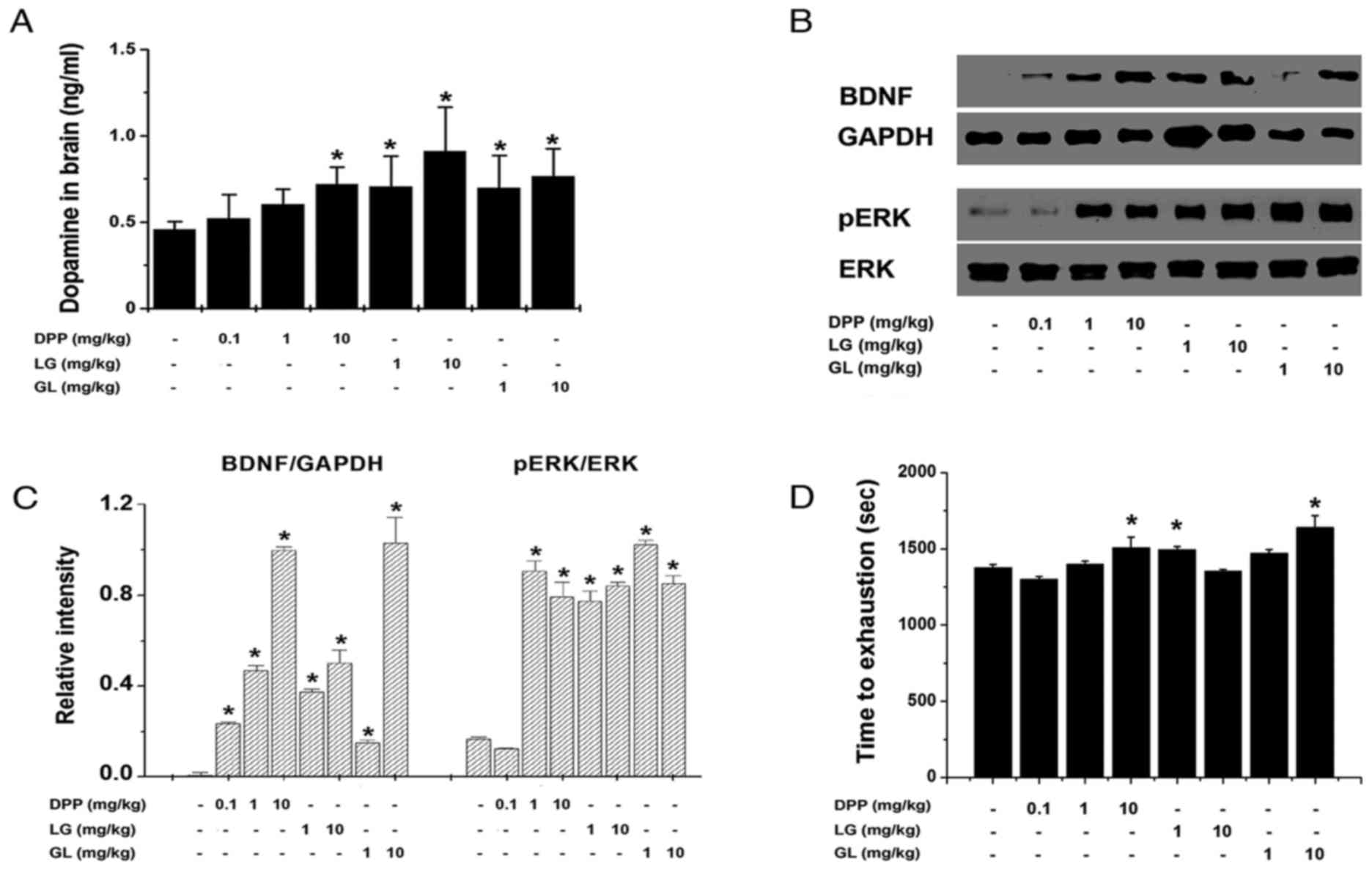
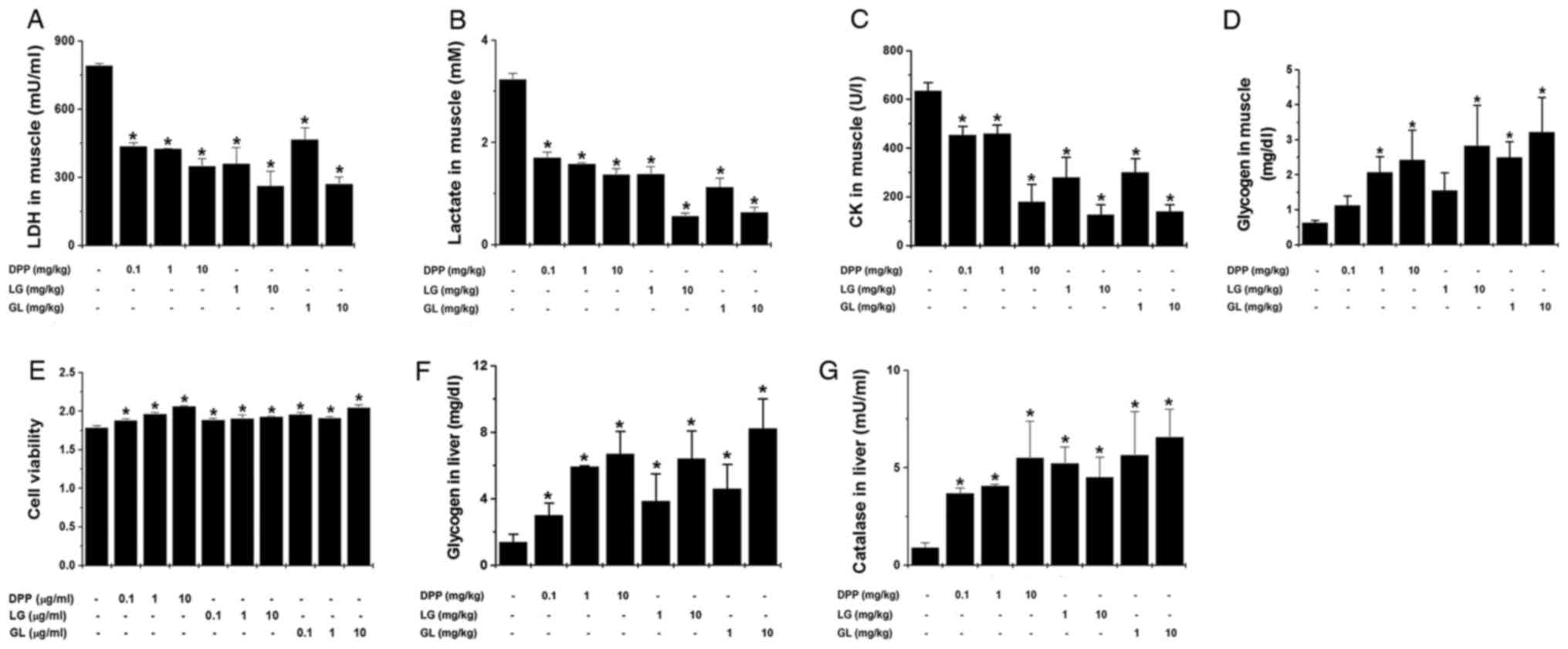
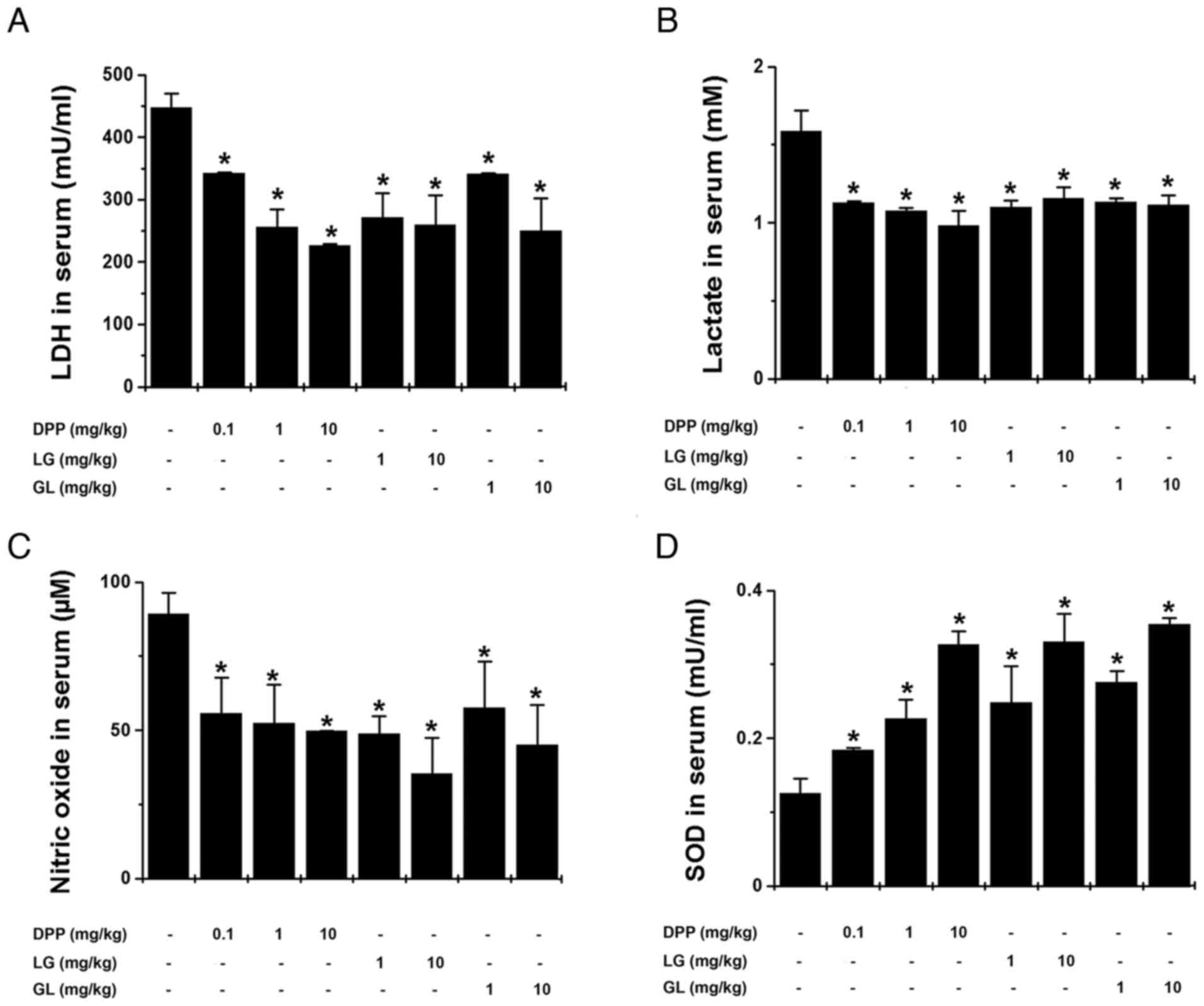
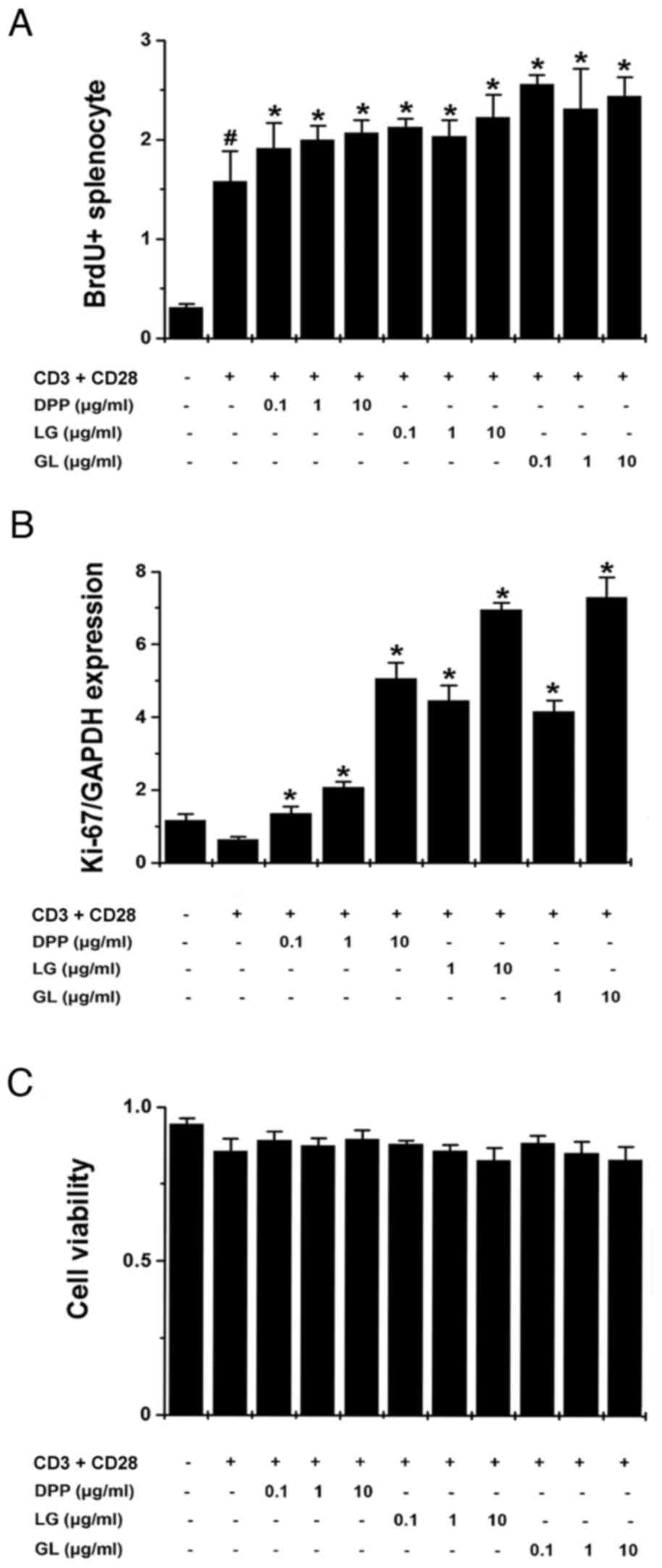
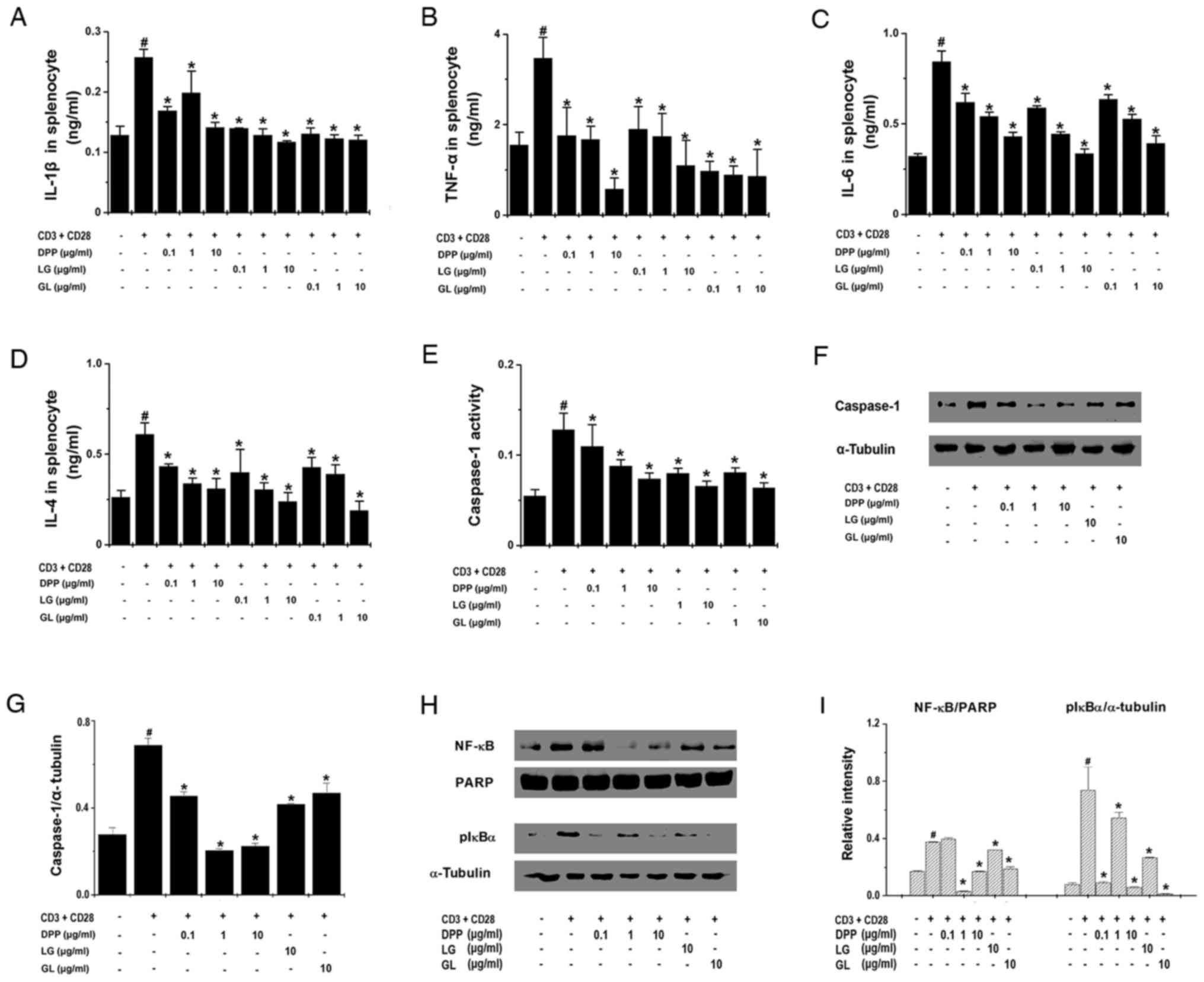
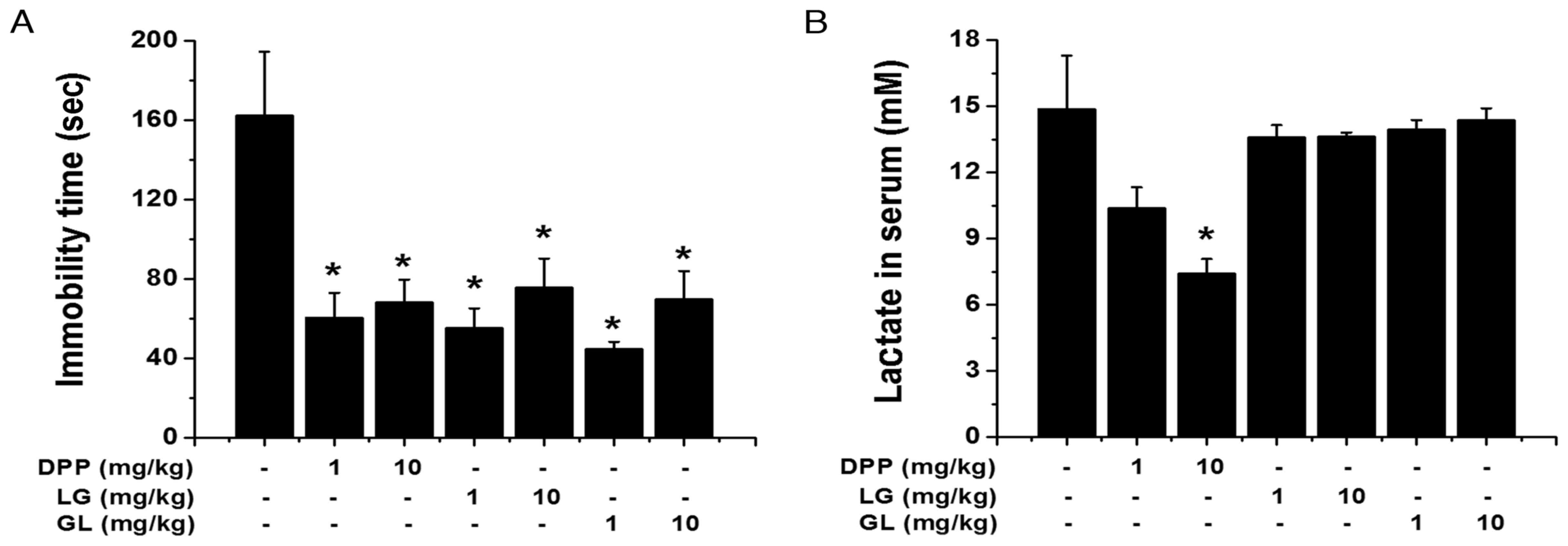
|
1
|
Gandevia SC: Spinal and supraspinal
factors in human muscle fatigue. Physiol Rev. 81:1725–1789. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Meeusen R and Watson P: Amino acids and
the brain: Do they play a role in ‘central fatigue’? Int J Sport
Nutr Exerc Metab. 17 Suppl:S37–S46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Balthazar CH, Leite LH, Rodrigues AG and
Coimbra CC: Performance-enhancing and thermoregulatory effects of
intracerebroventricular dopamine in running rats. Pharmacol Biochem
Behav. 93:465–469. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chaouloff F: Physical exercise and brain
monoamines: A review. Acta Physiol Scand. 137:1–13. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Basu S and Dasgupta PS: Dopamine, a
neurotransmitter, influences the immune system. J Neuroimmunol.
102:113–124. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meeusen R: Exercise, nutrition and the
brain. Sports Med. 44 Suppl 1:S47–S56. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Razgado-Hernandez LF, Espadas-Alvarez AJ,
Reyna-Velazquez P, Sierra-Sanchez A, Anaya-Martinez V,
Jimenez-Estrada I, Bannon MJ, Martinez-Fong D and Aceves-Ruiz J:
The transfection of BDNF to dopamine neurons potentiates the effect
of dopamine D3 receptor agonist recovering the striatal
innervation, dendritic spines and motor behavior in an aged rat
model of Parkinson's disease. PLoS One. 10:e01173912015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmidt HD and Duman RS: The role of
neurotrophic factors in adult hippocampal neurogenesis,
antidepressant treatments and animal models of depressive-like
behavior. Behav Pharmacol. 18:391–418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saligan LN, Lukkahatai N, Holder G, Walitt
B and Machado-Vieira R: Lower brain-derived neurotrophic factor
levels associated with worsening fatigue in prostate cancer
patients during repeated stress from radiation therapy. World J
Biol Psychiatry. 27:608–614. 2016.
|
|
10
|
Liburt NR, Adams AA, Betancourt A, Horohov
DW and McKeever KH: Exercise-induced increases in inflammatory
cytokines in muscle and blood of horses. Equine Vet J Suppl.
38:280–288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Felger JC and Miller AH: Cytokine effects
on the basal ganglia and dopamine function: The subcortical source
of inflammatory malaise. Front Neuroendocrinol. 33:315–327. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koo HN, Lee JK, Hong SH and Kim HM:
Herbkines increases physical stamina in mice. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:117–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pall ML: Elevated, sustained peroxynitrite
levels as the cause of chronic fatigue syndrome. Med Hypotheses.
54:115–125. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Coombes JS, Rowell B, Dodd SL, Demirel HA,
Naito H, Shanely RA and Powers SK: Effects of vitamin E deficiency
on fatigue and muscle contractile properties. Eur J Appl Physiol.
87:272–277. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Borah M, Sarma P and Das S: A study of the
protective effect of triticum aestivum L. in an experimental animal
model of chronic fatigue syndrome. Pharmacognosy Res. 6:285–291.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Finaud J, Lac G and Filaire E: Oxidative
stress: Relationship with exercise and training. Sports Med.
36:327–358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tennant KF, Takacs SE, Gau JT, Clark BC
and Russ DW: A preliminary study of symptomatic fatigue in rural
older adults. Aging Clin Exp Res. 24:324–330. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Han NR, Kim KY, Kim MJ, Kim MH, Kim HM and
Jeong HJ: Porcine placenta mitigates protein-energy
malnutrition-induced fatigue. Nutrition. 29:1381–1387. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wolfe RR: Protein supplements and
exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 72 2 Suppl:551S–557S. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim HY, Han NR, Kim NR, Lee M, Kim J, Kim
CJ, Jeong HJ and Kim HM: Effect of fermented porcine placenta on
physical fatigue in mice. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 241:1985–1996.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ye J, Shen C, Huang Y, Zhang X and Xiao M:
Anti-fatigue activity of sea cucumber peptides prepared from
Stichopus japonicus in an endurance swimming rat model. J Sci Food
Agric. 97:4548–4556. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Buel EM, Sigrist H, Seifritz E, Fikse
L, Bosker FJ, Schoevers RA, Klein HC, Pryce CR and Eisel UL: Mouse
repeated electroconvulsive seizure (ECS) does not reverse social
stress effects but does induce behavioral and hippocampal changes
relevant to electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) side-effects in the
treatment of depression. PLoS One. 12:e01846032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao YQ, Zeng L, Yang ZS, Huang FF, Ding
GF and Wang B: Anti-fatigue effect by peptide fraction from protein
hydrolysate of croceine croaker (pseudosciaena crocea) swim bladder
through inhibiting the oxidative reactions including DNA damage.
Mar Drugs. 14:pii: E2212016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Seo JH, Sung YH, Kim KJ, Shin MS, Lee EK
and Kim CJ: Effects of Phellinus linteus administration on
serotonin synthesis in the brain and expression of monocarboxylate
transporters in the muscle during exhaustive exercise in rats. J
Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 57:95–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kumar V, Aneesh KA, Kshemada K, Ajith KGS,
Binil RSS, Deora N, Sanjay G, Jaleel A, Muraleedharan TS, Anandan
EM, et al: Amalaki rasayana, a traditional Indian drug enhances
cardiac mitochondrial and contractile functions and improves
cardiac function in rats with hypertrophy. Sci Rep. 7:85882017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Motaghinejad M, Motevalian M,
Asadi-Ghalehni M and Motaghinejad O: Attenuation of morphine
withdrawal signs, blood cortisol and glucose level with forced
exercise in comparison with clonidine. Adv Biomed Res. 3:1712014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rim HK, Kim KY and Moon PD: Evidence of
hydrolyzed traditional Korean red ginseng by malted barley on
activation of receptor interacting proteins 2 and IkappaB
kinase-beta in mouse peritoneal macrophages. TANG. 2:e372015.
|
|
28
|
Jung HY, Lee AN, Song TJ, An HS, Kim YH,
Kim KD, Kim IB, Kim KS, Han BS, Kim CH, et al: Korean mistletoe
(Viscum album coloratum) extract improves endurance capacity in
mice by stimulating mitochondrial activity. J Med Food. 15:621–628.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Teng YS and Wu D: Anti-fatigue effect of
green tea polyphenols (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG).
Pharmacogn Mag. 13:326–331. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Azzinnari D, Sigrist H, Staehli S, Palme
R, Hildebrandt T, Leparc G, Hengerer B, Seifritz E and Pryce CR:
Mouse social stress induces increased fear conditioning,
helplessness and fatigue to physical challenge together with
markers of altered immune and dopamine function. Neuropharmacology.
85:328–341. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Flachenecker P, Bihler I, Weber F,
Gottschalk M, Toyka KV and Rieckmann P: Cytokine mRNA expression in
patients with multiple sclerosis and fatigue. Mult Scler.
10:165–169. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marin H and Menza MA: Specific treatment
of residual fatigue in depressed patients. Psychiatry (Edgmont).
1:12–18. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bailey SP, Davis JM and Ahlborn EN:
Neuroendocrine and substrate responses to altered brain 5-HT
activity during prolonged exercise to fatigue. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 74:3006–3012. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gerald MC: Effects of (+)-amphetamine on
the treadmill endurance performance of rats. Neuropharmacology.
17:703–704. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Heyes MP, Garnett ES and Coates G:
Nigrostriatal dopaminergic activity is increased during exhaustive
exercise stress in rats. Life Sci. 42:1537–1542. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sorenson M, Jason L, Peterson J,
Herrington J and Mathews H: Brain derived neurotrophic factor is
decreased in chronic fatigue syndrome and multiple sclerosis. J
Neurol Neurophysiol. 12 Suppl:S2–S13. 2014.
|
|
38
|
Foley TE and Fleshner M: Neuroplasticity
of dopamine circuits after exercise: Implications for central
fatigue. Neuromolecular Med. 10:67–80. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shen X, Li A, Zhang Y, Dong X, Shan T, Wu
Y, Jia J and Hu Y: The effect of different intensities of treadmill
exercise on cognitive function deficit following a severe
controlled cortical impact in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 14:21598–21612.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng P, Guan Z, Yang X and Fang J:
Impairments of ERK signal transduction in the brain in a rat model
of depression induced by neonatal exposure of clomipramine. Brain
Res. 991:195–205. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dobryakova E, Genova HM, DeLuca J and
Wylie GR: The dopamine imbalance hypothesis of fatigue in multiple
sclerosis and other neurological disorders. Front Neurol. 6:522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rahimi E, Moghadasi M, Mahani MN, Torkfar
A and Yadolazadeh A: Central and peripheral fatigue factors after
an exhaustive aerobic exercise following creatine supplementation.
Ann Biol Res. 3:4209–4214. 2012.
|
|
43
|
Watanabe A, Kato N and Kato T: Effects of
creatine on mental fatigue and cerebral hemoglobin oxygenation.
Neurosci Res. 42:279–285. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Su KY, Yu CY, Chen YW, Huang YT, Chen CT,
Wu HF and Chen YL: Rutin, a flavonoid and principal component of
saussurea involucrata, attenuates physical fatigue in a forced
swimming mouse model. Int J Med Sci. 11:528–537. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Calabrese F, Rossetti AC, Racagni G, Gass
P, Riva MA and Molteni R: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: A
bridge between inflammation and neuroplasticity. Front Cell
Neurosci. 8:4302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jason LA, Porter N, Herrington J, Sorenson
M and Kubow S: Kindling and oxidative stress as contributors to
myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. J Behav
Neurosci Res. 7:1–17. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Suárez A, Guillamó E, Roig T, Blázquez A,
Alegre J, Bermúdez J, Ventura JL, García-Quintana AM, Comella A,
Segura R and Javierre C: Nitric oxide metabolite production during
exercise in chronic fatigue syndrome: A case-control study. J
Womens Health (Larchmt). 19:1073–1077. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu J, Yeo HC, Overvik-Douki E, Hagen T,
Doniger SJ, Chu DW, Brooks GA and Ames BN: Chronically and acutely
exercised rats: Biomarkers of oxidative stress and endogenous
antioxidants. J Appl Physiol (1985). 89:21–28. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wu C, Chen R, Wang XS, Shen B, Yue W and
Wu Q: Antioxidant and anti-fatigue activities of phenolic extract
from the seed coat of Euryale ferox Salisb. and identification of
three phenolic compounds by LC-ESI-MS/MS. Molecules.
18:11003–11021. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lamkanfi M, Sarkar A, Vande Walle L,
Vitari AC, Amer AO, Wewers MD, Tracey KJ, Kanneganti TD and Dixit
VM: Inflammasome-dependent release of the alarmin HMGB1 in
endotoxemia. J Immunol. 185:4385–4392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sola-Penna M: Metabolic regulation by
lactate. IUBMB Life. 60:605–608. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Huang CC, Lin TJ, Lu YF, Chen CC, Huang CY
and Lin WT: Protective effects of L-arginine supplementation
against exhaustive exercise-induced oxidative stress in young rat
tissues. Chin J Physiol. 52:306–315. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cruzat VF, Rogero MM and Tirapegui J:
Effects of supplementation with free glutamine and the dipeptide
alanyl-glutamine on parameters of muscle damage and inflammation in
rats submitted to prolonged exercise. Cell Biochem Funct. 28:24–30.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang WC, Chiu WC, Chuang HL, Tang DW, Lee
ZM, Wei L, Chen FA and Huang CC: Effect of curcumin supplementation
on physiological fatigue and physical performance in mice.
Nutrients. 7:905–921. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
June CH, Ledbetter JA, Gillespie MM,
Lindsten T and Thompson CB: T-cell proliferation involving the CD28
pathway is associated with cyclosporine-resistant interleukin 2
gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 7:4472–4481. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Suarez Butler MF, Langkamp-Henken B,
Herrlinger-Garcia KA, Klash AE, Szczepanik ME, Nieves C Jr, Cottey
RJ and Bender BS: Arginine supplementation enhances mitogen-induced
splenocyte proliferation but does not affect in vivo indicators of
antigen-specific immunity in mice. J Nutr. 135:1146–1150. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Clancy RL, Gleeson M, Cox A, Callister R,
Dorrington M, D'Este C, Pang G, Pyne D, Fricker P and Henriksson A:
Reversal in fatigued athletes of a defect in interferon gamma
secretion after administration of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Br J
Sports Med. 40:351–354. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cheng M, Nguyen MH, Fantuzzi G and Koh TJ:
Endogenous interferon-gamma is required for efficient skeletal
muscle regeneration. Am J Phys Cell Phys. 294:C1183–C1191. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Fernstrom JD: Dietary amino acids and
brain function. J Am Diet Assoc. 94:71–77. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Davis JM, Alderson NL and Welsh RS:
Serotonin and central nervous system fatigue: Nutritional
considerations. Am J Clin Nutr. 72 2 Suppl:573S–578S.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Cruzat VF, Krause M and Newsholme P: Amino
acid supplementation and impact on immune function in the context
of exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 11:612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Smith WA, Fry AC, Tschume LC and Bloomer
RJ: Effect of glycine propionyl-L-carnitine on aerobic and
anaerobic exercise performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.
18:19–36. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Favano A, Santos-Silva PR, Nakano EY,
Pedrinelli A, Hernandez AJ and Greve JM: Peptide glutamine
supplementation for tolerance of intermittent exercise in soccer
players. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 63:27–32. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|