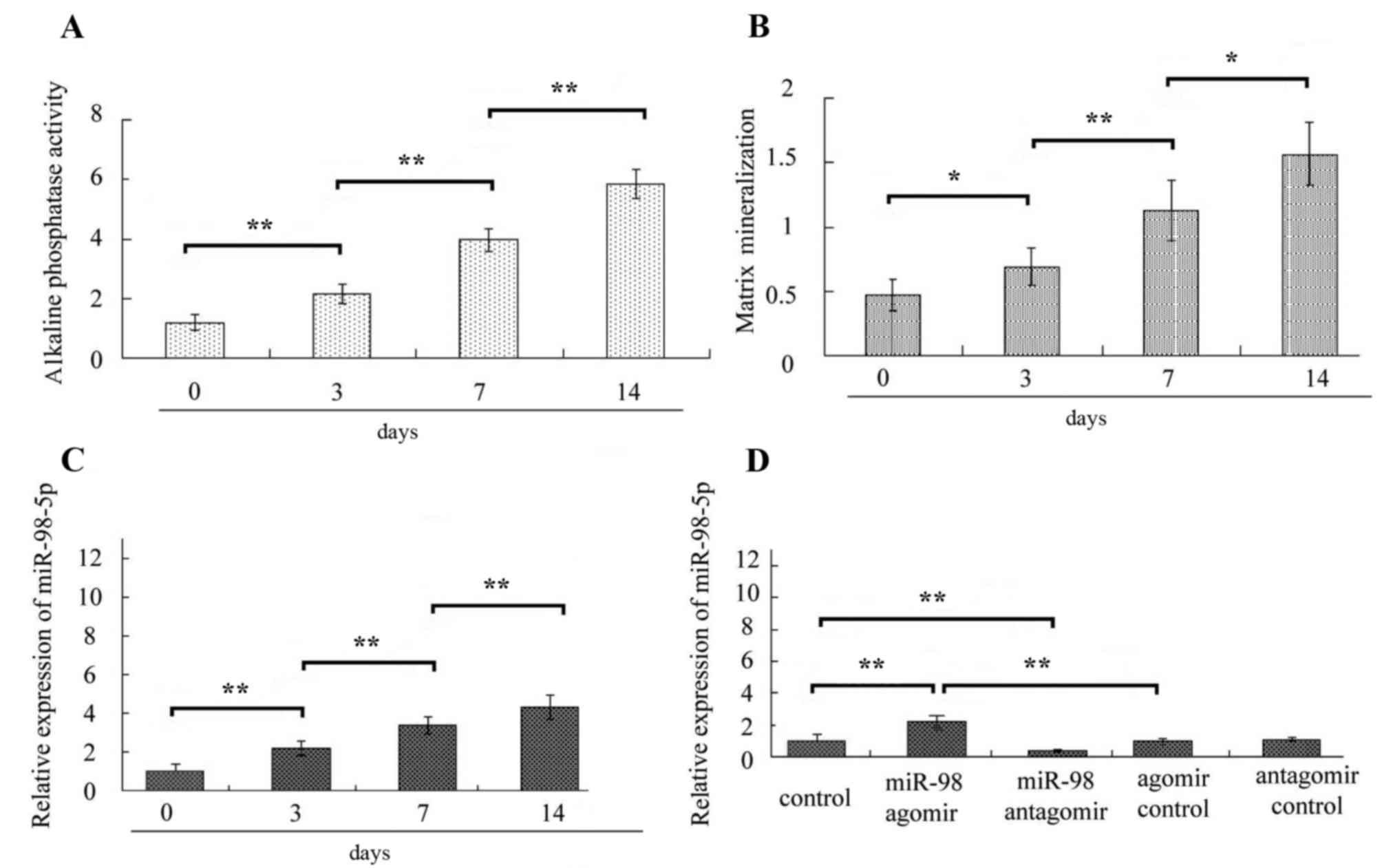
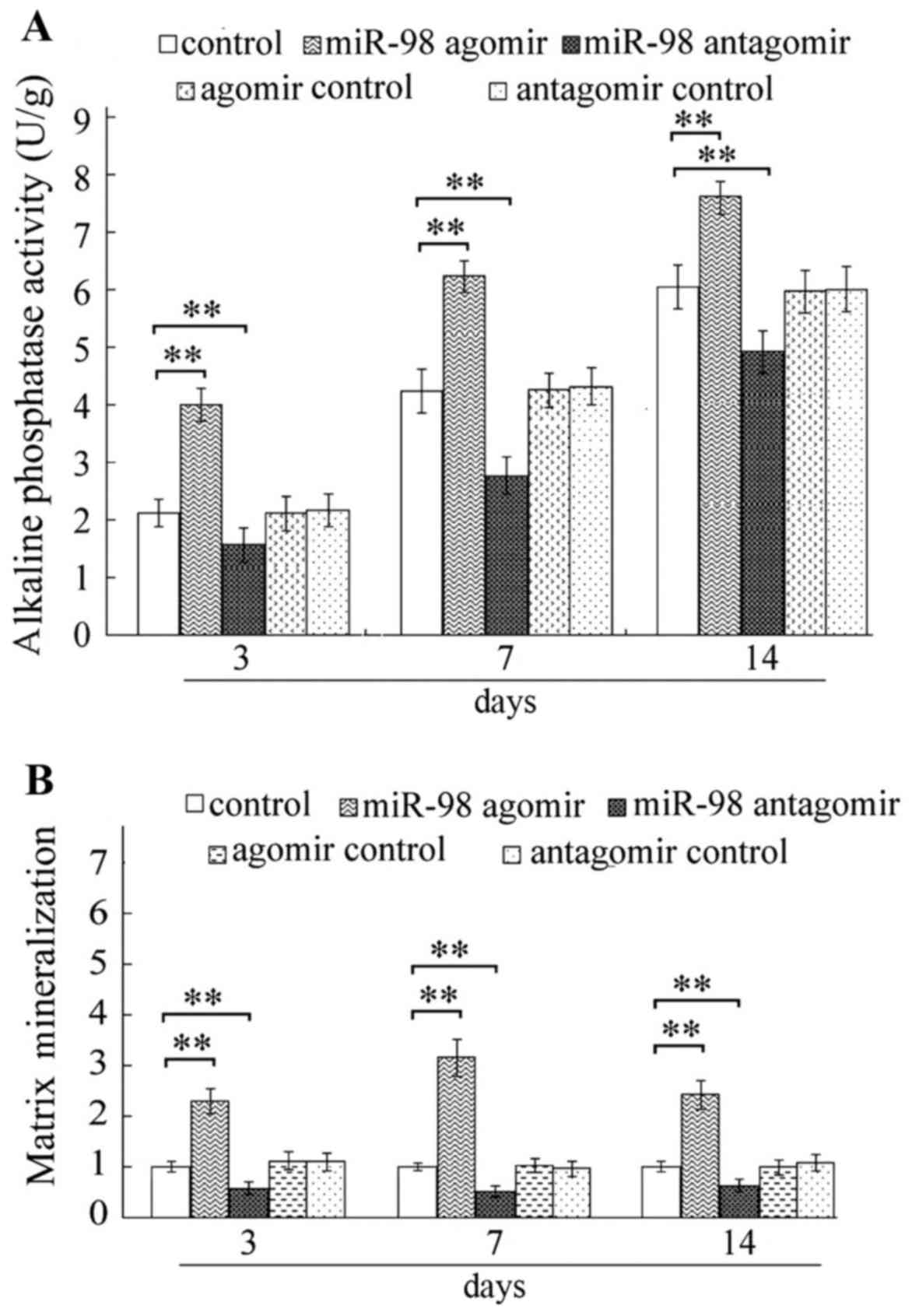
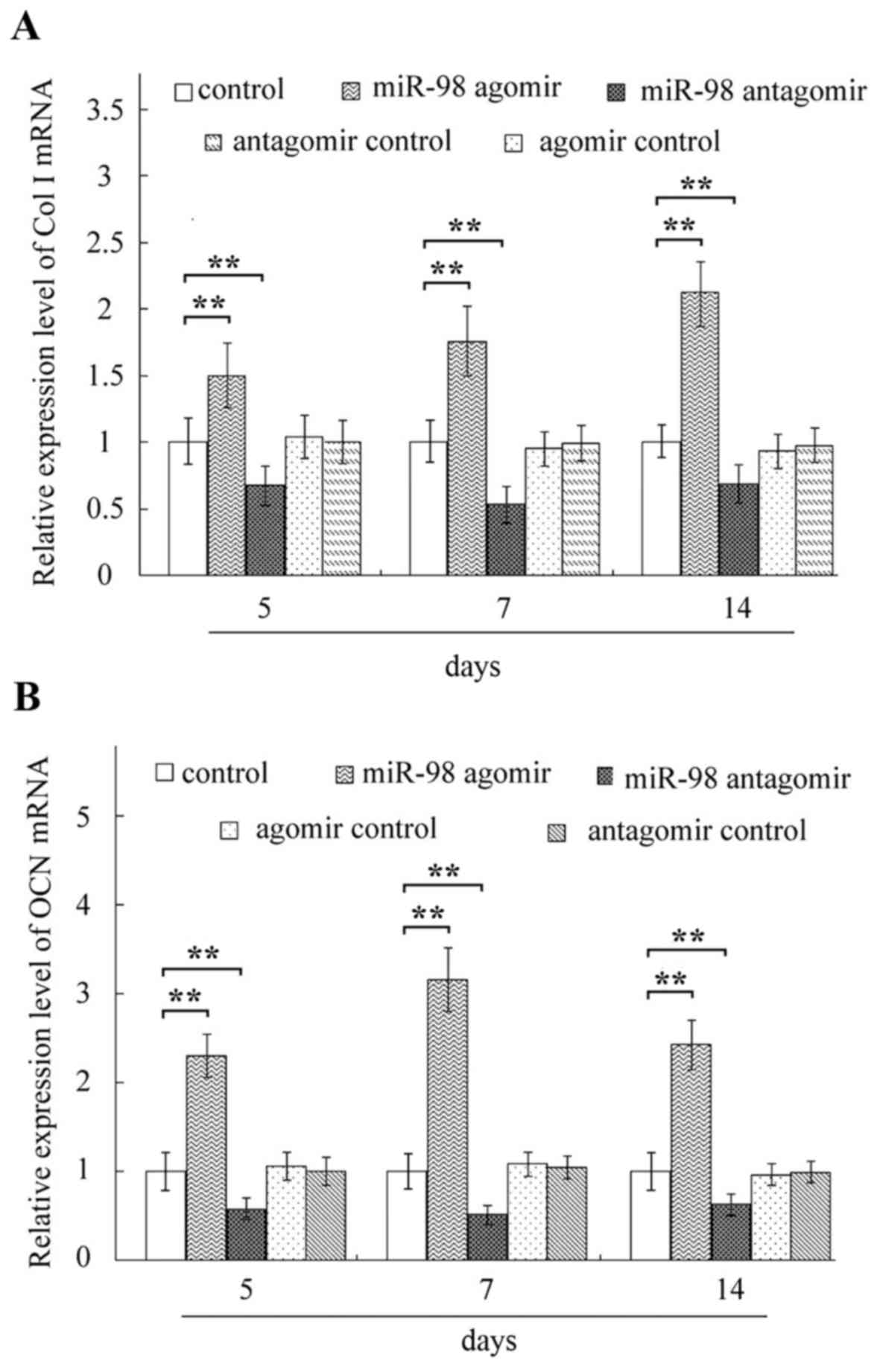
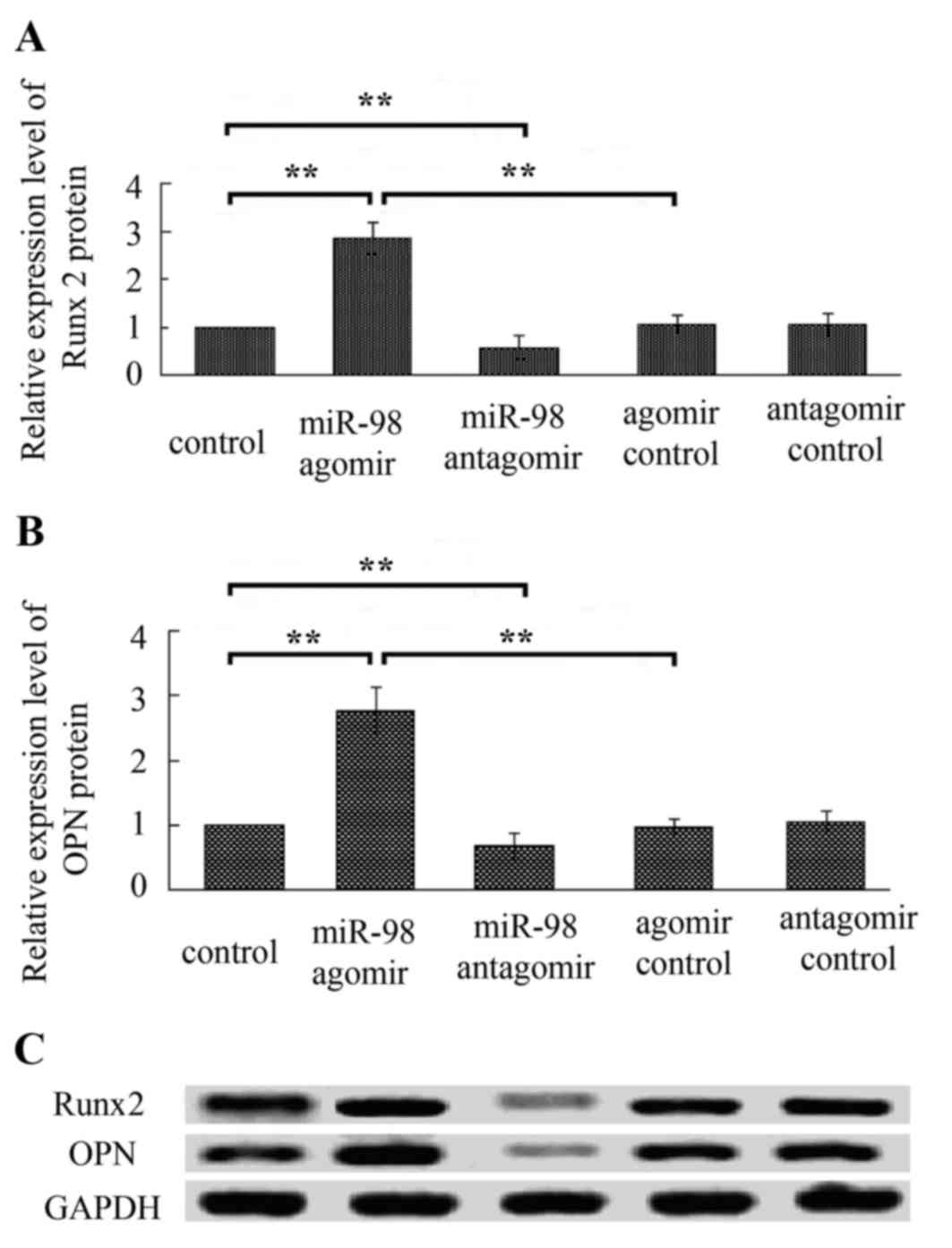
|
1
|
Lerner UH: Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and
osteocytes: Unveiling their intimate associated responses to
applied orthodontic forces. Semin in Orthodon. 18:237–248. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rolfe R, Roddy K and Murphy P: Mechanical
regulation of skeletal development. Curr Osteoporos Rep.
11:107–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu K, Yin X, Weng T, Xi S, Li L, Xing G,
Cheng X, Yang X, Zhang L and He F: Targeting WW domains linker of
HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat
Cell Biol. 10:994–1002. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nie J, Liu L, He F, Fu X, Han W and Zhang
L: CKIP-1: A scaffold protein and potential therapeutic target
integrating multiple signaling pathways and physiological
functions. Ageing Res Rev. 12:276–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang G, Guo B, Wu H, Tang T, Zhang BT,
Zheng L, He Y, Yang Z, Pan X, Chow H, et al: A delivery system
targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic
therapy. Nat Med. 18:307–314. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guo B, Zhang B, Zheng L, Tang T, Liu J, Wu
H, Yang Z, Peng S, He X, Zhang H, et al: Therapeutic RNA
interference targeting CKIP-1 with a cross-species sequence to
stimulate bone formation. Bone. 59:76–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI and
Diederichs S: Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways
and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol. 11:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mendell JT and Olson EN: MicroRNAs in
stress signaling and human disease. Cell. 148:1172–1187. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ranganathan K and Sivasankar V:
MicroRNAs-biology and clinical applications. J Oral Maxillofac
Pathol. 18:229–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vimalraj S and Selvamurugan N: MicroRNAs:
Synthesis, gene regulation and osteoblast differentiation. Curr
Issues Mol Biol. 15:7–18. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang J, Zhao L, Xing L and Chen D:
MicroRNA-204 regulates Runx2 protein expression and mesenchymal
progenitor cell differentiation. Stem Cells. 28:357–364.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hassan MQ, Maeda Y, Taipaleenmaki H, Zhang
W, Jafferji M, Gordon JA, Li Z, Croce CM, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL,
et al: miR-218 directs a Wnt signaling circuit to promote
differentiation of osteoblasts and osteomimicry of metastatic
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 287:42084–42092. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Beck GR Jr, Zerler B and Moran E:
Phosphate is a specific signal for induction of osteopontin gene
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:pp. 8352–8357. 2000;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu M, Hesse E, Morvan F, Zhang JP, Correa
D, Rowe GC, Kiviranta R, Neff L, Philbrick WM, Horne WC and Baron
R: Zfp521 antagonizes Runx2, delays osteoblast differentiation in
vitro and promotes bone formation in vivo. Bone. 44:528–536. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mahalingam CD, Datta T, Patil RV, Kreider
J, Bonfil RD, Kirkwood KL, Goldstein SA, Abou-Samra AB and Datta
NS: Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1 regulates bone
mass, osteoblast gene expression, and responsiveness to parathyroid
hormone. J Endocrinol. 211:145–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo Y, Liu L, Hao Q, Li R, Zhang X, Wang L
and Ning B: Effects of extracellular matrix produced in vitro on
growth and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng
Xue Bao. 27:1606–1612. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo Y, Zhang CQ, Zeng QC, Li RX, Liu L,
Hao QX, Shi CH, Zhang XZ and Yan YX: Mechanical strain promotes
osteoblast ECM formation and improves its osteoinductive potential.
Biomed Eng Online. 11:802012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhatt KA, Chang EI, Warren SM, Lin SE,
Bastidas N, Ghali S, Thibboneir A, Capla JM, McCarthy JG and
Gurtner GC: Uniaxial mechanical strain: An in vitro correlate to
distraction osteogenesis. J Surg Res. 143:329–336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu G, Zhou R, Liu J, Gong AY, Eischeid AN,
Dittman JW and Chen XM: MicroRNA-98 and let-7 confer cholangiocyte
expression of cytokine-inducible Src homology 2-containing protein
in response to microbial challenge. J Immunol. 183:1617–1624. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Chen Q, Song Y, Lai L, Wang J, Yu
H, Cao X and Wang Q: MicroRNA-98 negatively regulates IL-10
production and endotoxin tolerance in macrophages after LPS
stimulation. FEBS Lett. 585:1963–1968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ting HJ, Messing J, Yasmin-Karim S and Lee
YF: Identification of microRNA-98 as a therapeutic target
inhibiting prostate cancer growth and a biomarker induced by
vitamin D. J Biol Chem. 288:1–9. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu T, Hou L and Huang Y: EZH2-specific
microRNA-98 inhibits human ovarian cancer stem cell proliferation
via regulating the pRb-E2F pathway. Tumour Biol. 35:7239–7247.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou W, Zou B, Liu L, Cui K, Gao J, Yuan S
and Cong N: MicroRNA-98 acts as a tumor suppressor in
hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting SALL4. Oncotarget.
7:74059–74073. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang CY, Zhang JJ, Hua L, Yao KH, Chen JT
and Ren XQ: MicroRNA-98 suppresses cell proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting collagen triple helix repeat containing 1
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:2639–2644. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu X, Ouyang Y, Zhong F, Wang Q, Ding L,
Zhang P, Chen L, Liu H and He S: Silencing of CKIP-1 promotes tumor
proliferation and cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance via
regulating AKT activity in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Oncol Rep.
37:622–630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Wang Y, Xiao F, Wang S, Xing G,
Li Y, Yin X, Lu K, Wei R, Fan J, et al: CKIP-1 regulates macrophage
proliferation by inhibiting TRAF6-mediated Akt activation. Cell
Res. 24:742–761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang X, Wang Q, Wan Z, Li J, Liu L and
Zhang X: CKIP-1 knockout offsets osteoporosis induced by simulated
microgravity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 122:140–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou ZC, Che L, Kong L, Lei DL, Liu R and
Yang XJ: CKIP-1 silencing promotes new bone formation in rat
mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol. 123:e1–e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|