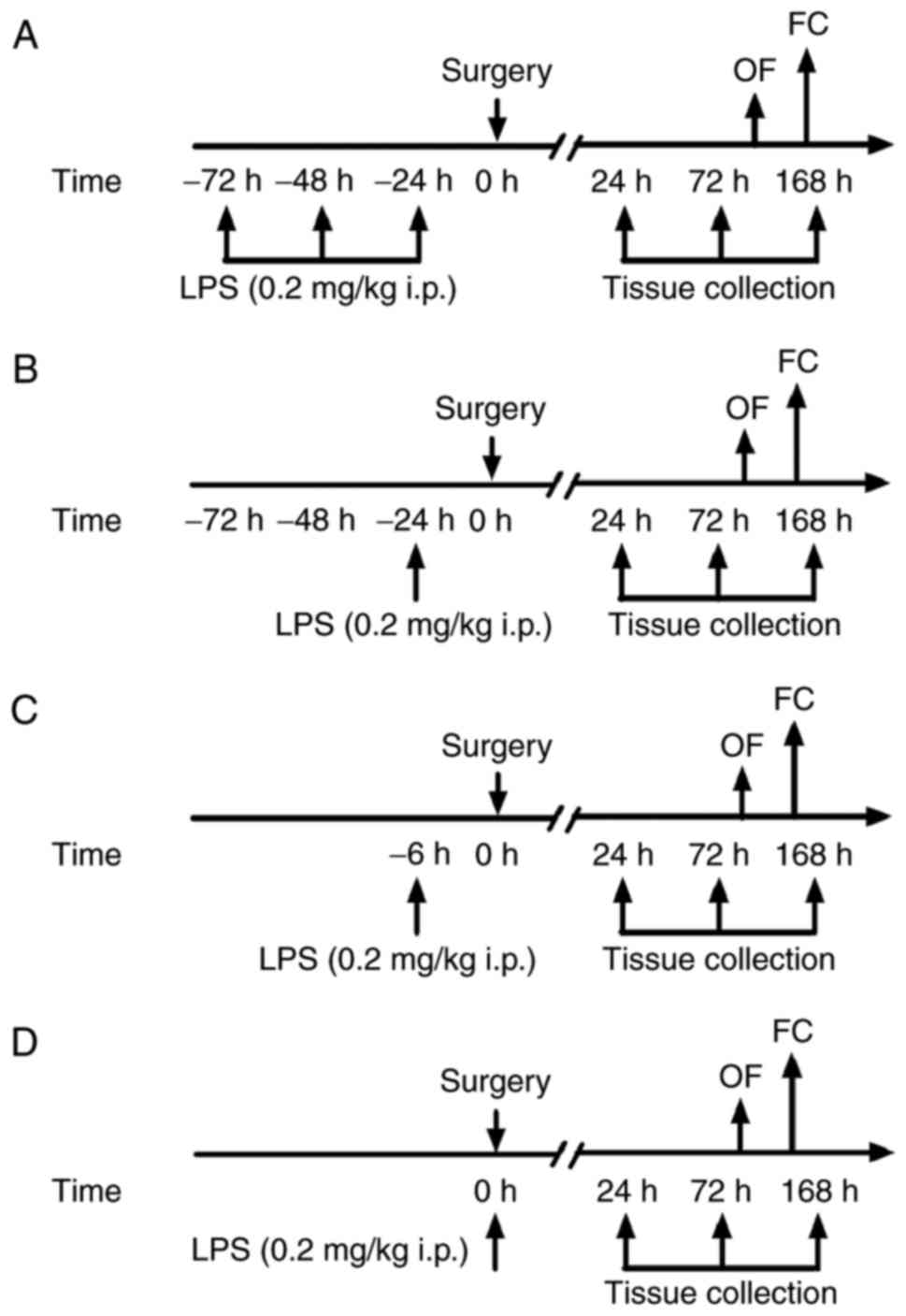
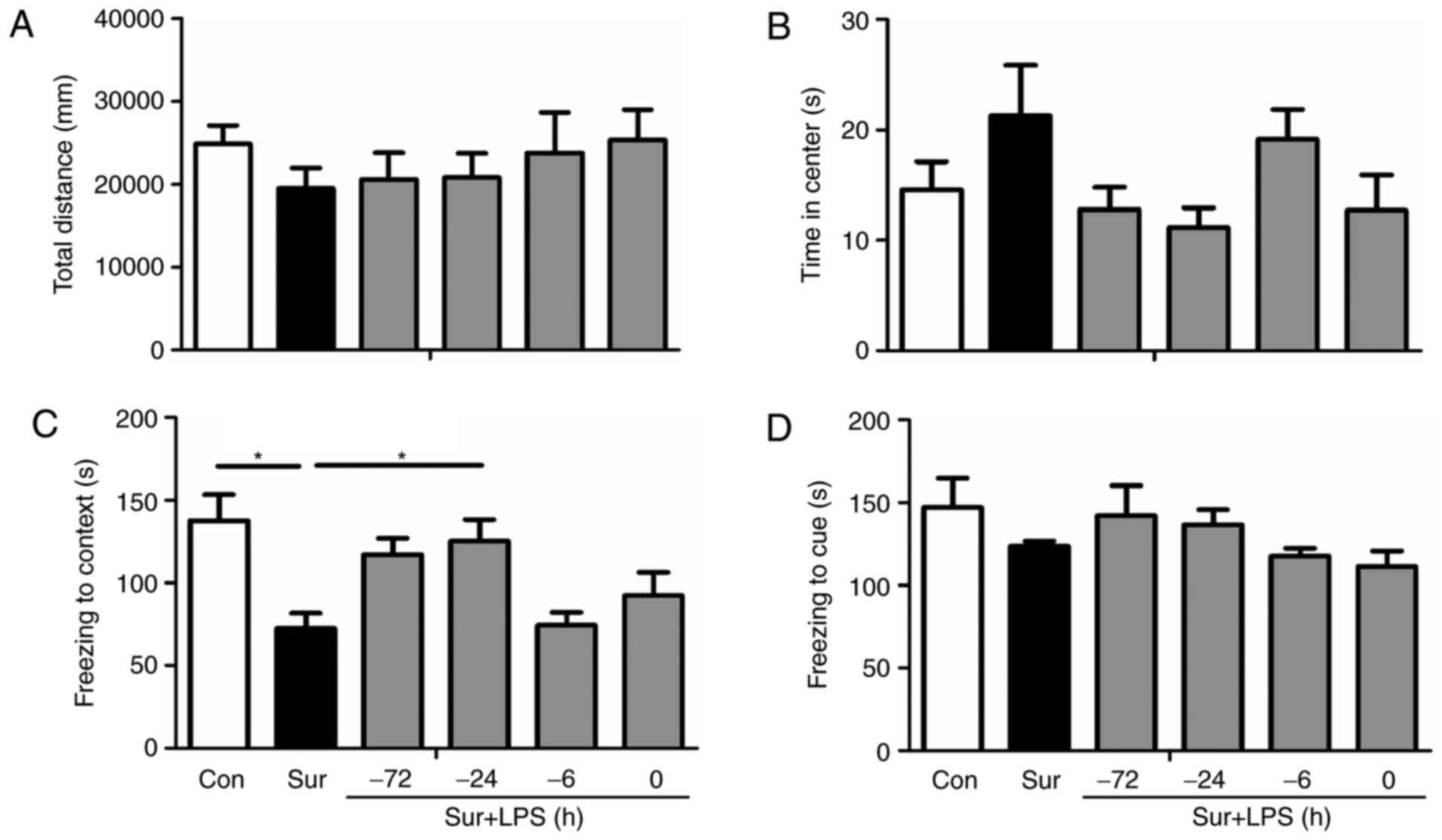
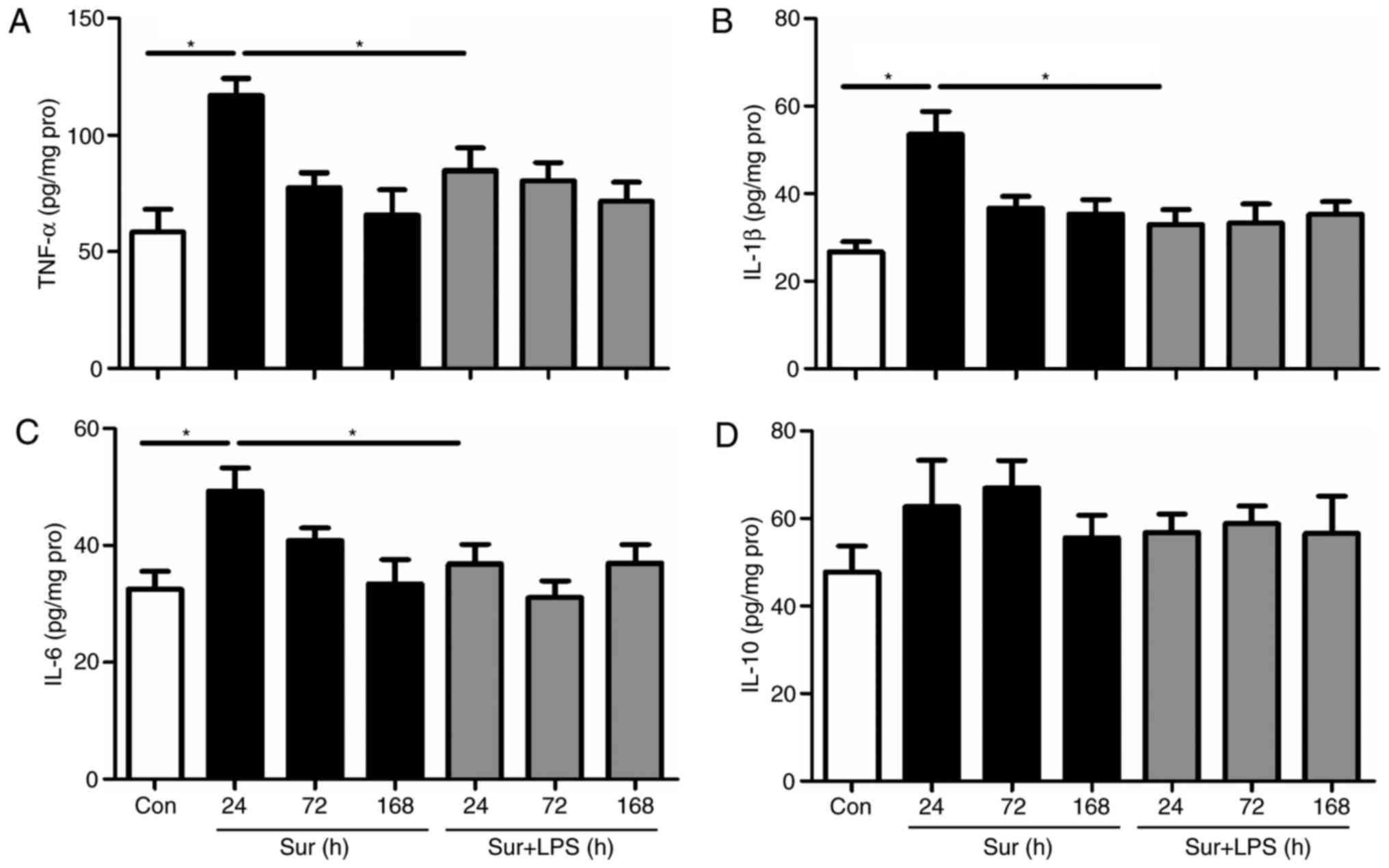
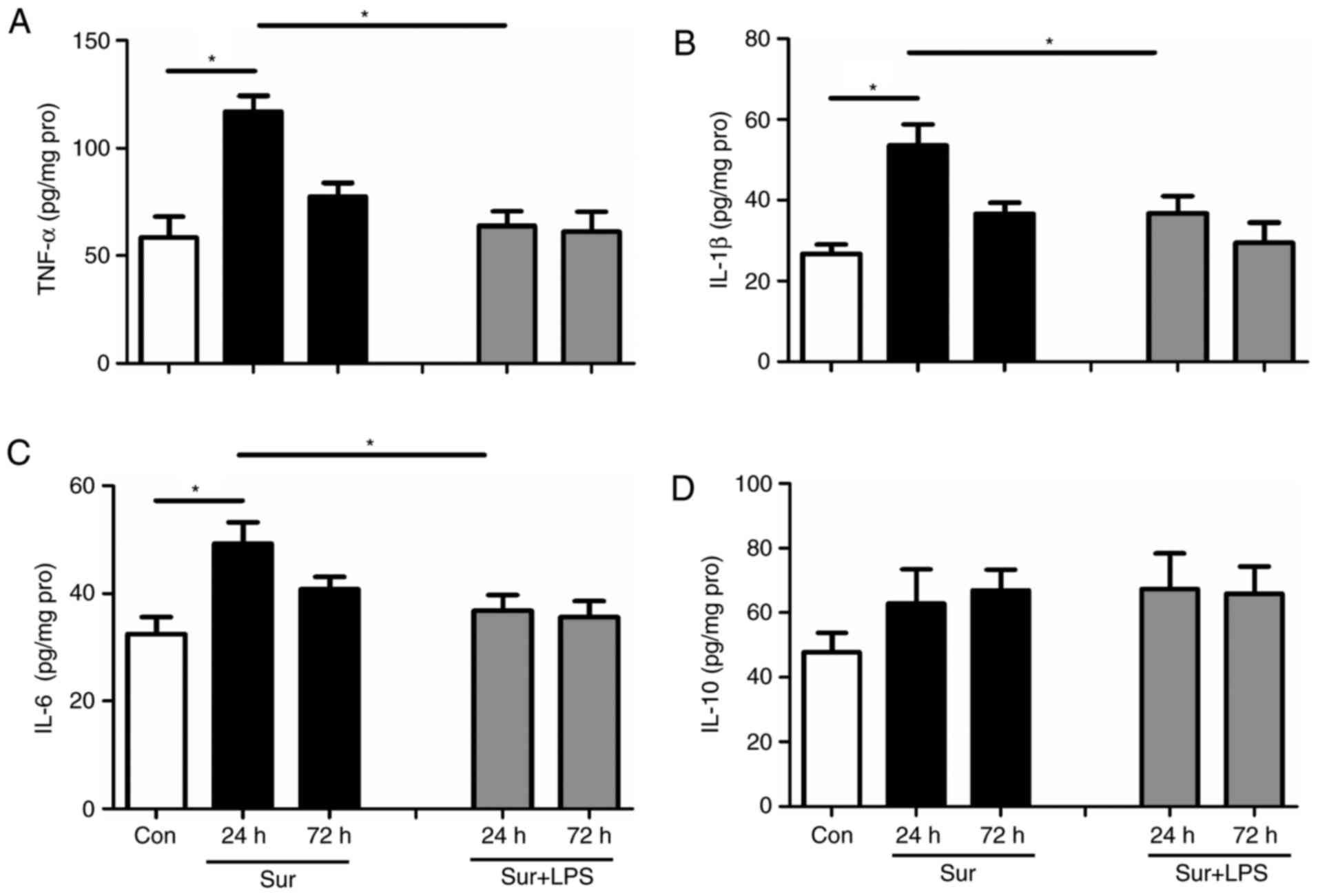
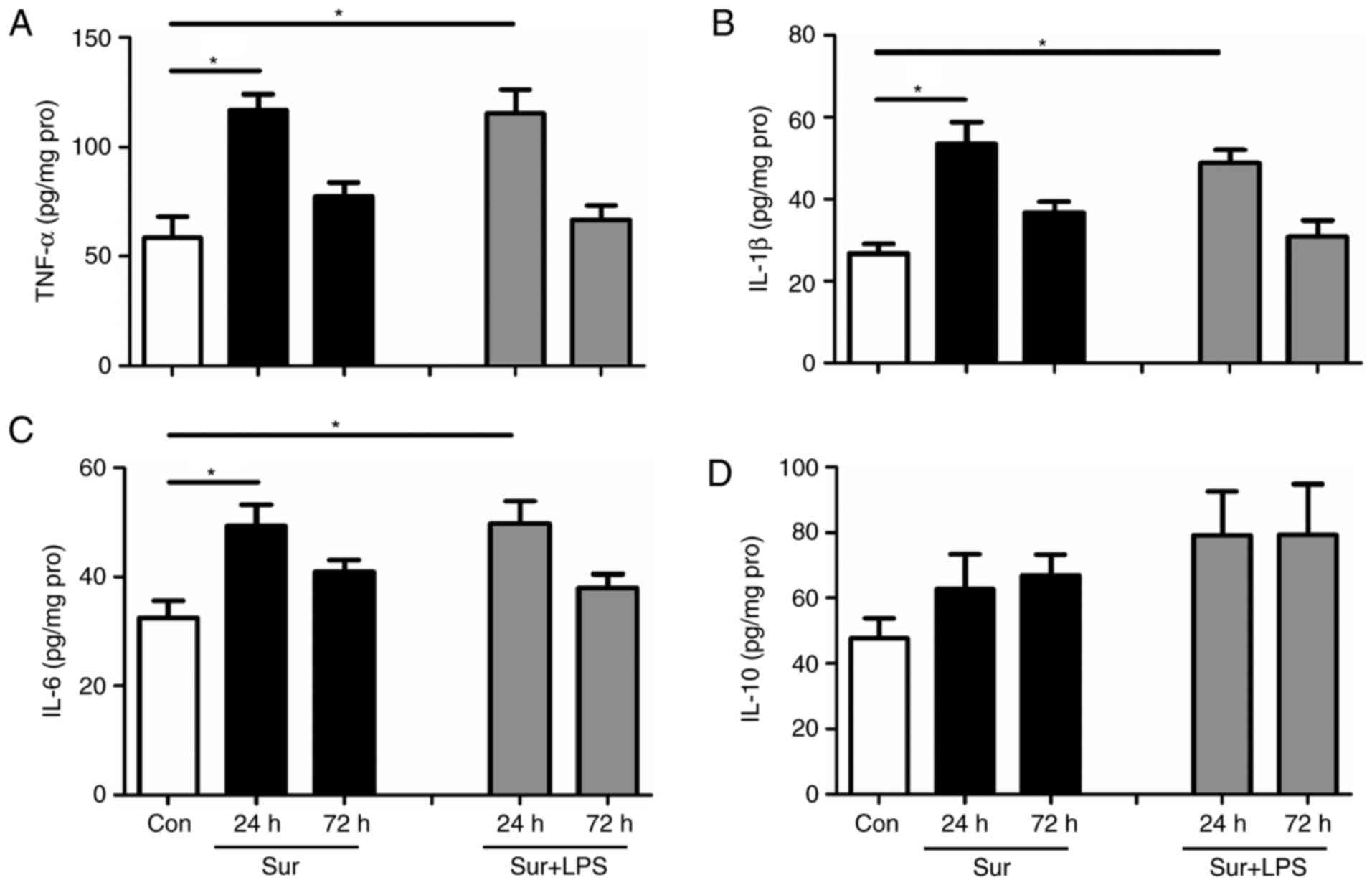
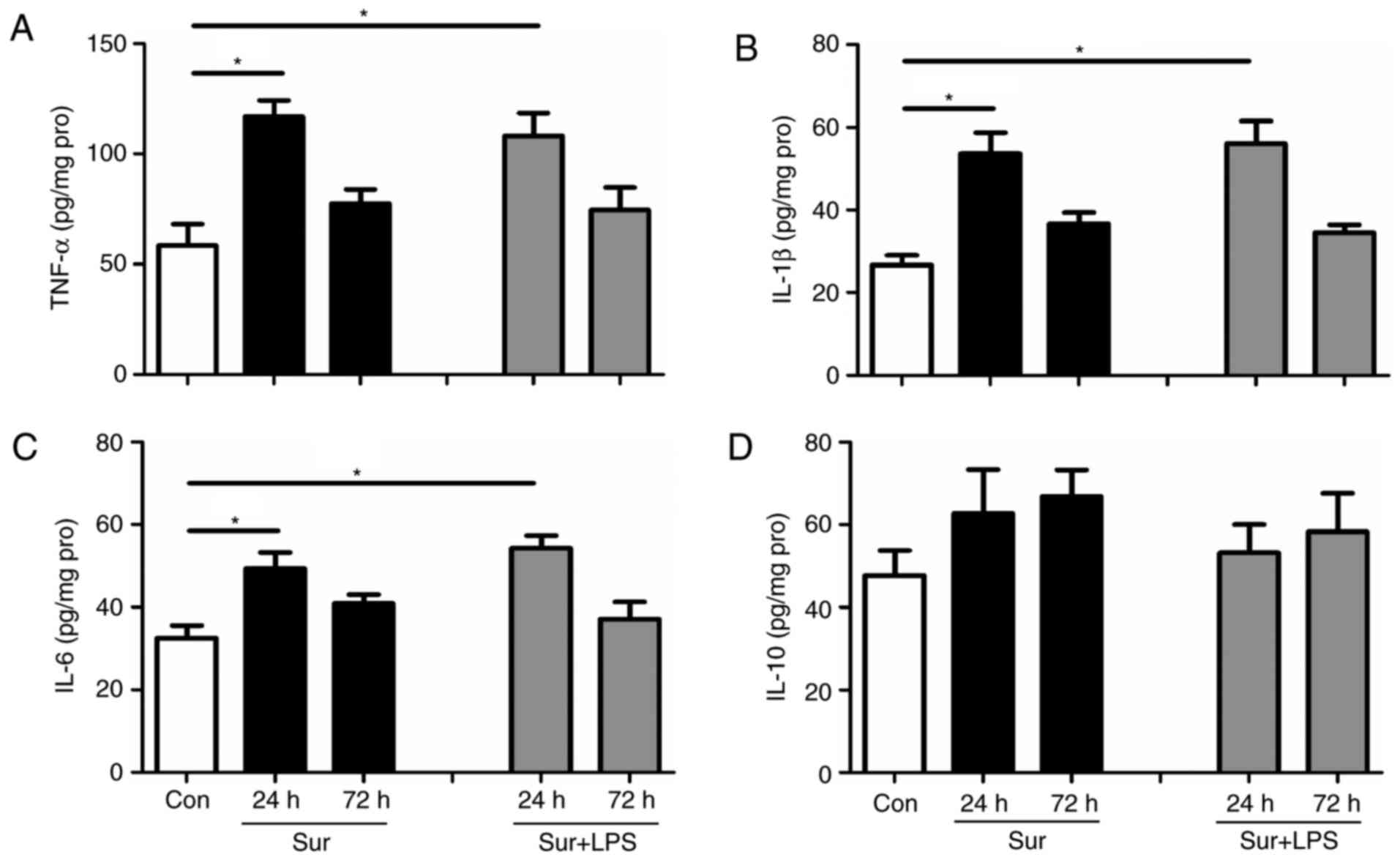
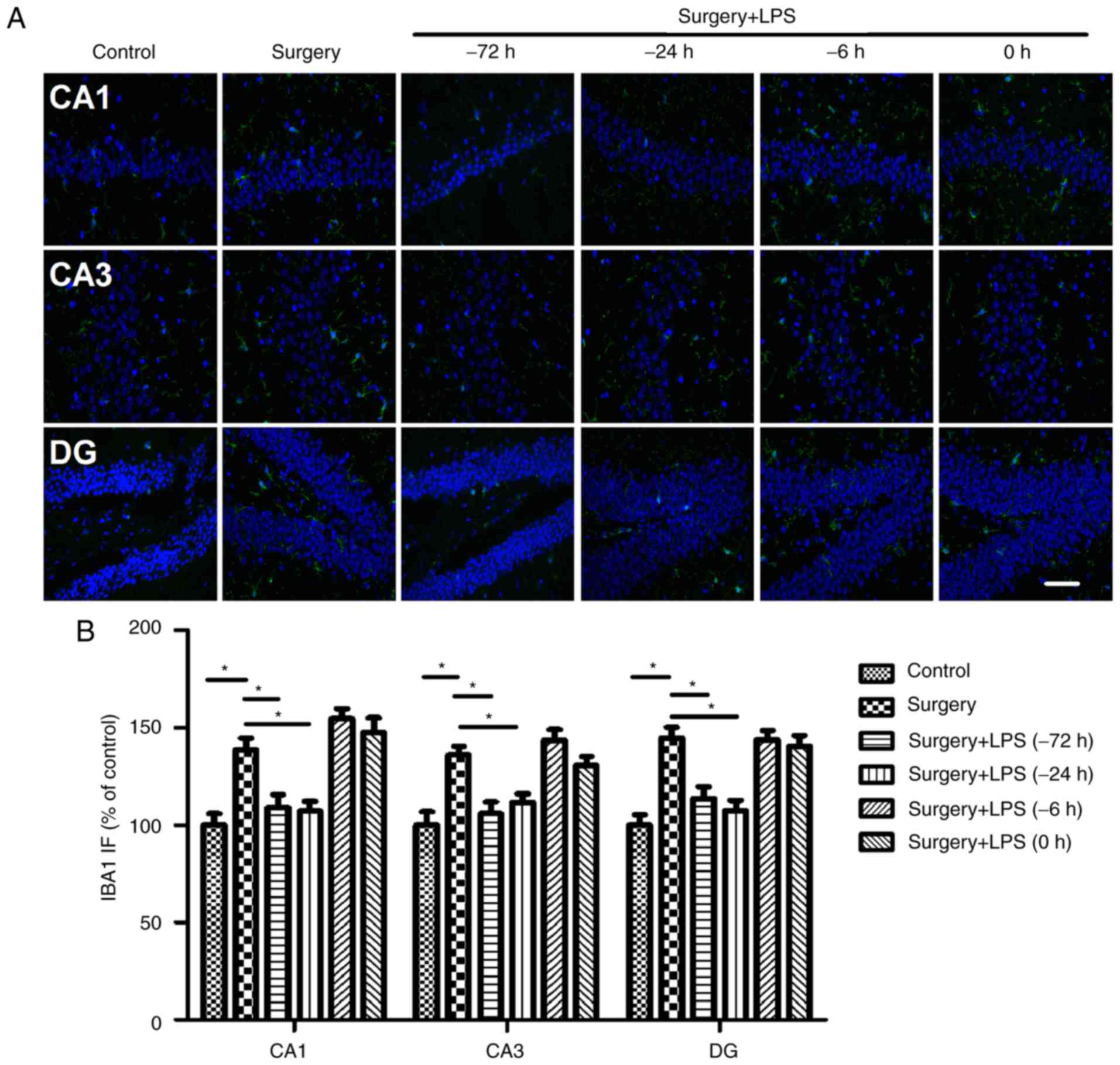
|
1
|
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse
N and Rasmussen LS; ISPOCD Group, : Long-term consequences of
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology. 110:548–555.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE,
van der Aa MT, Heilman KM and Gravenstein JS: Predictors of
cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery.
Anesthesiology. 108:18–30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx
P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, Rabbitt P, Jolles J, Larsen K, Hanning CD,
et al: Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly
ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International study of
post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Lancet. 351:857–861. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Krenk L, Rasmussen LS and Kehlet H: New
insights into the pathophysiology of postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 54:951–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qiu LL, Ji MH, Zhang H and Yang JJ, Sun
XR, Tang H, Wang J, Liu WX and Yang JJ: NADPH oxidase 2-derived
reactive oxygen species in the hippocampus might contribute to
microglial activation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction in
aged mice. Brain Behav Immun. 51:109–118. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tan H, Cao J, Zhang J and Zuo Z: Critical
role of inflammatory cytokines in impairing biochemical processes
for learning and memory after surgery in rats. J Neuroinflammation.
11:932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hovens IB, Schoemaker RG, van der Zee EA,
Absalom AR, Heineman E and van Leeuwen BL: Postoperative cognitive
dysfunction: Involvement of neuroinflammation and neuronal
functioning. Brain Behav Immun. 38:202–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Z, Liu F, Ma H, White PF, Yumul R,
Jiang Y, Wang N and Cao X: Age exacerbates surgery-induced
cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in Sprague-Dawley rats:
The role of IL-4. Brain Res. 1665:65–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li N, Zhang X, Dong H, Hu Y and Qian Y:
Bidirectional relationship of mast cells-neurovascular unit
communication in neuroinflammation and its involvement in POCD.
Behav Brain Res. 322:60–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM,
Feldmann M and Maze M: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a
cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:pp. 20518–20522. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vacas S, Degos V, Tracey KJ and Maze M:
High-mobility group box 1 protein initiates postoperative cognitive
decline by engaging bone marrow-derived macrophages.
Anesthesiology. 120:1160–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Terrando N, Yang T, Wang X, Fang J, Cao M,
Andersson U, Erlandsson HH, Ouyang W and Tong J: Systemic HMGB1
neutralization prevents postoperative neurocognitive dysfunction in
aged rats. Front Immunol. 7:4412016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Turner RC, Naser ZJ, Lucke-Wold BP,
Logsdon AF, Vangilder RL, Matsumoto RR, Huber JD and Rosen CL:
Single low-dose lipopolysaccharide preconditioning: Neuroprotective
against axonal injury and modulates glial cells. Neuroimmunol
Neuroinflamm. 4:6–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stevens SL, Leung PY, Vartanian KB,
Gopalan B, Yang T, Simon RP and Stenzel-Poore MP: Multiple
preconditioning paradigms converge on interferon regulatory
factor-dependent signaling to promote tolerance to ischemic brain
injury. J Neurosci. 31:8456–8463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Jiang D, Li Q, Yao S, Sun X, Yang Y,
Meng Z and Liu W: Lipopolysaccharide-induced preconditioning
protects against traumatic spinal cord injury by upregulating Nrf2
expression in rats. Life Sci. 162:14–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schaafsma W, Zhang X, van Zomeren KC,
Jacobs S, Georgieva PB, Wolf SA, Kettenmann H, Janova H, Saiepour
N, Hanisch UK, et al: Long-lasting pro-inflammatory suppression of
microglia by LPS-preconditioning is mediated by RelB-dependent
epigenetic silencing. Brain Behav Immun. 48:205–221. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang Z, Yuan H, Zhao H, Qi B, Li F and An
L: PPARγ activation ameliorates postoperative cognitive decline
probably through suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation in aged
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 43:53–61. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Z, Li X, Li F and An L: Berberine
alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing
neuroinflammation in aged mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 38:426–433.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barrientos RM, Hein AM, Frank MG, Watkins
LR and Maier SF: Intracisternal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist
prevents postoperative cognitive decline and neuroinflammatory
response in aged rats. J Neurosci. 32:14641–14648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dinarello CA: Anti-cytokine therapeutics
and infections. Vaccine. 21 Suppl 2:S24–S34. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Terrando N, Gómez-Galán M, Yang T,
Carlström M, Gustavsson D, Harding RE, Lindskog M and Eriksson LI:
Aspirin-triggered resolvin D1 prevents surgery-induced cognitive
decline. FASEB J. 27:3564–3571. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Murphey ED, Fang G and Sherwood ER:
Endotoxin pretreatment improves bacterial clearance and decreases
mortality in mice challenged with Staphylococcus aureus. Shock.
29:512–518. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arbibe L and Sansonetti PJ: Epigenetic
regulation of host response to LPS: Causing tolerance while
avoiding Toll errancy. Cell Host Microbe. 1:244–246. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fensterheim BA, Guo Y, Sherwood ER and
Bohannon JK: The cytokine response to lipopolysaccharide does not
predict the host response to infection. J Immunol. 198:3264–3273.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fernández-Ruiz I, Arnalich F,
Cubillos-Zapata C, Hernández-Jiménez E, Moreno-González R, Toledano
V, Fernández-Velasco M, Vallejo-Cremades MT, Esteban-Burgos L, de
Diego RP, et al: Mitochondrial DAMPs induce endotoxin tolerance in
human monocytes: An observation in patients with myocardial
infarction. PLoS One. 9:e950732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai Y, Jia P, Fang Y, Liu H, Jiao X, He JC
and Ding X: miR-146a is essential for lipopolysaccharide
(LPS)-induced cross-tolerance against kidney ischemia/reperfusion
injury in mice. Sci Rep. 6:270912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vartanian KB, Stevens SL, Marsh BJ,
Williams-Karnesky R, Lessov NS and Stenzel-Poore MP: LPS
preconditioning redirects TLR signaling following stroke: TRIF-IRF3
plays a seminal role in mediating tolerance to ischemic injury. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Eklind S, Mallard C, Arvidsson P and
Hagberg H: Lipopolysaccharide induces both a primary and a
secondary phase of sensitization in the developing rat brain.
Pediatr Res. 58:112–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Markus T, Cronberg T, Cilio C, Pronk C,
Wieloch T and Ley D: Tumor necrosis factor receptor-1 is essential
for LPS-induced sensitization and tolerance to oxygen-glucose
deprivation in murine neonatal organotypic hippocampal slices. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:73–86. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seeley JJ and Ghosh S: Molecular
mechanisms of innate memory and tolerance to LPS. J LeukocBiol.
101:107–119. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kohman RA, Crowell B and Kusnecov AW:
Differential sensitivity to endotoxin exposure in young and
middle-age mice. Brain Behav Immun. 24:486–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|