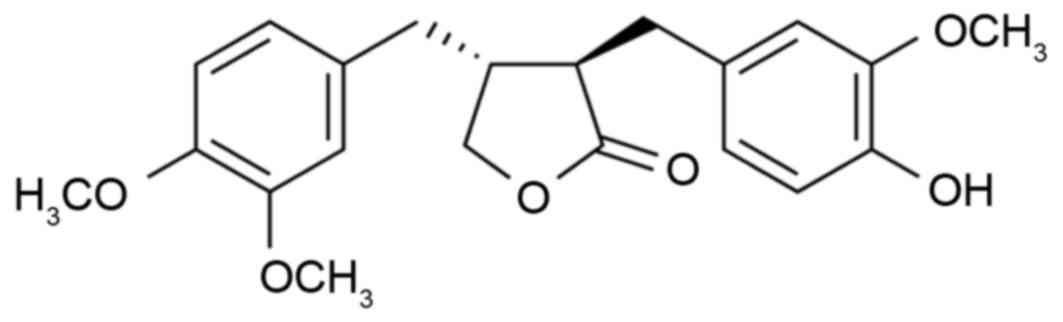
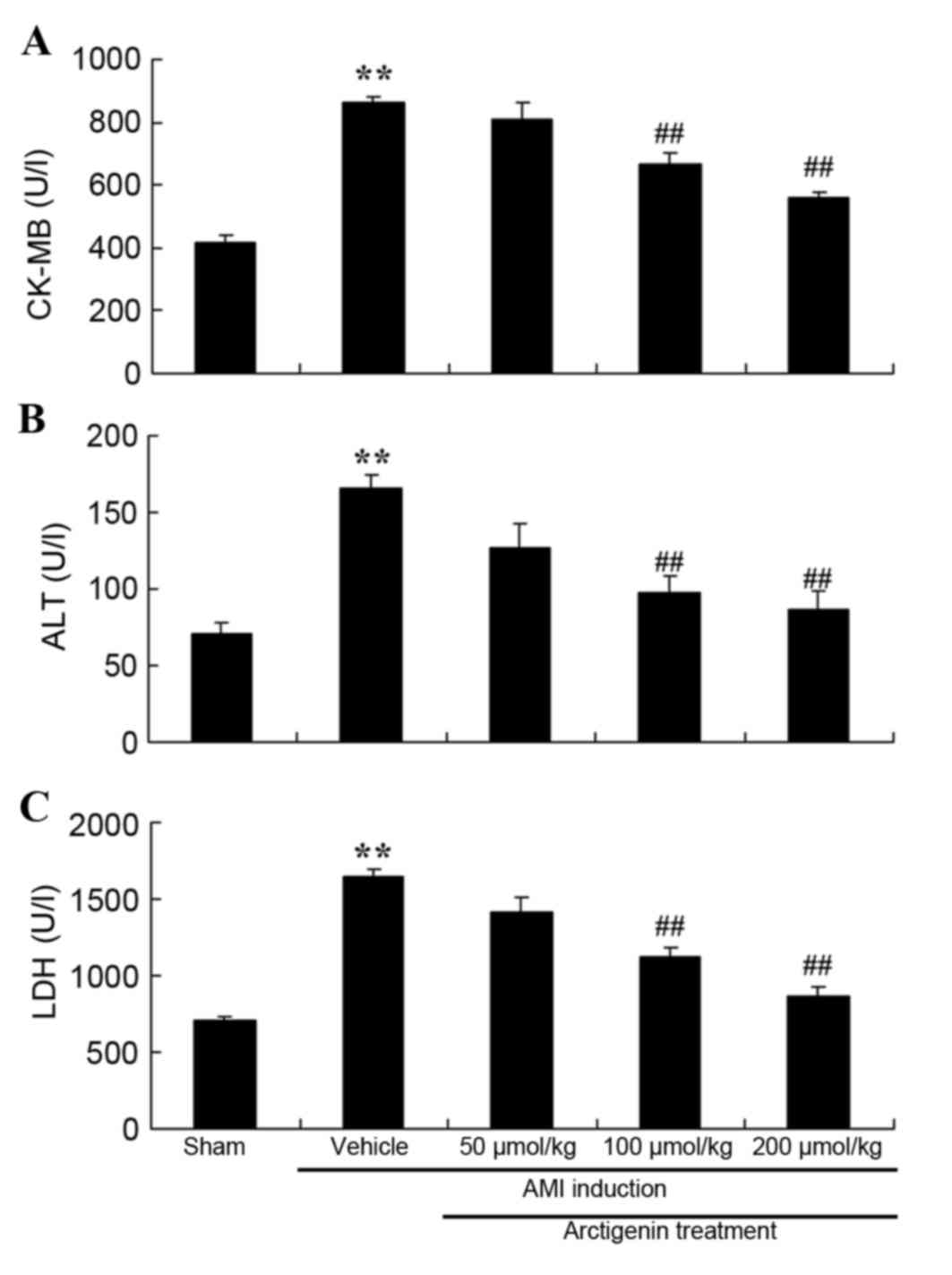
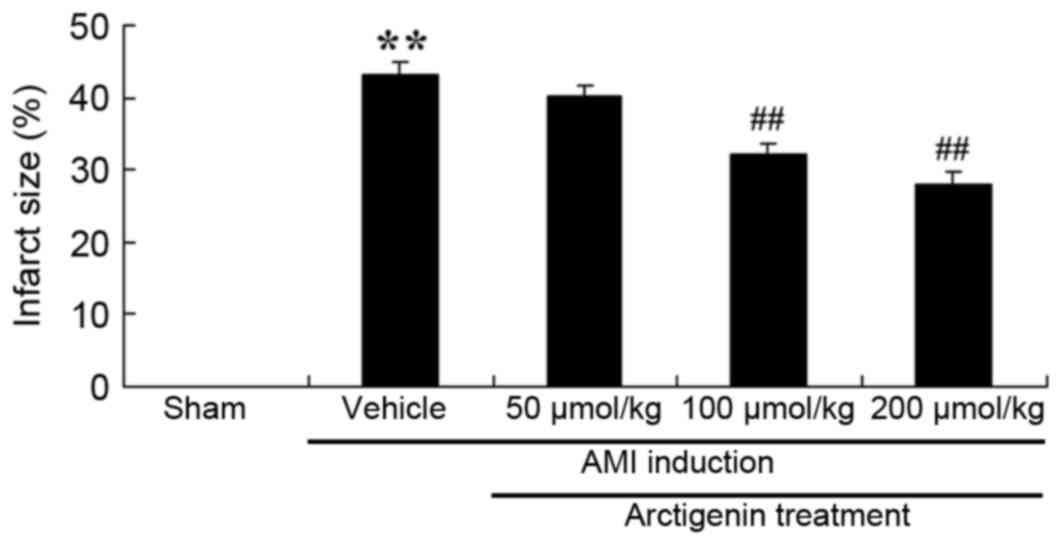
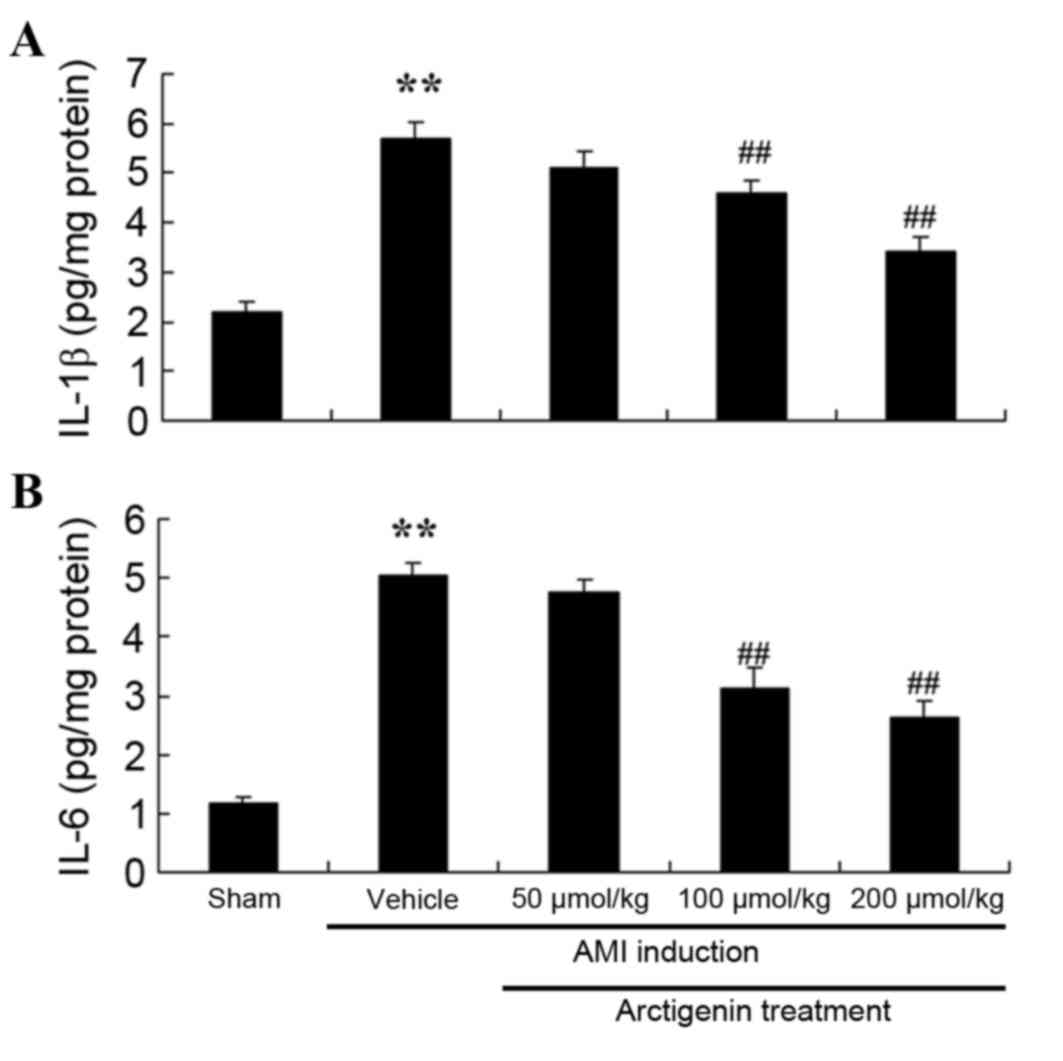
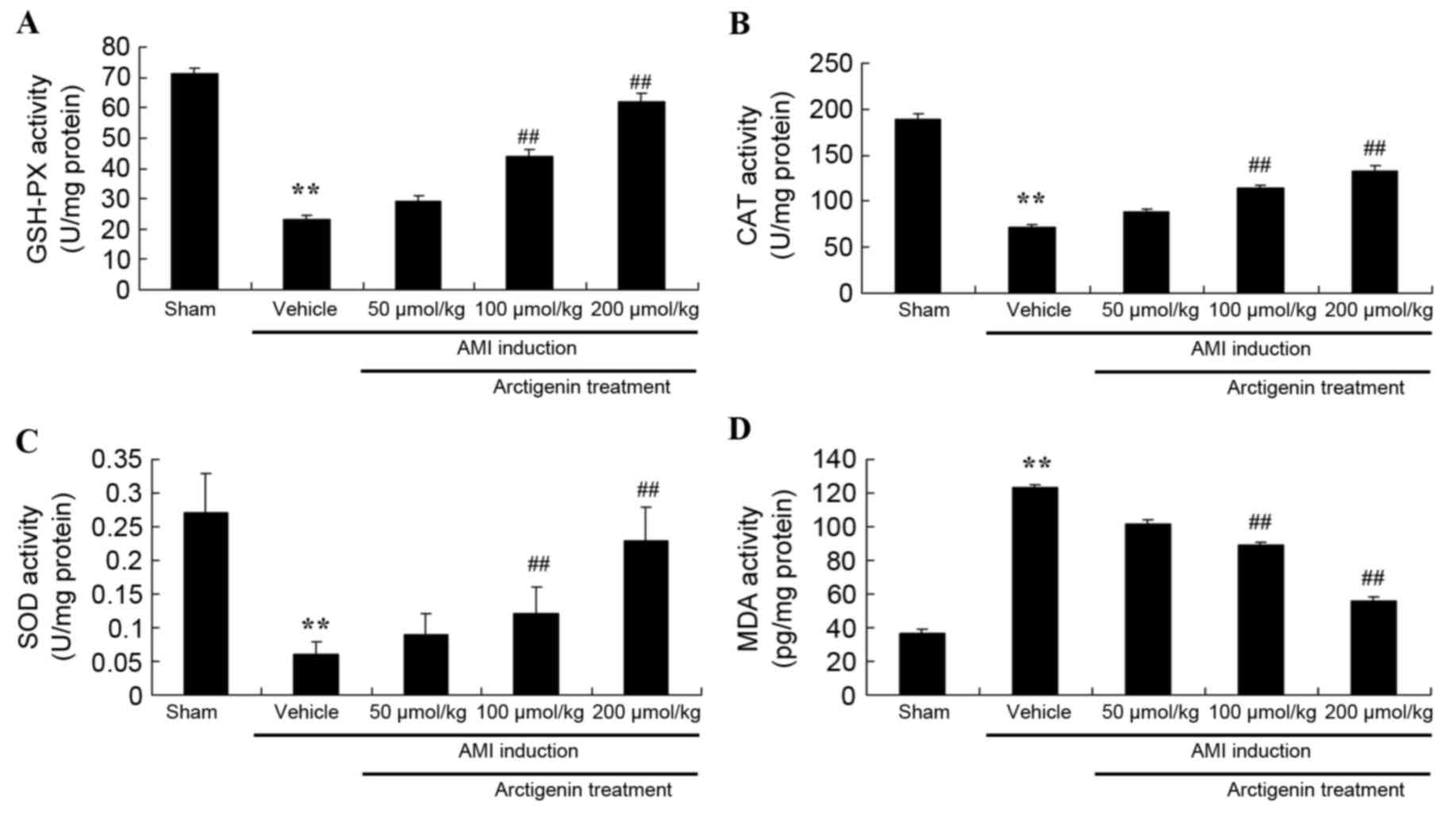
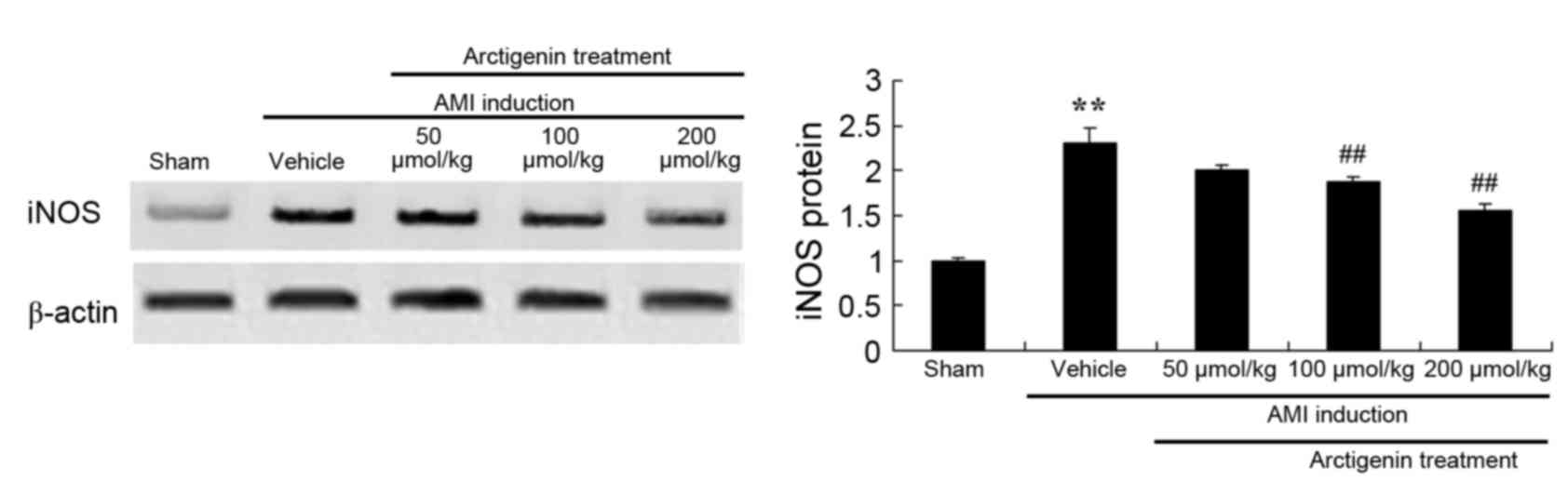
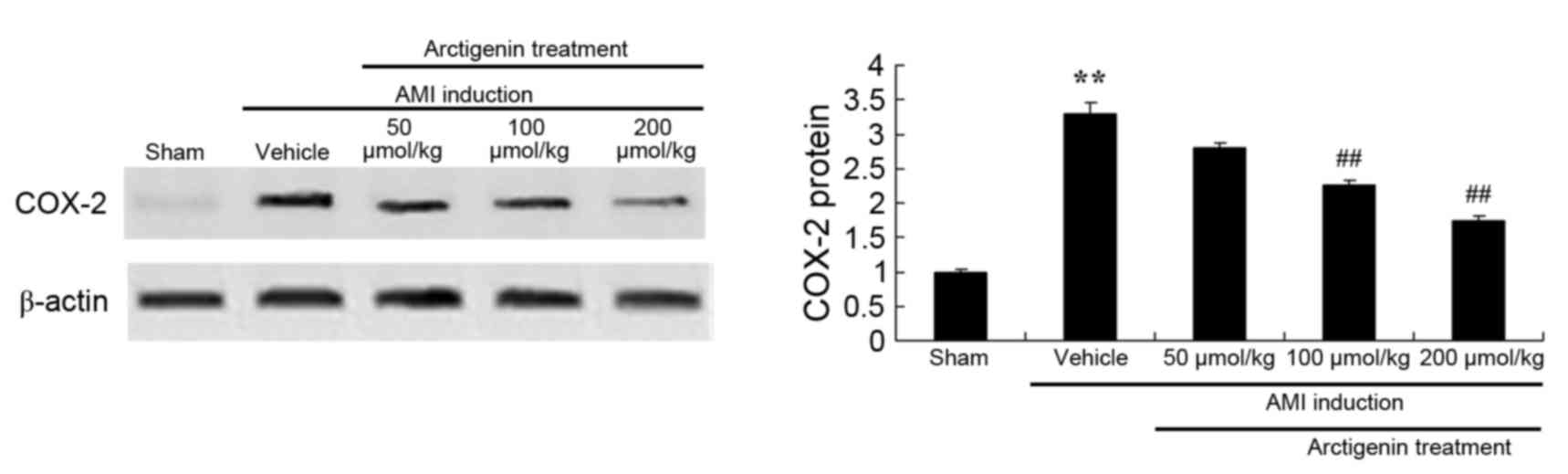
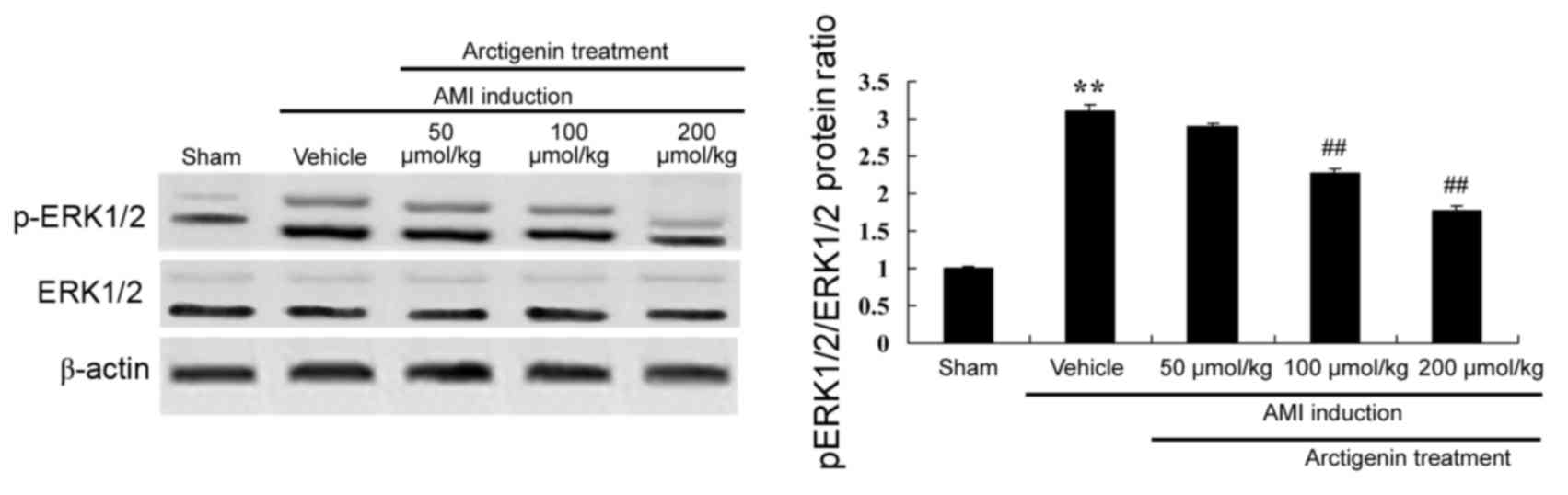
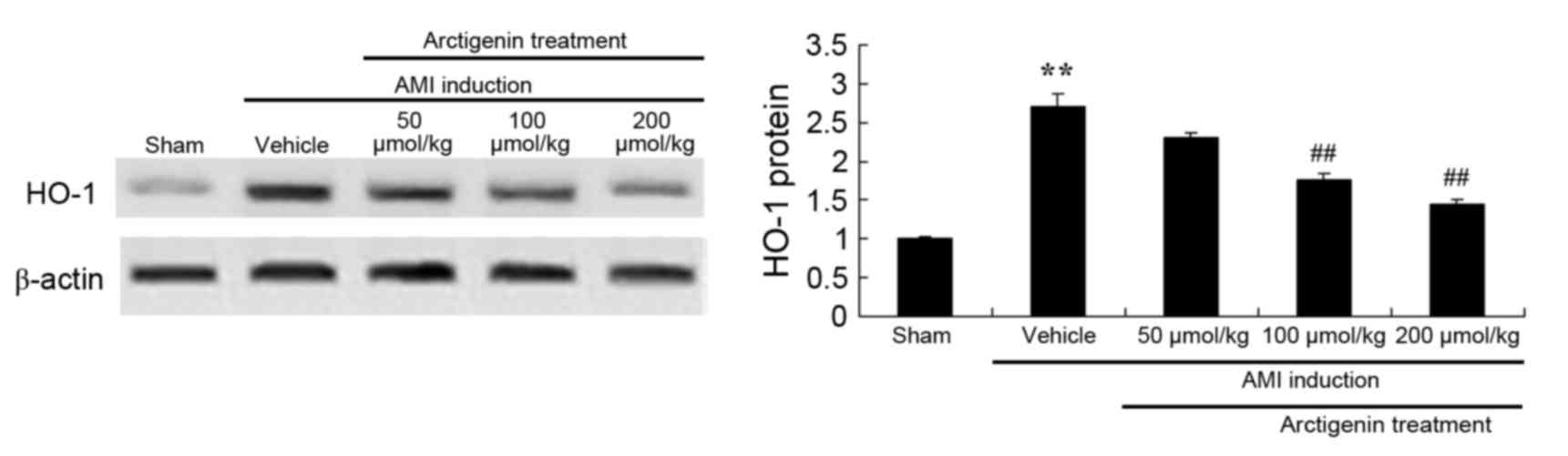
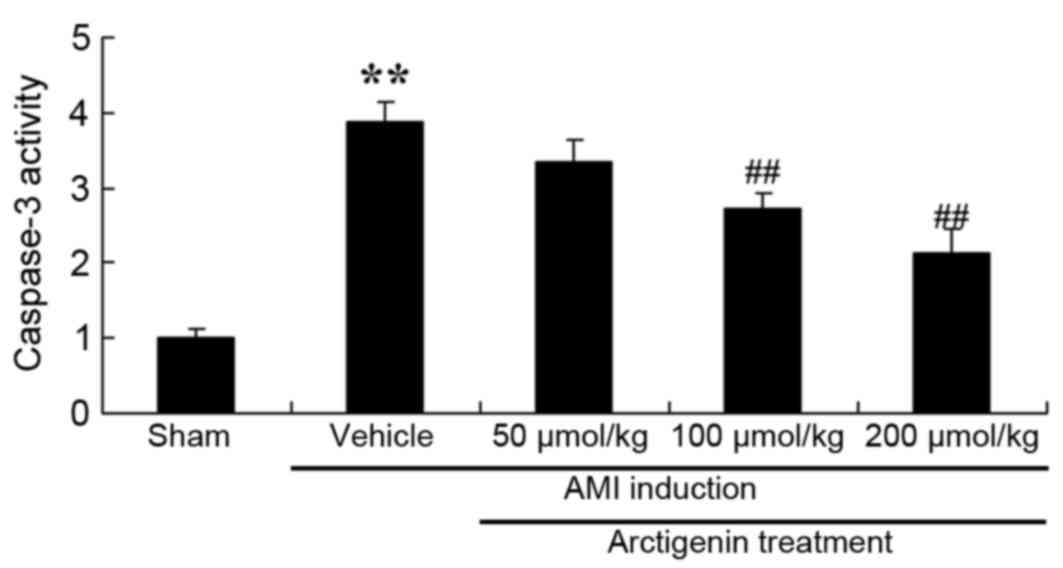
|
1
|
Voors AA, von Haehling S, Anker SD,
Hillege HL, Struck J, Hartmann O, Bergmann A, Squire I, van
Veldhuisen DJ and Dickstein K; OPTIMAAL Investigators, : C-terminal
provasopressin (copeptin) is a strong prognostic marker in patients
with heart failure after an acute myocardial infarction: Results
from the OPTIMAAL study. Eur Heart J. 30:1187–1194. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wijnbergen I, Tijssen J, van't Veer M,
Michels R and Pijls NH: Gender differences in long-term outcome
after primary percutaneous intervention for ST-segment elevation
myocardial infarction. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 82:379–384.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Young JJ, Cox DA, Stuckey T, Babb J, Turco
M, Lansky AJ, Mehran R and Stone GW: Prospective, multicenter study
of thrombectomy in patients with acute myocardial infarction: The
X-Tract AMI registry. J Interv Cardiol. 20:44–50. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Baird SH, Menown IB, McBride SJ, Trouton
TG and Wilson C: Randomized comparison of enoxaparin with
unfractionated heparin following fibrinolytic therapy for acute
myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 23:627–632. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhu XY, Zhang ZL, Li P, Liang WY, Feng XR
and Liu ML: Shenyuan, an extract of American Ginseng and Corydalis
tuber formula, attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition of
endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in a porcine
model of acute myocardial infarction. J Ethnopharmacol.
150:672–681. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ghyasi R, Sepehri G, Mohammadi M,
Badalzadeh R and Ghyasi A: Effect of mebudipine on oxidative stress
and lipid peroxidation in myocardial ischemic-reperfusion injury in
male rat. J Res Med Sci. 17:1150–1155. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C,
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E and Cerretani D: Cardiac oxidative stress
and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:26–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie N, Zhang W, Li J, Liang H, Zhou H,
Duan W, Xu X, Yu S, Zhang H and Yi D: alpha-Linolenic acid intake
attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through
anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress effects in diabetic but
not normal rats. Arch Med Res. 42:171–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Wang Z, Chen H, Chen Z and Tian
Y: Antioxidants: Potential antiviral agents for Japanese
encephalitis virus infection. Int J Infect Dis. 24:30–36. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shin HS, Jung SY, Back SY, Do JR and Shon
DH: Arctigenin from fructus arctii (Seed of Burdock) reinforces
intestinal barrier function in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2015:3681052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang WZ, Jiang ZK, He BX and Liu XB:
Arctigenin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary
oxidative stress and inflammation in a mouse model via suppression
of MAPK, HO-1, and iNOS signaling. Inflammation. 38:1406–1414.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan T, Jiang WL, Zhu J and Feng Zhang Y:
Arctigenin protects focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats
through inhibiting neuroinflammation. Biol Pharm Bull.
35:2004–2009. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu F, Ming Q and Hou L: The effect of sex
counselling in the sexual activity of acute myocardial infarction
patients after primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Acta
Cardiol. 70:460–464. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Limalanathan S, Andersen GO, Klow NE,
Abdelnoor M, Hoffmann P and Eritsland J: Effect of ischemic
postconditioning on infarct size in patients with ST-elevation
myocardial infarction treated by primary PCI results of the POSTEMI
(POstconditioning in ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction) randomized
trial. J Am Heart Assoc. 3:e0006792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Palmerini T, Brener SJ, Mehran R, Dangas
G, Genereux P, Riva DD, Mariani A, Xu K and Stone GW: Leukocyte
count is a modulating factor for the mortality benefit of
bivalirudin in ST-segment-elevation acute myocardial infarction:
The HORIZONS-AMI trial. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 6:518–526. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Palmerini T, Brener SJ, Genereux P,
Maehara A, Della Riva D, Mariani A, Witzenbichler B, Godlewski J,
Parise H, Dambrink JH, et al: Relation between white blood cell
count and final infarct size in patients with ST-segment elevation
acute myocardial infarction undergoing primary percutaneous
coronary intervention (from the INFUSE AMI trial). Am J Cardiol.
112:1860–1866. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Wang Y, Jiang M, Zhu Y, Hu L, Fan
G, Wang Y, Li X and Gao X: Differential cardioprotective effects of
salvianolic acid and tanshinone on acute myocardial infarction are
mediated by unique signaling pathways. J Ethnopharmacol.
135:662–671. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bagatini MD, Martins CC, Battisti V,
Gasparetto D, da Rosa CS, Spanevello RM, Ahmed M, Schmatz R,
Schetinger MR and Morsch VM: Oxidative stress versus antioxidant
defenses in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Heart
Vessels. 26:55–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lorgis L, Zeller M, Dentan G, Sicard P,
Richard C, Buffet P, L'Huillier I, Beer JC, Cottin Y, Rochette L,
et al: The free oxygen radicals test (FORT) to assess circulating
oxidative stress in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Atherosclerosis. 213:616–621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kou X, Qi S, Dai W, Luo L and Yin Z:
Arctigenin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS expression in
RAW264.7 cells through suppressing JAK-STAT signal pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 11:1095–1102. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Abe Y, Ito K, Hao K, Shindo T, Ogata T,
Kagaya Y, Kurosawa R, Nishimiya K, Satoh K, Miyata S, et al:
Extracorporeal low-energy shock-wave therapy exerts
anti-inflammatory effects in a rat model of acute myocardial
infarction. Circ J. 78:2915–2925. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
White DA, Fang L, Chan W, Morand EF,
Kiriazis H, Duffy SJ, Taylor AJ, Dart AM, Du XJ and Gao XM:
Pro-inflammatory action of MIF in acute myocardial infarction via
activation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PLoS One.
8:e762062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oliveira NL, Ribeiro F, Silva G, Alves AJ,
Silva N, Guimaraes JT, Teixeira M and Oliveira J: Effect of
exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation on arterial stiffness and
inflammatory and endothelial dysfunction biomarkers: A randomized
controlled trial of myocardial infarction patients.
Atherosclerosis. 239:150–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ammirati E, Cannistraci CV, Cristell NA,
Vecchio V, Palini AG, Tornvall P, Paganoni AM, Miendlarzewska EA,
Sangalli LM, Monello A, et al: Identification and predictive value
of interleukin-6+ interleukin-10+ and interleukin-6-interleukin-10+
cytokine patterns in ST-elevation acute myocardial infarction. Circ
Res. 111:1336–1348. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Monu SR, Pesce P, Sodhi K, Boldrin M, Puri
N, Fedorova L, Sacerdoti D, Peterson SJ, Abraham NG and Kappas A:
HO-1 induction improves the type-1 cardiorenal syndrome in mice
with impaired angiotensin II-induced lymphocyte activation.
Hypertension. 62:310–316. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng B, Lin G, Ren X, Zhang Y and Chen H:
Over-expression of HO-1 on mesenchymal stem cells promotes
angiogenesis and improves myocardial function in infarcted
myocardium. J Biomed Sci. 17:802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Czibik G, Derumeaux G, Sawaki D, Valen G
and Motterlini R: Heme oxygenase-1: An emerging therapeutic target
to curb cardiac pathology. Basic Res Cardiol. 109:4502014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shu T, Zeng B, Ren X and Li Y: HO-1
modified mesenchymal stem cells modulate MMPs/TIMPs system and
adverse remodeling in infarcted myocardium. Tissue Cell.
42:217–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carnieto A Jr, Dourado PM, Luz PL and
Chagas AC: Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition protects against
myocardial damage in experimental acute ischemia. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 64:245–252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vaithianathan R, Hockey PM, Moore TJ and
Bates DW: Iatrogenic effects of COX-2 inhibitors in the US
population: Findings from the medical expenditure panel survey.
Drug Saf. 32:335–343. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma Y, Li H, Yue Z, Guo J, Xu S, Xu J, Jia
Y, Yu N, Zhang B, Liu S, et al: Cryptotanshinone attenuates cardiac
fibrosis via downregulation of COX-2, NOX-2, and NOX-4. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 64:28–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Davies NM, Smith GD, Windmeijer F and
Martin RM: COX-2 selective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and
risk of gastrointestinal tract complications and myocardial
infarction: An instrumental variable analysis. Epidemiology.
24:352–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Duan J, Yang Y, Liu H, Dou PC and Tan SY:
Osthole ameliorates acute myocardial infarction in rats by
decreasing the expression of inflammatory-related cytokines,
diminishing MMP-2 expression and activating p-ERK. Int J Mol Med.
37:207–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peake BF, Nicholson CK, Lambert JP, Hood
RL, Amin H, Amin S and Calvert JW: Hydrogen sulfide preconditions
the db/db diabetic mouse heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury
by activating Nrf2 signaling in an Erk-dependent manner. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 304:H1215–H1224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koizumi K and Nakajima H: Serotonin
induces the migration of PC12 cells via the serotonin receptor
6/cAMP/ERK pathway. Biomed Rep. 2:29–33. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Reid EA, Kristo G, Yoshimura Y,
Ballard-Croft C, Keith BJ, Mentzer RM Jr and Lasley RD: In vivo
adenosine receptor preconditioning reduces myocardial infarct size
via subcellular ERK signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
288:H2253–H2259. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li A, Wang J, Zhu D, Zhang X, Pan R and
Wang R: Arctigenin suppresses transforming growth
factor-beta1-induced expression of monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 and the subsequent epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through reactive oxygen species-dependent ERK/NF-kappaB signaling
pathway in renal tubular epithelial cells. Free Radic Res.
49:1095–1113. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|