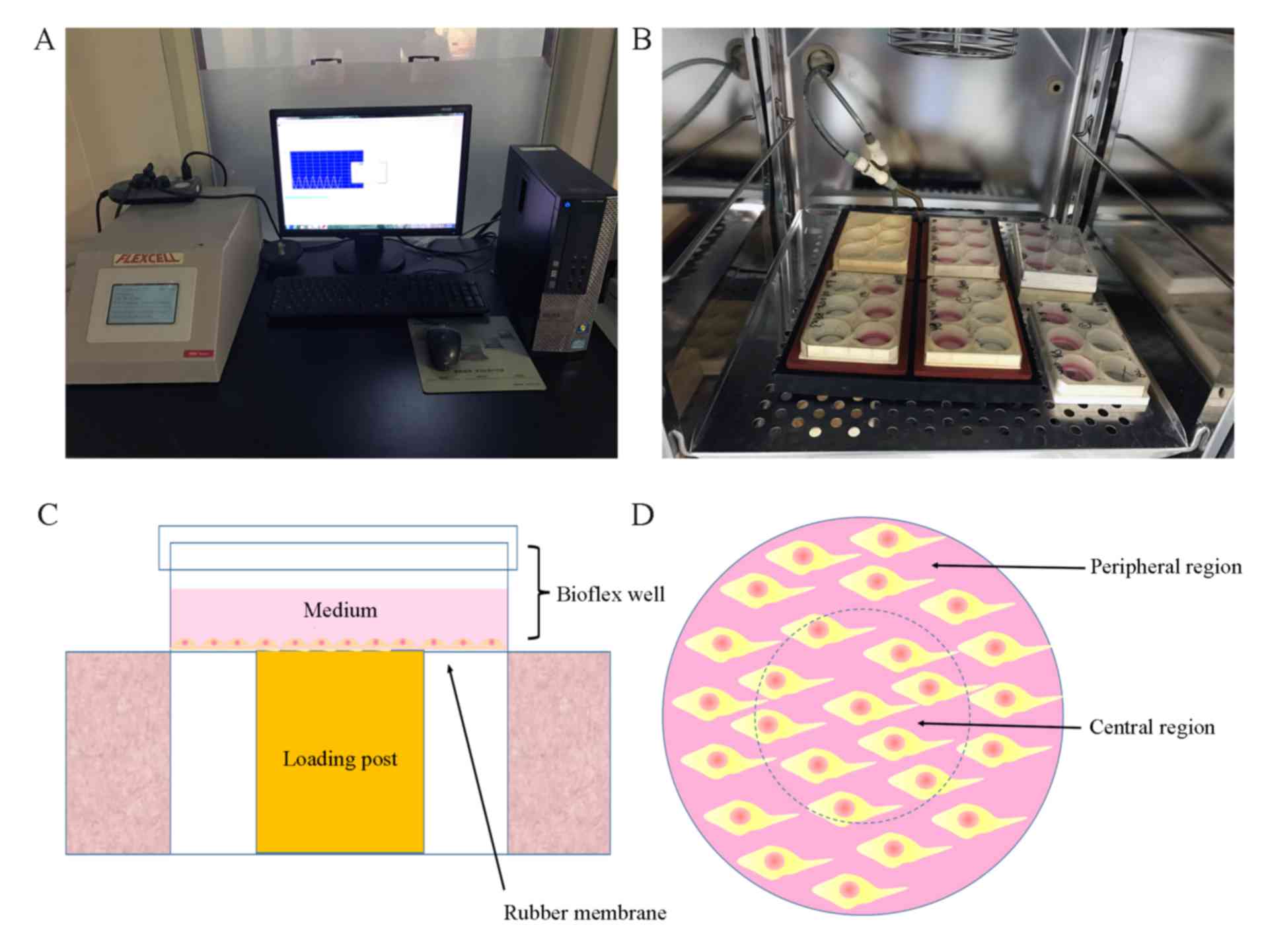
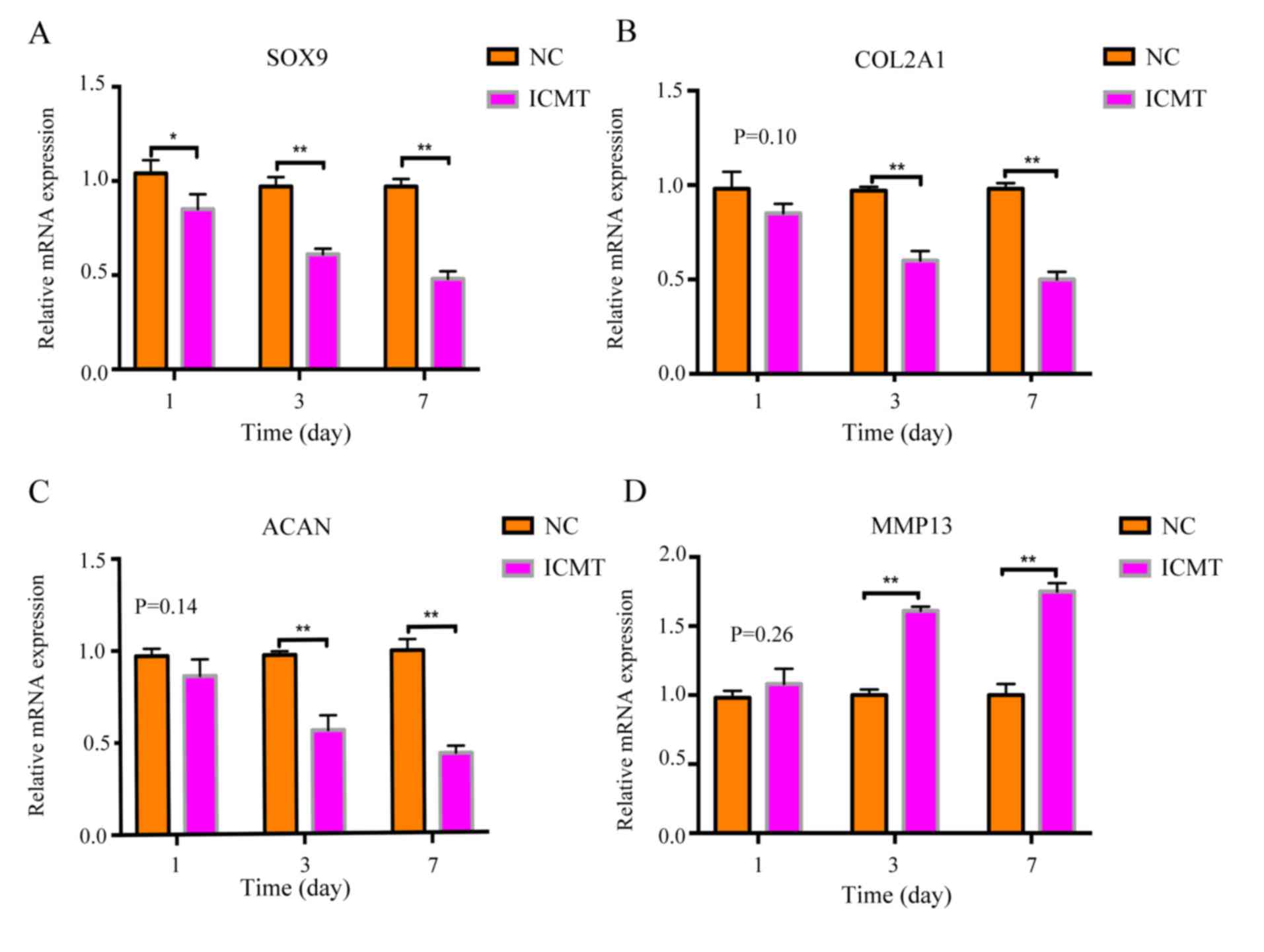
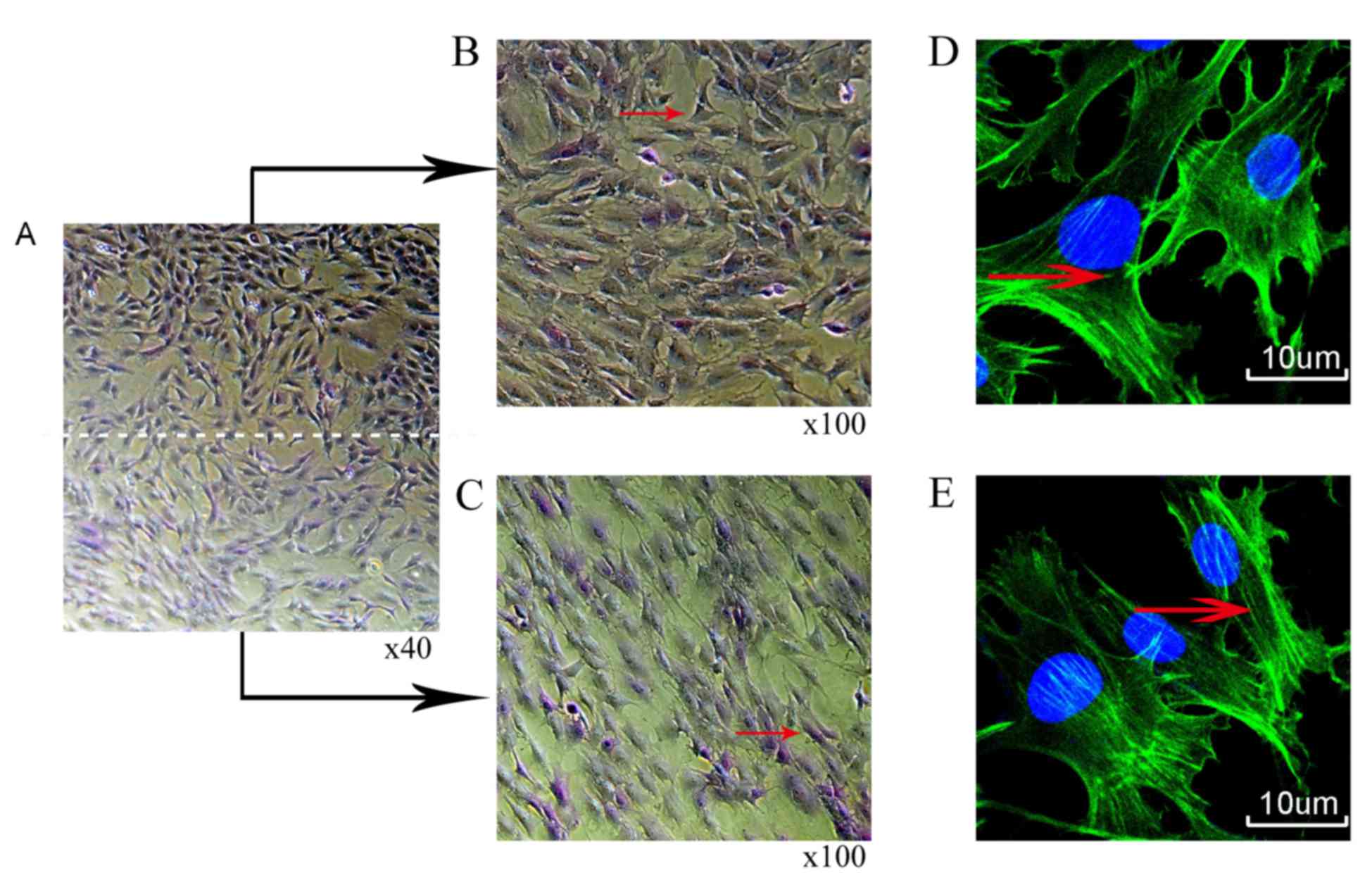
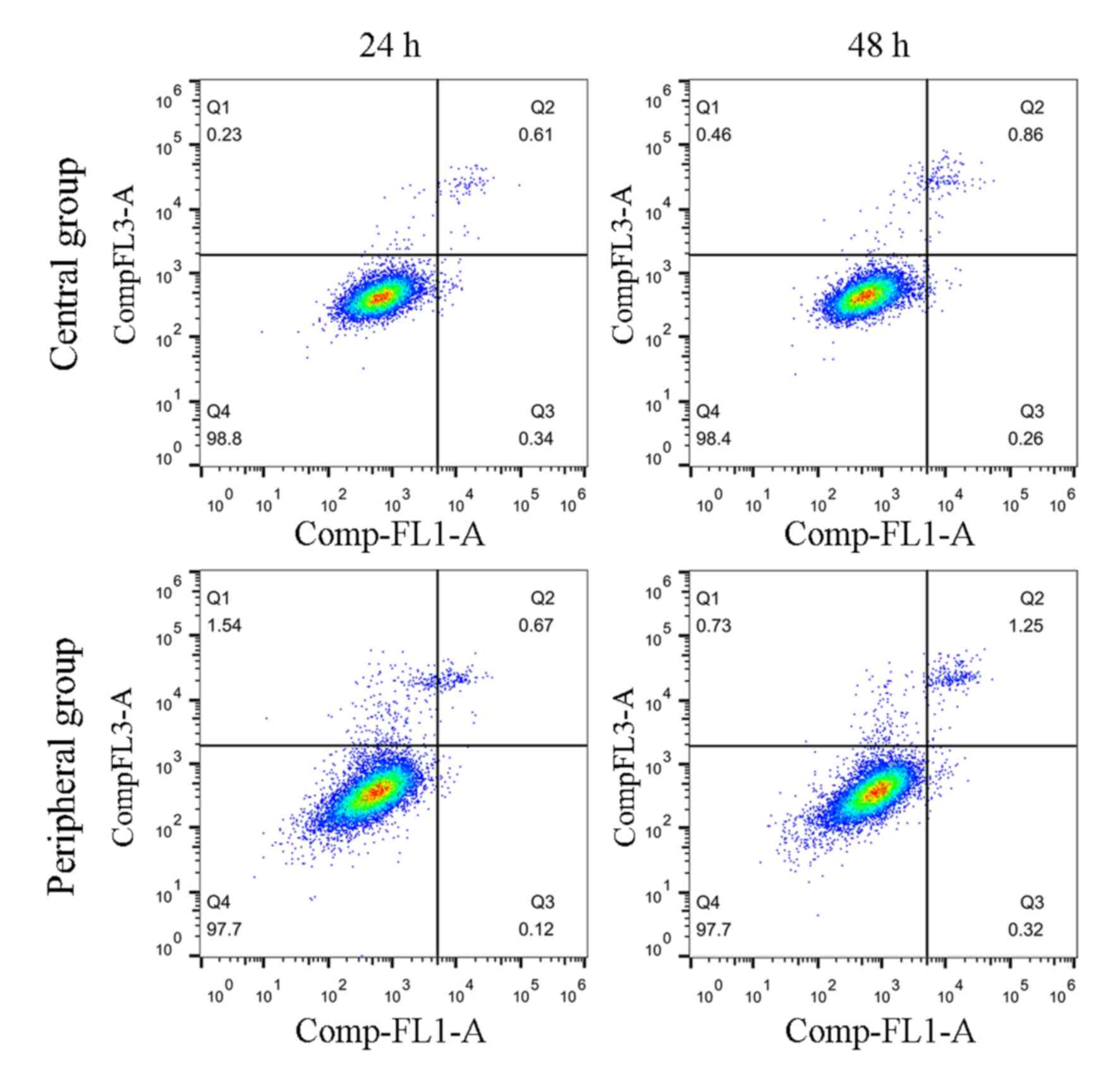
|
1
|
Manek NJ and MacGregor AJ: Epidemiology of
back disorders: Prevalence, risk factors, and prognosis. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 17:134–140. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodriguez AG, Rodriguez-Soto AE, Burghardt
AJ, Berven S, Majumdar S and Lotz JC: Morphology of the human
vertebral endplate. J Orthop Res. 30:280–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walter BA, Korecki CL, Purmessur D,
Roughley PJ, Michalek AJ and Iatridis JC: Complex loading affects
intervertebral disc mechanics and biology. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 19:1011–1018. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS,
Hoogendoorn RJ, Welting TJ, van Royen BJ, van Dieën JH and Smit TH:
Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: A
vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 23:1057–1070. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu HG, Yu YF, Zheng Q, Zhang W, Wang CD,
Zhao XY, Tong WX, Wang H, Liu P and Zhang XL: Autophagy protects
end plate chondrocytes from intermittent cyclic mechanical tension
induced calcification. Bone. 66:232–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pan J, Wang T, Wang L, Chen W and Song M:
Cyclic strain-induced cytoskeletal rearrangement of human
periodontal ligament cells via the Rho signaling pathway. PLoS One.
9:e915802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu HG, Ma MM, Zheng Q, Shen X, Wang H,
Zhang SF, Xu JJ, Wang CD and Zhang XL: P120-catenin protects
endplate chondrocytes from intermittent cyclic mechanical tension
induced degeneration by inhibiting the expression of RhoA/ROCK-1
signaling pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:1261–1271. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang J, Wang CD, Zhang N, Tong WX, Zhang
YF, Shan SZ, Zhang XL and Li QF: Mechanical stimulation
orchestrates the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow
stromal cells by regulating HDAC1. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22212016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang R, Mao P, Fu W, Pang XQ, Wang YY,
Yang C, He WQ, Liu XQ and Li YM: Effects of cyclic stretch on the
induction of the transdifferentiation in human lung epithelial
cells. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 25:455–459. 2013.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Witt F, Duda GN, Bergmann C and Petersen
A: Cyclic mechanical loading enables solute transport and oxygen
supply in bone healing: An in vitro investigation. Tissue Eng Part
A. 20:486–493. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu HG, Hu CJ, Wang H, Liu P, Yang XM,
Zhang Y and Wang LT: Effects of mechanical strain on ANK, ENPP1 and
TGF-β1 expression in rat endplate chondrocytes in vitro. Mol Med
Rep. 4:831–835. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ferguson SJ and Steffen T: Biomechanics of
the aging spine. Eur Spine J. 12 Suppl 2:S97–S103. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alkhatib B, Rosenzweig DH, Krock E,
Roughley PJ, Beckman L, Steffen T, Weber MH, Ouellet JA and Haglund
L: Acute mechanical injury of the human intervertebral disc: Link
to degeneration and pain. Eur Cells Mater. 28:98–111. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sowa GA, Coelho JP, Vo NV, Pacek C,
Westrick E and Kang JD: Cells from degenerative intervertebral
discs demonstrate unfavorable responses to mechanical and
inflammatory stimuli: A pilot study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil.
91:846–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bruckner P and van der Rest M: Structure
and function of cartilage collagens. Microsc Res Tech. 28:378–384.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu HG, Zheng Q, Song JX, Li J, Wang H, Liu
P, Wang J, Wang CD and Zhang XL: Intermittent cyclic mechanical
tension promotes endplate cartilage degeneration via canonical Wnt
signaling pathway and E-cadherin/β-catenin complex cross-talk.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:158–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Benya PD, Brown PD and Padilla SR:
Microfilament modification by dihydrocytochalasin B causes retinoic
acid-modulated chondrocytes to reexpress the differentiated
collagen phenotype without a change in shape. J Cell Biol.
106:161–170. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guilak F: Compression-induced changes in
the shape and volume of the chondrocyte nucleus. J Biomech.
28:1529–1541. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li S, Jia X, Duance VC and Blain EJ: The
effects of cyclic tensile strain on the organisation and expression
of cytoskeletal elements in bovine intervertebral disc cells: An in
vitro study. Eur Cell Mater. 21:508–522. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nofal GA and Knudson CB: Latrunculin and
cytochalasin decrease chondrocyte matrix retention. J Histochem
Cytochem. 50:1313–1324. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|