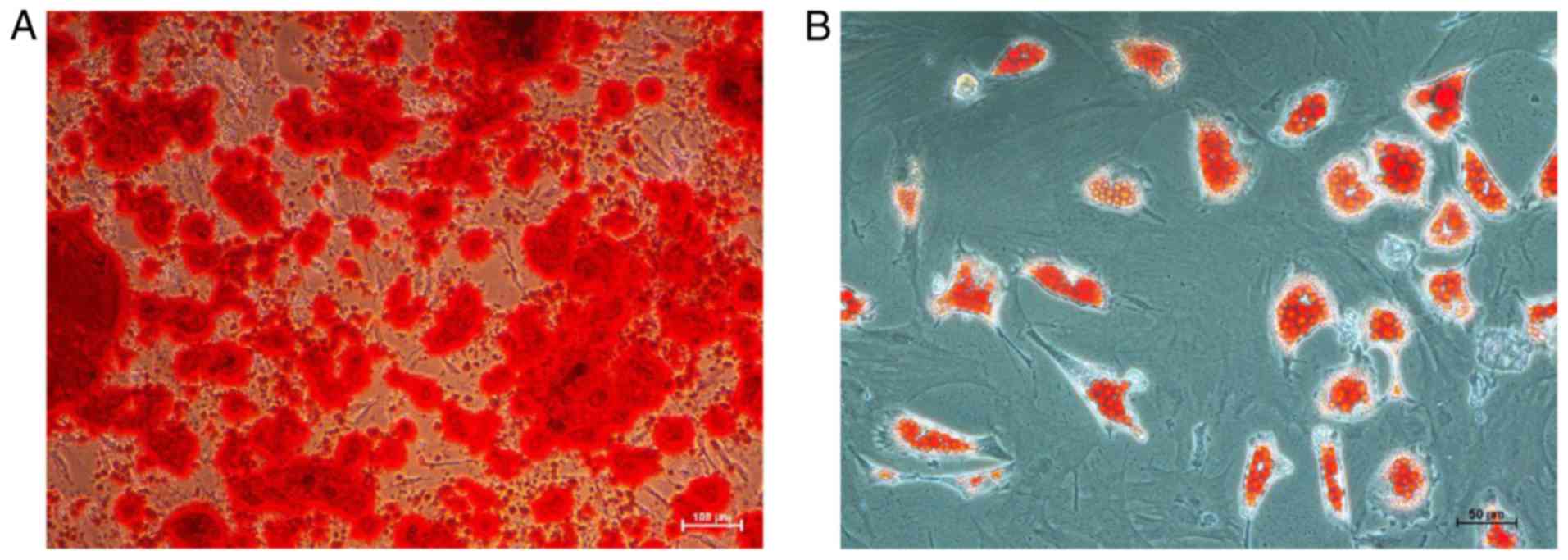
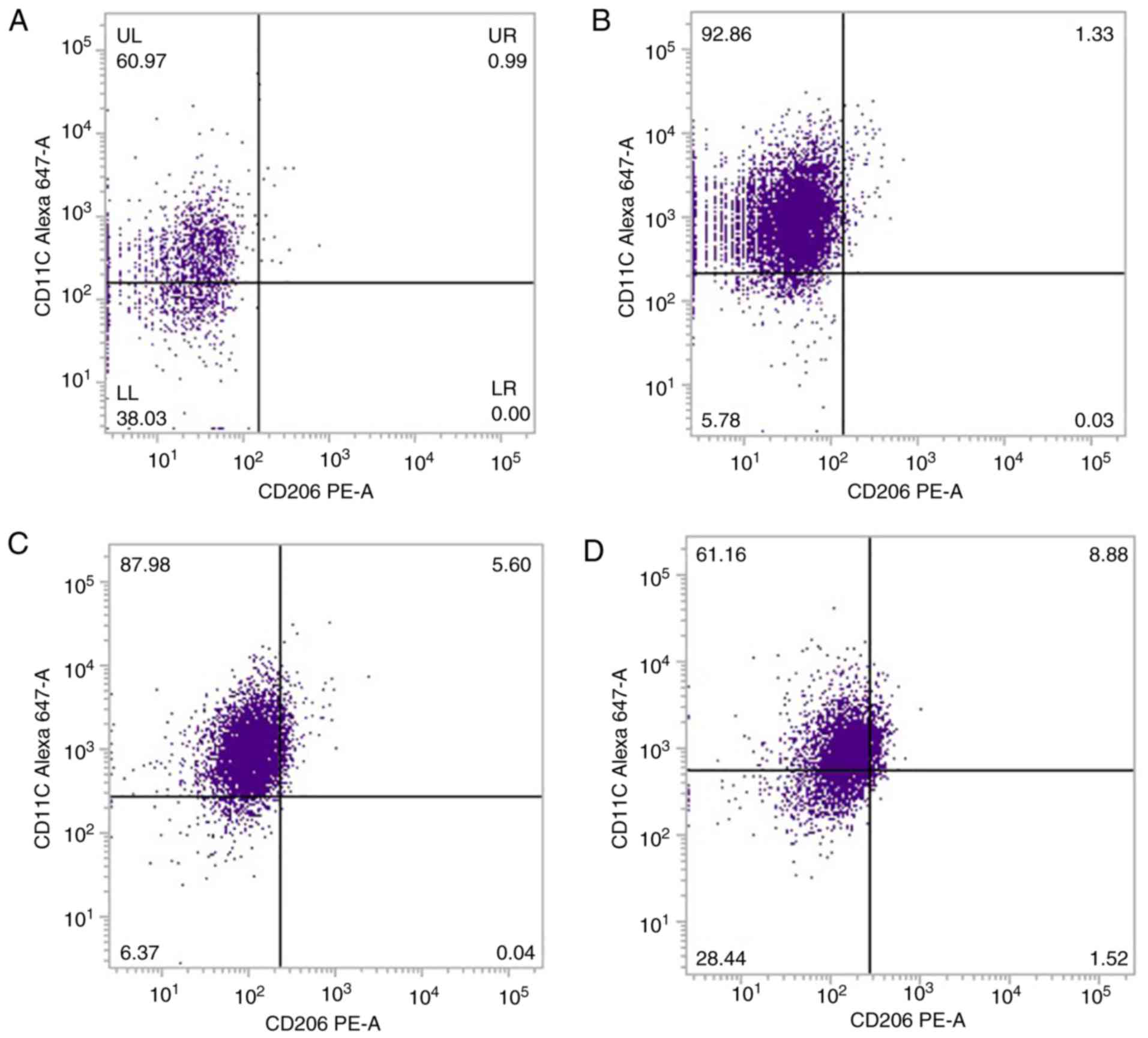
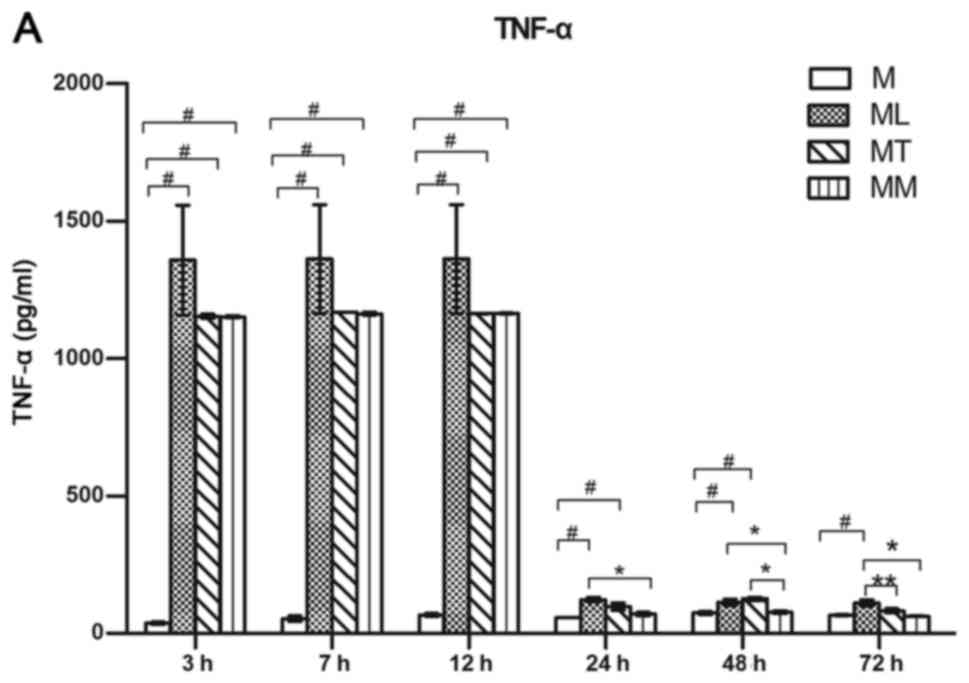
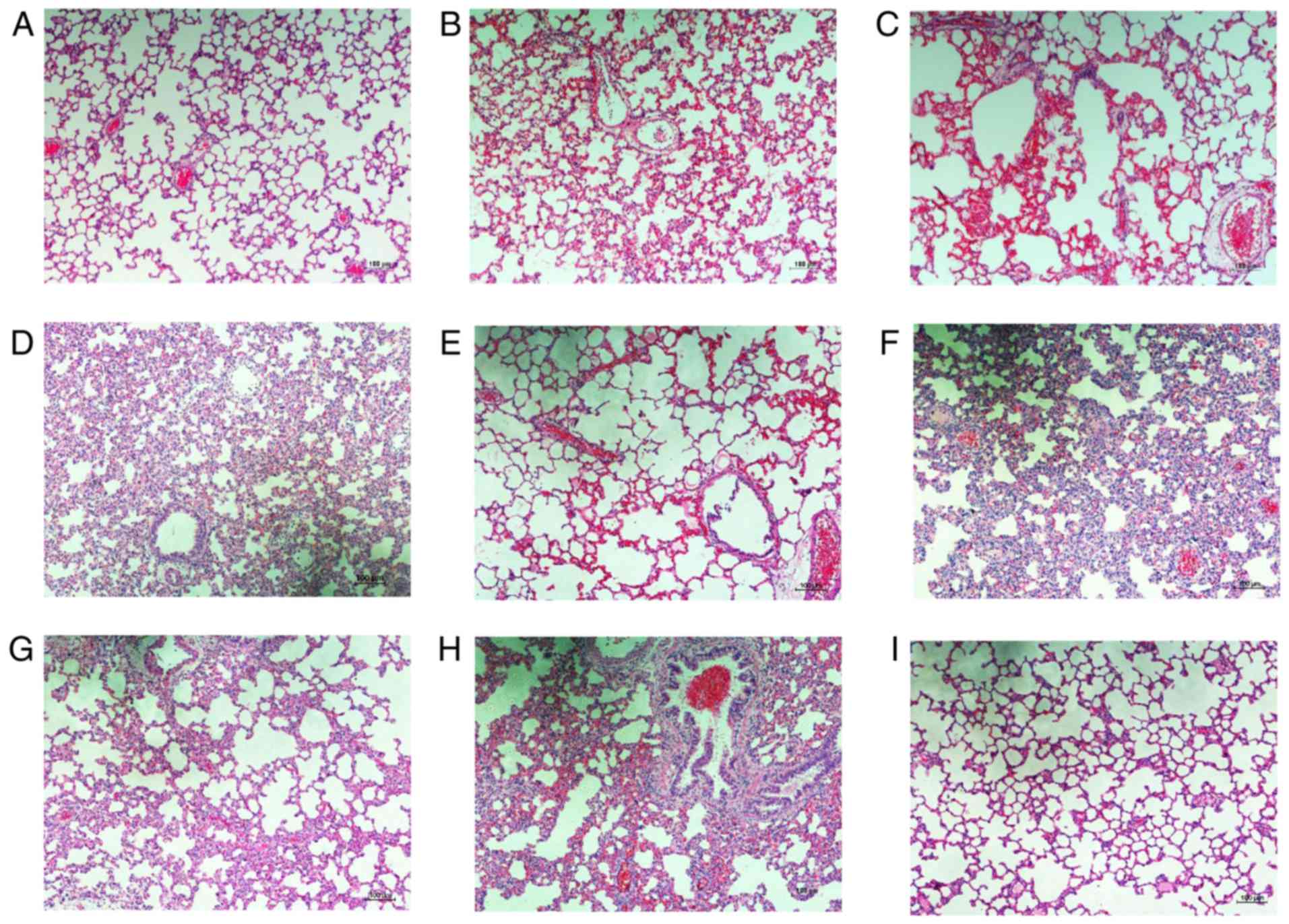
|
1
|
Annane D, Bellissant E and Cavaillon JM:
Septic shock. Lancet. 365:63–78. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). Jama.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cohen J, Vincent JL, Adhikari NK, Machado
FR, Angus DC, Calandra T, Jaton K, Giulieri S, Delaloye J, Opal S,
et al: Sepsis: A roadmap for future research. Lancet Infect Dis.
15:581–614. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seymour CW, Rea TD, Kahn JM, Walkey AJ,
Yealy DM and Angus DC: Severe sepsis in pre-hospital emergency
care: Analysis of incidence, care and outcome. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 186:1264–1271. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wynn TA, Chawla A and Pollard JW:
Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature.
496:445–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Goncalves R and Mosser DM: The
isolation and characterization of murine macrophages. Curr Protoc
Immunol. 14Unit 14.1. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ying W, Cheruku PS, Bazer FW, Safe SH and
Zhou B: Investigation of macrophage polarization using bone marrow
derived macrophages. J Vis Exp. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ivashkiv LB: Epigenetic regulation of
macrophage polarization and function. Trends Immunol. 34:216–223.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ka MB, Daumas A, Textoris J and Mege JL:
Phenotypic diversity and emerging new tools to study macrophage
activation in bacterial infectious diseases. Front Immunol.
5:5002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
López-Bojórquez LN, Dehesa AZ and
Reyes-Terán G: Molecular mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of
septic shock. Arch Med Res. 35:465–479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu LL, Gong LK, Wang H, Xiao Y, Wu XF,
Zhang YH, Xue X, Qi XM and Ren J: Baicalin inhibits macrophage
activation by lipopolysaccharide and protects mice from endotoxin
shock. Biochem Pharmacol. 75:914–922. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Simovart HE, Põldoja E, Kokk K, Tapfer H,
Liigant A, Talvik R and Roosaar P: Changes of activated macrophages
and apoptotic cell count in the organs of rats during experimental
sepsis. Medicina (Kaunas). 39:932–939. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Prockop DJ and Oh JY: Mesenchymal
stem/stromal cells (MSCs): Role as guardians of inflammation. Mol
Ther. 20:14–20. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Soleimani M and Nadri S: A protocol for
isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse bone
marrow. Nat Protoc. 4:102–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin HJ, Bae YK, Kim M, Kwon SJ, Jeon HB,
Choi SJ, Kim SW, Yang YS, Oh W and Chang JW: Comparative analysis
of human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, adipose tissue,
and umbilical cord blood as sources of cell therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
14:17986–18001. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang QZ, Su WR, Shi SH, Wilder-Smith P,
Xiang AP, Wong A, Nguyen AL, Kwon CW and Le AD: Human
gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2
macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells.
28:1856–1868. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wise AF, Williams TM, Kiewiet MB, Payne
NL, Siatskas C, Samuel CS and Ricardo SD: Human mesenchymal stem
cells alter macrophage phenotype and promote regeneration via
homing to the kidney following ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 306:F1222–F1235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Geng Y, Zhang L, Fu B, Zhang J, Hong Q, Hu
J, Li D, Luo C, Cui S, Zhu F and Chen X: Mesenchymal stem cells
ameliorate rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury via the
activation of M2 macrophages. Stem Cell Res Ther. 5:802014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao S, Mao F, Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang X,
Wang M, Yan Y, Yang T, Zhang J, Zhu W, et al: Mouse bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce macrophage M2
polarization through the nuclear factor-κB and signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
239:366–375. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ray A and Dittel BN: Isolation of mouse
peritoneal cavity cells. J Vis Exp. 28:pii: 14882010.
|
|
21
|
Chai X, Guo Y, Jiang M, Hu B, Li Z, Fan J,
Deng M, Billiar TR, Kucera HR, Gaikwad NW, et al: Oestrogen
sulfotransferase ablation sensitizes mice to sepsis. Nat Commun.
6:79792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zheng G, Ge M, Qiu G, Shu Q and Xu J:
Mesenchymal stromal cells affect disease outcomes via macrophage
polarization. Stem Cells Int. 2015:9894732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim J and Hematti P: Mesenchymal stem
cell-educated macrophages: A novel type of alternatively activated
macrophages. Exp Hematol. 37:1445–1453. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee JW, Gupta N, Serikov V and Matthay MA:
Potential application of mesenchymal stem cells in acute lung
injury. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 9:1259–1270. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Murray PJ and Wynn TA: Obstacles and
opportunities for understanding macrophage polarization. J Leukoc
Biol. 89:557–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abumaree MH, Al Jumah MA, Kalionis B,
Jawdat D, Al Khaldi A, Abomaray FM, Fatani AS, Chamley LW and Knawy
BA: Human placental mesenchymal stem cells (pMSCs) play a role as
immune suppressive cells by shifting macrophage differentiation
from inflammatory M1 to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Stem Cell
Rev. 9:620–641. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mei SH, Haitsma JJ, Dos Santos CC, Deng Y,
Lai PF, Slutsky AS, Liles WC and Stewart DJ: Mesenchymal stem cells
reduce inflammation while enhancing bacterial clearance and
improving survival in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
182:1047–1057. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zenker S, Panteleev-Ivlev J, Wirtz S,
Kishimoto T, Waldner MJ, Ksionda O, Tybulewicz VLJ, Neurath MF and
Atreya I: A key regulatory role for Vav1 in controlling
lipopolysaccharide endotoxemia via macrophage-derived IL-6. J
Immunol. 192:2830–2836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Boomer JS, To K, Chang KC, Takasu O,
Osborne DF, Walton AH, Bricker TL, Jarman SD II, Kreisel D,
Krupnick AS, et al: Immunosuppression in patients who die of sepsis
and multiple organ failure. Jama. 306:2594–2605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fang SH, Hou YC, Chang WC, Hsiu SL, Lee
Chao PD and Chiang BL: Morin sulfates/glucuronides exert
anti-inflammatory activity on activated macrophages and decreased
the incidence of septic shock. Life Sci. 74:743–756. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ayala A, Elphick GF, Kim YS, Huang X,
Carreira-Rosario A, Santos SC, Shubin NJ, Chen Y, Reichner J and
Chung CS: Sepsis-induced potentiation of peritoneal macrophage
migration is mitigated by programmed cell death receptor-1 gene
deficiency. J Innate Immun. 6:325–338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oh JY, Ko JH, Lee HJ, Yu JM, Choi H, Kim
MK, Wee WR and Prockop DJ: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells inhibit
the NLRP3 inflammasome by decreasing mitochondrial reactive oxygen
species. Stem Cells. 32:1553–1563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gotts JE and Matthay MA: Mesenchymal stem
cells and acute lung injury. Crit Care Clin. 27:719–733. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao G, Miao H, Li X, Chen S, Hu Y, Wang Z
and Hou Y: TGF-beta3-induced miR-494 inhibits macrophage
polarization via suppressing PGE2 secretion in mesenchymal stem
cells. FEBS Lett. 590:1602–1613. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Luz-Crawford P, Djouad F, Toupet K, Bony
C, Franquesa M, Hoogduijn MJ, Jorgensen C and Noël D: Mesenchymal
stem cell-derived interleukin 1 receptor antagonist promotes
macrophage polarization and inhibits B cell differentiation. Stem
Cells. 34:483–492. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nemeth K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS,
Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller
BH, Brown JM, et al: Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via
prostaglandin E (2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to
increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 15:42–49. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhu YG, Feng XM, Abbott J, Fang XH, Hao Q,
Monsel A, Qu JM, Matthay MA and Lee JW: Human mesenchymal stem cell
microvesicles for treatment of Escherichia coli endotoxin-induced
acute lung injury in mice. Stem Cells. 32:116–125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Weil BR, Herrmann JL, Abarbanell AM,
Manukyan MC, Poynter JA and Meldrum DR: Intravenous infusion of
mesenchymal stem cells is associated with improved myocardial
function during endotoxemia. Shock. 36:235–241. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bernardo ME and Fibbe WE: Mesenchymal
stromal cells: Sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem
Cell. 13:392–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|