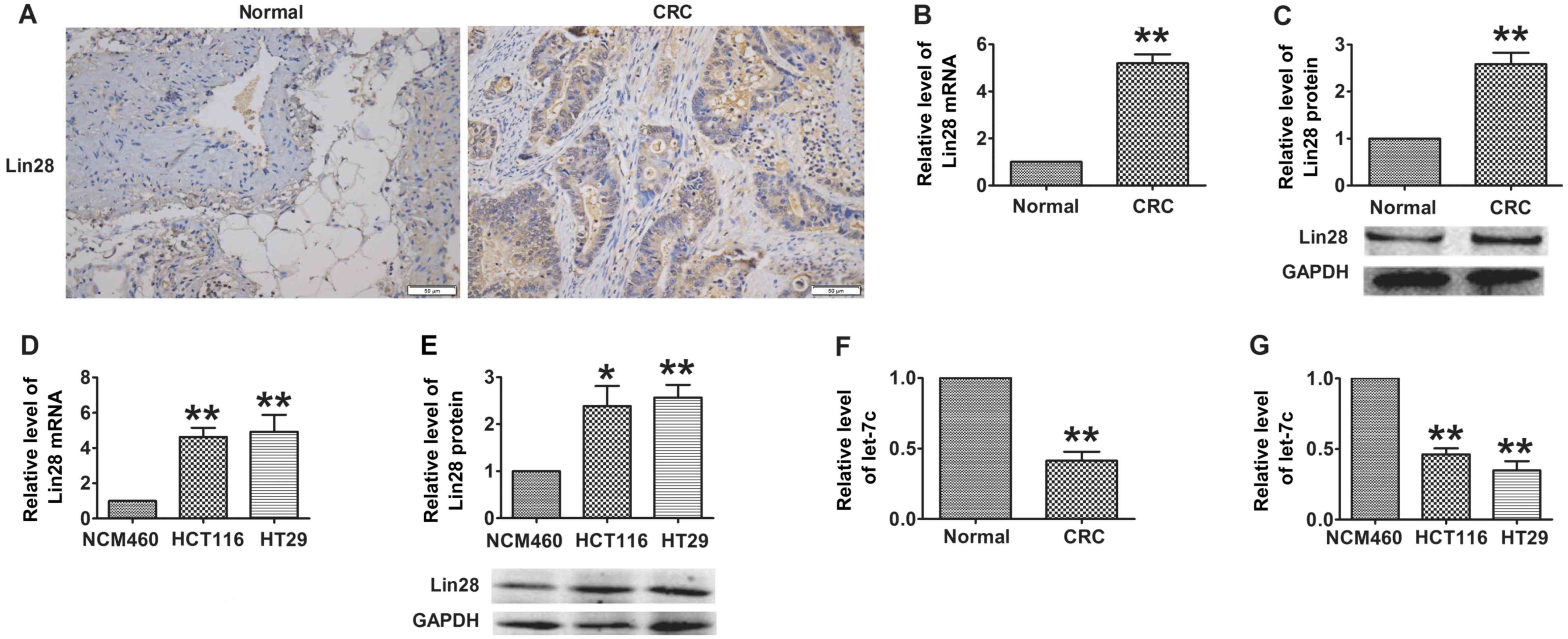
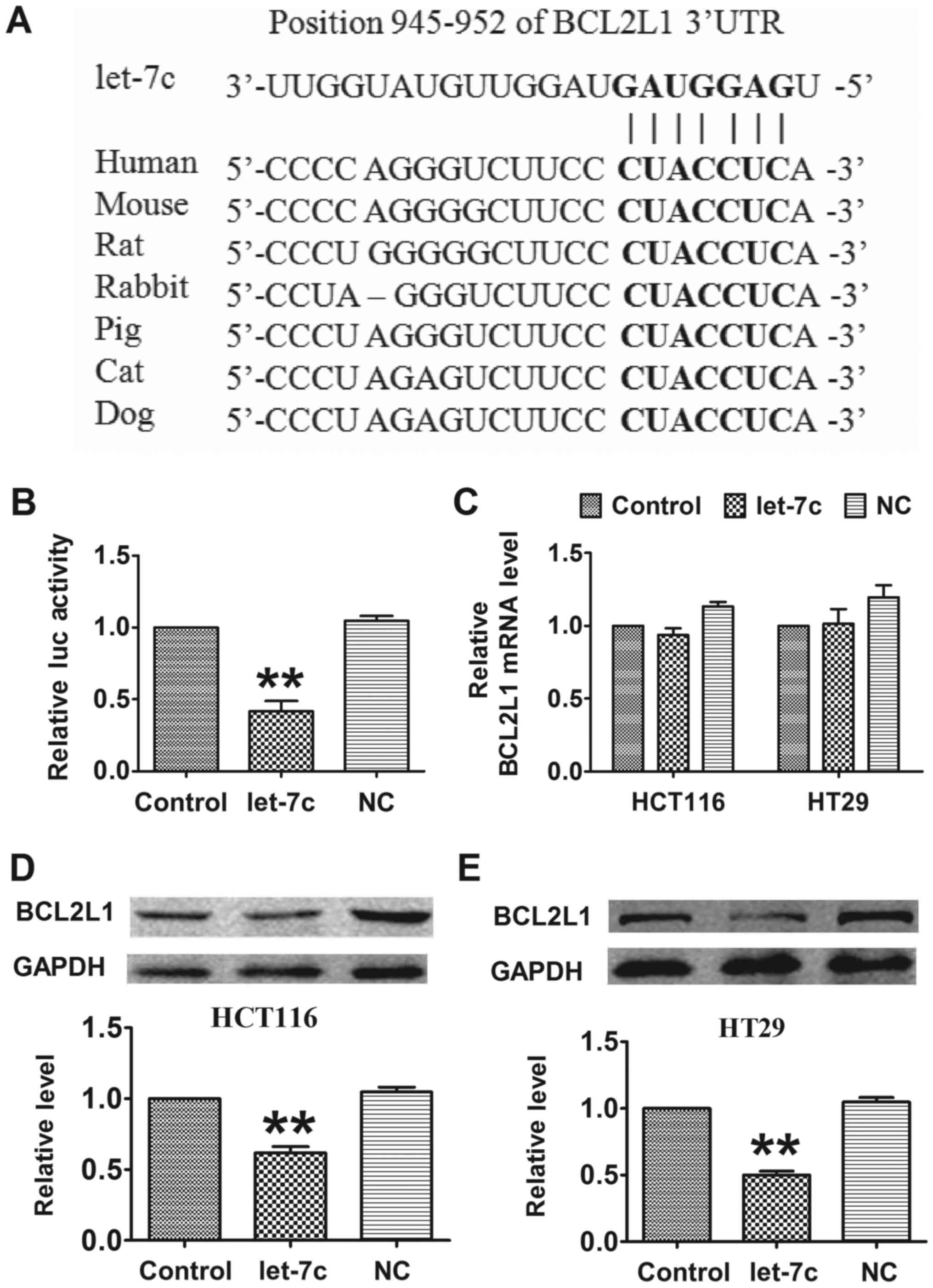
|
1
|
Sforza V, Martinelli E, Ciardiello F,
Gambardella V, Napolitano S, Martini G, Della Corte C, Cardone C,
Ferrara ML, Reginelli A, et al: Mechanisms of resistance to
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in metastatic
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:6345–6361. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ciasca G, Papi M, Minelli E, Palmieri V
and De Spirito M: Changes in cellular mechanical properties during
onset or progression of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
22:7203–7214. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Greef K, Rolfo C, Russo A, Chapelle T,
Bronte G, Passiglia F, Coelho A, Papadimitriou K and Peeters M:
Multisciplinary management of patients with liver metastasis from
colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:7215–7225. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sanz-Garcia E, Grasselli J, Argiles G,
Elez ME and Tabernero J: Current and advancing treatments for
metastatic colorectal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 16:93–110.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yin TF, Wang M, Qing Y, Lin YM and Wu D:
Research progress on chemopreventive effects of phytochemicals on
colorectal cancer and their mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol.
22:7058–7068. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Arora H, Qureshi R, Rizvi MA, Shrivastava
S and Parihar MS: Study of apoptosis-related interactions in
colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:14415–14425. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Behbahani GD, Ghahhari NM, Javidi MA,
Molan AF, Feizi N and Babashah S: MicroRNA-mediated
post-transcriptional regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 23:1–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun X, Liu J, Xu C, Tang SC and Ren H: The
insights of Let-7 miRNAs in oncogenesis and stem cell potency. J
Cell Mol Med. 20:1779–1788. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nguyen LH and Zhu H: Lin28 and let-7 in
cell metabolism and cancer. Transl Pediatr. 4:4–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A,
Sepulveda AR, Lee JS and Rustgi AK: LIN28B promotes colon cancer
progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:4260–4268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tu HC, Schwitalla S, Qian Z, LaPier GS,
Yermalovich A, Ku YC, Chen SC, Viswanathan SR, Zhu H, Nishihara R,
et al: LIN28 cooperates with WNT signaling to drive invasive
intestinal and colorectal adenocarcinoma in mice and humans. Genes
Dev. 29:1074–1086. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liang H, Liu S, Chen Y, Bai X, Liu L, Dong
Y, Hu M, Su X, Chen Y, Huangfu L, et al: miR-26a suppresses EMT by
disrupting the Lin28B/let-7d axis: Potential cross-talks among
miRNAs in IPF. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:655–665. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang H, Zhao Q, Deng K, Guo X and Xia J:
Lin28: An emerging important oncogene connecting several aspects of
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:2841–2848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Piletič K and Kunej T: MicroRNA epigenetic
signatures in human disease. Arch Toxicol. 90:2405–2419. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sethupathy P: The promise and challenge of
therapeutic MicroRNA silencing in diabetes and metabolic diseases.
Curr Diab Rep. 16:522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen E, Diao X, Wei C, Wu Z, Zhang L and
Hu B: MicroRNAs target gene and signaling pathway by bioinformatics
analysis in the cardiac hypertrophy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
397:380–385. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao MH, Feng X, Zhang YW, Lou XY, Cheng Y
and Zhou HH: Let-7 in cardiovascular diseases, heart development
and cardiovascular differentiation from stem cells. Int J Mol Sci.
14:23086–23102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li X, Wang B, Cui H, Du Y, Song Y, Yang L,
Zhang Q, Sun F, Luo D, Xu C, et al: let-7e replacement yields
potent anti-arrhythmic efficacy via targeting beta 1-adrenergic
receptor in rat heart. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1334–1343. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trang P, Medina PP, Wiggins JF, Ruffino L,
Kelnar K, Omotola M, Homer R, Brown D, Bader AG, Weidhaas JB and
Slack FJ: Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA.
Oncogene. 29:1580–1587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xia Y, Zhu Y, Zhou X and Chen Y: Low
expression of let-7 predicts poor prognosis in patients with
multiple cancers: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 35:5143–5148. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ghanbari R, Mosakhani N, Sarhadi VK,
Armengol G, Nouraee N, Mohammadkhani A, Khorrami S, Arefian E,
Paryan M, Malekzadeh R and Knuutila S: Simultaneous underexpression
of let-7a-5p and let-7f-5p microRNAs in plasma and stool samples
from early stage colorectal carcinoma. Biomark Cancer. 7 Suppl
1:S39–S48. 2016.
|
|
23
|
Han HB, Gu J, Zuo HJ, Chen ZG, Zhao W, Li
M, Ji DB, Lu YY and Zhang ZQ: Let-7c functions as a metastasis
suppressor by targeting MMP11 and PBX3 in colorectal cancer. J
Pathol. 226:544–555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang T, Han P, He Y, Zhao C, Wang G, Yang
W, Shan M, Zhu Y, Yang C, Weng M, et al: Lin28A enhances
chemosensitivity of colon cancer cells to 5-FU by promoting
apoptosis in a let-7 independent manner. Tumour Biol. 37:7657–7665.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Geng L, Zhu B, Dai BH, Sui CJ, Xu F, Kan
T, Shen WF and Yang JM: A let-7/Fas double-negative feedback loop
regulates human colon carcinoma cells sensitivity to Fas-related
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 408:494–499. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Renault TT, Teijido O, Antonsson B, Dejean
LM and Manon S: Regulation of Bax mitochondrial localization by
Bcl-2 and Bcl-× (L): Keep your friends close but your enemies
closer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:64–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McDaniel K, Hall C, Sato K, Lairmore T,
Marzioni M, Glaser S, Meng F and Alpini G: Lin28 and let-7: Roles
and regulation in liver diseases. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 310:G757–G765. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang Y: A mirror of two faces: Lin28 as a
master regulator of both miRNA and mRNA. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA.
3:483–494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jun-Hao ET, Gupta RR and Shyh-Chang N:
Lin28 and let-7 in the metabolic physiology of aging. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:132–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chien CS, Wang ML, Chu PY, Chang YL, Liu
WH, Yu CC, Lan YT, Huang PI, Lee YY, Chen YW, et al: Lin28B/Let-7
regulates expression of Oct4 and Sox2 and reprograms oral squamous
cell carcinoma cells to a stem-like state. Cancer Res.
75:2553–2565. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Li H, Feng J, Cui X, Huang W, Li Y,
Su F, Liu Q, Zhu J, Lv X, et al: Lin28 induces
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness via
downregulation of let-7a in breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e830832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fu X, Meng Z, Liang W, Tian Y, Wang X, Han
W, Lou G, Wang X, Lou F, Yen Y, et al: miR-26a enhances miRNA
biogenesis by targeting Lin28B and Zcchc11 to suppress tumor growth
and metastasis. Oncogene. 33:4296–4306. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roos M, Pradère U, Ngondo RP, Behera A,
Allegrini S, Civenni G, Zagalak JA, Marchand JR, Menzi M, Towbin H,
et al: A small-molecule inhibitor of Lin28. ACS Chem Biol.
11:2773–2781. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|