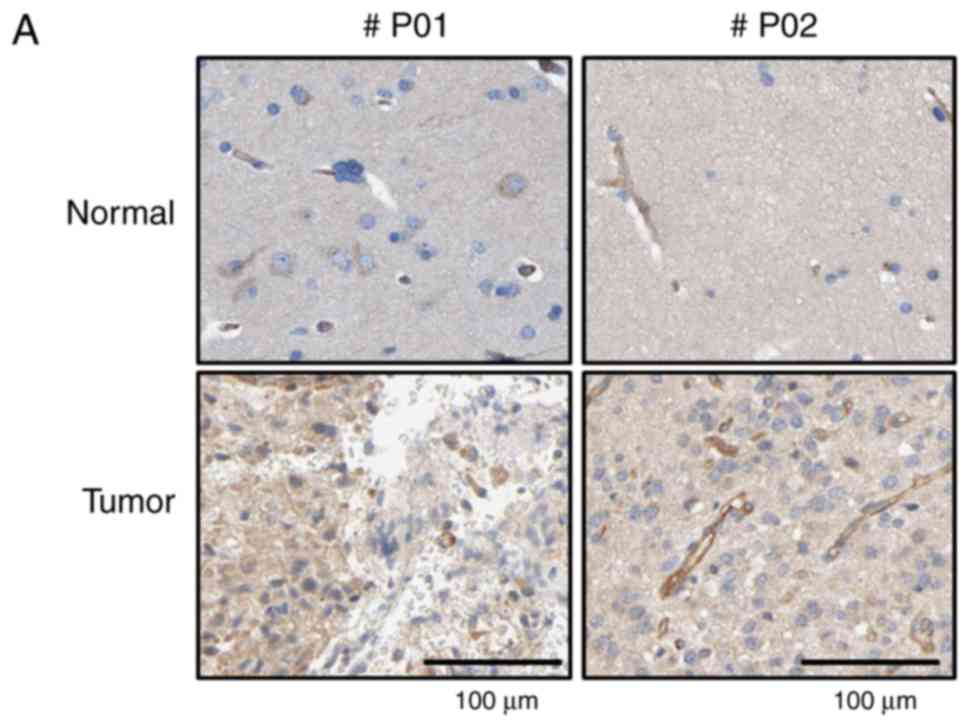
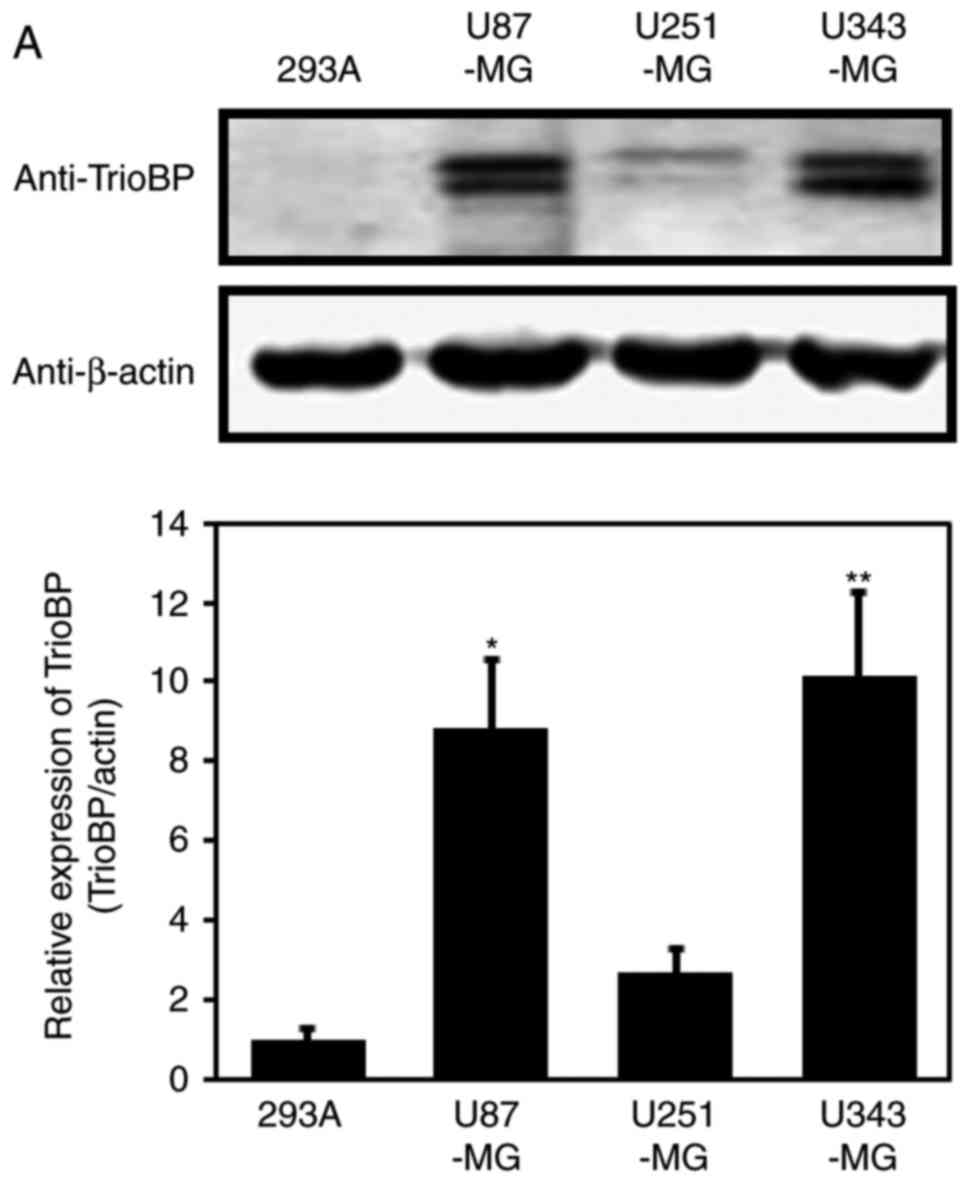
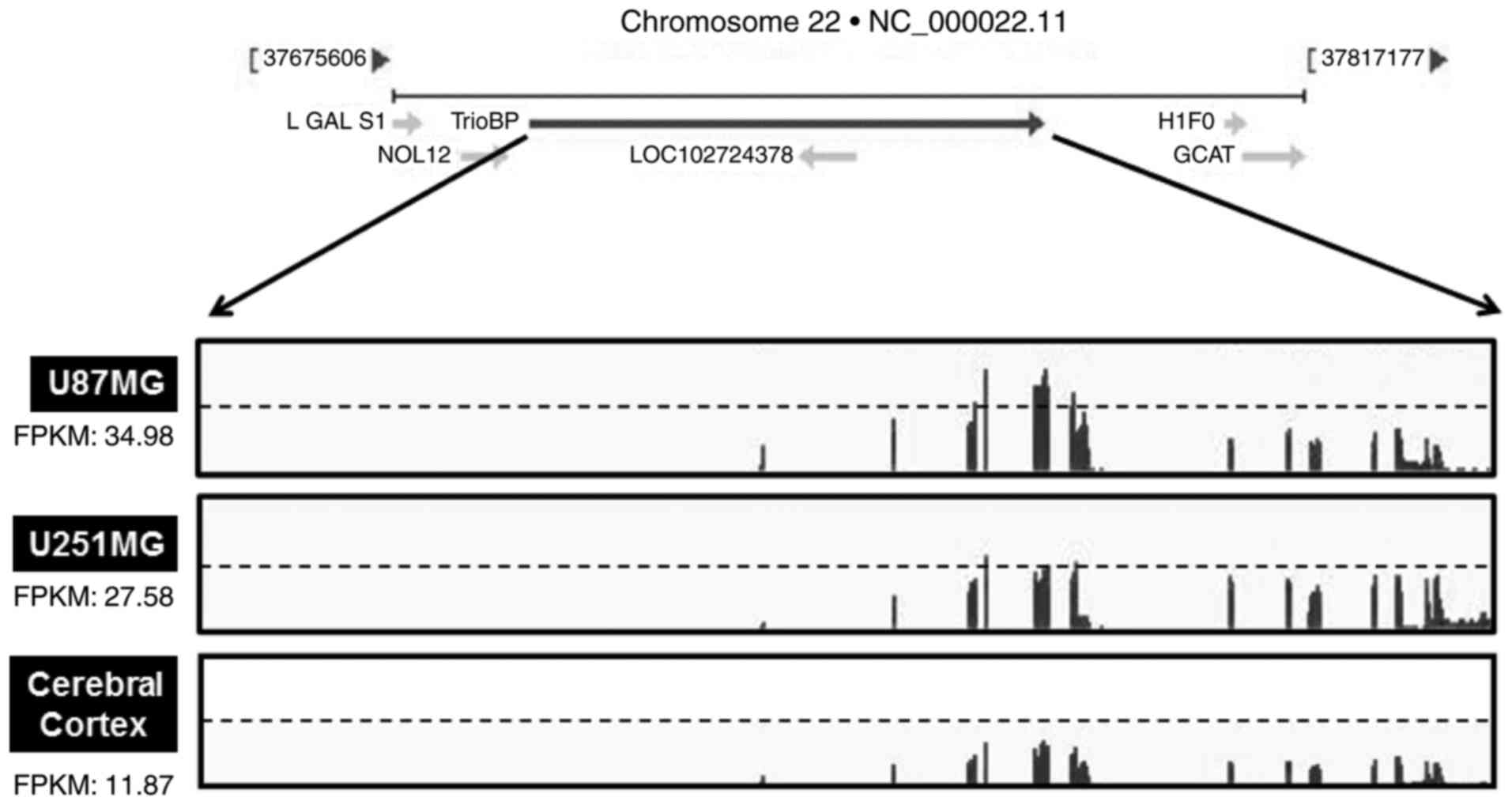
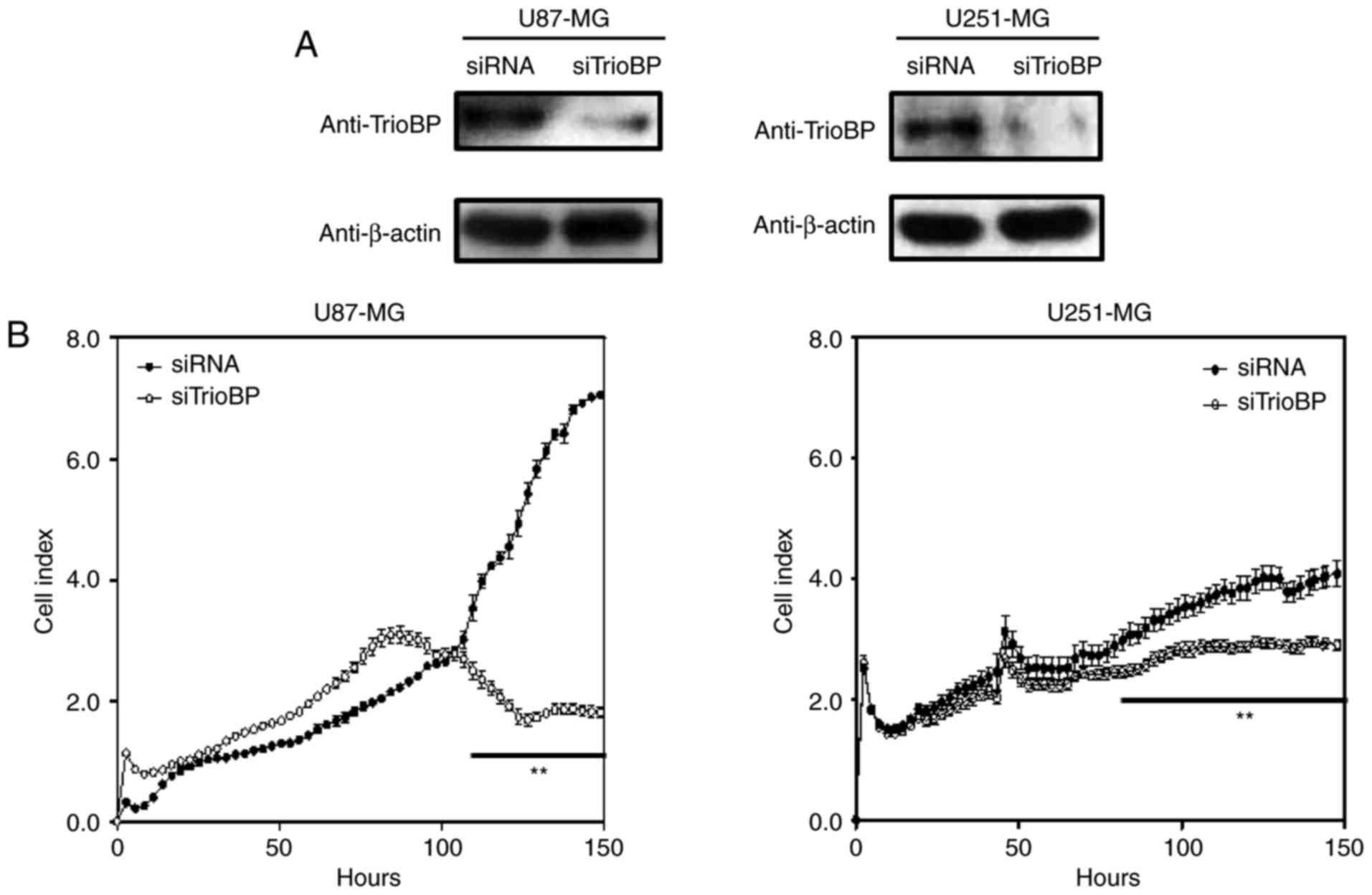
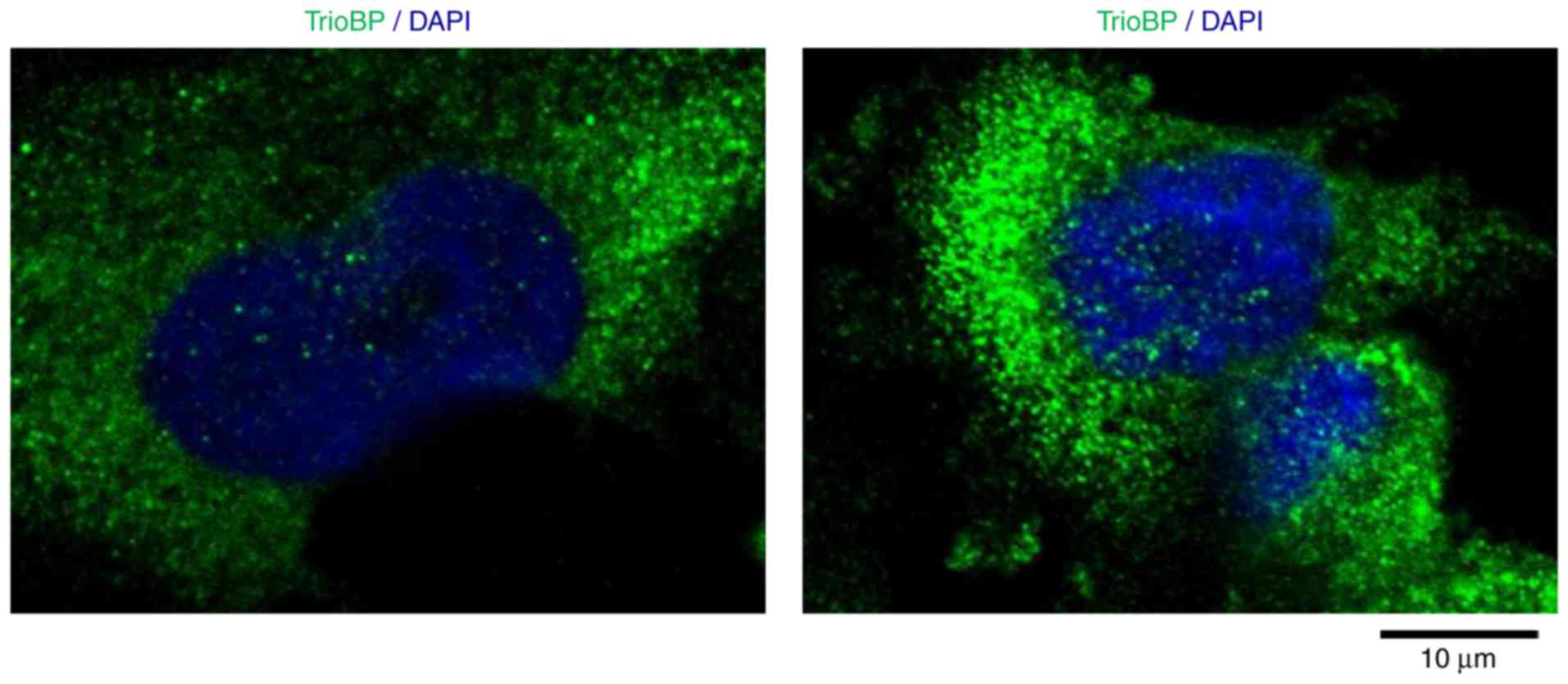
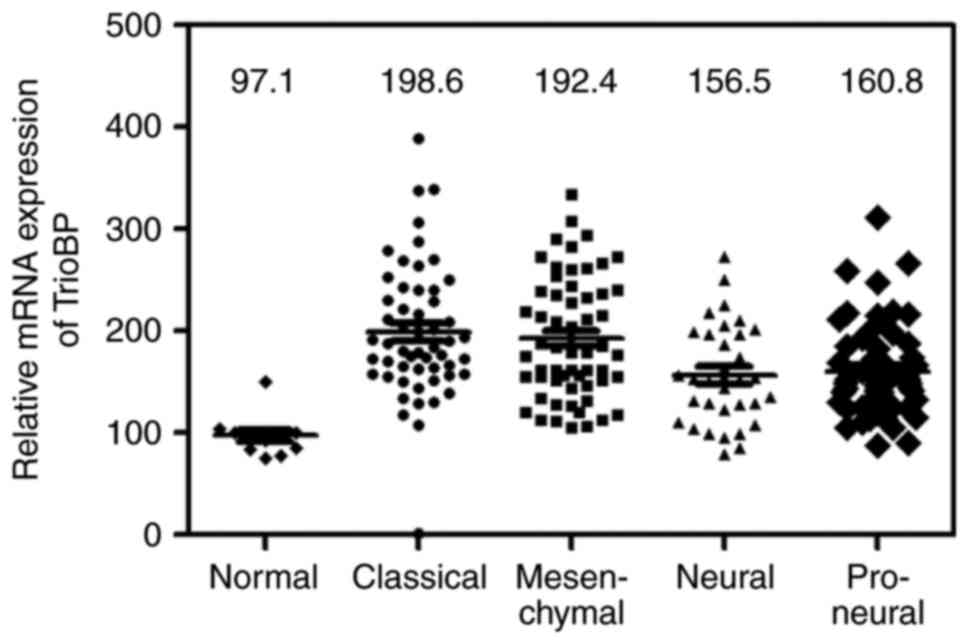
|
1
|
Glaser T, Han I, Wu L and Zeng X: Targeted
nanotechnology in glioblastoma multiforme. Front Pharmacol.
8:1662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arif SH, Pandith AA, Bhat AR, Ramzan AU,
Malik Nk, Chibber SS, Wani AA, Tabasum R and Altaf Kirmani A: EGFR
and PTEN Gene Mutation Status in Glioblastoma Patients and their
Prognostic Impact on Patient's Survival. J Carcinog Mutagen.
6:2182015.
|
|
3
|
Virk SM, Gibson RM, Quinones-Mateu ME and
Barnholtz-Sloan JS: Identification of variants in primary and
recurrent glioblastoma using a cancer-specific gene panel and whole
exome sequencing. PLoS One. 10:e01241782015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bergers G and Benjamin LE: Tumorigenesis
and the angiogenic switch. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:401–410. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wesseling P, Ruiter DJ and Burger PC:
Angiogenesis in brain tumors; pathobiological and clinical aspects.
J Neurooncol. 32:253–265. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Das S and Marsden PA: Angiogenesis in
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 369:1561–1563. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Molecular
mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature.
473:298–307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Norden AD, Drappatz J and Wen PY: Novel
anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol.
7:1152–1160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R,
Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea
D, et al: Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly
diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:709–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel
JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, Colman H, Chakravarti A, Pugh S,
Won M, et al: A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:699–708. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seipel K, O'Brien SP, Iannotti E, Medley
QG and Streuli M: Tara, a novel F-actin binding protein, associates
with the Trio guanine nucleotide exchange factor and regulates
actin cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Sci. 114:389–399.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shahin H, Walsh T, Sobe T, Abu Sa'ed J,
Abu Rayan A, Lynch ED, Lee MK, Avraham KB, King MC and Kanaan M:
Mutations in a novel isoform of TRIOBP that encodes a
filamentous-actin binding protein are responsible for DFNB28
recessive nonsyndromic hearing loss. Am J Hum Genet. 78:144–152.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Riazuddin S, Khan SN, Ahmed ZM, Ghosh M,
Caution K, Nazli S, Kabra M, Zafar AU, Chen K, Naz S, et al:
Mutations in TRIOBP, which encodes a putative
cytoskeletal-organizing protein, are associated with nonsyndromic
recessive deafness. Am J Hum Genet. 78:137–143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lenz DR and Avraham KB: Hereditary hearing
loss: From human mutation to mechanism. Hear Res. 281:3–10. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kitajiri S, Sakamoto T, Belyantseva IA,
Goodyear RJ, Stepanyan R, Fujiwara I, Bird JE, Riazuddin S,
Riazuddin S, Ahmed ZM, et al: Actin-bundling protein TRIOBP forms
resilient rootlets of hair cell stereocilia essential for hearing.
Cell. 141:786–798. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salhia B, Tran NL, Chan A, Wolf A, Nakada
M, Rutka F, Ennis M, McDonough WS, Berens ME, Symons M and Rutka
JT: The guanine nucleotide exchange factors trio, Ect2 and Vav3
mediate the invasive behavior of glioblastoma. Am J Pathol.
173:1828–1838. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim HB and Yoo BS: Propolis inhibits
UVA-induced Apoptosis of human keratinocyte HaCaT cells by
scavenging ROS. Toxicol Res. 32:345–351. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Park J, Piao L, Kong G, Kim Y, Park
KA, Zhang T, Hong J, Hur GM, Seok JH, et al: PKB-mediated PHF20
phosphorylation on Ser291 is required for p53 function in DNA
damage. Cell Signal. 25:74–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bioinformatics UG: The International Human
Genome Sequencing Consortium. http://genome.ucsc.eduAccessed. 20:20162015.
|
|
20
|
Kim D and Salzberg S: TopHat 2.1.0.
https://ccb.jhu.edu/software/tophat/index.shtmlJuly
29–2015
|
|
21
|
Na CH, Hong JH, Kim WS, Shanta SR, Bang
JY, Park D, Kim HK and Kim KP: Identification of protein markers
specific for papillary renal cell carcinoma using imaging mass
spectrometry. Mol Cells. 38:624–629. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Rijssel J and van Buul JD: The many
faces of the guanine-nucleotide exchange factor trio. Cell Adh
Migr. 6:482–487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fortin Ensign SP, Mathews IT, Symons MH,
Berens ME and Tran NL: Implications of Rho GTPase signaling in
glioma cell invasion and tumor progression. Front Oncol. 3:2412013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li A, Dawson JC, Forero-Vargas M, Spence
HJ, Yu X, König I, Anderson K and Machesky LM: The actin-bundling
protein fascin stabilizes actin in invadopodia and potentiates
protrusive invasion. Curr Biol. 20:339–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yun SP, Ryu JM, Jang MW and Han HJ:
Interaction of profilin-1 and F-actin via a β-arrestin-1/JNK
signaling pathway involved in prostaglandin E(2)-induced human
mesenchymal stem cells migration and proliferation. J Cell physiol.
226:559–571. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao J, Wang S, Gunther LK, Kitajiri S, Li
C and Sakamoto T: The actin-bundling protein TRIOBP-4 and −5
promotes the motility of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
356:367–373. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|