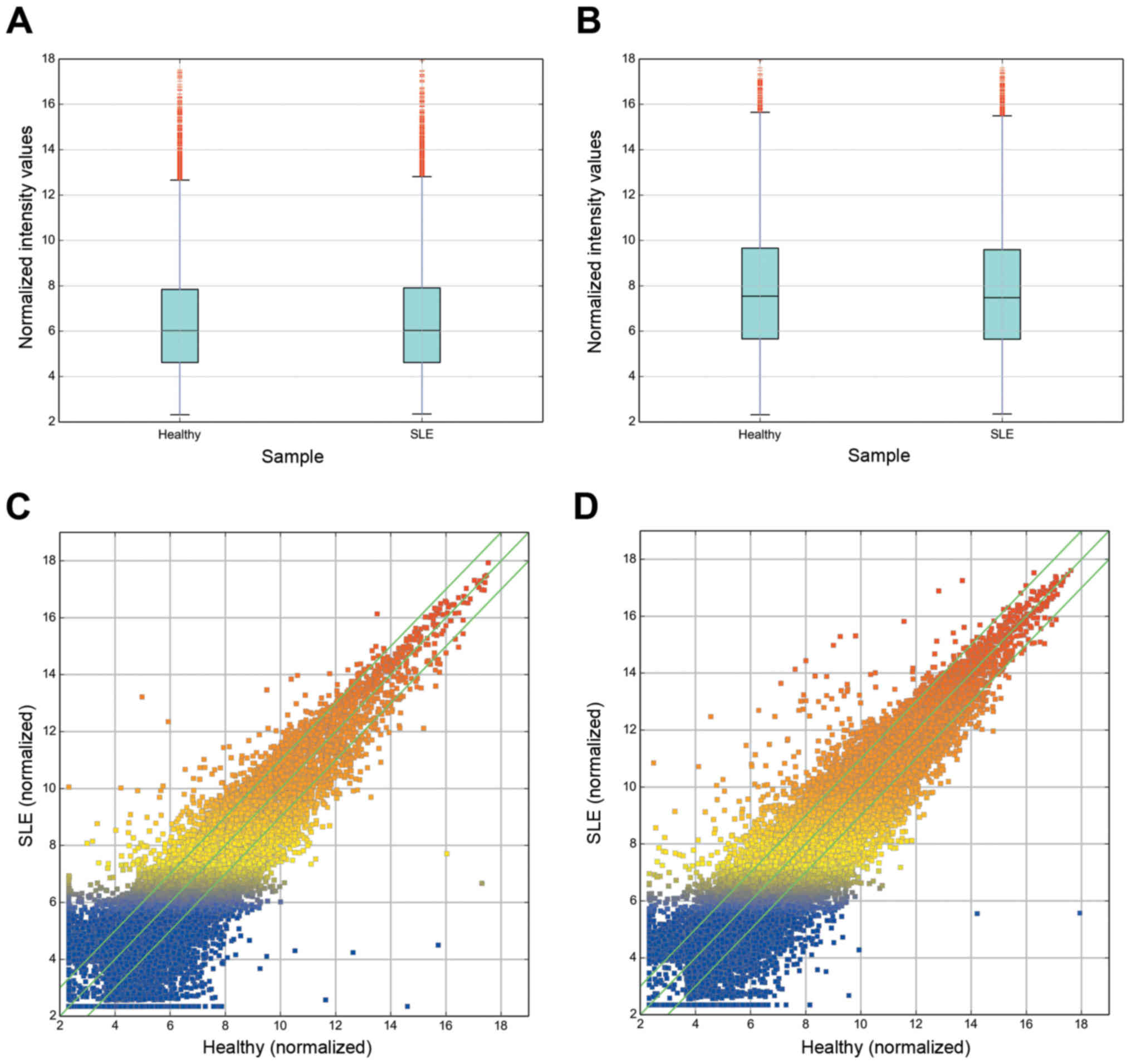
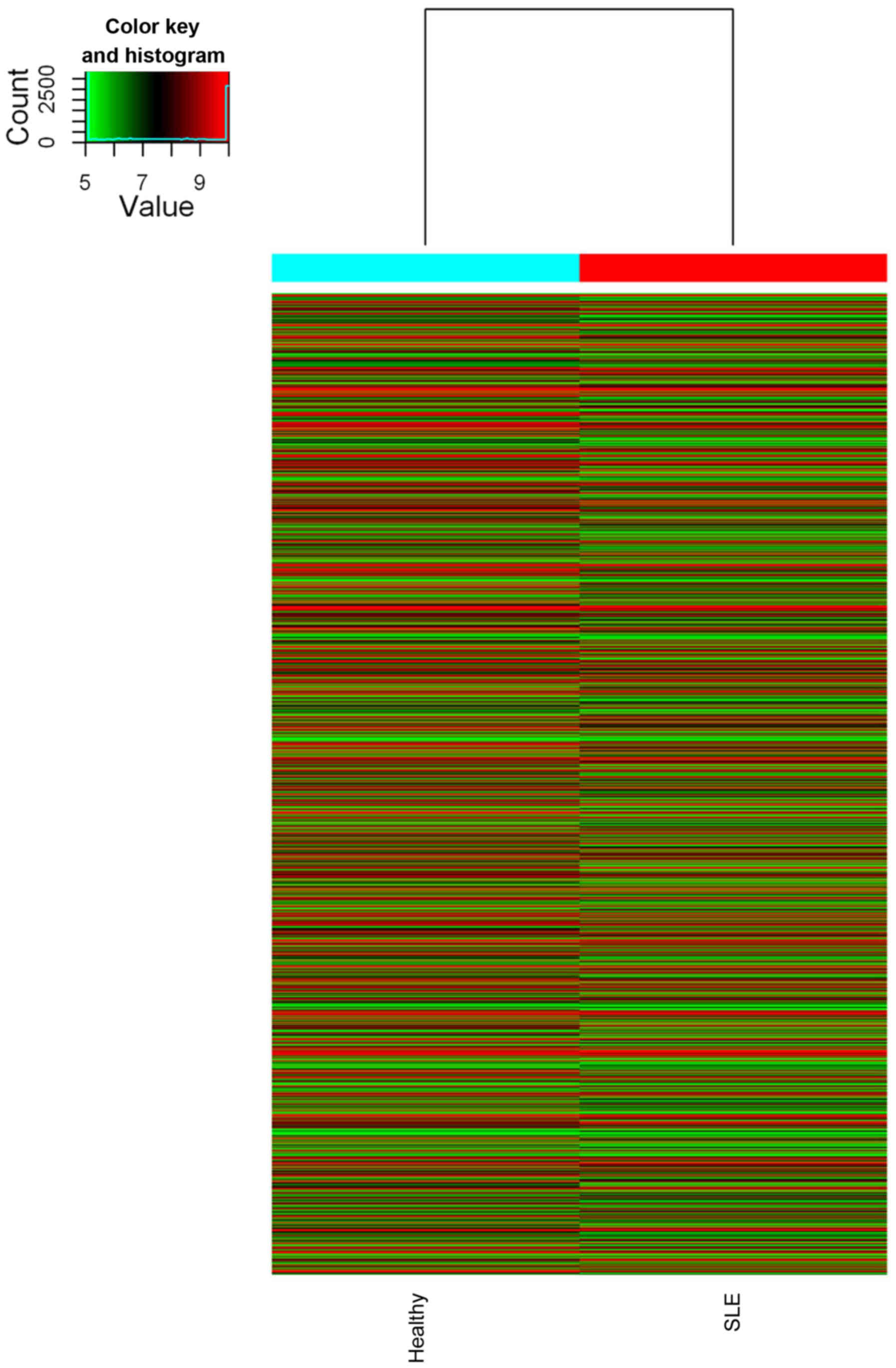
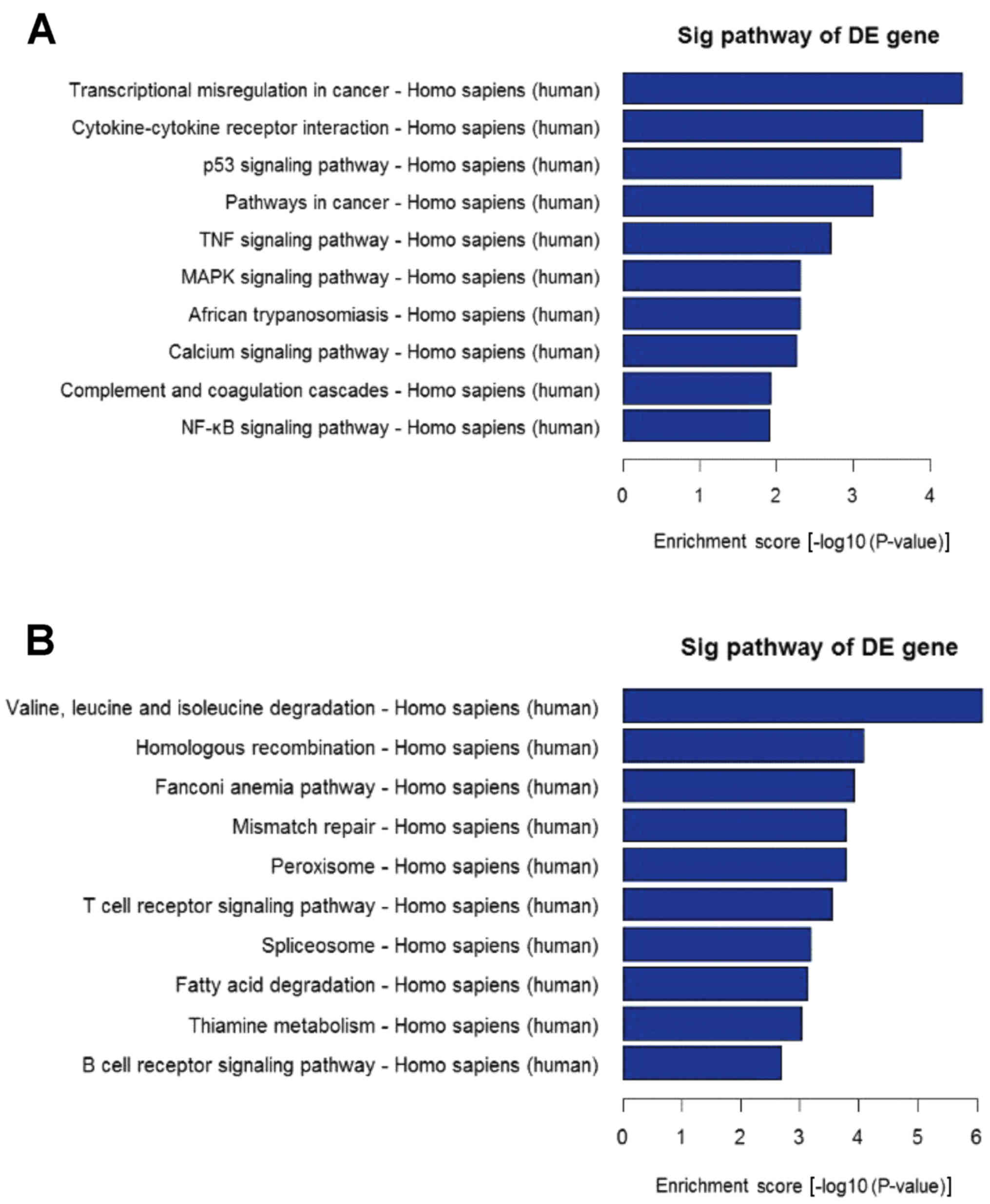
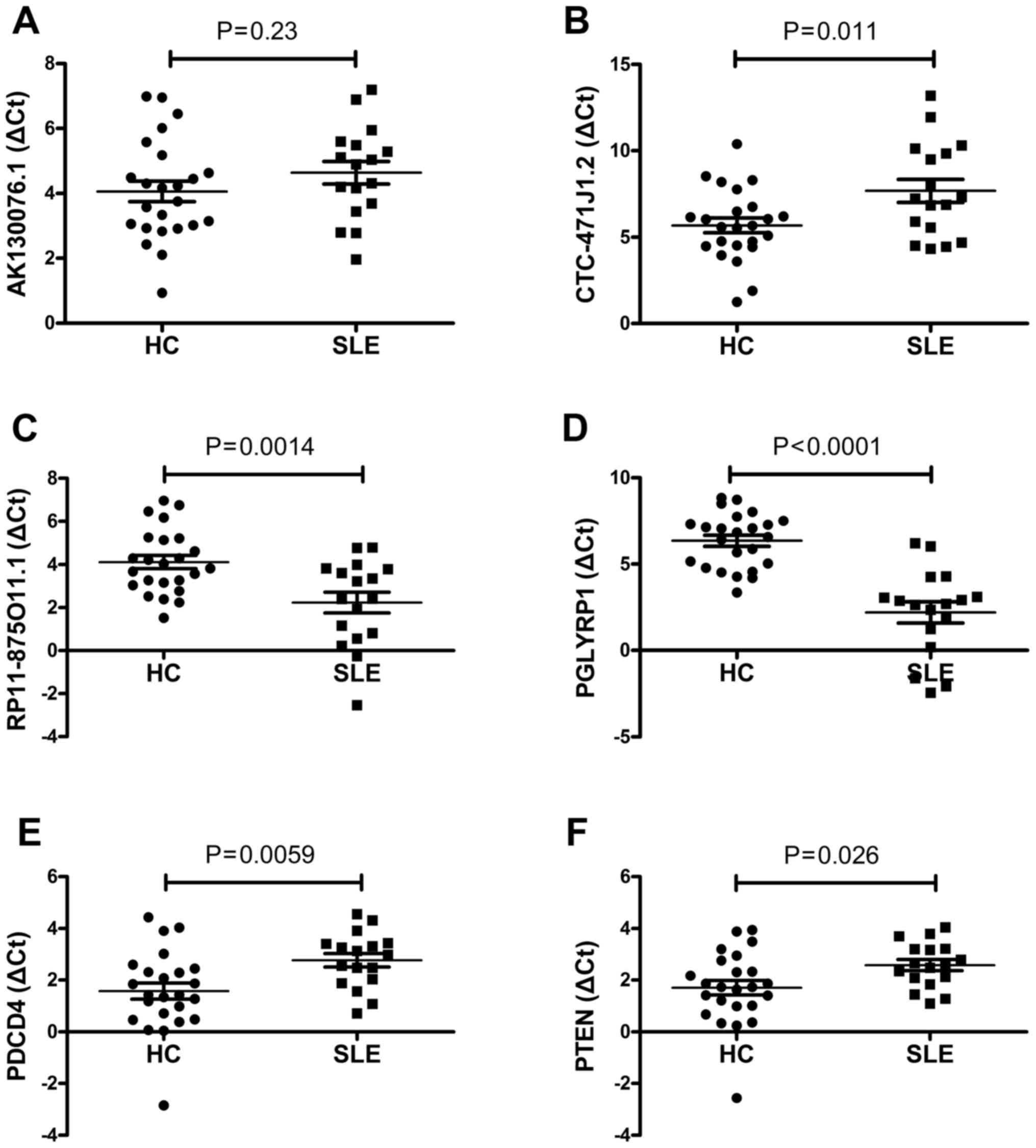
|
1
|
Bertsias GK, Salmon JE and Boumpas DT:
Therapeutic opportunities in systemic lupus erythematosus: State of
the art and prospects for the new decade. Ann Rheum Dis.
69:1603–1611. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kow NY and Mak A: Costimulatory pathways:
Physiology and potential therapeutic manipulation in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:2459282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kirou KA and Gkrouzman E: Anti-interferon
alpha treatment in SLE. Clin Immunol. 148:303–312. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kowalczyk MS, Higgs DR and Gingeras TR:
Molecular biology: RNA discrimination. Nature. 482:310–311. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shirasawa S, Harada H, Furugaki K, Akamizu
T, Ishikawa N, Ito K, Ito K, Tamai H, Kuma K, Kubota S, et al: SNPs
in the promoter of a B cell-specific antisense transcript,
SAS-ZFAT, determine susceptibility to autoimmune thyroid disease.
Hum Mol Genet. 13:2221–2231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Song J, Kim D, Han J, Kim Y, Lee M and Jin
EJ: PBMC and exosome-derived Hotair is a critical regulator and
potent marker for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Med. 15:121–126.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heward JA and Lindsay MA: Long non-coding
RNAs in the regulation of the immune response. Trends Immunol.
35:408–419. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Willingham AT, Orth AP, Batalov S, Peters
EC, Wen BG, Aza-Blanc P, Hogenesch JB and Schultz PG: A strategy
for probing the function of noncoding RNAs finds a repressor of
NFAT. Science. 309:1570–1573. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Collier SP, Collins PL, Williams CL,
Boothby MR and Aune TM: Cutting edge: Influence of Tmevpg1, a long
intergenic noncoding RNA, on the expression of Ifng by Th1 cells. J
Immunol. 189:2084–2088. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Z, Chao TC, Chang KY, Lin N, Patil VS,
Shimizu C, Head SR, Burns JC and Rana TM: The long noncoding RNA
THRIL regulates TNFα expression through its interaction with
hnRNPL. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:pp. 1002–1007. 2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li B, Tsoi LC, Swindell WR, Gudjonsson JE,
Tejasvi T, Johnston A, Ding J, Stuart PE, Xing X, Kochkodan JJ, et
al: Transcriptome analysis of psoriasis in a large case-control
sample: RNA-seq provides insights into disease mechanisms. J Invest
Dermatol. 134:1828–1838. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Q, Zhang X, Dai L, Hu X, Zhu J, Li L,
Zhou C and Ao Y: Long noncoding RNA related to cartilage injury
promotes chondrocyte extracellular matrix degradation in
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:969–978. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Müller N, Döring F, Klapper M, Neumann K,
Schulte DM, Türk K, Schröder JO, Zeuner RA, Freitag-Wolf S,
Schreiber S and Laudes M: Interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis
factor-α differentially regulate lincRNA transcripts in cells of
the innate immune system in vivo in human subjects with rheumatoid
arthritis. Cytokine. 68:65–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT,
McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N and Winchester RJ:
The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus
erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 25:1271–1277. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tian M, Chen R, Li T and Xiao B: Reduced
expression of circRNA hsa_circ_0003159 in gastric cancer and its
clinical significance. J Clin Lab Anal. Jun 15–2017.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xu G, Chen J, Pan Q, Huang K, Pan J, Zhang
W, Chen J, Yu F, Zhou T and Wang Y: Long noncoding RNA expression
profiles of lung adenocarcinoma ascertained by microarray analysis.
PLoS One. 9:e1040442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ørom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, Gumireddy
K, Gardini A, Bussotti G, Lai F, Zytnicki M, Notredame C, Huang Q,
et al: Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human
cells. Cell. 143:46–58. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wan ZY, Song F, Sun Z, Chen YF, Zhang WL,
Samartzis D, Ma CJ, Che L, Liu X, Ali MA, et al: Aberrantly
expressed long noncoding RNAs in human intervertebral disc
degeneration: A microarray related study. Arthritis Res Ther.
16:4652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gurevitz SL, Snyder JA, Wessel EK, Frey J
and Williamson BA: Systemic lupus erythematosus: A review of the
disease and treatment options. Consult Pharm. 28:110–121. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong W and Lahita RG: Pragmatic
approaches to therapy for systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev
Rheumatol. 10:97–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu Y, Zhang F, Ma J, Zhang X, Wu L, Qu B,
Xia S, Chen S, Tang Y and Shen N: Association of large intergenic
noncoding RNA expression with disease activity and organ damage in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:1312015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang F, Wu L, Qian J, Qu B, Xia S, La T,
Wu Y, Ma J, Zeng J, Guo Q, et al: Identification of the long
noncoding RNA NEAT1 as a novel inflammatory regulator acting
through MAPK pathway in human lupus. J Autoimmun. 75:96–104. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Toonen EJ, Barrera P, Radstake TR, van
Riel PL, Scheffer H, Franke B and Coenen MJ: Gene expression
profiling in rheumatoid arthritis: Current concepts and future
directions. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:1663–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shaffer AL, Wright G, Yang L, Powell J,
Ngo V, Lamy L, Lam LT, Davis RE and Staudt LM: A library of gene
expression signatures to illuminate normal and pathological
lymphoid biology. Immunol Rev. 210:67–85. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamagata T, Benoist C and Mathis DA:
Shared gene-expression signature in innate-like lymphocytes.
Immunol Rev. 210:52–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Te JL, Dozmorov IM, Guthridge JM, Nguyen
KL, Cavett JW, Kelly JA, Bruner GR, Harley JB and Ojwang JO:
Identification of unique microRNA signature associated with lupus
nephritis. PLoS One. 5:e103442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu D, Zhao H, Zhao S and Wang X: MicroRNA
expression profiles of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Acta Histochem.
116:891–897. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mattick JS and Gagen MJ: The evolution of
controlled multitasked gene networks: The role of introns and other
noncoding RNAs in the development of complex organisms. Mol Biol
Evol. 18:1611–1630. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mattick JS: Lincing long noncoding RNAs
and enhancer function. Dev Cell. 19:485–486. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yougbaré I, Boire G, Roy M, Lugnier C and
Rouseau E: NCS 613 exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on PBMCs from
lupus patients by inhibiting p38 MAPK and NF-κB signalling pathways
while reducing proinflammatory cytokine production. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 91:353–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu LJ, Landolt-Marticorena C, Li T, Yang
X, Yu XQ, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Fortin PR and Wither JE: Altered
expression of TNF-alpha signaling pathway proteins in systemic
lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 37:1658–1666. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|