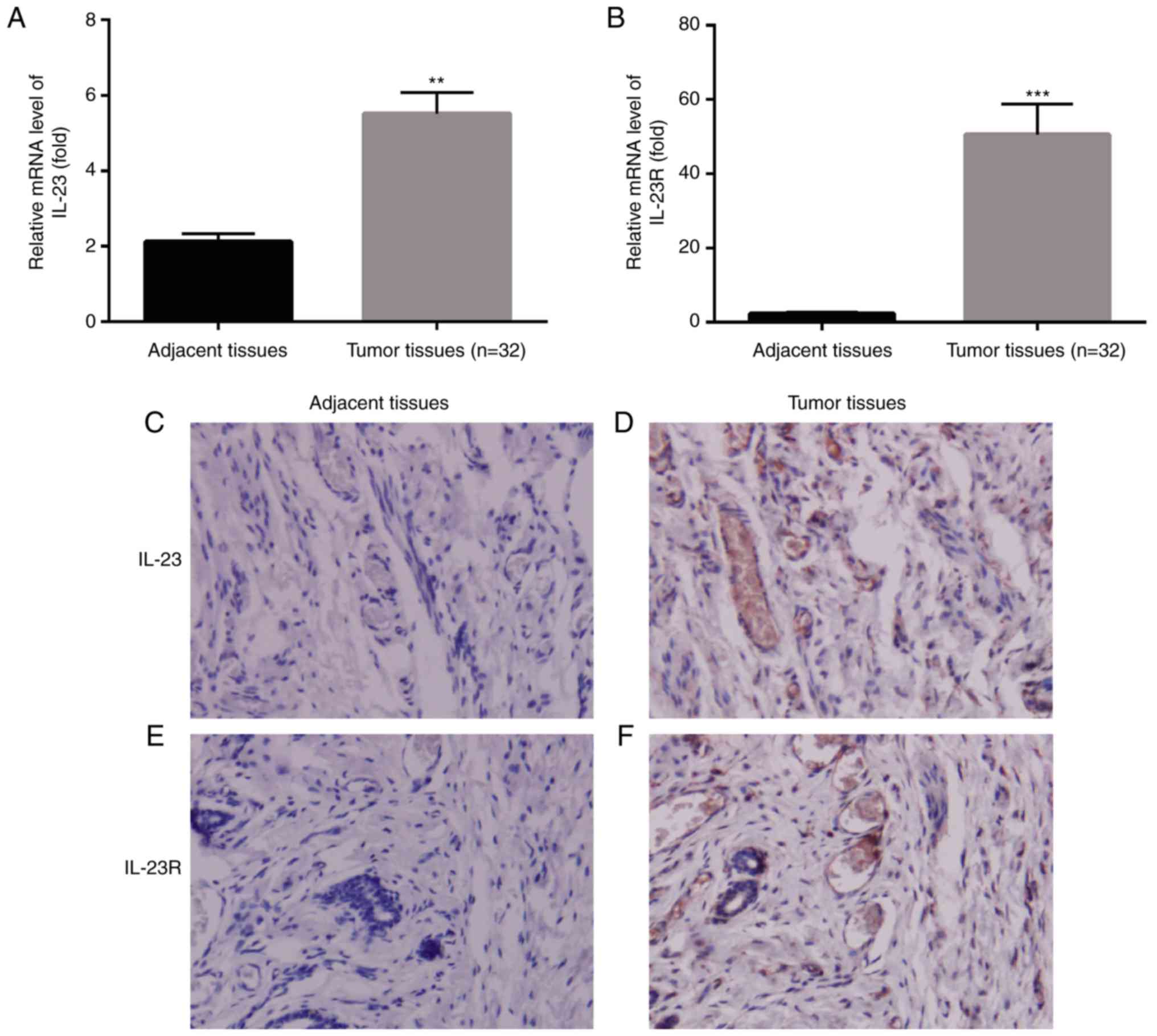
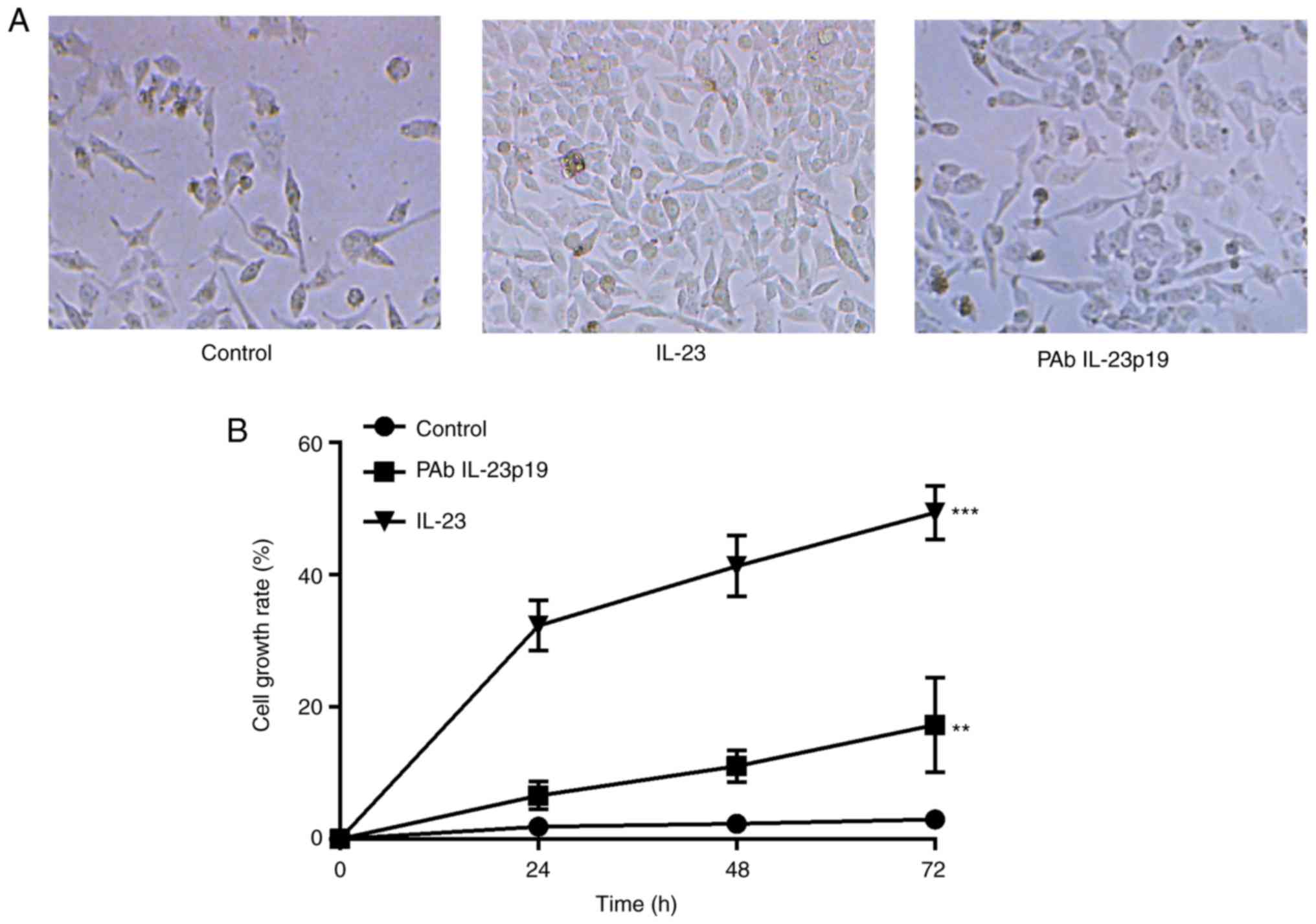
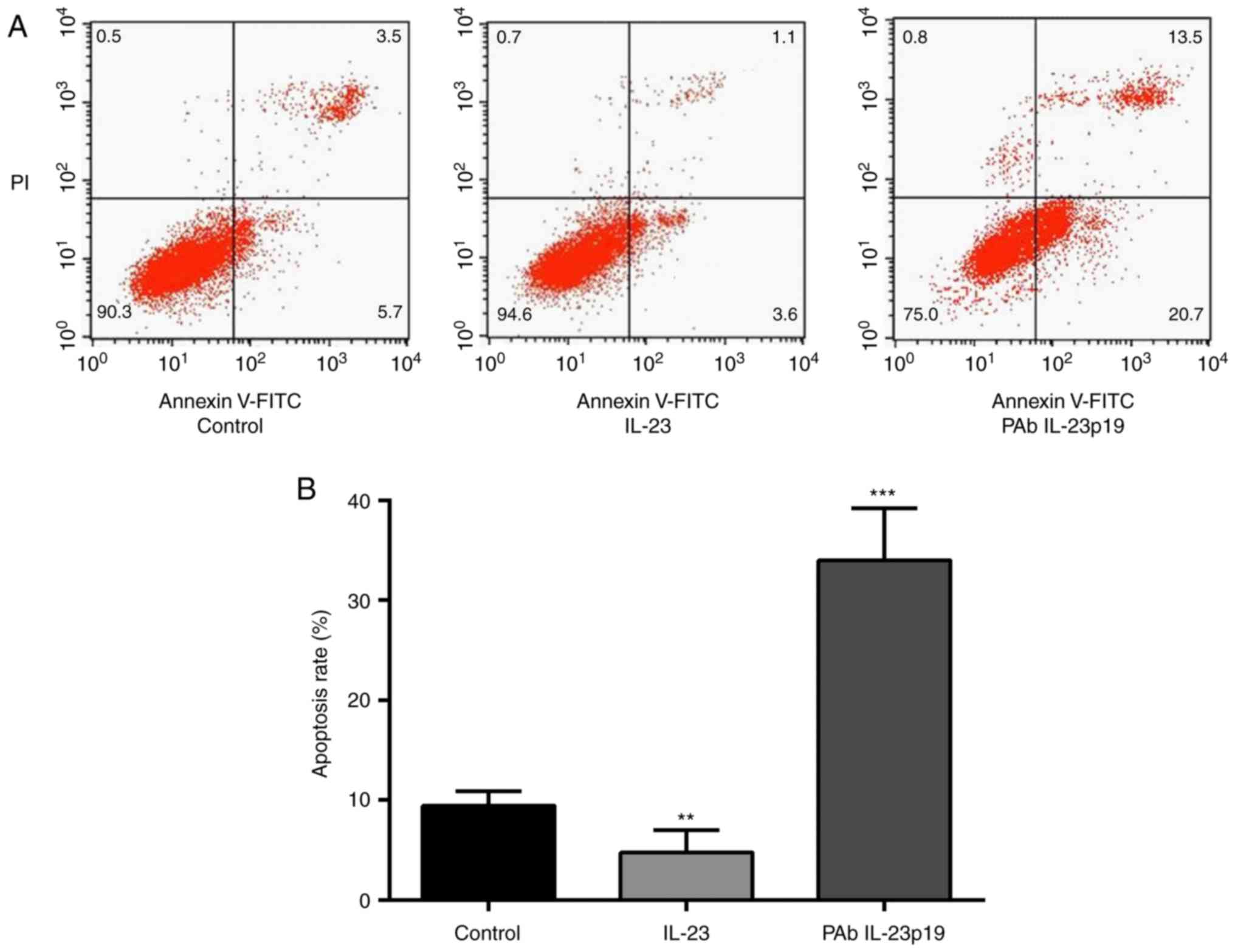
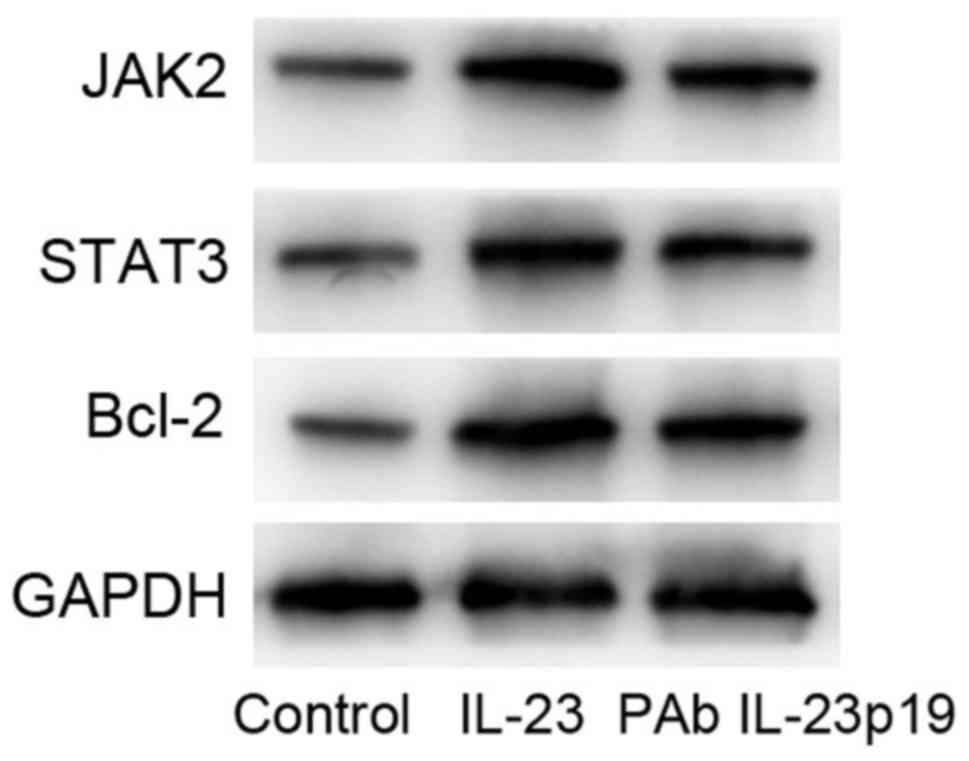
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cardoso F, Harbeck N, Barrios CH, Bergh J,
Cortés J, EI Saghir N, Francis PA, Hudis CA, Ohno S, Partridge AH,
et al: Research needs in breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 28:208–217.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ahern PP, Izcue A, Maloy KJ and Powrie F:
The interleukin-23 axis in intestinal inflammation. Immunol Rev.
226:147–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Langrish CL, Chen Y, Blumenschein WM,
Mattson J, Basham B, Sedgwick JD, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA and
Cua DJ: IL-23 drives a pathogenic T cell population that induces
autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 201:233–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL,
Pittman D, Wang F, Chamian F, Dhodapkar M and Krueger JG: Increased
expression of interleukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of
patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med. 199:125–130. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Z, Laurence A and O'Shea JJ: Signal
transduction pathways and transcriptional regulation in the control
of Th17 differentiation. Semin Immunol. 19:400–408. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Volpe E, Servant N, Zollinger R, Bogiatzi
SI, Hupé P, Barillot E and Soumelis V: A critical function for
transforming growth factorbeta, interleukin 23 and proinflammatory
cytokines in driving and modulating human T(H)-17 responses. Nat
Immunol. 9:650–657. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cho JH and Weaver CT: The genetics of
inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 133:1327–1339. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Le Gouvello S, Bastuji-Garin S, Aloulou N,
Mansour H, Chaumette MT, Berrehar F, Seikour A, Charachon A, Karoui
M, Leroy K, et al: High prevalence of Foxp3 and IL17 in MMR
proficient colorectal carcinomas. Gut. 57:772–779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Langowski JL, Zhang X, Wu L, Mattson JD,
Chen T, Smith K, Basham B, McClanahan T, Kastelein RA and Oft M:
IL-23 promotes tumor incidence and growth. Nature. 442:461–465.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Balkwill F and Mantovani A: Inflammation
and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet. 357:539–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fukuda M, Ehara M, Suzuki S and Sakashita
H: Expression of interleukin-23 and its receptors in human squamous
cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Mol Med Rep. 3:89–93.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gangemi S, Minciullo P, Adamo B, Franchina
T, Ricciardi GR, Ferraro M, Briguglio R, Toscano G, Saitta S and
Adamo V: Clinical significance of circulating interleukin-23 as a
prognostic factor in breast cancer patients. J Cell Biochem.
113:2122–2125. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Y, Liu Y, Pan S, Liu L, Liu J, Zhai X,
Shen H and Hu Z: IL-23R polymorphisms, HBV infection and risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma in a high-risk Chinese population. J
Gastroenterol. 48:125–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Q, Zhou J, Zhang B, Tian Z, Tang J,
Zheng Y, Huang Z, Tian Y, Jia Z, Tang Y, et al: Hepatitis B virus
induces IL-23 production in antigen presenting cells and causes
liver damage via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. PLoS Pathog. 9:e10034102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Kortylewski M and Pardoll D:
Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: Role of STAT3 in the
tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:41–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Balkwill F, Charles KA and Mantovani A:
Smoldering and polarized inflammation in the initiation and
promotion of malignant disease. Cancer Cell. 7:211–217. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, Vaisberg E,
Travis M, Cheung J, Pflanz S, Zhang R, Singh KP, Vega F, et al: A
receptor for the heterodi-meric cytokine IL-23 is composed of
IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J
Immunol. 168:5699–5708. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aaronson DS and Horvath CM: A road map for
those who don't know JAK-STAT. Science. 296:1653–1655. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hebenstreit D, Horejs-Hoeck J and Duschl
A: JAK/STAT-dependent gene regulation by cytokines. Drug News
Perspect. 18:243–249. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marotta LL, Almendro V, Marusyk A,
Shipitsin M, Schemme J, Walker SR, Bloushtain-Qimron N, Kim JJ,
Choudhury SA, Maruyama R, et al: The JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway
is required for growth of CD44+CD24 stem cell-like
breast cancer cells in human tumors. J Clin Invest. 121:2723–2735.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hennessy BT, Gonzalez-Angulo AM,
Stemke-Hale K, Gilcrease MZ, Krishnamurthy S, Lee JS, Fridlyand J,
Sahin A, Agarwal R, Joy C, et al: Characterization of a naturally
occurring breast cancer subset enriched in
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell characteristics.
Cancer Res. 69:4116–4124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|