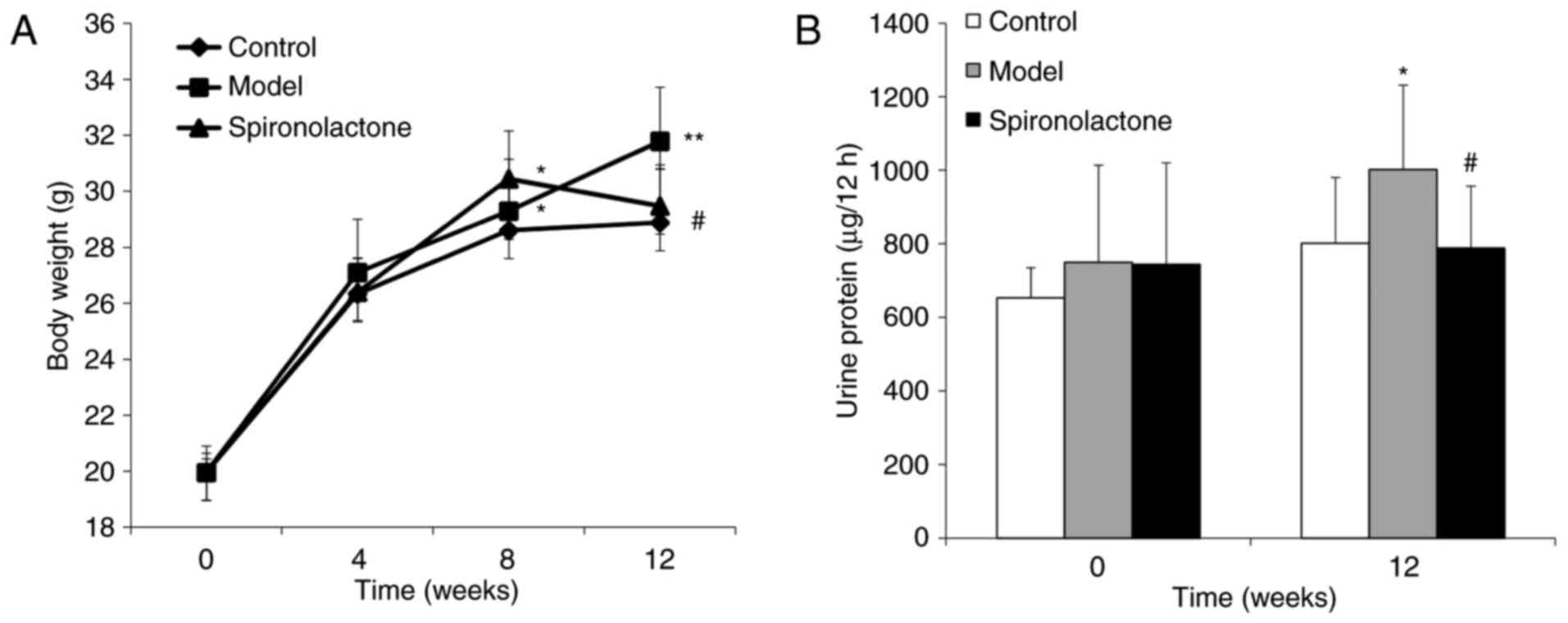
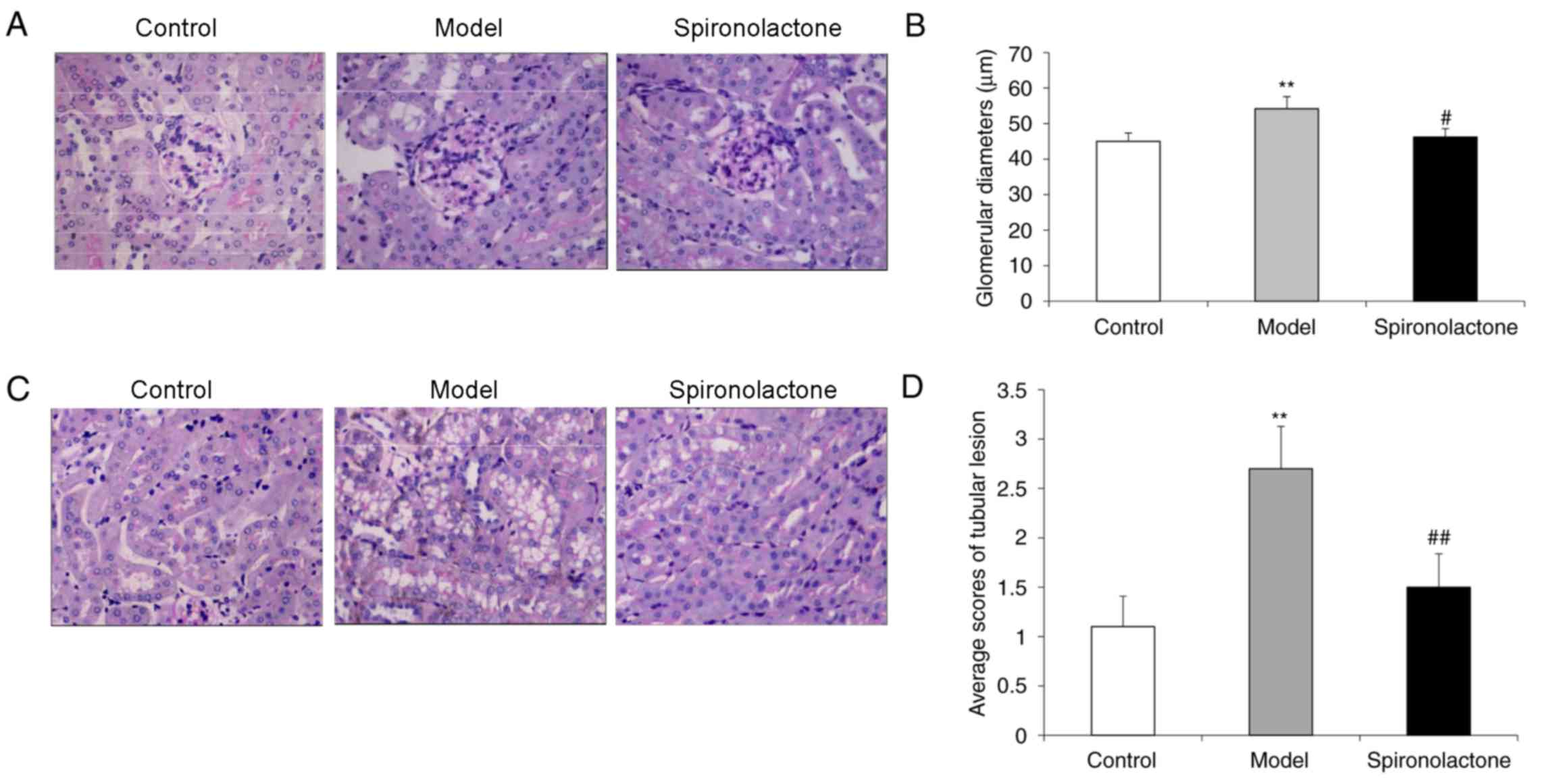
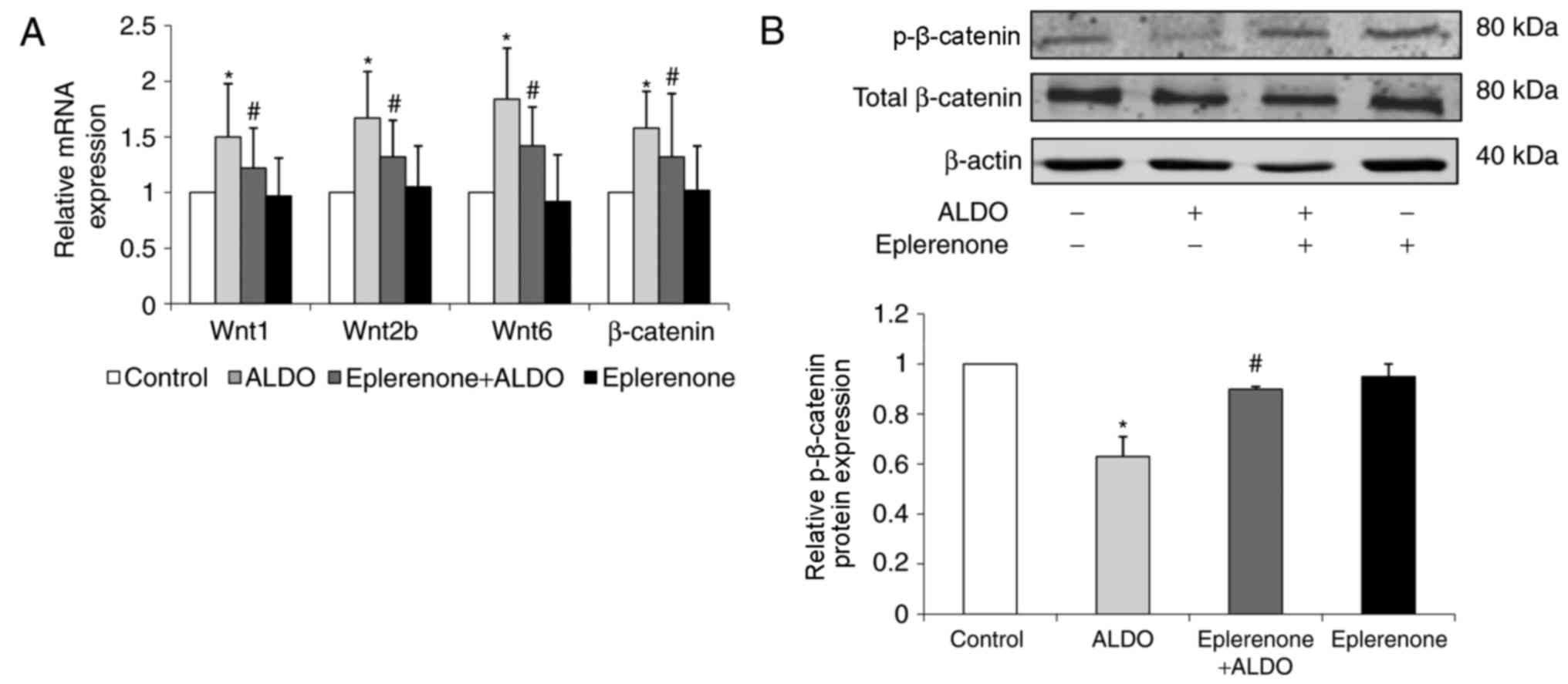
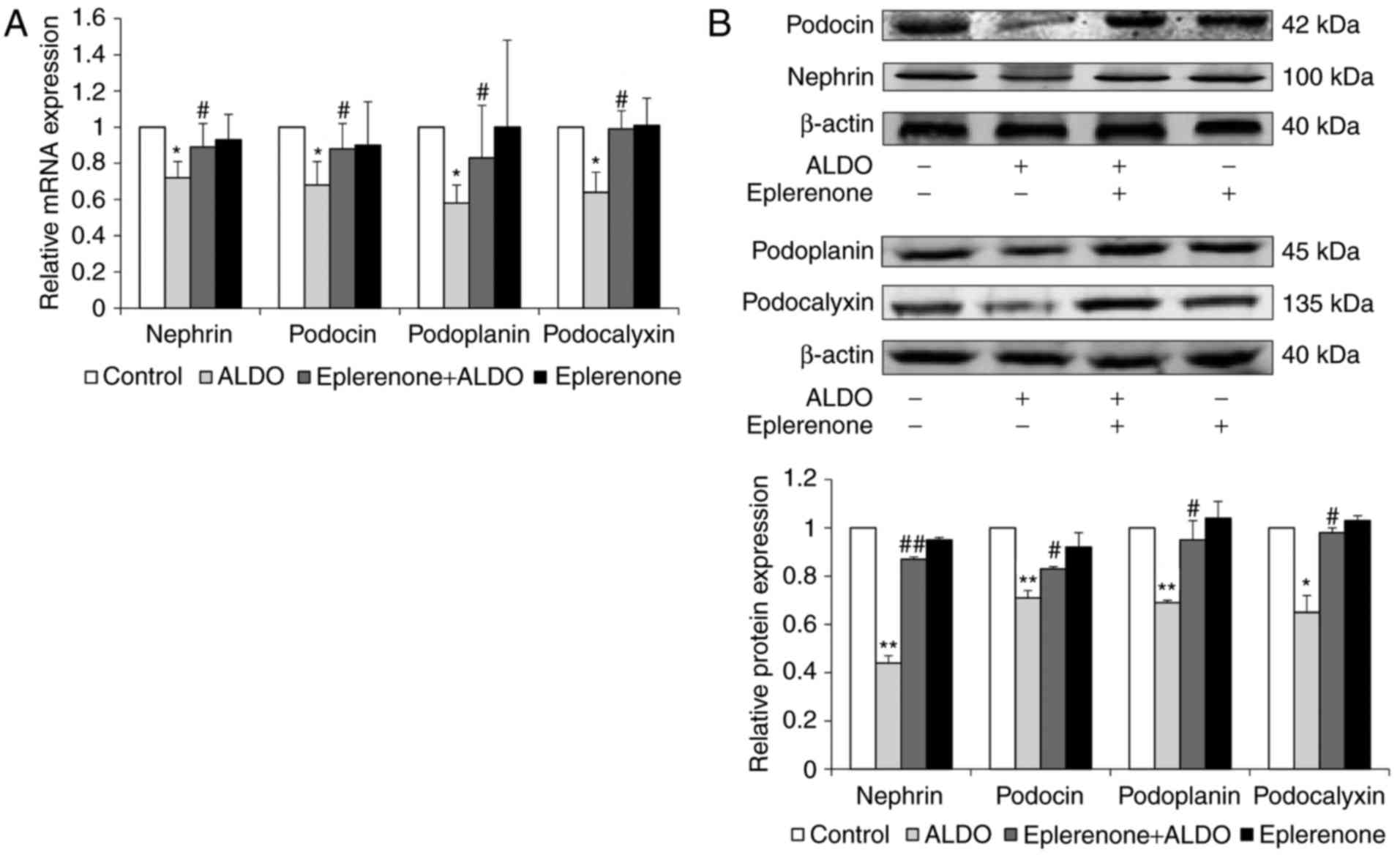
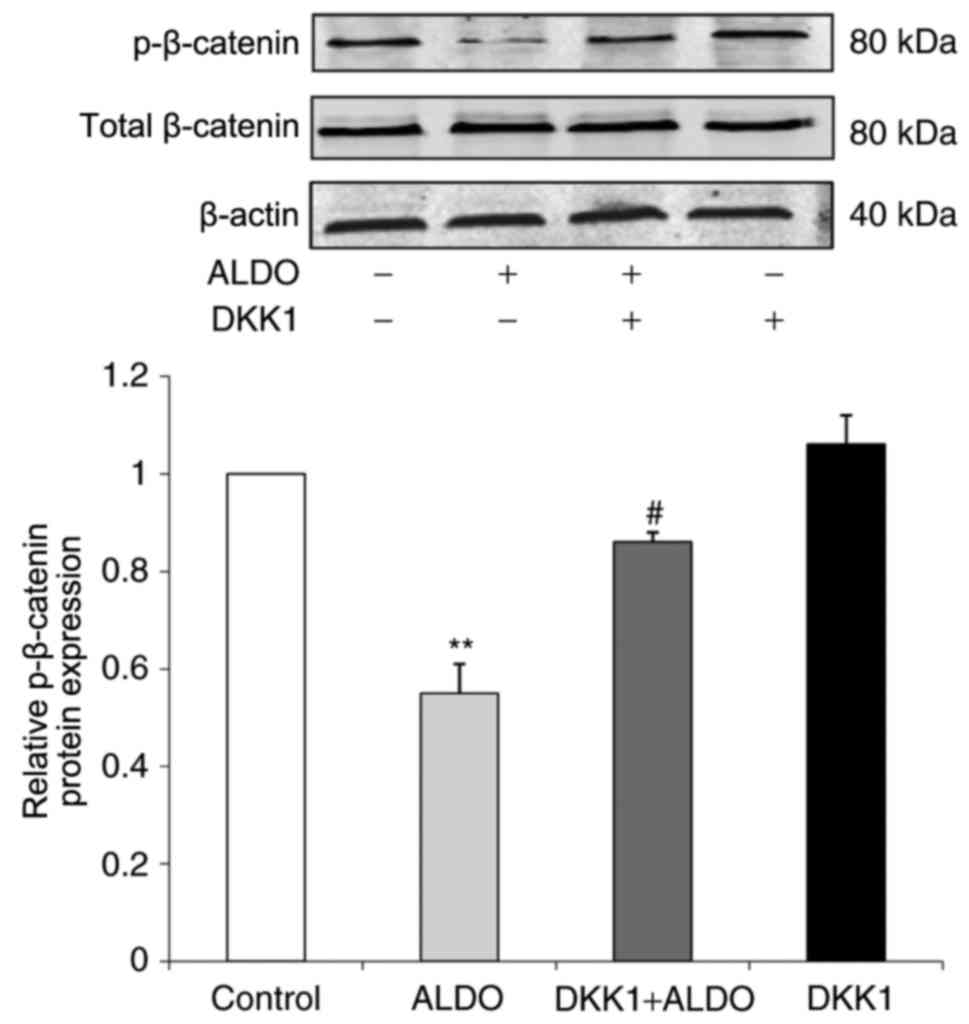
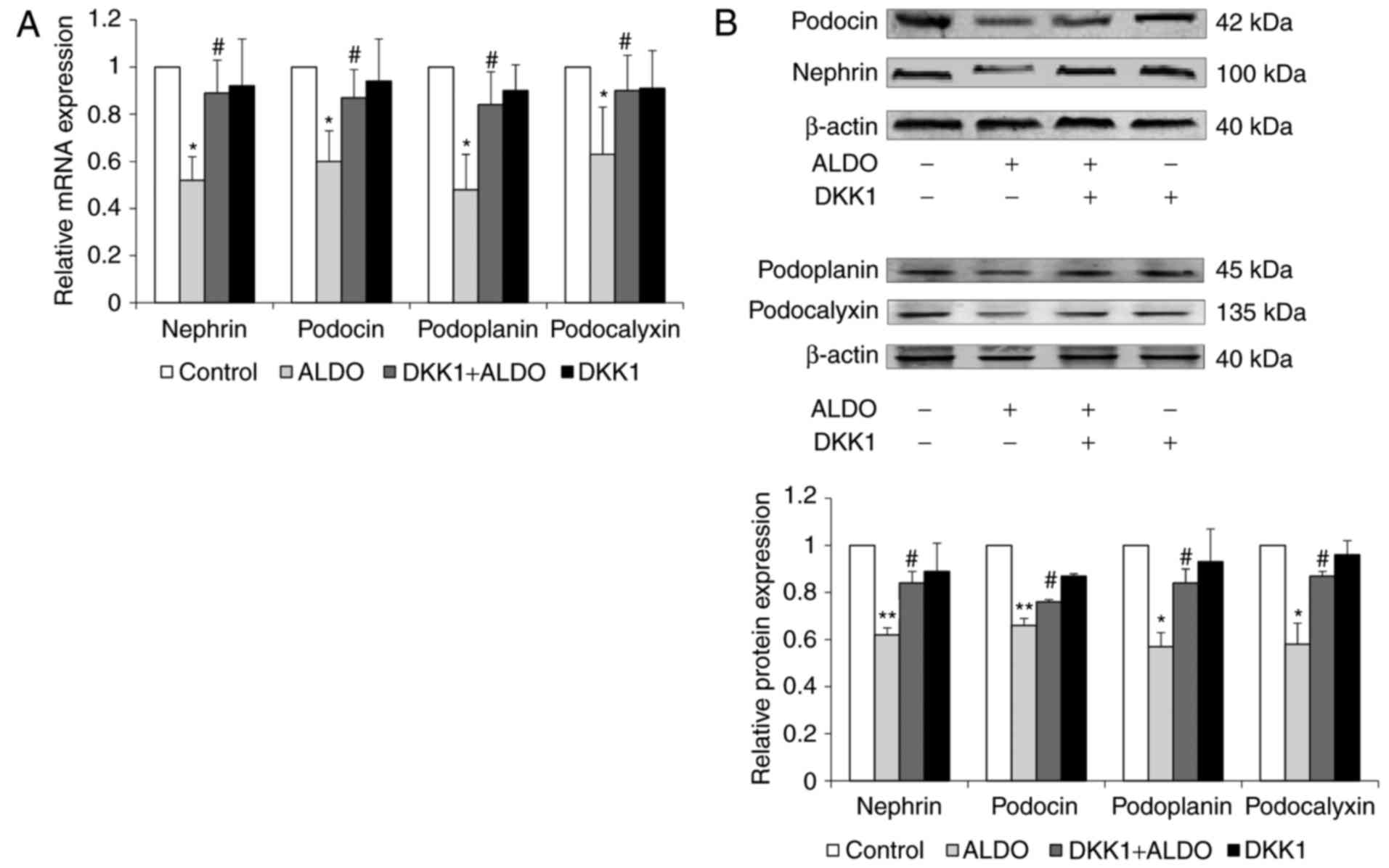
|
1
|
Wang Y and Beydoun MA: The Obesity
epidemic in the United States-gender, age, socioeconomic,
racial/ethnic, and geographic characteristics: A systematic review
and meta-regression analysis. Epidemiol Rev. 29:6–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arroyo-Johnson C and Mincey KD: Obesity
epidemiology worldwide. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 45:571–579.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wickman C and Kramer H: Obesity and kidney
disease: Potential mechanisms. Semin Nephrol. 33:14–22. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xie D and Bollag WB: Obesity, hypertension
and aldosterone: Is leptin the link? J Endocrinol. 230:F7–F11.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hsu CY, McCulloch CE, Iribarren C,
Darbinian J and Go AS: Body mass index and risk for end-stage renal
disease. Ann Intern Med. 144:21–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kambham N, Markowitz GS, Valeri AM, Lin J
and D'Agati VD: Obesity-related glomerulopathy: An emerging
epidemic. Kidney Int. 59:1498–1509. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cheng H, Chen YP, Zhang C, Fang J, Dong
HR, Li WG and Zou WZ: Comparative study of clinicopathological
features between two kinds of obesity-related glomerulopathy. Clin
J Nephrol. 25:261–264. 2009.
|
|
8
|
D'Agati VD, Chagnac A, de Vries AP, Levi
M, Porrini E, Herman-Edelstein M and Praga M: Obesity-related
glomerulopathy: Clinical and pathologic characteristics and
pathogenesis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 12:453–471. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen HM, Liu ZH, Zeng CH, Li SJ, Wang QW
and Li LS: Podocyte lesions in patients with obesity-related
glomerulopathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 48:772–779. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zoccali C and Mallamaci F: Obesity,
diabetes, adiponectin and the kidney: A podocyte affair. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 23:3767–3770. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Camici M, Galetta F, Abraham N and Carpi
A: Obesity-related glomerulopathy and podocyte injury: A mini
review. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:1058–1070. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nagase M, Yoshida S, Shibata S, Nagase T,
Gotoda T, Ando K and Fujita T: Enhanced aldosterone signaling in
the early nephropathy of rats with metabolic syndrome: Possible
contribution of fat-derived factors. J Am Soc Nephrol.
17:3438–3446. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawachi H
and Fujita T: Podocyte as the target for aldosterone: Roles of
oxidative stress and Sgk1. Hypertension. 49:355–364. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nagase M and Fujita T: Aldosterone and
glomerular podocyte injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 12:233–242. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nagase M: Activation of the
aldosterone/mineralocorticoid receptor system in chronic kidney
disease and metabolic syndrome. Clin Exp Nephrol. 14:303–314. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shibata S and Fujita T: Mineralocorticoid
receptors in the pathophysiology of chronic kidney diseases and the
metabolic syndrome. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 350:273–280. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kato H, Gruenwald A, Suh JH, Miner JH,
Barisoni-Thomas L, Taketo MM, Faul C, Millar SE, Holzman LB and
Susztak K: Wnt/β-catenin pathway in podocytes integrates cell
adhesion, differentiation, and survival. J Biol Chem.
286:26003–26015. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heikkilä E, Juhila J, Lassila M, Messing
M, Perälä N, Lehtonen E, Lehtonen S, Sjef Verbeek J and Holthofer
H: β-catenin mediates adriamycin-induced albuminuria and podocyte
injury in the adult mouse kidneys. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
25:2437–2446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou L and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signalling
and podocyte dysfunction in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 11:535–545. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang D, Dai C, Li Y and Liu Y: Canonical
Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth
factor-β1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int.
80:1159–1169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiao L, Wang M, Yang S, Liu F and Sun L: A
glimpse of the pathogenetic mechanisms of Wnt/β-catenin signaling
in diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Res Int. 2013:9870642013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Z, Xu J, Xu P, Liu S and Yang Z:
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway mediates high glucose induced cell
injury through activation of TRPC6 in podocytes. Cell Prolif.
46:76–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He W, Kang YS, Dai C and Liu Y: Blockade
of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by paricalcitol ameliorates proteinuria
and kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:90–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu BL, Chen YP, Cheng H, Wang YY, Rui HL,
Yang M, Dong HR, Han DN and Dong J: The Protective Effects of
Curcumin on obesity-related glomerulopathy are associated with
inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling activation in podocytes. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:8274722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pei YY, Yang M, Zuo HL, Wang YY, Dong HR,
Cheng H and Zuo ZZ: The establishment of obesity-related
glomerulopathy mouse model. Chin J Integr Tradit West Nephrol.
15:110–113. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Toyonaga J, Tsuruya K, Ikeda H, Noguchi H,
Yotsueda H, Fujisaki K, Hirakawa M, Taniguchi M, Masutani K and
Iida M: Spironolactone inhibits hyperglycemia-induced podocyte
injury by attenuating ROS production. Nephrol Dial Transpalnt.
26:2475–2484. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Huang H, You Y, Lin X, Tang C, Gu X, Huang
M, Qin Y, Tan J and Huang F: Inhibition of TRPC6 signal pathway
alleviates podocyte injury induced by TGF-β1. Cell Physiol Biochem.
41:163–172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ji ZZ and Xu YC: Melatonin protects
podocytes from angiotensin II-induced injury in an in vitro
diabetic nephropathy model. Mol Med Rep. 14:920–926. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rebuffé-Scrive M, Surwit R, Feinglos M,
Kuhn C and Rodin J: Regional fat distribution and metabolism in a
new mouse model (C57BL/6J) of non-insulin-dependent diabetes
mellitus. Metabolism. 42:1405–1409. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang XX, Ye T, Li M, Li X, Qiang O, Tang
CW and Liu R: Effects of octreotide on hepatic glycogenesis in rats
with high fat diet-induced obesity. Mol Med Rep. 16:109–118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li X, Yang J, Zhu Y, Liu Y, Shi X and Yang
G: Mouse maternal high-fat intake dynamically programmed mRNA
m6A modifications in adipose and skeletal muscle tissues
in offspring. Int J Mol Sci. 17(pii): E13362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oksay T, Yunusoğlu S, Calapoğlu M, Aydın
Candan I, Onaran İ, Ergün O and Özorak A: Protective impact of
resveratrol in experimental rat model of hyperoxaluria. Int Urol
Nephrol. 49:769–775. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng H, Dong HR, Lin RQ, Sun LJ and Chen
YP: Determination of normal value of glomerular size in Chinese
adults by different measurement methods. Nephrology (Carlton).
17:488–492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Paller MS, Hoidal JR and Ferris TF: Oxygen
free radicals in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat. J Clin
Invest. 74:1156–1164. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Darouich S, Goucha R, Jaafoura MH, Zekri
S, Ben Maiz H and Kheder A: Clinicopathological characteristics of
obesity-associated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Ultrastruct
Pathol. 35:176–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Suwanpen C, Nouanthong P, Jaruvongvanich
V, Pongpirul K, Pongpirul WA, Leelahavanichkul A and Kanjanabuch T:
Urinary podocalyxin, the novel biomarker for detecting early renal
change in obesity. J Nephrol. 29:37–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dinh Cat AN, Friederich-Persson M, White A
and Touyz RM: Adipocytes, aldosterone and obesity-related
hypertension. J Mol Endocrinol. 57:F7–F21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kawarazaki W and Fujita T: The role of
aldosterone in obesity-related hypertension. Am J Hypertens.
29:415–423. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ehrhart-Bornstein M, Lamounier-Zepter V,
Schraven A, Langenbach J, Willenberg HS, Barthel A, Hauner H,
McCann SM, Scherbaum WA and Bornstein SR: Human adipocytes secrete
mineralocorticoid-releasing factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:pp. 14211–14216. 2003; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Luther JM: Aldosterone in vascular and
metabolic dysfunction. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 25:16–21. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Briones AM, Nguyen Dinh Cat A, Callera GE,
Yogi A, Burger D, He Y, Corrêa JW, Gagnon AM, Gomez-Sanchez CE,
Gomez-Sanchez EP, et al: Adipocytes produce aldosterone through
calcineurin-dependent signaling pathways: Implications in diabetes
mellitus-associated obesity and vascular dysfunction. Hypertension.
59:1069–1078. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Angers S and Moon RT: Proximal events in
Wnt signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:468–477. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gordon MD and Nusse R: Wnt signaling:
Multiple pathways, multiple receptors and multiple transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 281:22429–22433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|