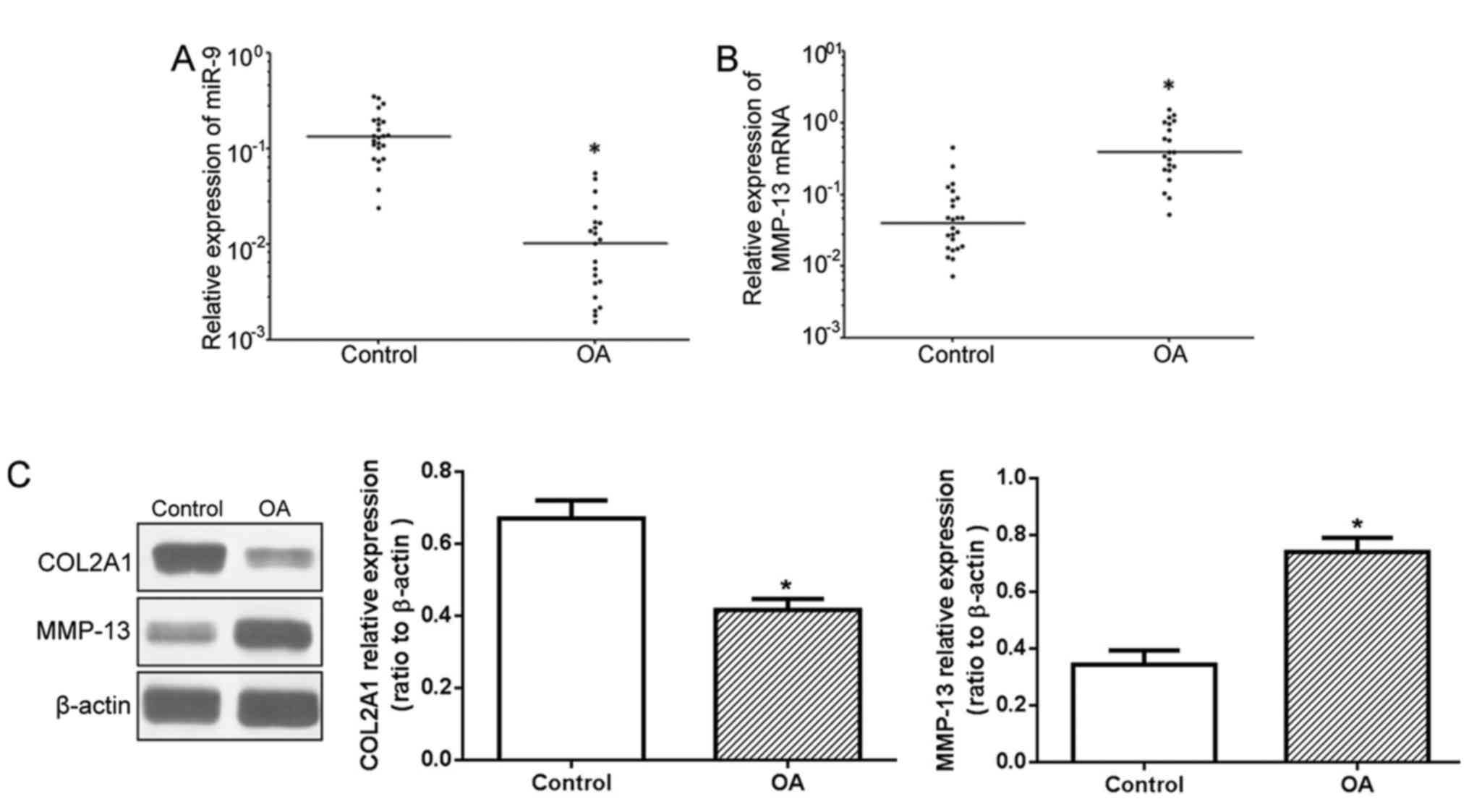
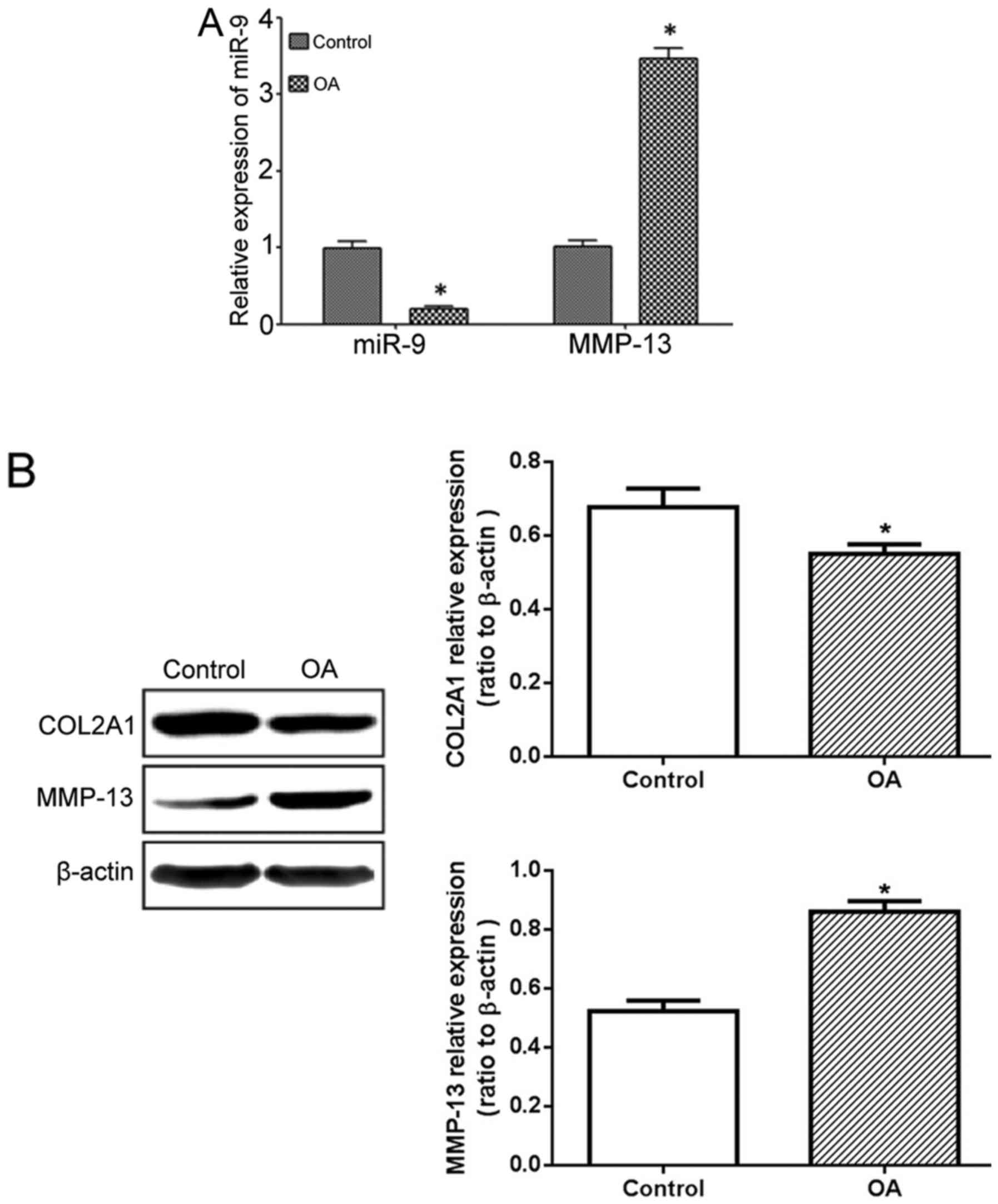
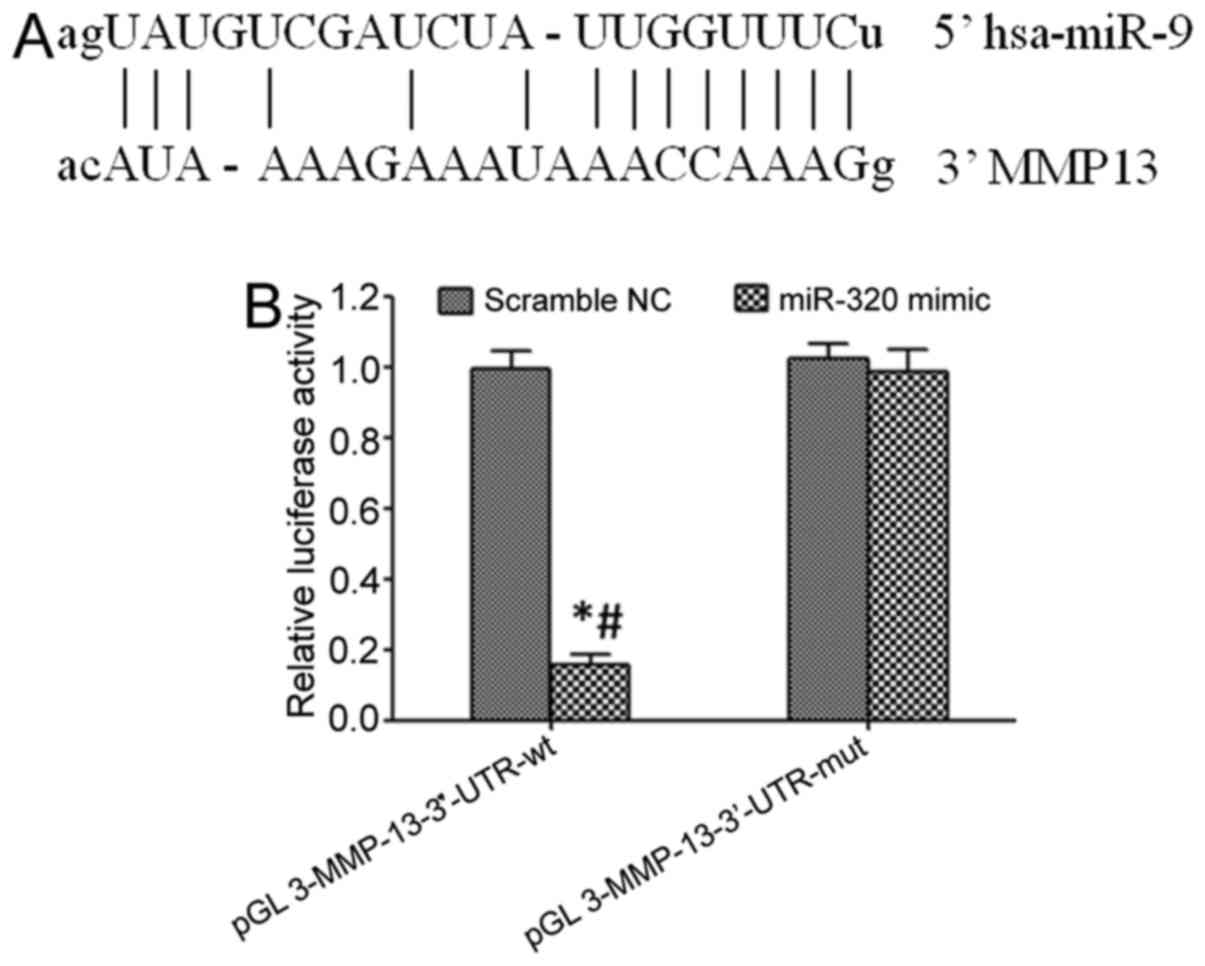
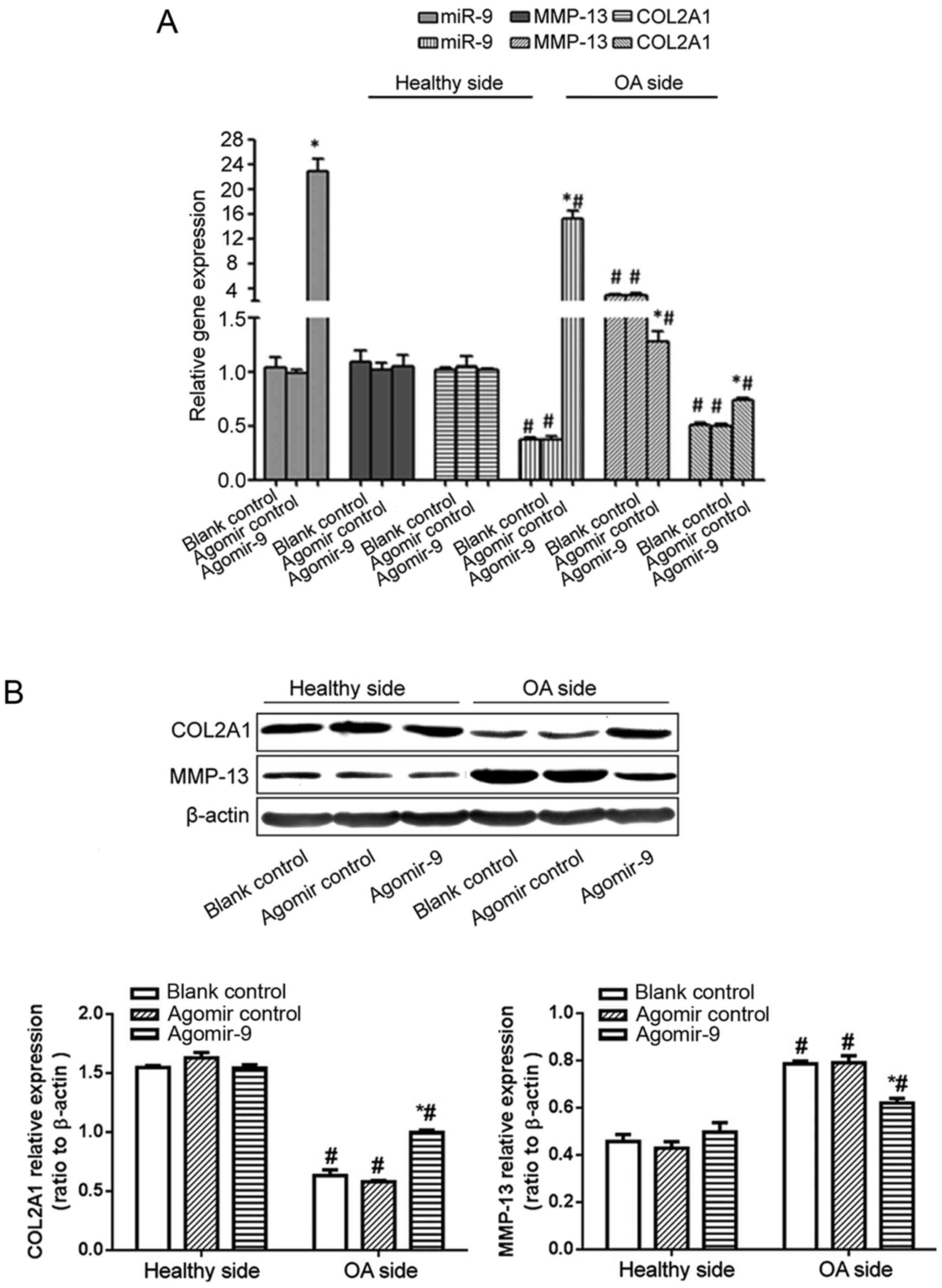
|
1
|
Coudeyre E, Byers Kraus V and Rannou F:
Osteoarthritis in physical medicine and rehabilitation. Ann Phys
Rehabil Med. 59:1332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Queen RM, Sparling TL and Schmitt D: Hip,
knee, and ankle osteoarthritis negatively affects mechanical energy
exchange. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 474:2055–2063. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang X, Zhao X and Tang S: Inhibitory
effects of EGb761 on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases
(MMPs) and cartilage matrix destruction. Cell Stress Chaperones.
20:781–786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jabłońska-Trypuć A, Matejczyk M and
Rosochacki S: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), the main
extracellular matrix (ECM) enzymes in collagen degradation, as a
target for anticancer drugs. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 31:177–183.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li P, Deng J, Wei X, Jayasuriya CT, Zhou
J, Chen Q, Zhang J, Wei L and Wei F: Blockade of hypoxia-induced
CXCR4 with AMD3100 inhibits production of OA-associated catabolic
mediators IL-1beta and MMP-13. Mol Med Rep. 14:1475–1482. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen YT, Hou CH, Hou SM and Liu JF: The
effects of amphiregulin induced MMP-13 production in human
osteoarthritis synovial fibroblast. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:7590282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Asahara H: Current status and strategy of
microrna research for cartilage development and osteoarthritis
pathogenesis. J Bone Metab. 23:121–127. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gu R, Liu N, Luo S, Huang W, Zha Z and
Yang J: MicroRNA-9 regulates the development of knee osteoarthritis
through the NF-kappaB1 pathway in chondrocytes. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e43152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Song J, Kim D, Chun CH and Jin EJ:
MicroRNA-9 regulates survival of chondroblasts and cartilage
integrity by targeting protogenin. Cell Commun Signal. 11:662013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peat G, Thomas E, Duncan R, Wood L, Hay E
and Croft P: Clinical classification criteria for knee
osteoarthritis: performance in the general population and primary
care. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1363–1367. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dziri C, Aloulou I, Loubiri I, Rekik M,
Zohra Ben Salah F and Abdallah A: Assessment of disability in
osteoarthritis of the knee. Annals of physical and rehabilitation
medicine. 59s:e1152016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim YH, Dorj A, Han A, Kim K and Nha KW:
Improvements in spinal alignment after high tibial osteotomy in
patients with medial compartment knee osteoarthritis. Gait Posture.
48:131–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mayorga AJ, Wang S, Kelly KM and
Thipphawong J: Efficacy and safety of fulranumab as monotherapy in
patients with moderate to severe, chronic knee pain of primary
osteoarthritis: a randomised, placebo- and active-controlled trial.
Int J Clin Pract. 70:493–505. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Kraan PM, Berenbaum F, Blanco FJ,
Cosimo de B, Lafeber F, Hauge E, Higginbottom A, Ioan-Facsinay A,
Loughlin J, Meulenbelt I, et al: Translation of clinical problems
in osteoarthritis into pathophysiological research goals. RMD Open.
2:e0002242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cushnaghan J and Dieppe P: Study of 500
patients with limb joint osteoarthritis. I. Analysis by age, sex,
and distribution of symptomatic joint sites. Ann Rheum Dis.
50:8–13. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Arden N and Nevitt MC: Osteoarthritis:
Epidemiology. Best Prac Res Clin Reheum. 20:3–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Montero A, Mulero JF, Tornero C, Guitart J
and Serrano M: Pain, disability and health-related quality of life
in osteoarthritis-joint matters: An observational, multi-specialty
trans-national follow-up study. Clin Rheumatol. 35:2293–2305. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frioui Mahmoudi S, Toulgui E, Ben Jeddou
K, Gaddour M, Jemni S and Khachnaoui F: Quality of life for patient
with knee osteoarthritis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 59S:e158–e159.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wainwright TW, Immins T and Middleton RG:
A cycling and education programme for the treatment of hip
osteoarthritis: A quality improvement study. Int J Orthop Trauma
Nurs. 23:14–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu D, Zhao Y, Shen J, Cai Z and Hua Y:
Comparison of venous thromboembolism after total artificial joint
replacement between musculoskeletal tumors and osteoarthritis of
the knee by a single surgeon. PLoS One. 11:e01582152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Neuhold LA, Killar L, Zhao W, Sung ML,
Warner L, Kulik J, Turner J, Wu W, Billinghurst C, Meijers T, et
al: Postnatal expression in hyaline cartilage of constitutively
active human collagenase-3 (MMP-13) induces osteoarthritis in mice.
J Clin Invest. 107:35–44. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Blaney Davidson EN, Remst DF, Vitters EL,
van Beuningen HM, Blom AB, Goumans MJ, van den Berg WB and van der
Kraan PM: Increase in ALK1/ALK5 ratio as a cause for elevated
MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritis in humans and mice. J Immunol.
182:7937–7945. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lim NH, Meinjohanns E, Meldal M,
Bou-Gharios G and Nagase H: In vivo imaging of MMP-13 activity in
the murine destabilised medial meniscus surgical model of
osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 22:862–868. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pelletier JP, Boileau C, Martin Boily,
Brunet J, Mineau F, Geng C, Reboul P, Laufer S, Lajeunesse D and
Martel-Pelletier J: The protective effect of licofelone on
experimental osteoarthritis is correlated with the downregulation
of gene expression and protein synthesis of several major cartilage
catabolic factors: MMP-13, cathepsin K and aggrecanases. Arthritis
Res Ther. 7:R1091–1102. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li NG, Shi ZH, Tang YP, Wang ZJ, Song SL,
Qian LH, Qian DW and Duan JA: New hope for the treatment of
osteoarthritis through selective inhibition of MMP-13. Curr Med
Chem. 18:977–1001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|