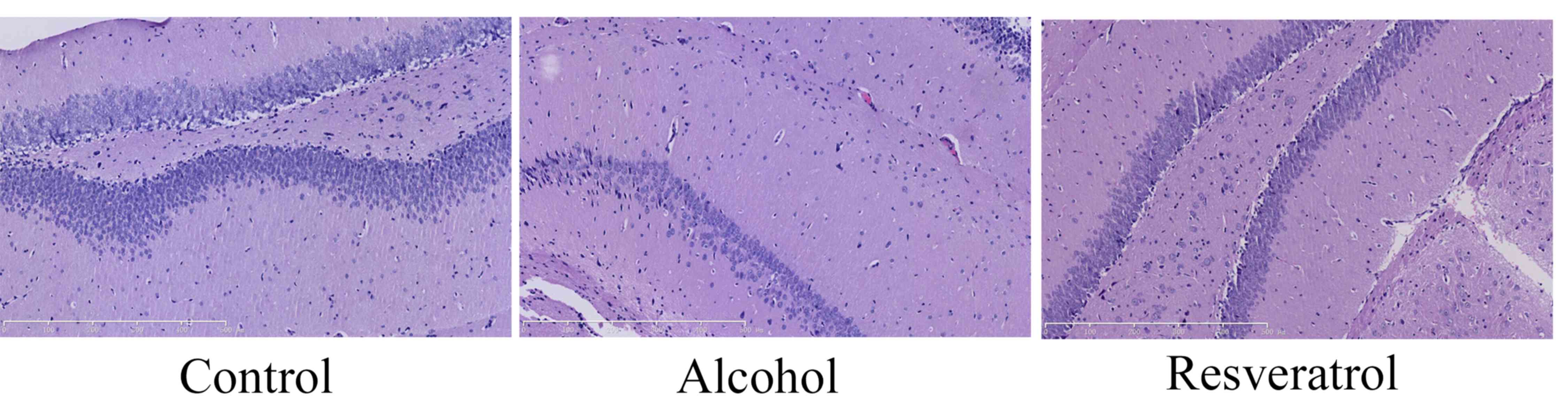
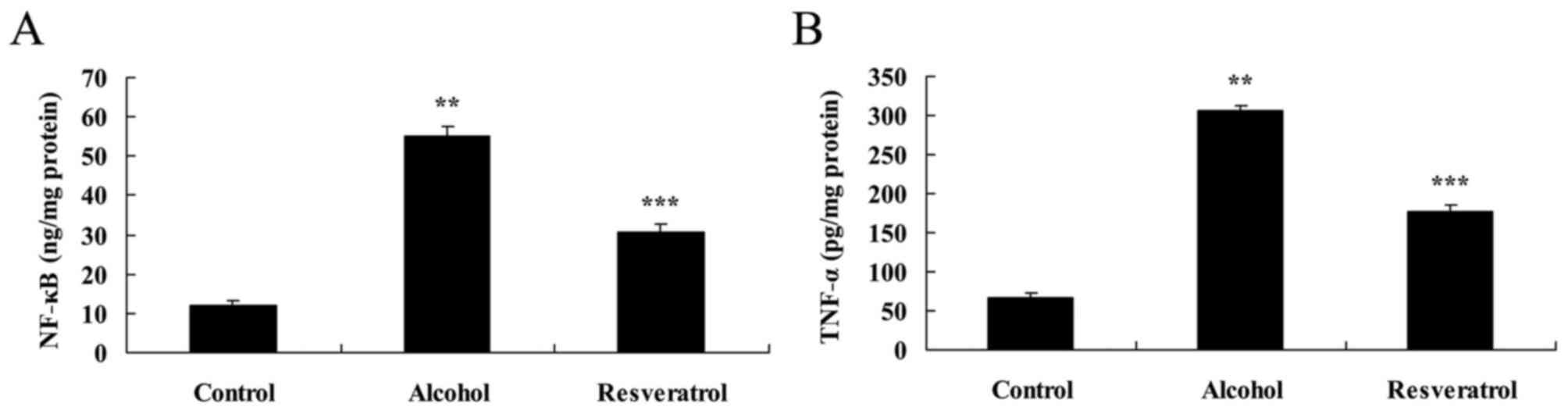
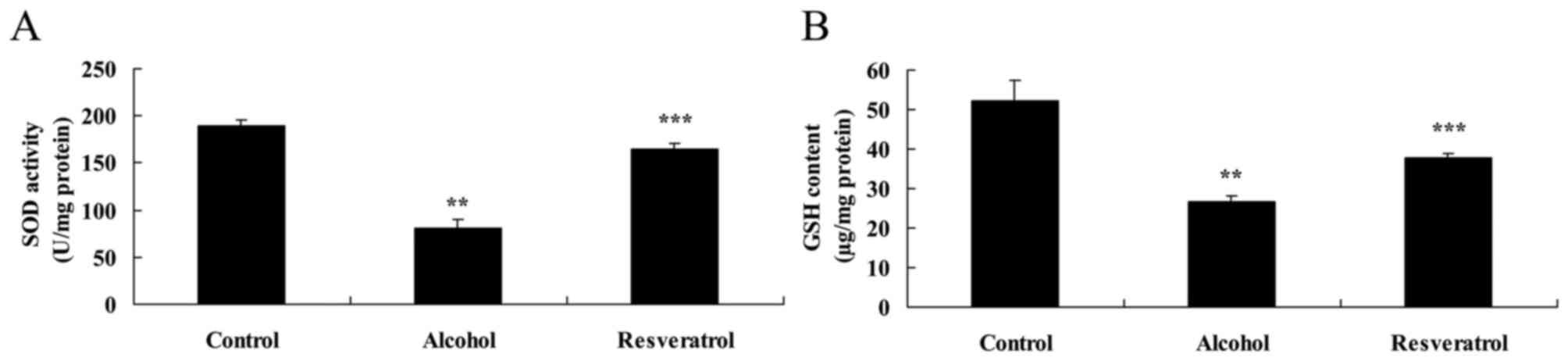
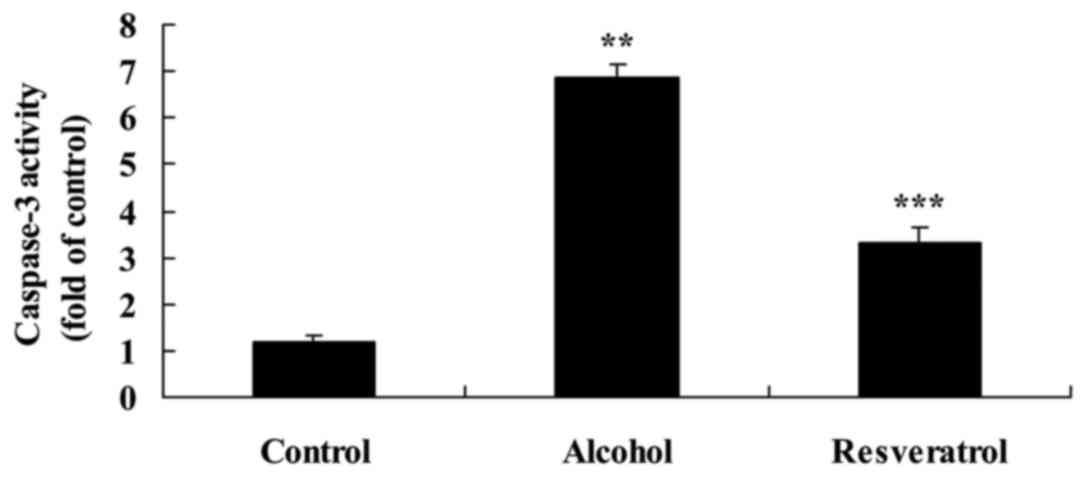
|
1
|
Goodlett CR and Eilers AT: Alcohol-induced
Purkinje cell loss with a single binge exposure in neonatal rats: A
stereological study of temporal windows of vulnerability. Alcohol
Clin Exp Res. 21:738–744. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qin L and Crews FT: NADPH oxidase and
reactive oxygen species contribute to alcohol-induced microglial
activation and neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation. 9:52012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Takeuchi M and Saito T: Cytotoxicity of
acetaldehyde-derived advanced glycation end-products (AA-AGE) in
alcoholic-induced neuronal degeneration. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 29
12 Suppl:220S–224S. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weiss B: The first 83 and the next 83:
Perspectives on neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicology. 30:832–850. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Myers J, London L and Lucchini RG:
Neurotoxicology and development: Human, environmental and social
impacts. Neurotoxicology. 45:217–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Berman JW, Carson MJ, Chang L, Cox BM, Fox
HS, Gonzalez RG, Hanson GR, Hauser KF, Ho WZ, Hong JS, et al:
NeuroAIDS, drug abuse, and inflammation: Building collaborative
research activities. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 1:351–399. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trickler WJ, Lantz SM, Murdock RC, Schrand
AM, Robinson BL, Newport GD, Schlager JJ, Oldenburg SJ, Paule MG,
Slikker W Jr, et al: Silver nanoparticle induced blood-brain
barrier inflammation and increased permeability in primary rat
brain microvessel endothelial cells. Toxicol Sci. 118:160–170.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park I, Lee Y, Kim HD and Kim K: Effect of
resveratrol, a SIRT1 activator, on the interactions of the
CLOCK/BMAL1 complex. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 29:379–387. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sonnemann J, Kahl M, Siranjeevi PM,
Blumrich A, Blümel L, Becker S, Wittig S, Winkler R, Krämer OH and
Beck JF: Reverse chemomodulatory effects of the SIRT1 activators
resveratrol and SRT1720 in Ewing's sarcoma cells: Resveratrol
suppresses and SRT1720 enhances etoposide- and vincristine-induced
anticancer activity. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 142:17–26. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Allen JW, Mutkus LA and Aschner M: Chronic
ethanol produces increased taurine transport and efflux in cultured
astrocytes. Neurotoxicology. 23:693–700. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wan W and DePetrillo PB: Ritonavir
protects hippocampal neurons against oxidative stress-induced
apoptosis. Neurotoxicology. 23:301–306. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Overstreet DH: Organophosphate pesticides,
cholinergic function and cognitive performance in advanced age.
Neurotoxicology. 21:75–81. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polizzi S, Pira E, Ferrara M, Bugiani M,
Papaleo A, Albera R and Palmi S: Neurotoxic effects of aluminium
among foundry workers and Alzheimer's disease. Neurotoxicology.
23:761–774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang LN, Hao L, Wang HY, Su HN, Sun YJ,
Yang XY, Che B, Xue J and Gao ZB: Neuroprotective effect of
resveratrol against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. Adv Clin Exp
Med. 24:161–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abengózar-Vela A, Calonge M, Stern ME,
González-Garcia MJ and Enriquez-De-Salamanca A: Quercetin and
resveratrol decrease the inflammatory and oxidative responses in
human ocular surface epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
56:2709–2719. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leyton L, Hott M, Acuña F, Caroca J, Nuñez
M, Martin C, Zambrano A, Concha MI and Otth C: Nutraceutical
activators of AMPK/Sirt1 axis inhibit viral production and protect
neurons from neurodegenerative events triggered during HSV-1
infection. Virus Res. 205:63–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Choi JS, Park C and Jeong JW:
AMP-activated protein kinase is activated in Parkinson's disease
models mediated by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 391:147–151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hao W, Takano T, Guillemette J, Papillon
J, Ren G and Cybulsky AV: Induction of apoptosis by the Ste20-like
kinase SLK, a germinal center kinase that activates apoptosis
signal-regulating kinase and p38. J Biol Chem. 281:3075–3084. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu K, Yang Y and Mansbridge J: Comparison
of the stress response to cryopreservation in monolayer and
three-dimensional human fibroblast cultures: Stress proteins, MAP
kinases, and growth factor gene expression. Tissue Eng. 6:539–554.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo S, Yao Q, Ke Z, Chen H, Wu J and Liu
C: Resveratrol attenuates high glucose-induced oxidative stress and
cardiomyocyte apoptosis through AMPK. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
412:85–94. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoshida K, Bacal J, Desmarais D, Padioleau
I, Tsaponina O, Chabes A, Pantesco V, Dubois E, Parrinello H,
Skrzypczak M, et al: The histone deacetylases sir2 and rpd3 act on
ribosomal DNA to control the replication program in budding yeast.
Mol Cell. 54:691–697. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zill OA, Scannell D, Teytelman L and Rine
J: Co-evolution of transcriptional silencing proteins and the DNA
elements specifying their assembly. PLoS Biol. 8:e10005502010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gallagher JE, Babiarz JE, Teytelman L,
Wolfe KH and Rine J: Elaboration, diversification and regulation of
the Sir1 family of silencing proteins in Saccharomyces. Genetics.
181:1477–1491. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hou Z, Bernstein DA, Fox CA and Keck JL:
Structural basis of the Sir1-origin recognition complex interaction
in transcriptional silencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp.
8489–8494. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Donauer J, Schreck I, Liebel U and Weiss
C: Role and interaction of p53, BAX and the stress-activated
protein kinases p38 and JNK in benzo(a)pyrene-diolepoxide induced
apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Arch Toxicol. 86:329–337.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dziegielewska B, Brautigan DL, Larner JM
and Dziegielewski J: T-type Ca2+ channel inhibition induces
p53-dependent cell growth arrest and apoptosis through activation
of p38-MAPK in colon cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 12:348–358.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hishida T, Nozaki Y, Nakachi Y, Mizuno Y,
Iseki H, Katano M, Kamon M, Hirasaki M, Nishimoto M, Okazaki Y and
Okuda A: Sirt1, p53, and p38(MAPK) are crucial regulators of
detrimental phenotypes of embryonic stem cells with Max expression
ablation. Stem Cells. 30:1634–1644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu XP, Xiong M, Xu CS, Duan LN, Dong YQ,
Luo Y, Niu TH and Lu CR: Resveratrol induces apoptosis of human
chronic myelogenous leukemia cells in vitro through p38 and
JNK-regulated H2AX phosphorylation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 36:353–361.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|