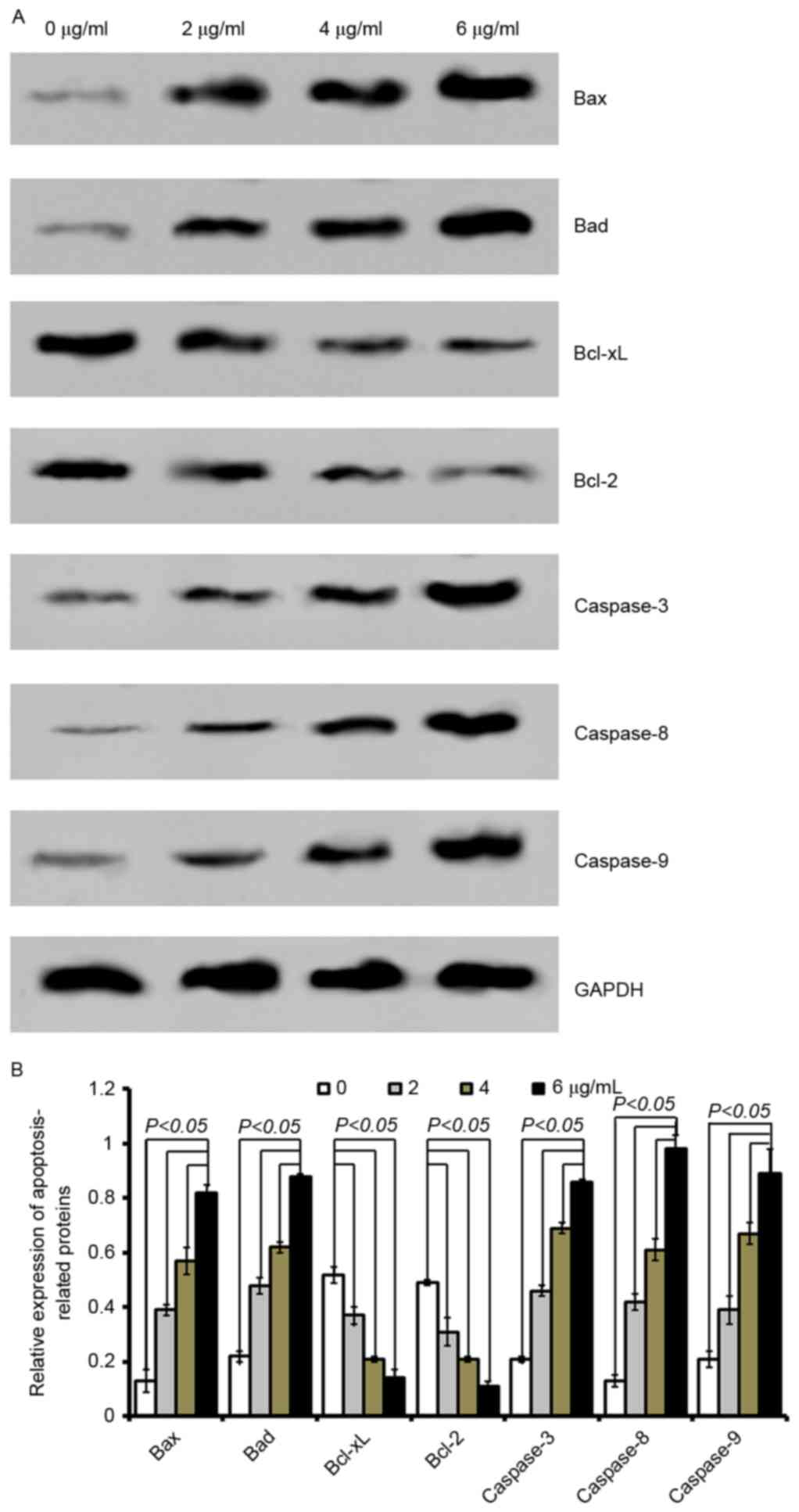
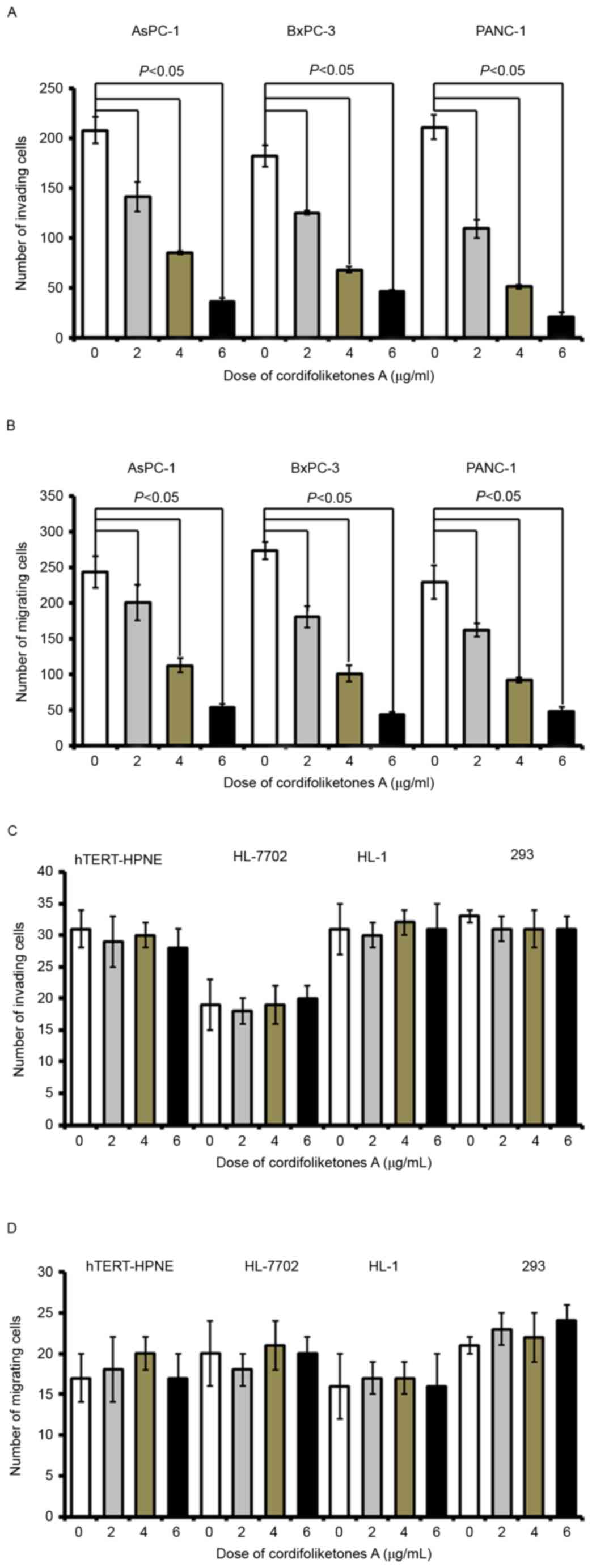
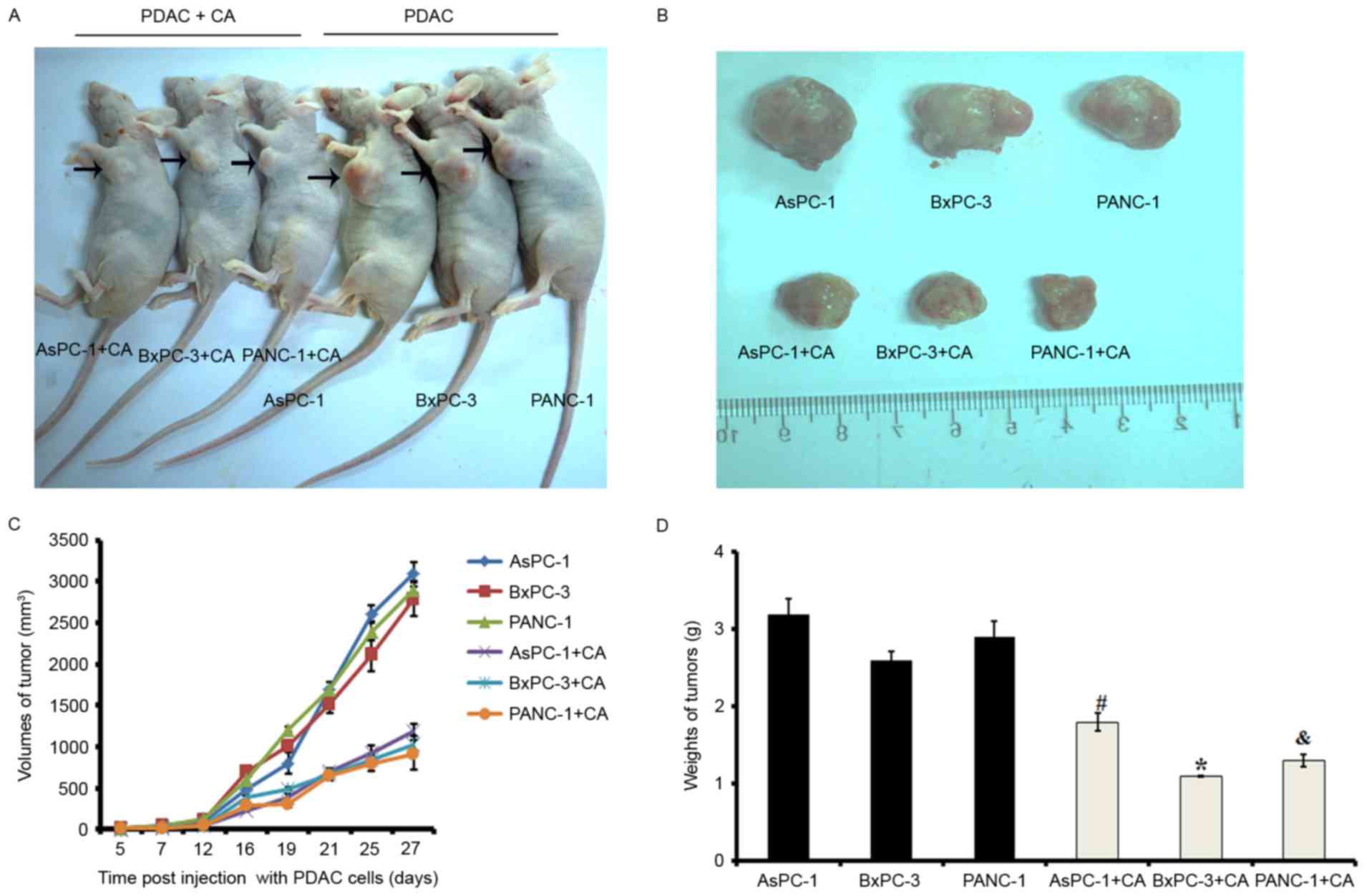
|
1
|
Stathis A and Moore MJ: Advanced
pancreatic carcinoma: Current treatment and future challenges. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 7:163–172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hariharan D, Saied A and Kocher HM:
Analysis of mortality rates for gallbladder cancer across the
world. HPB (Oxford). 10:327–331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang SH, He P, Ma MZ, Wang Y, Li RK, Fang
F, Fu Y, Tian GA, Qin WX and Zhang ZG: PNMA1 promotes cell growth
in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:3827–3835. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O,
Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de
la Fouchardière C, et al: FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for
metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Molejon MI, Tellechea JI, Moutardier V,
Gasmi M, Ouaissi M, Turrini O, Delpero JR, Dusetti N and Iovanna J:
Targeting CD44 as a novel therapeutic approach for treating
pancreatic cancer recurrence. Oncoscience. 2:572–575. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang W, Yao JL, Dong SC, Hou FQ and Shi
HP: SLPI knockdown induced pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells
proliferation and invasion. Cancer Cell Int. 15:372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YJ, Kim DB, Lee JS, Cho JH, Kim BK,
Choi HS, Lee BY and Lee OH: Antioxidant activity and
anti-adipogenic effects of wild herbs mainly cultivated in Korea.
Molecules. 18:12937–12950. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xin T, Zhang F, Jiang Q, Chen C, Huang D,
Li Y, Shen W, Jin Y and Sui G: The inhibitory effect of a
polysaccharide from Codonopsis pilosula on tumor growth and
metastasis in vitro. Int J Biol Macromol. 51:788–793. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin JA, Kim JS, Hong IS and Cho SD: Bak
is a key molecule in apoptosis induced by methanol extracts of
Codonopsis lanceolata and Tricholoma matsutake in HSC-2 human oral
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 4:1379–1383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huo J, Qin F, Cai X, Ju J, Hu C, Wang Z,
Lu W, Wang X and Cao P: Chinese medicine formula ‘Weikang Keli’
induces autophagic cell death on human gastric cancer cell line
SGC-7901. Phytomedicine. 20:159–165. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu QF, Xuesen Li XS, Huang HT, Mu HX, Tu
PF and Li GP: Phenylpropanoids from the roots of codonopsis
cordifolioidea and their biological activities. Bull Korean Chem
Soc. 33:278–280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hong DY, Lian YS and Shen LD: Flora of
China. Science Press: Beijing. 73:321983.
|
|
15
|
Yunnan Corporation of Materia Medica, .
List of Chinese Herb Medicine Resources in Yunnan. Science
Publishing; pp. 5441993
|
|
16
|
Duang QF, Zhao H and Wang YQ: The
cytotoxicity of Nature medicine in Yunnan province. Chin J Yunnan
Med. 12:392003.
|
|
17
|
Chen ZJ, Wei QH and Zhou JY: The effects
of Codonopis bulleynana on the growth and proliferation of HL60
cells. Yunnan J Tradit Chin Med Mater. 27:492006.
|
|
18
|
Sun J, Wang L, Wang M, Wang Z and Li F:
Two new polyacetylene glycosides from the roots of Codonopsis
tangshen Oliv. Nat Prod Res. 30:2338–2343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen ZJ, Wei QH and Zhou JY: The research
development in Tsoong. Yunnan J Tradit Chin Med Mater. 27:49–50.
2006.
|
|
20
|
Luan YP, Zheng SQ and Li YM:
Identification of active ingredient of codonopsis cordifolioidea by
n-butyl alcohol. Adv Eng Res. 178–182. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Li C, Ni J, Liu YX, Wang H, Liang ZQ and
Wang X: Response of MiRNA-22-3p and MiRNA-149-5p to Folate
Deficiency and the Differential Regulation of MTHFR Expression in
Normal and Cancerous Human Hepatocytes. PLoS One. 12:e01680492017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee KW, Jung HJ, Park HJ, Kim DG, Lee JY
and Lee KT: Beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-beta-D-glucuronopyranosyl
echinocystic acid isolated from the roots of Codonopsis lanceolata
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human acute promyelocytic
leukemia HL-60 cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 28:854–859. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kuete V, Fankam AG, Wiench B and Efferth
T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of the methanol extracts of six
Cameroonian medicinal plants against multidrug-resistant tumor
cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:859032013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kuete V, Tankeo SB, Saeed ME, Wiench B,
Tane P and Efferth T: Cytotoxicity and modes of action of five
Cameroonian medicinal plants against multi-factorial drug
resistance of tumor cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 153:207–219. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kuete V, Sandjo LP, Mbaveng AT, Seukep JA,
Ngadjui BT and Efferth T: Cytotoxicity of selected Cameroonian
medicinal plants and Nauclea pobeguinii towards multi-factorial
drug-resistant cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:3092015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Skup M, Dwornik A, Macias M, Suleczak D,
Wiater M and Czarkoeska-Bauch J: Long-term locomotor training
upregulates TrkBFL receptor-like proteins, brain-derived
neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin 4 with different topographies
of expression in oligodendroglia and neurons in the spinal cord.
Exp Neurol. 176:289–307. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qin DX, Zou XL, Luo W, Zhang W, Zhang HT,
Li XL, Zhang H, Wang XY and Wang TH: Expression of some
neurotrophins in the spinal motoneurons after cord hemisection in
adult rats. Neurosci Lett. 410:222–227. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu T, Zhang C, Tang Q, Su Y, Li B, Chen L,
Zhang Z, Cai T and Zhu Y: Variant G6PD levels promote tumor cell
proliferation or apoptosis via the STAT3/5 pathway in the human
melanoma xenograft mouse model. BMC Cancer. 13:2512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Niu G, Heller R, Catlett-Falcone R,
Coppola D, Jaroszeski M, Dalton W, Jove R and Yu H: Gene therapy
with dominant-negative Stat3 suppresses growth of the murine
melanoma B16 tumor in vivo. Cancer Res. 59:5059–5063.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Xu ML, Hu JH, Rasmussen SK and
Wang MH: Codonopsis lanceolata extract induces G0/G1 arrest and
apoptosis in human colon tumor HT-29 cells-involvement of ROS
generation and polyamine depletion. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:149–154.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu ZY: Herbal in Yunnan. Science Press:
Beijing. 5:4871991.
|
|
32
|
Chen ZJ, Li YS, Wei QH, Chen SL and Chen
DX: Efects of Codonopis bulleynana Forest ex Diels on enhancing
sensitivity, reducing toxicity of chemotherapy and regulating
immune function in Sarcoma 180 tumor-bearing mice. Chin Trad Patent
Med. 34:1848–1851. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hockenbery D, Nuñez G, Milliman C,
Schreiber RD and Korsmeyer SJ: Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial
membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature.
22:334–336. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vaux D and Korsmeyer S: Cell death in
development. Cell. 96:245–254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiang FX and Guo YJ: Apoptosis in
oncology. Cell Res. 11:1–7. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Korsmeyer SJ: BCL-2 gene family and the
regulation of programmed cell death. Cancer Res. 59:1693–1700.
1999.
|
|
39
|
Cohen GM: Caspases: The executioners of
apoptosis. Biochem. J. 326:1–16. 1997.
|
|
40
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|