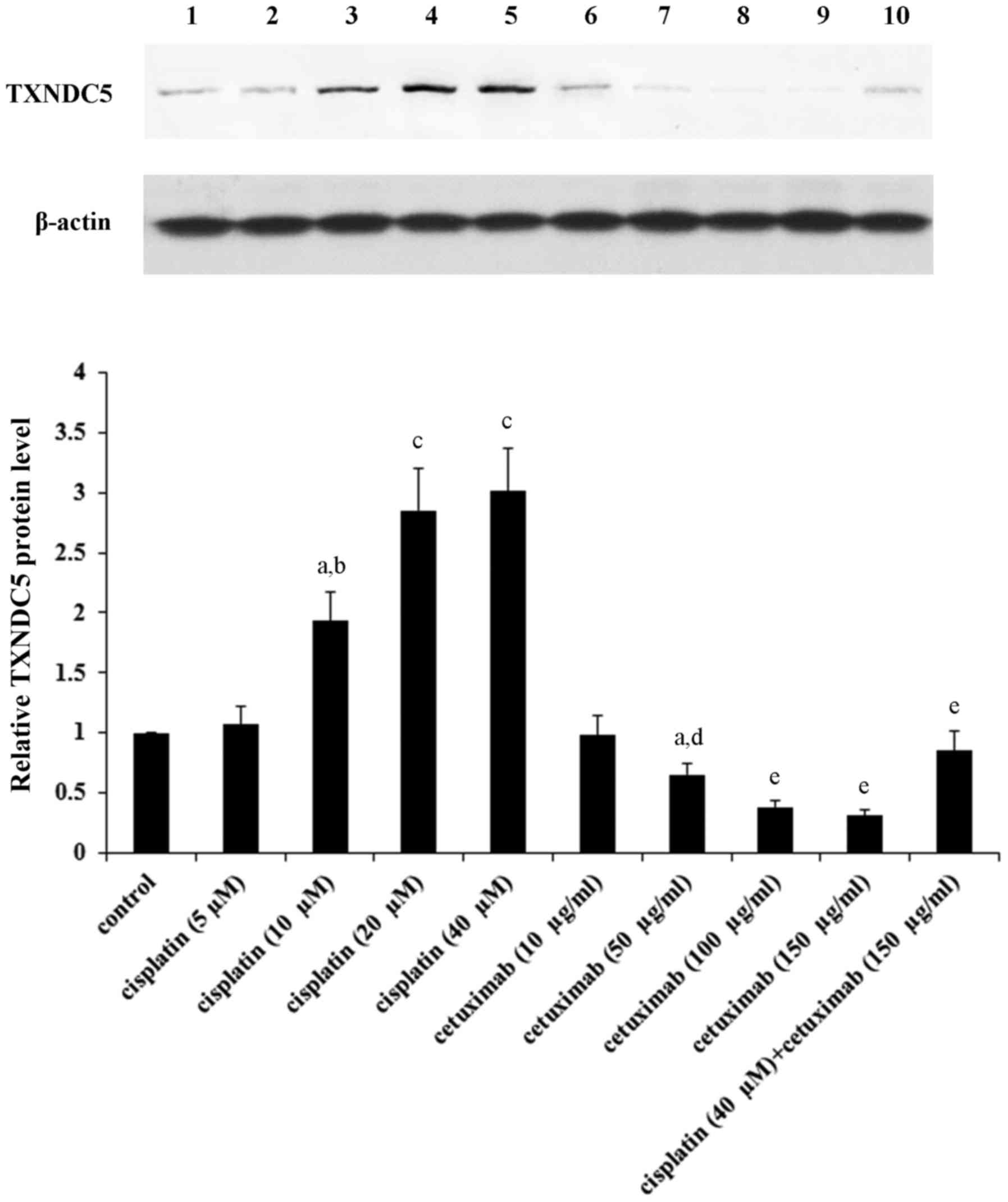
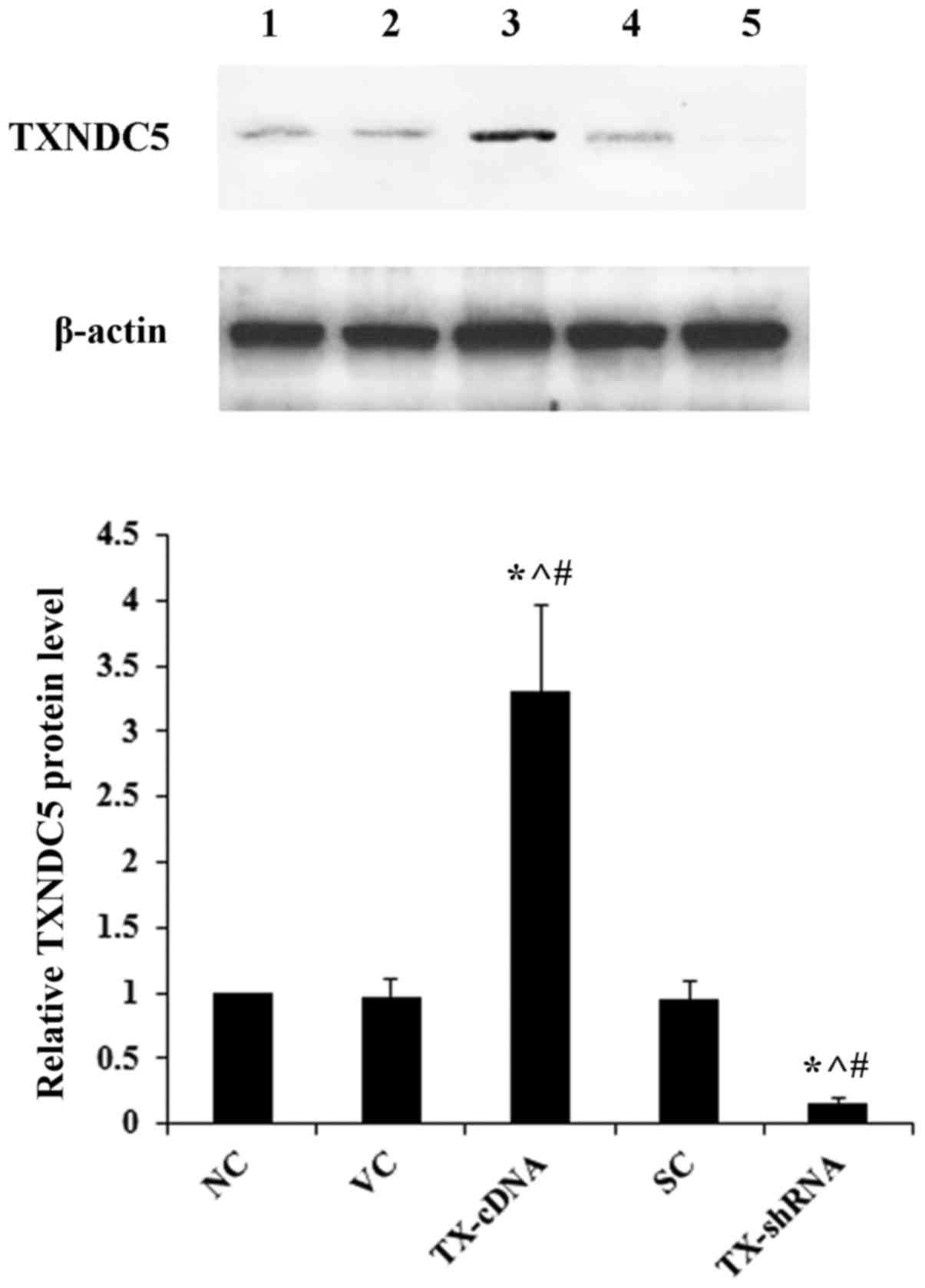
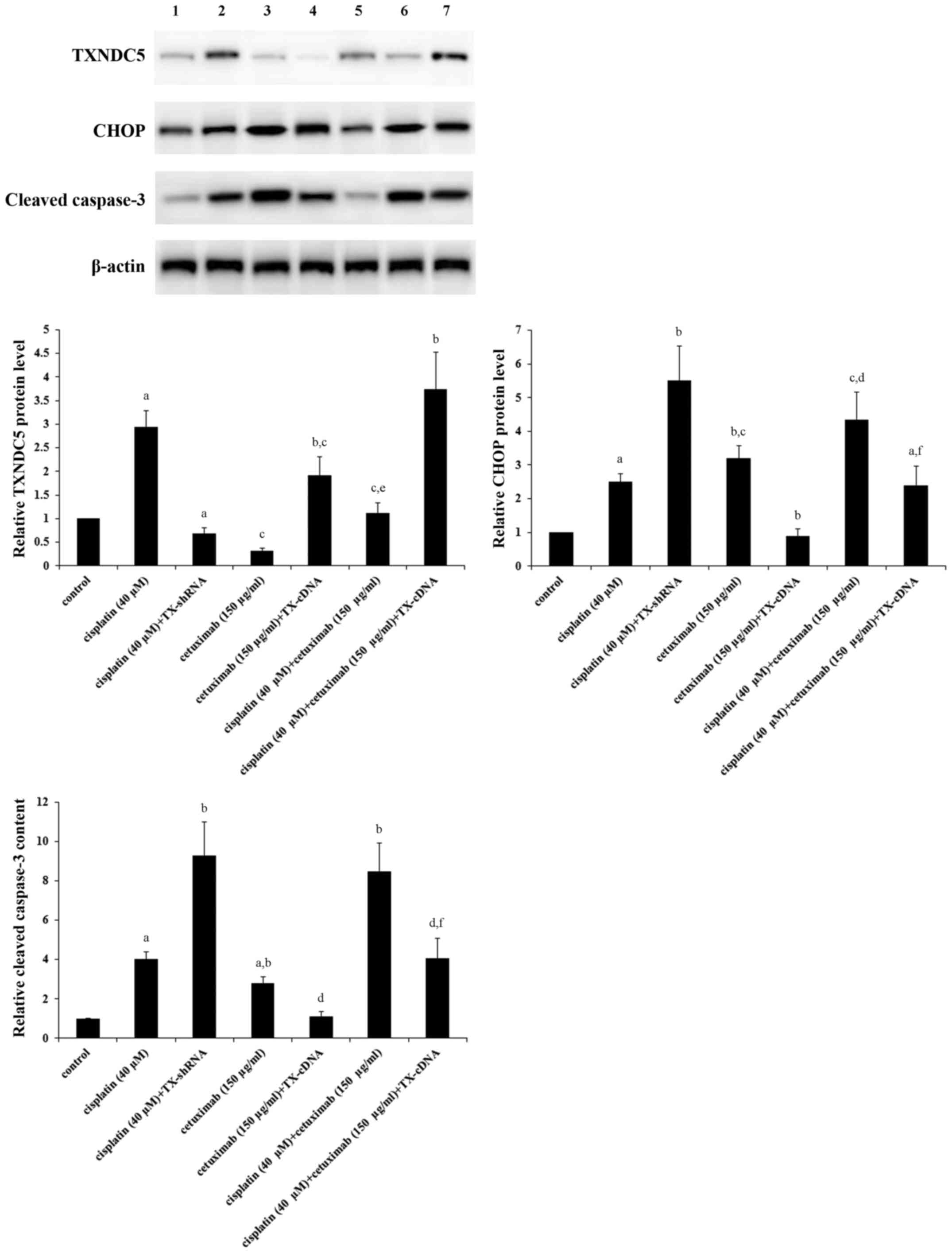
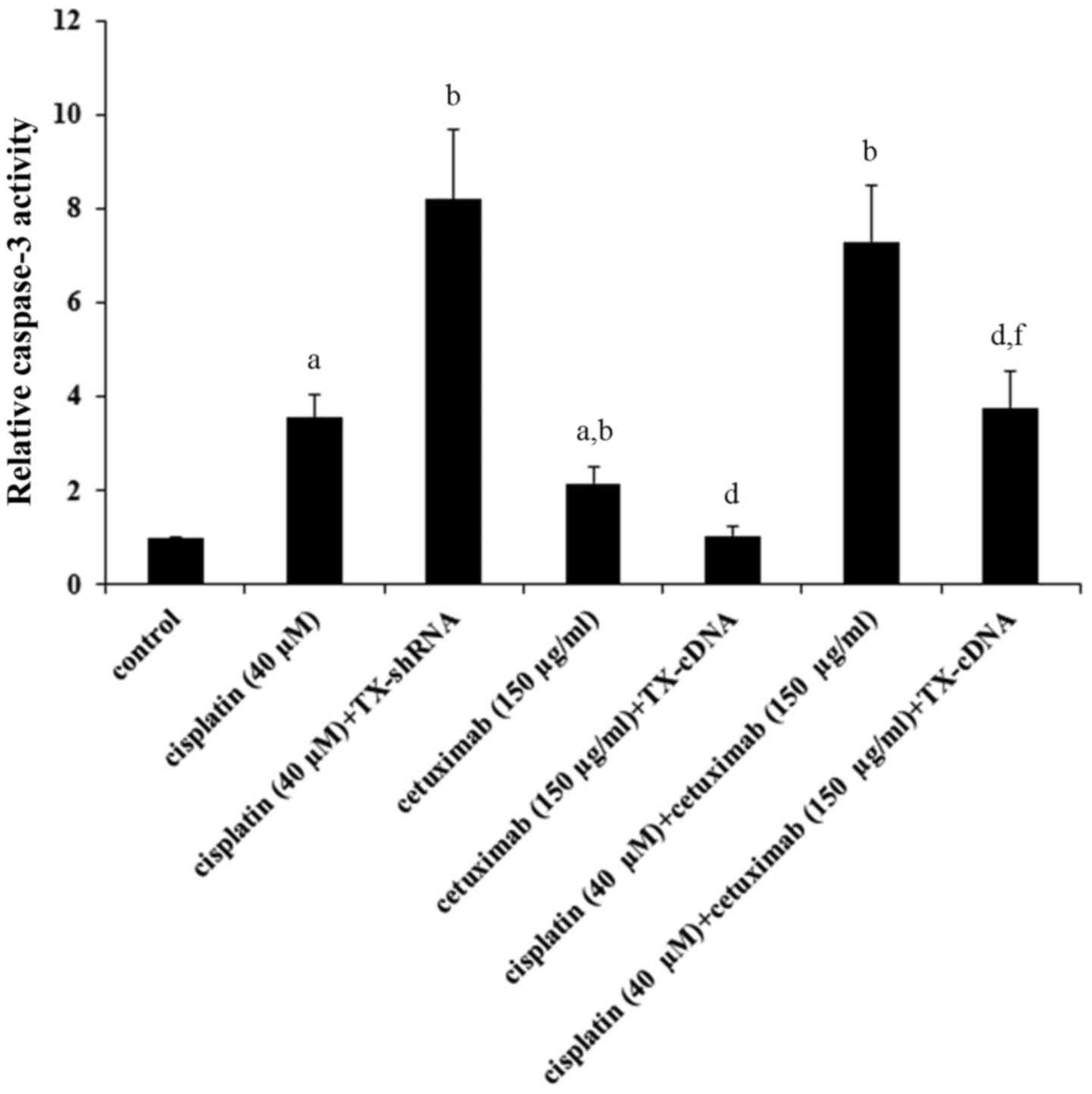
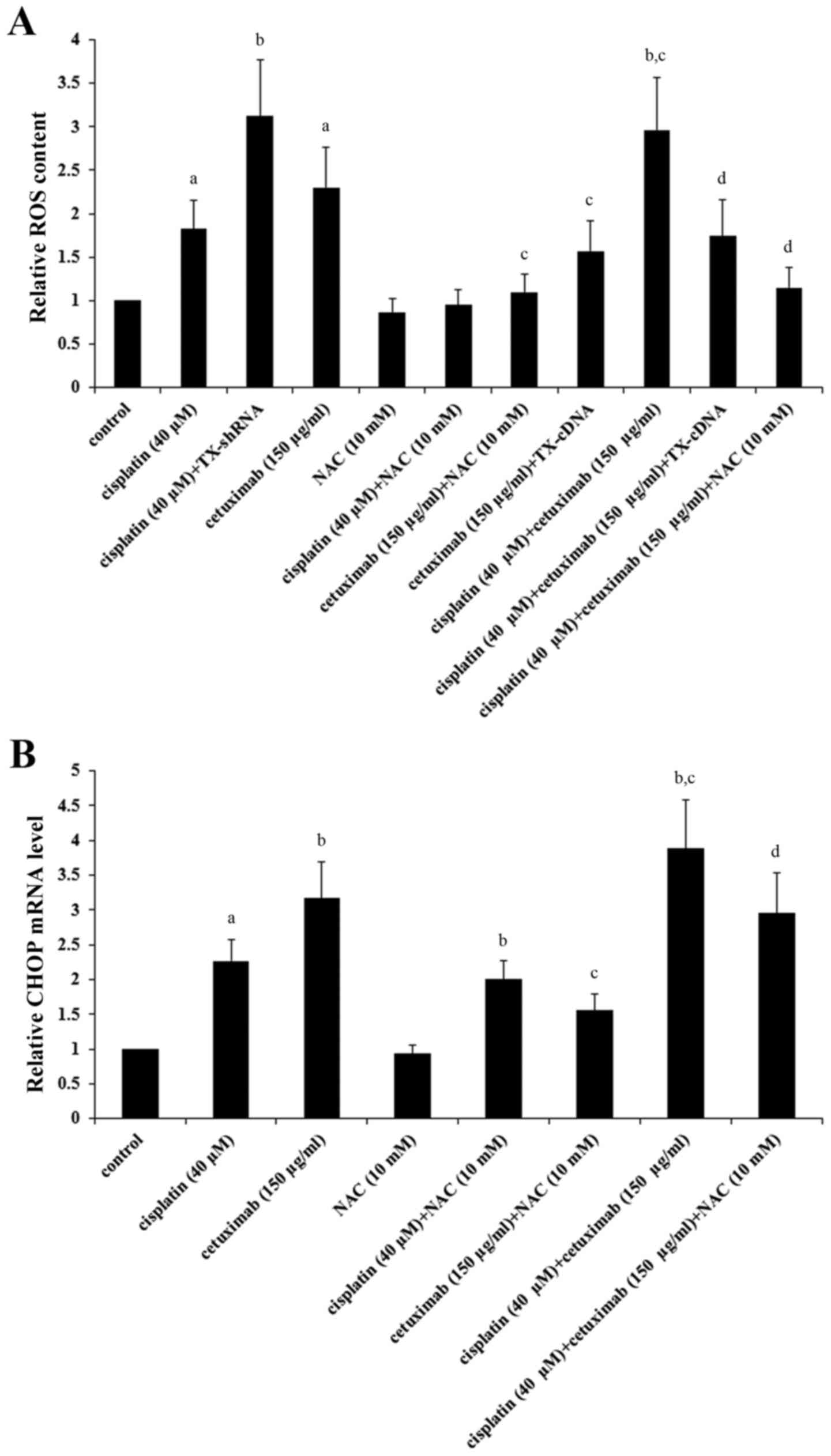
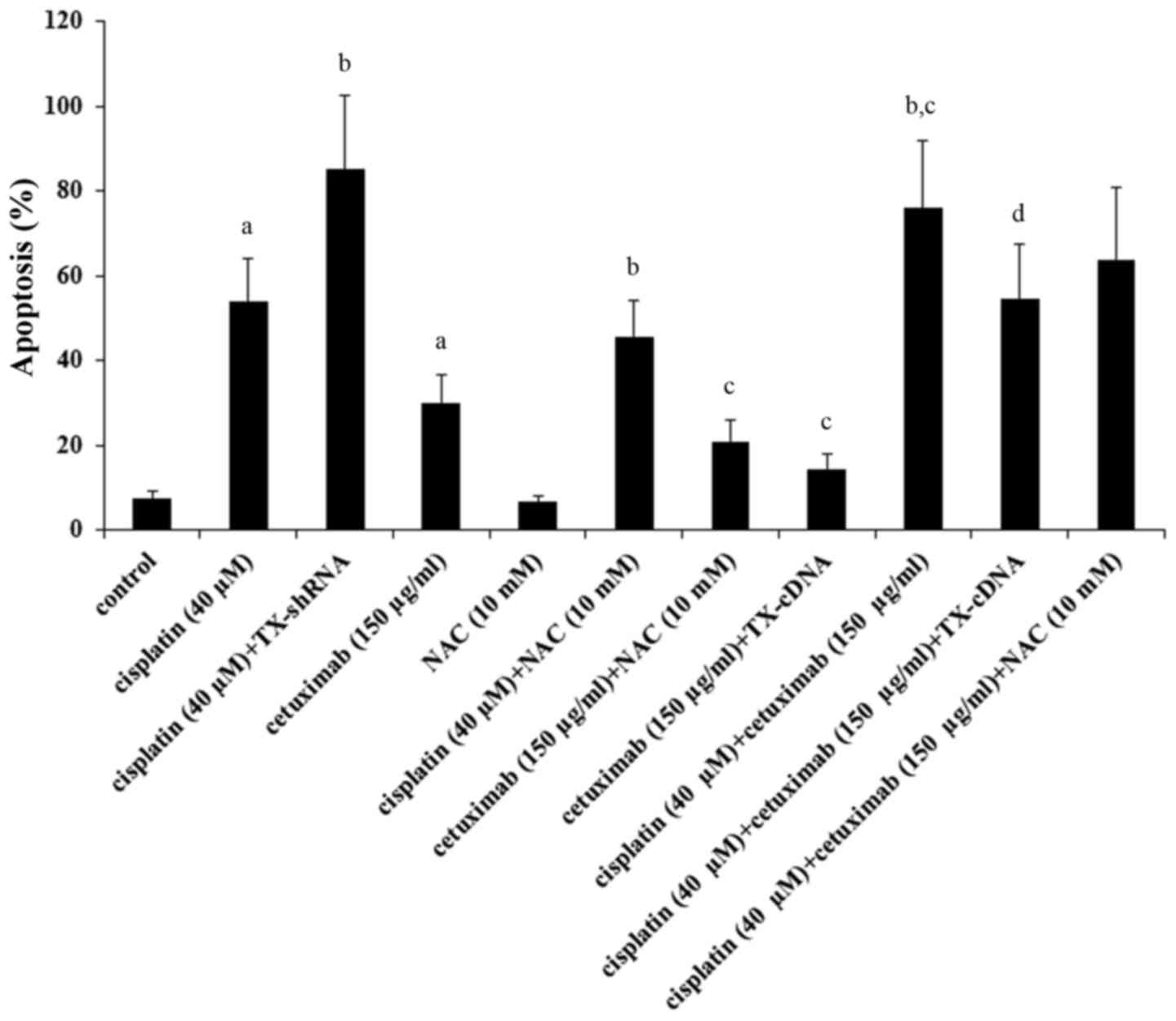
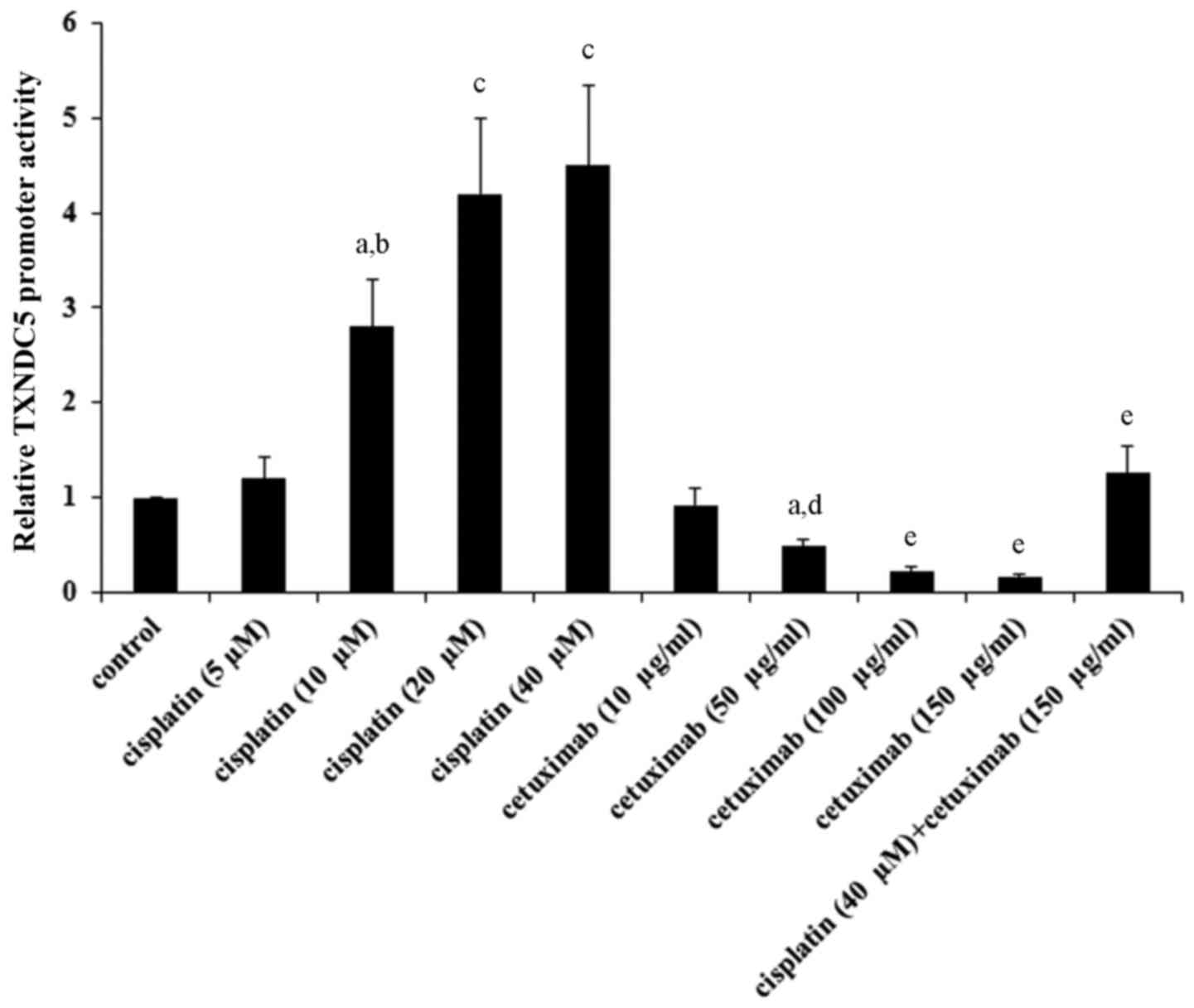
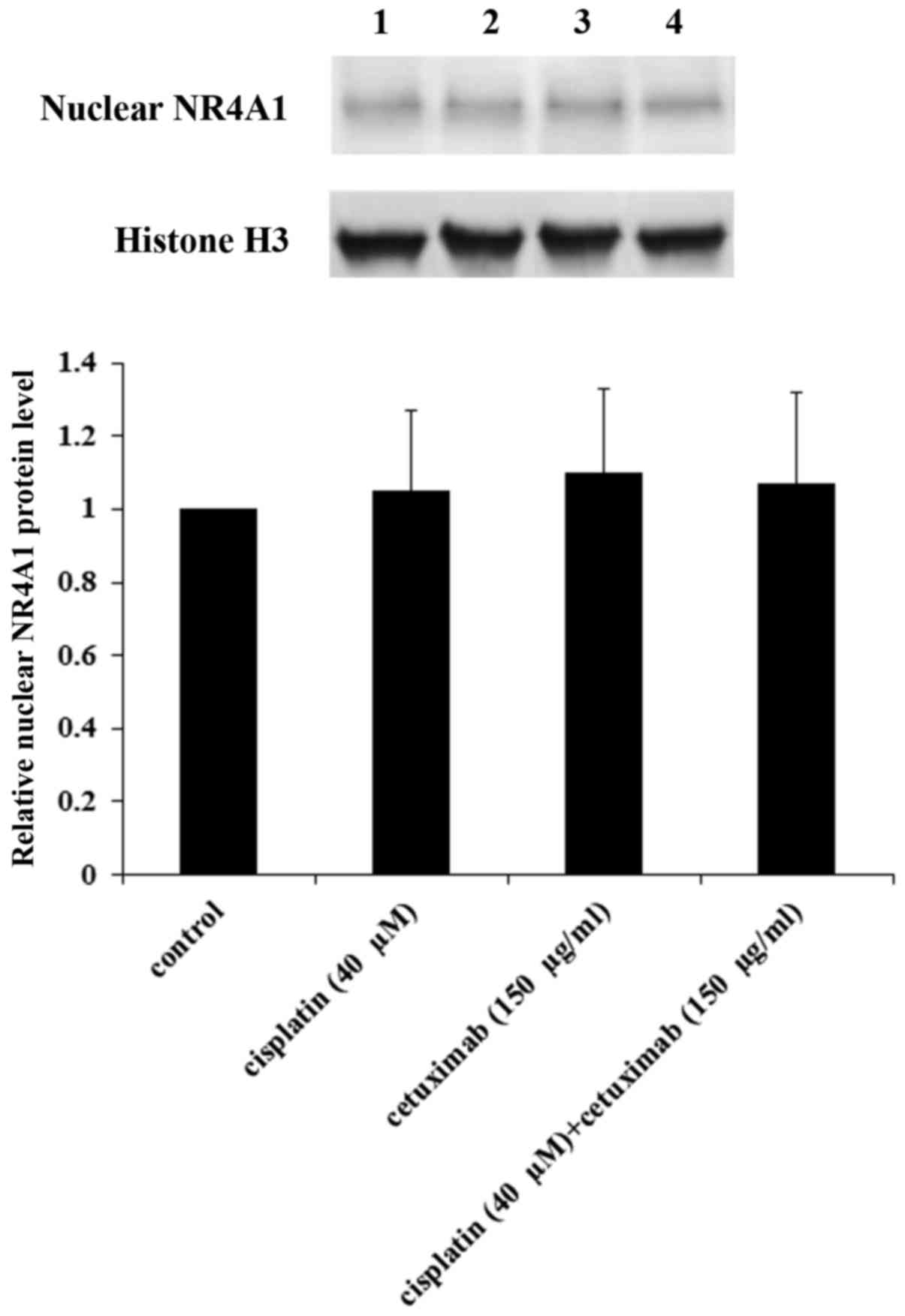
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mnejja M, Hammami B, Bougacha L, Chakroun
A, Charfeddine I, Khabir A, Boudaoura T and Ghorbel A: Occult lymph
node metastasis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Therapeutic
and prognostic impact. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis.
127:173–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Amar A, Chedid HM, Franzi SA and Rapoport
A: Diagnostic and therapeutic delay in patients with larynx cancer
at a reference public hospital. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol.
76:700–703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hitt R, López-Pousa A, Martinez-Trufero J,
Escrig V, Carles J, Rizo A, Isla D, Vega ME, Marti JL, Lobo F, et
al: Phase III study comparing cisplatin plus fluorouracil to
paclitaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil induction chemotherapy
followed by chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced head and neck
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:8636–8645. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bussu F, Pozzoli G, Giglia V, Rizzo D,
Limongelli A, De Corso E, Graziani C, Paludetti G, Navarra P and
Almadori G: Effects of the administration of epidermal growth
factor receptor specific inhibitor cetuximab, alone and in
combination with cisplatin, on proliferation and apoptosis of Hep-2
laryngeal cancer cells. J Laryngol Otol. 128:902–908. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Burtness B, Goldwasser MA, Flood W, Mattar
B and Forastiere AA; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, : Phase
III randomized trial of cisplatin plus placebo compared with
cisplatin plus cetuximab in metastatic/recurrent head and neck
cancer: An Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol.
23:8646–8654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lv X, Song DM, Niu YH and Wang BS:
Inhibition of heme oxygenase-1 enhances the chemosensitivity of
laryngeal squamous cell cancer Hep-2 cells to cisplatin. Apoptosis.
21:489–501. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Macciò A and Madeddu C: Cisplatin: An old
drug with a newfound efficacy - from mechanisms of action to
cytotoxicity. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 14:1839–1857. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sancho-Martínez SM, Prieto-García L,
Prieto M, López-Novoa JM and López-Hernández FJ: Subcellular
targets of cisplatin cytotoxicity: An integrated view. Pharmacol
Ther. 136:35–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu F, Megyesi J and Price PM: Cytoplasmic
initiation of cisplatin cytotoxicity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
295:F44–F52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peyrou M, Hanna PE and Cribb AE:
Cisplatin, gentamicin, and p-aminophenol induce markers of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in the rat kidneys. Toxicol Sci.
99:346–353. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mandic A, Hansson J, Linder S and Shoshan
MC: Cisplatin induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and
nucleus-independent apoptotic signaling. J Biol Chem.
278:9100–9106. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu H and Baliga R: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated caspase 12 mediates cisplatin-induced LLC-PK1
cell apoptosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1985–1992. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Y, Wang C and Li Z: A new strategy of
promoting cisplatin chemotherapeutic efficiency by targeting
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol Clin Oncol. 2:3–7. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miao Y, Bi XY, Zhao M, Jiang HK, Liu JJ,
Li DL, Yu XJ, Yang YH, Huang N and Zang WJ: Acetylcholine inhibits
tumor necrosis factor α activated endoplasmic reticulum apoptotic
pathway via EGFR-PI3K signaling in cardiomyocytes. J Cell Physiol.
230:767–774. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hong S, Gu Y, Gao Z, Guo L, Guo W, Wu X,
Shen Y, Sun Y, Wu X and Xu Q: EGFR inhibitor-driven endoplasmic
reticulum stress-mediated injury on intestinal epithelial cells.
Life Sci. 119:28–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Walter P and Ron D: The unfolded protein
response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science.
334:1081–1086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Berridge MJ: The endoplasmic reticulum: A
multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium. 32:235–249.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jørgensen MM, Bross P and Gregersen N:
Protein quality control in the endoplasmic reticulum. APMIS Suppl.
1–91. 2003.
|
|
20
|
Xu Y, Li D, Zeng L, Wang C, Zhang L, Wang
Y, Yu Y, Liu S and Li Z: Proteasome inhibitor lactacystin enhances
cisplatin cytotoxicity by increasing endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated apoptosis in HeLa cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:189–195.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang R, Wang R, Chen Q and Chang H:
Inhibition of autophagy using 3-methyladenine increases
cisplatin-induced apoptosis by increasing endoplasmic reticulum
stress in U251 human glioma cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1727–1732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nishitoh H: CHOP is a multifunctional
transcription factor in the ER stress response. J Biochem.
151:217–219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Horna-Terrón E, Pradilla-Dieste A,
Sánchez-de-Diego C and Osada J: TXNDC5, a newly discovered
disulfide isomerase with a key role in cell physiology and
pathology. Int J Mol Sci. 15:23501–23518. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sullivan DC, Huminiecki L, Moore JW, Boyle
JJ, Poulsom R, Creamer D, Barker J and Bicknell R: EndoPDI, a novel
protein-disulfide isomerase-like protein that is preferentially
expressed in endothelial cells acts as a stress survival factor. J
Biol Chem. 278:47079–47088. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Funkner A, Parthier C, Schutkowski M,
Zerweck J, Lilie H, Gyrych N, Fischer G, Stubbs MT and Ferrari DM:
Peptide binding by catalytic domains of the protein disulfide
isomerase-related protein ERp46. J Mol Biol. 425:1340–1362. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kojima R, Okumura M, Masui S, Kanemura S,
Inoue M, Saiki M, Yamaguchi H, Hikima T, Suzuki M, Akiyama S and
Inaba K: Radically different thioredoxin domain arrangement of
ERp46, an efficient disulfide bond introducer of the mammalian PDI
family. Structure. 22:431–443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Johnson DR, Levanat S and Bale AE: Direct
molecular analysis of archival tumor tissue for loss of
heterozygosity. Biotechniques. 19:190–192. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Woo M, Hakem R, Soengas MS, Duncan GS,
Shahinian A, Kägi D, Hakem A, McCurrach M, Khoo W, Kaufman SA, et
al: Essential contribution of caspase 3/CPP32 to apoptosis and its
associated nuclear changes. Genes Dev. 12:806–819. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee SO, Jin UH, Kang JH, Kim SB, Guthrie
AS, Sreevalsan S, Lee JS and Safe S: The orphan nuclear receptor
NR4A1 (Nur77) regulates oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress
in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 12:527–538. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO, Doddapaneni R, Singh M
and Safe S: Nuclear receptor 4A1 as a drug target for breast cancer
chemotherapy. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:831–840. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hedrick E, Lee SO, Kim G, Abdelrahim M,
Jin UH, Safe S and Abudayyeh A: Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) as a
drug target for renal cell adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
10:e01283082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yao LM, He JP, Chen HZ, Wang Y, Wang WJ,
Wu R, Yu CD and Wu Q: Orphan receptor TR3 participates in
cisplatin-induced apoptosis via Chk2 phosphorylation to repress
intestinal tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis. 33:301–311. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin H, Lin Q, Liu M, Lin Y, Wang X, Chen
H, Xia Z, Lu B, Ding F, Wu Q and Wang HR: PKA/Smurf1
signaling-mediated stabilization of Nur77 is required for
anticancer drug cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Oncogene.
33:1629–1639. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
ATCC, . http://atcc.org/Products/All/CCL-23.aspx#characteristicsJuly
1–2016
|
|
36
|
Xu L, Chen Z, Xue F, Chen W, Ma R, Cheng S
and Cui P: MicroRNA-24 inhibits growth, induces apoptosis, and
reverses radioresistance in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by
targeting X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Cancer Cell Int.
15:612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mendelsohn J and Baselga J: The EGF
receptor family as targets for cancer therapy. Oncogene.
19:6550–6565. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Saglar E, Unlu S, Babalioglu I, Gokce SC
and Mergen H: Assessment of ER Stress and autophagy induced by
ionizing radiation in both radiotherapy patients and ex vivo
irradiated samples. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 28:413–417. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhu H, Abulimiti M, Liu H, Su XJ, Liu CH
and Pei HP: RITA enhances irradiation-induced apoptosis in
p53-defective cervical cancer cells via upregulation of IRE1α/XBP1
signaling. Oncol Rep. 34:1279–1288. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|