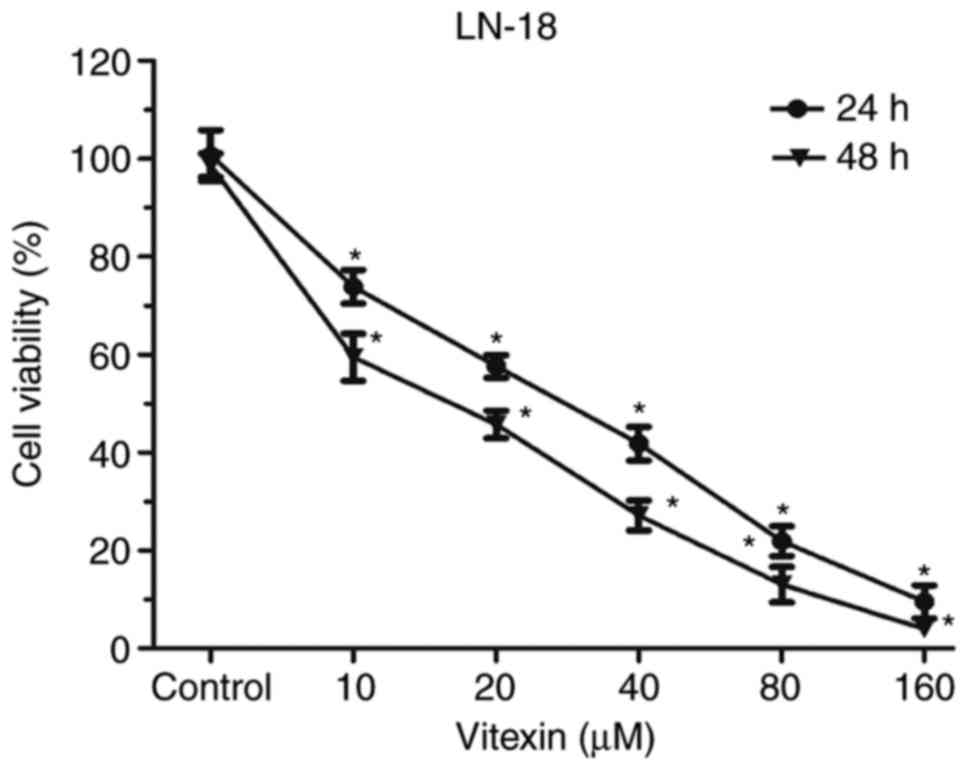
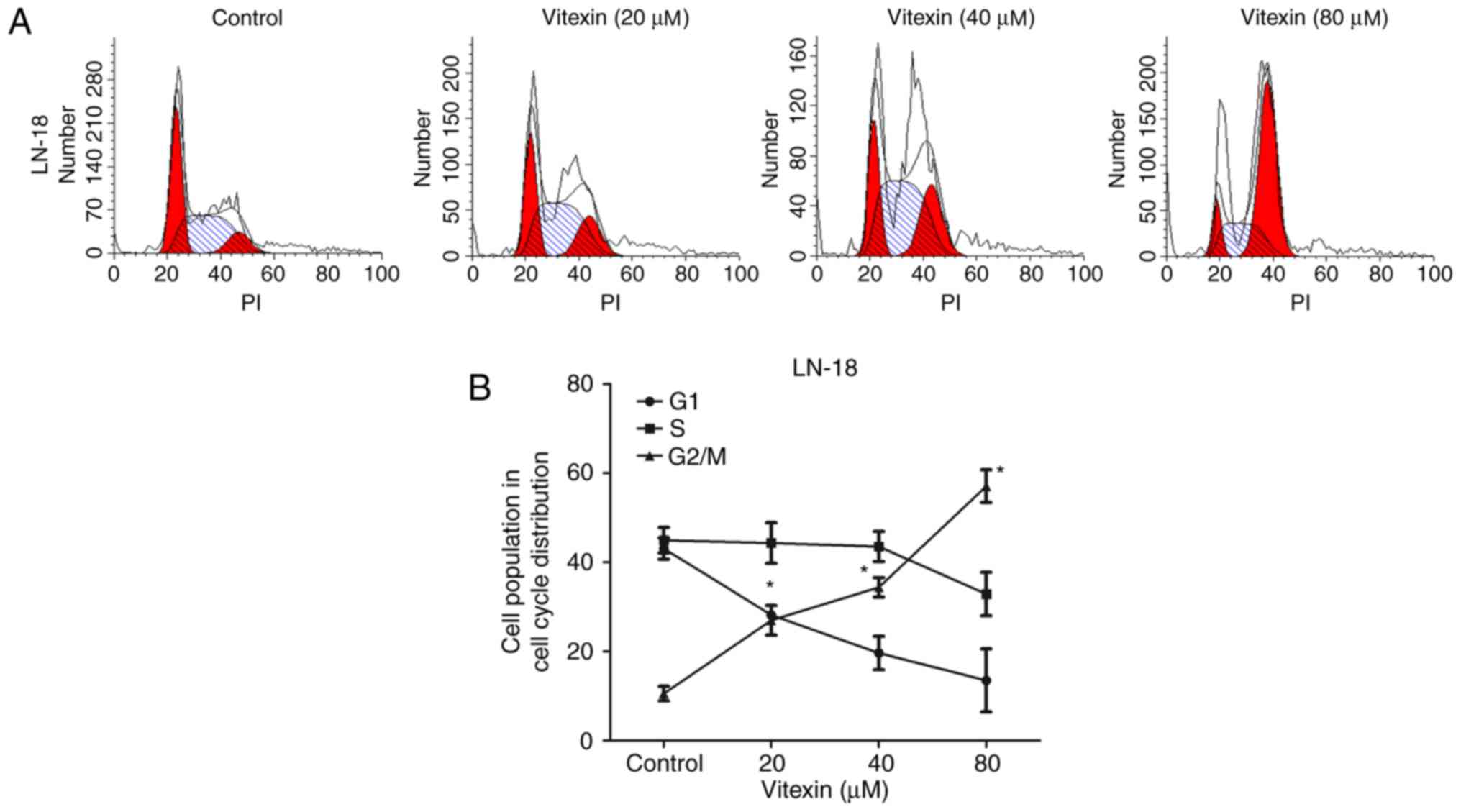
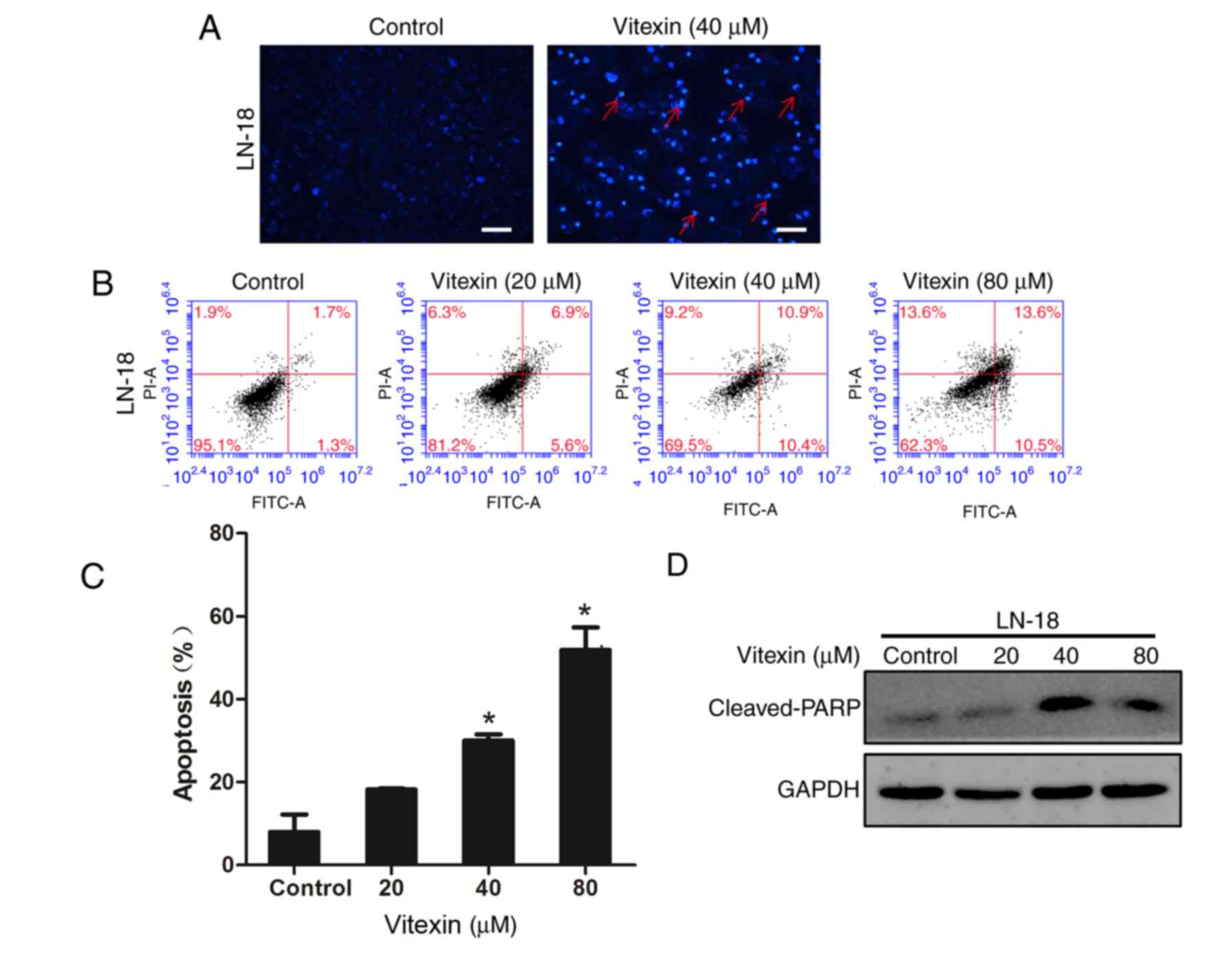
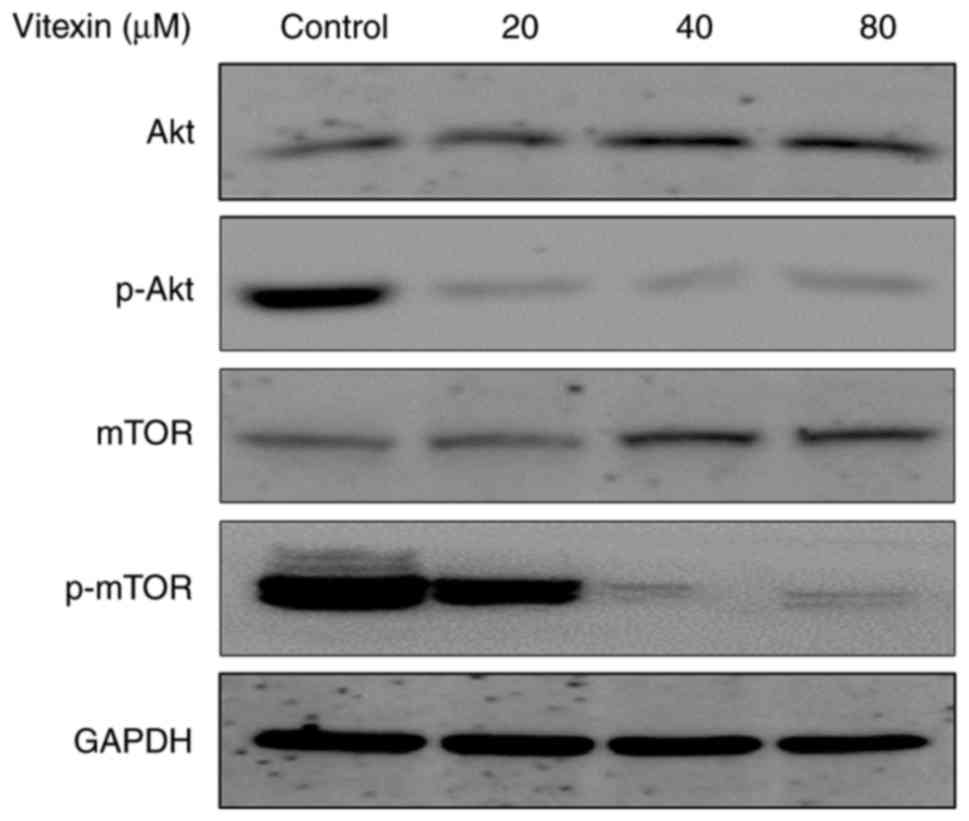
|
1
|
Kubelt C, Hattermann K, Sebens S, Mehdorn
HM and Held-Feindt J: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
paired human primary and recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Oncol.
46:2515–2525. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Omuro A and DeAngelis LM: Glioblastoma and
other malignant gliomas: A clinical review. JAMA. 310:1842–1850.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woehrer A, Bauchet L and Barnholtz-Sloan
JS: Glioblastoma survival: Has it improved? Evidence from
population-based studies. Curr Opin Neurol. 27:666–674.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cuddapah VA, Robel S, Watkins S and
Sontheimer H: A neurocentric perspective on glioma invasion. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 15:455–465. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wirsching HG, Galanis E and Weller M:
Glioblastoma. Handb Clin Neurol. 134:381–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arévalo ÁST, Erices JI, Uribe DA, Howden
J, Niechi I, Muñoz S, Martín RS and Monrás CAQ: Current therapeutic
alternatives and new perspectives in glioblastoma multiforme. Curr
Med Chem. 24:2781–2795. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Desjardins A, Rich JN, Quinn JA,
Vredenburgh J, Gururangan S, Sathornsumetee S, Reardon DA, Friedman
AH, Bigner DD and Friedman HS: Chemotherapy and novel therapeutic
approaches in malignant glioma. Front Biosci. 10:2645–2668. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gaitan E, Cooksey RC, Legan J and Lindsay
RH: Antithyroid effects in vivo and in vitro of vitexin: A
C-glucosylflavone in millet. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 80:1144–1147.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He M, Min JW, Kong WL, He XH, Li JX and
Peng BW: A review on the pharmacological effects of vitexin and
isovitexin. Fitoterapia. 115:74–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Zhen Y, Wu X, Jiang Q, Li X, Chen
Z, Zhang G and Dong L: Vitexin protects brain against
ischemia/reperfusion injury via modulating mitogen-activated
protein kinase and apoptosis signaling in mice. Phytomedicine.
22:379–384. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Che X, Wang X, Zhang J, Peng C, Zhen Y,
Shao X, Zhang G and Dong L: Vitexin exerts cardioprotective effect
on chronic myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats via
inhibiting myocardial apoptosis and lipid peroxidation. Am J Transl
Res. 8:3319–3328. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
An F, Yang G, Tian J and Wang S:
Antioxidant effects of the orientin and vitexin in Trollius
chinensis Bunge in D-galactose-aged mice. Neural Regen Res.
7:2565–2575. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Yang ZM, Zhang N, Tian Z, Liu SB
and Zhao MG: Neuroprotective effects of vitexin by inhibition of
NMDA receptors in primary cultures of mouse cerebral cortical
neurons. Mol Cell Biochem. 386:251–258. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He JD, Wang Z, Li SP, Xu YJ, Yu Y, Ding
YJ, Yu WL, Zhang RX, Zhang HM and Du HY: Vitexin suppresses
autophagy to induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via
activation of the JNK signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 7:84520–84532.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang SH, Liao PH, Pan YF, Chen SL, Chou SS
and Chou MY: The novel p53-dependent metastatic and apoptotic
pathway induced by vitexin in human oral cancer OC2 cells.
Phytother Res. 27:1154–1161. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
An F, Wang S, Tian Q and Zhu D: Effects of
orientin and vitexin from Trollius chinensis on the growth and
apoptosis of esophageal cancer EC-109 cells. Oncol Lett.
10:2627–2633. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schwartz GK and Shah MA: Targeting the
cell cycle: A new approach to cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol.
23:9408–9421. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stewart ZA, Westfall MD and Pietenpol JA:
Cell-cycle dysregulation and anticancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 24:139–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim G, Kim TH, Hwang EH, Chang KT, Hong JJ
and Park JH: Withaferin A inhibits the proliferation of gastric
cancer cells by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Oncol Lett. 14:416–422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liberal J, Carmo A, Gomes C, Cruz MT and
Batista MT: Urolithins impair cell proliferation, arrest the cell
cycle and induce apoptosis in UMUC3 bladder cancer cells. Invest
New Drugs. Jun 20–2017.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Silva IT, Geller FC, Persich L, Dudek SE,
Lang KL, Caro MS, Durán FJ, Schenkel EP, Ludwig S and Simões CM:
Cytotoxic effects of natural and semisynthetic cucurbitacins on
lung cancer cell line A549. Invest New Drugs. 34:139–148. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
King KL and Cidlowski JA: Cell cycle and
apoptosis: Common pathways to life and death. J Cell Biochem.
58:175–180. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kiraz Y, Adan A, Kartal Yandim M and Baran
Y: Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis.
Tumour Biol. 37:8471–8486. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Burgess DJ: Apoptosis: Refined and lethal.
Nat Rev Cancer. 13:792013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Germain M, Affar EB, D'Amours D, Dixit VM,
Salvesen GS and Poirier GG: Cleavage of automodified
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase during apoptosis. Evidence for
involvement of caspase-7. J Biol Chem. 274:28379–28384. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Granato M, Rizzello C, Gilardini Montani
MS, Cuomo L, Vitillo M, Santarelli R, Gonnella R, D'Orazi G,
Faggioni A and Cirone M: Quercetin induces apoptosis and autophagy
in primary effusion lymphoma cells by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR and
STAT3 signaling pathways. J Nutr Biochem. 41:124–136. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding L, Ding L, Wang S, Wang S, Wang W,
Wang W, Lv P, Lv P, Zhao D, Zhao D, et al: Tanshinone IIA affects
autophagy and apoptosis of glioma cells by inhibiting
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin
signaling pathway. Pharmacology. 99:188–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Sun Y, Wu Y and Zhang J:
Cucurbitacin E inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and
invasion through attenuation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Biosci
Rep. BSR201601652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Li S, Meng X, Gan RY, Zhang JJ and
Li HB: Dietary natural products for prevention and treatment of
breast cancer. Nutrients. 9:E7282017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kou X, Fan J and Chen N: Potential
molecular targets of ampelopsin in prevention and treatment of
cancers. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. Apr 12–2017.(Epub ahead of
print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou J, Hu H, Long J, Wan F, Li L, Zhang
S, Shi YE and Chen Y: Vitexin 6, a novel lignan, induces autophagy
and apoptosis by activating the Jun N-terminal kinase pathway.
Anticancer Drugs. 24:928–936. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan Z and Zhang Y, Deng J, Zeng G and
Zhang Y: Purified vitexin compound 1 suppresses tumor growth and
induces cell apoptosis in a mouse model of human choriocarcinoma.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:360–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xia Y, Lei Q, Zhu Y, Ye T, Wang N, Li G,
Shi X, Liu Y, Shao B, Yin T, et al: SKLB316, a novel small-molecule
inhibitor of cell-cycle progression, induces G2/M phase arrest and
apoptosis in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Lett.
355:297–309. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bendale Y, Bendale V and Paul S:
Evaluation of cytotoxic activity of platinum nanoparticles against
normal and cancer cells and its anticancer potential through
induction of apoptosis. Integr Med Res. 6:141–148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao FJ, Zhu LF, Kuang Q, Li XQ, Zhou BH,
Yang XJ and Zhou L: Cytotoxic activity, apoptosis induction and
structure-activity relationship of
8-OR-2-aryl-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2-ium salts as promising
anticancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 27:55–60. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ivanovska I, Muhoro CN and Irusta PM:
Anti-tumor therapeutic molecules that target the programmed cell
death machinery. Mini Rev Med Chem. 6:1033–1042. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kolenko VM, Uzzo RG, Bukowski R and Finke
JH: Caspase-dependent and -independent death pathways in cancer
therapy. Apoptosis. 5:17–20. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Zhang T, Sun W, Wang Z, Zuo D,
Zhou Z, Li S, Xu J, Yin F, Hua Y and Cai Z: Erianin induces
G2/M-phase arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via the ROS/JNK
signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e22472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Croce CM and Reed JC: Finally, an
apoptosis-targeting therapeutic for cancer. Cancer Res.
76:5914–5920. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, Chen Y and Yu Q:
Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol
Cancer. 14:482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang G, Zou B, Lv J, Li T, Huai G, Xiang
S, Lu S, Luo H, Zhang Y, Jin Y and Wang Y: Notoginsenoside R1
attenuates glucose-induced podocyte injury via the inhibition of
apoptosis and the activation of autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 39:559–568. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ko JH, Lee JH, Jung SH, Lee SG,
Chinnathambi A, Alharbi SA, Yang WM, Um JY, Sethi G and Ahn KS:
2,5-Dihydroxyacetophenone induces apoptosis of multiple myeloma
cells by regulating the MAPK activation pathway. Molecules.
22:E11572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fulda S: Synthetic lethality by
co-targeting mitochondrial apoptosis and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.
Mitochondrion. 19:85–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|